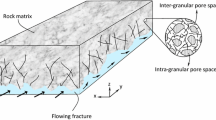
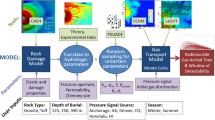
Abstract
This paper provides an overview and information on radon migration in the crust. In the past several decades, numerous studies on radon migration have been published. However, there is no there is no comprehensive review of large-scale radon transport in the earth crust. A literature review was conducted to present the research on the mechanism of radon migration, geogas theory, investigation of multiphase flow, and modeling method of fractures. Molecular diffusion was long considered the primary mechanism for radon migration in the crust. However, a molecular diffusion mechanism cannot explain the understanding of anomalous radon concentrations. In contrast with early views, the process of radon migration and redistribution within the Earth may be determined by geogas (mainly CO2 and CH4). Microbubbles rising in fractured rocks may be a rapid and efficient way of radon migration, as reported by recent studies. All these hypotheses on the mechanisms of geogas migration are summarized into a theoretical framework, defined as “geogas theory.” According to geogas theory, fractures are the principal channel of gas migration. The development of the discrete fracture network (DFN) method is expected to supply a new tool for fracture modeling. It is hoped that this paper will contribute to a deeper understanding of radon migration and fracture modeling.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this article.
References
Abdi MR, Mirzaeifar H (2017) Experimental and PIV evaluation of grain size and distribution on soil–geogrid interactions in pullout test. Soils Found 57(6):1045–1058. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sandf.2017.08.030
Adamczyk WP, Klimanek A, Białecki RA, Wȩcel G, Kozołub P, Czakiert T (2014) Comparison of the standard Euler-Euler and hybrid Euler-Lagrange approaches for modeling particle transport in a pilot-scale circulating fluidized bed. Particuology 15:129–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.partic.2013.06.008
Adrian RJ, Gharib M, Merzkirch W, Rockwell D, and Whitelaw JH (1998) Particle Image Velocimetry A Practical Guide.
Africa N, Africa S, America S, Asia S, States U (1997) Rock fractures and fluid flow, contemporary understanding and applications. Rock Fract Fluid Flow Contemp Underst Appl 78(49). https://doi.org/10.1029/97eo00345
Ahkami M, Roesgen T, Saar MO, Kong XZ (2019) High-resolution temporo-ensemble PIV to resolve pore-scale flow in 3D-printed fractured porous media. Transp Porous Media 129(2):467–483. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-018-1174-3
Algar CK, Boudreau BP, Barry MA (2011) Initial rise of bubbles in cohesive sediments by a process of viscoelastic fracture. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 116(4):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1029/2010JB008133
Alghalandis YF (2014) PhD thesis: Stochastic modelling of fractures in rock masses. University of Adelaide http://www.leeds.ac.uk/StochasticRockFractures/
Ambrosino F, Thinová L, Briestenský M, Šebela S, Sabbarese C (2020) Detecting time series anomalies using hybrid methods applied to Radon signals recorded in caves for possible correlation with earthquakes. Acta Geodyn Geomater 55(3):405–420. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40328-020-00298-1
Andersen CE, Forskningscenter Risø, and Danmarks Tekniske Højskole. (1992) Entry of soil gas and radon into houses.
Andersson J (1984) A stochastic model of a fractured rock conditioned by measured information. Water Resour 20(1):79–88
Andrews JN, Hussain N, Batchelor AS, Kwakwa K (1986) 222Rn solution by the circulating fluids in a “hot dry rock” geothermal reservoir. Appl Geochem 1(6):647–657. https://doi.org/10.1016/0883-2927(86)90086-7
Antonenkov DA (2021) Device for research of water flow dynamics in situ based on the PIV method. IOP Conf Ser Earth Environ Sci 666(2). https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/666/2/022081
Babanezhad M, Taghvaie Nakhjiri A, Rezakazemi M, Shirazian S (2020) Developing intelligent algorithm as a machine learning overview over the big data generated by euler-euler method to simulate bubble column reactor hydrodynamics. ACS Omega 5(32):20558–20566. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.0c02784
Baghbanan A, Jing L (2007) Hydraulic properties of fractured rock masses with correlated fracture length and aperture. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 44(5):704–719. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2006.11.001
Baghbanan A, Jing L (2008) Stress effects on permeability in a fractured rock mass with correlated fracture length and aperture. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 45(8):1320–1334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2008.01.015
Bai Y, Lin Y, Chang G, and Wu H (1995) The radon migration mechanism and influence factors of the radon measurement in uranium prospecting (CNIC--01006). China. https://inis.iaea.org/search/search.aspx?orig_q=RN:27034711
Balachandar S, Liu K, Lakhote M (2019) Self-induced velocity correction for improved drag estimation in Euler–Lagrange point-particle simulations. J Comput Phys 376:160–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcp.2018.09.033
Baskaran M (2016) Radon: a tracer for geological, geophysical and geochemical studies. Radon Tracer Geol Geophys Geochem Stud. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-21329-3_8
Baubron JC, Allard P, Toutain J (1990) Diffuse volcanic emissions of carbon dioxide from Vulcano Island, Italy. Nature 344:51–53
Baumberger T, Embley RW, Merle SG (2018) Mantle-derived helium and multiple methane sources in gas bubbles of cold seeps along the Cascadia Continental Margin. Geochem Geophys Geosyst 19:4476–4486. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018GC007859
Belayneh MW, Matthai SK, Blunt MJ, Rogers SF (2009) Comparison of deterministic with stochastic fracture models in water-flooding numerical simulations. AAPG Bull 93(11):1633–1648. https://doi.org/10.1306/07220909031
Berkowitz B (2002) Characterizing flow and transport in fractured geological media: a review. Adv Water Resour 25(8–12):861–884. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0309-1708(02)00042-8
Besagni G, Inzoli F (2016a) Bubble size distributions and shapes in annular gap bubble column. Exp Thermal Fluid Sci 74:27–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expthermflusci.2015.11.020
Besagni G, Inzoli F (2016b) Comprehensive experimental investigation of counter-current bubble column hydrodynamics: holdup, flow regime transition, bubble size distributions and local flow properties. Chem Eng Sci 146:259–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2016.02.043
Bhat NUH, Pahar G (2021) Euler–Lagrange framework for deformation of granular media coupled with the ambient fluid flow. Appl Ocean Res 116:102857. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apor.2021.102857
Bisdom K, Bertotti G, Nick HM (2016) A geometrically based method for predicting stress-induced fracture aperture and flow in discrete fracture networks. AAPG Bull 100(7):1075–1097. https://doi.org/10.1306/02111615127
Bonneau F, Caumon G, Renard P, Bonneau F, Caumon G, Renard P, Bonneau F, Caumon G, Renard P (2017) Impact of a stochastic sequential initiation of fractures on the spatial correlations and connectivity of discrete fracture networks. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 121(8):5641–5658
Bonnet E, Bour O, Odling NE, Davy P, Main I, Cowie P, Berkowitz B (2001) Scaling of fracture systems in geological media. Rev Geophys 39(3):347–383
Botros FE, Hassan AE, Reeves DM, Pohll G (2008) On mapping fracture networks onto continuum. Water Resour Res 44:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1029/2007WR006092
Boudreau BP, Algar C, Johnson BD, Croudace I, Reed A, Furukawa Y, Dorgan KM, Jumars PA, Grader AS, Gardiner BS (2005) Bubble growth and rise in soft sediments. Geology 33(6):517–520. https://doi.org/10.1130/G21259.1
Bour O (2002) A statistical scaling model for fracture network geometry, with validation on a multiscale mapping of a joint network (Hornelen Basin, Norway). J Geophys Res 107(B6):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1029/2001jb000176
Brown A (2000) Evaluation of possible gas microseepage mechanisms. AAPG Bull 84(11):1775–1789. https://doi.org/10.1306/8626c389-173b-11d7-8645000102c1865d
Busciglio A, Grisafi F, Scargiali F, Brucato A (2013) On the measurement of local gas hold-up, interfacial area and bubble size distribution in gas-liquid contactors via light sheet and image analysis: Imaging technique and experimental results. Chem Eng Sci 102:551–566. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2013.08.029
Cai Z, Zhang Q, Li X, Lei B, Hong C, Shao Z (2021) Research on radon exhalation characteristics of uranium tailings with cover materials under the coupling load of low-frequency vibration and seepage gradient. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 327(1):359–371. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-020-07478-x
Cao J (2011) Migration mechanisms of gold nanoparticles explored in geogas of the Hetai ore district, southern China. Geochem J 45(6):9–13. https://doi.org/10.2343/geochemj.1.0128
Cao J, Hu R, Liang Z, Peng Z (2009) TEM observation of geogas-carried particles from the Changkeng concealed gold deposit, Guangdong Province, South China. J Geochem Explor 101(3):247–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2008.09.001
Cao H, Jia X, Li Y, Amador C, Ding Y (2020) CFD-DNS simulation of irregular-shaped particle dissolution. Particuology 50:144–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.partic.2019.08.003
Cao L, Wu C, Xu H, Yu H, Li M, Han Y, Chen Z (2022) Study on characteristics of the water-sediment two-phase flow in fractures based on numerical simulation. Geofluids 2022. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/6235044
Carvajal D, Melendez-Vejar V, Irrázabal M, and Carlesi-Jara C (2013) Numerical simulation of a high viscosity bubble column Proceedings - 20th International Congress on Modelling and Simulation, MODSIM 2013, December, 719–725. https://doi.org/10.36334/modsim.2013.c4.carvajal
Chen X, Shi X, Zhou J, Du X, Chen Q, Qiu X (2019) Effect of overflow tailings properties on cemented paste backfill. J Environ Manag 235:133–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.01.040
Chilès J-P (2005) Stochastic modeling of natural fractured media: a review 285–294. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4020-3610-1_29
Chiodini G, Frondini F, Kerrick DM, Rogie J, Parello F, Peruzzi L, Zanzari AR (1999) Quantification of deep CO2 fluxes from Central Italy. Examples of carbon balance for regional aquifers and of soil diffuse degassing. Chem Geol 159(1–4):205–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0009-2541(99)00030-3
Chyi LL, Quick TJ, Yang TF, Chen CH (2010) The experimental investigation of soil gas radon migration mechanisms and its implication in earthquake forecast. Geofluids 10(4):556–563. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-8123.2010.00308.x
Cihan A, Corapcioglu MY (2008) Effect of compressibility on the rise velocity of an air bubble in porous media. Water Resour Res 44(4):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1029/2006WR005415
Ciotoli G, Etiope G, Guerra M, Lombardi S, Duddridge GA, Grainger P (2005) Migration of gas injected into a fault in low-permeability ground. Q J Eng Geol Hydrogeol 38(3):305–320. https://doi.org/10.1144/1470-9236/03-058
Costanzo CP, Vidal AC, Marshall B (2021) Integration of discrete fracture networks and flow simulator for quantification of hydrogeological uncertainty. Aguas Subterraneas 35(2):1–9. https://doi.org/10.14295/ras.v35i2.30024
Cressie N (1993) Statistics for Spatial Data.
Cueto-Felgueroso L, Suarez-Navarro MJ, Fu X, Juanes R (2020) Numerical simulation of unstable preferential flow during water infiltration into heterogeneous dry soil. Water 12(3):1–19. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12030909
Cvetković M, Kapuralić J, Pejić M, Močilac IK, Rukavina D, Smirčić D, Kamenski A, Matoš B, Špelić M (2021) Soil gas measurements of radon, CO2 and hydrocarbon concentrations as indicators of subsurface hydrocarbon accumulation and hydrocarbon seepage. Sustainability 13(7):1–16. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13073840
Dahan O, Nativ R, Adar EM, Berkowitz B, Ronen Z (1999) Field observation of flow in a fracture intersecting unsaturated chalk. Water Resour Res 35(11):3315–3326
Dane JH, and Topp GC (2002) Soil-atmosphere gas exchange. In Methods of Soil Analysis. Part 4: Physical Methods (pp. 1159–1182).
Darcel C, and Sa IC (2006) Discrete fracture network for the Forsmark site.
Darcel C, Bour O, Davy P (2003) Stereological analysis of fractal fracture networks. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 108(B9):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1029/2002jb002091
Davy P, Sornette A, Sornette D (1990) Some consequences of a proposed fractal nature of continental faulting In. Nature 348(6296):56–58. https://doi.org/10.1038/348056a0
Deen NG, Solberg T, Hjertager BH (2002) Fixed coordinate system. Can J Chem Eng 80:1–15
Delnoij E, Westerweel J, Deen NG, Kuipers JAM, Van Swaaij WPM (1999) Ensemble correlation PIV applied to bubble plumes rising in a bubble column. Chem Eng Sci 54(21):5159–5171. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0009-2509(99)00233-X
Dershowitz WS, Einstein HH (1988) Characterizing rock joint geometry with joint system models. Rock Mech Rock Eng 18(31)
Dharodi VS (2021) A numerical study of gravity-driven instability in strongly coupled dusty plasma. Part 2. Hetero-interactions between a rising bubble and a falling droplet. J Plasma Phys 87(4). https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022377821000684
Di Nunno F, Alves Pereira F, De Marinis G, Di Felice F, Gargano R, Granata F, Miozzi M (2018) Experimental study of air-water two-phase jet: bubble size distribution and velocity measurements. J Phys Conf Ser 1110(1). https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1110/1/012011
Dickson B (2010) Rapid gas transport in the near-surface of the earth. ASEG Ext Abstr 2010(1):1–4. https://doi.org/10.1081/22020586.2010.12041834
Dong H, Wang X, Liu L, Zhang X, Zhang S (2010) The rise and deformation of a single bubble in ionic liquids. Chem Eng Sci 65(10):3240–3248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2010.02.011
Dong S, Zeng L, Xu C, Cao H, Wang S, Lv W (2018) Some progress in reservoir fracture stochastic modeling research. Oil Geophys Prospect 53(3):625–641
Doolaeghe D, Davy P, Hyman JD, Darcel C (2020) Graph-based flow modeling approach adapted to multiscale discrete-fracture-network models. Phys Rev E 102(5):53312. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.102.053312
Dowd PA, Xu C, Mardia KV, Fowell RJ (2007) A comparison of methods for the stochastic simulation of rock fractures. Math Geol 39(7):697–714. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11004-007-9116-6
Duggan MJ, Soilleux PJ, Strong JC, Howell DM (1970) The exposure of United Kingdom miners to radon. Br J Ind Med 27(2):106–109. https://doi.org/10.1136/oem.27.2.106
Dutta S, Kr H, Ranjan S, Kakati K (2020) Estimation of indoor radon levels and their progeny using SSNTD LR115 (type -II) detector in Oil Field Areas of Upper Assam. 7(7):1655–1661
Elghobashi S (2019) Direct numerical simulation of turbulent flows laden with droplets or bubbles. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 51:217–244. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-fluid-010518-040401
Elsworth D (1986) A model to evaluate the transient hydraulic response of three-dimensional sparsely fractured rock masses. 22(13):1809–1819
Etiope G (1999) Subsoil COz and CH 4 and their advective transfer from faulted grassland to the atmosphere. 104:889–894
Etiope G (2015) Natural Gas Seepage. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-14601-0_2
Etiope G, Lombardi S (1995) Evidence for radon transport by carrier gas through faulted clays in Italy. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 193(2):291–300. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02039886
Etiope G, Lombardi S (1996) Laboratory simulation of geogas microbubble flow. Environ Geol 27(3):226–232. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00770436
Etiope G, Martinelli G (2002) Migration of carrier and trace gases in the geosphere: an overview. Phys Earth Planet Inter 129(3–4):185–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0031-9201(01)00292-8
Etiope G, Klusman RW (2002) Geologic emissions of methane to the atmosphere. Chemosphere 49(8):777–789. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-6535(02)00380-6
Etiope G, Guerra M, Raschi A (2005) Carbon dioxide and radon geohazards over a gas-bearing fault in the Siena Graben (central Italy). Terr Atmos Ocean Sci 16(4):885–896. https://doi.org/10.3319/TAO.2005.16.4.885(GIG)
Fadakar Alghalandis Y (2017) ADFNE: Open source software for discrete fracture network engineering, two and three dimensional applications. Comput Geosci 102:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2017.02.002
Fan M, McClure J, Han Y, Li Z, Chen C (2018) Interaction between proppant compaction and single-/multiphase flows in a hydraulic fracture. SPE J 23(4):1290–1303. https://doi.org/10.2118/189985-pa
Fardin N, Stephansson O, Jing L (2001) The scale dependence of rock joint surface roughness. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 38(5):659–669. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1365-1609(01)00028-4
Faybishenko B, Doughty C, Steiger M, Long JCS, Wood TR, Jacobsen JS, Lore J, Zawislanski PT (2000) Conceptual model of the geometry and physics of water flow in a fractured basalt vadose zone. Water Resour Res 36(12):3499–3520
Feng SY, Wang HQ, Cui Y, Ye YJ, Li XY, Xie D, He ZZ, Yang R (2019) Monte Carlo method for determining radon diffusion coefficients in porous media. Radiat Meas 126:106130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radmeas.2019.106130
Feng S, Wang H, Cui Y, Ye Y, Liu Y, Li X, Wang H, Yang R (2020) Fractal discrete fracture network model for the analysis of radon migration in fractured media. Comput Geol 128:103810. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2020.103810
Feng G, Wang Y, Xu T, Wang F, Shi Y (2021a) Multiphase flow modeling and energy extraction performance for supercritical geothermal systems. Renew Energy 173:442–454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2021.03.107
Feng S, Li C, Cui Y, Ye Y, Li X, Liu Y, Wang H, Yang R (2021b) Novel method for measuring temperature-dependent diffusion coefficient of radon in porous media. Appl Radiat Isot 169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apradiso.2020.109506
Feng S, Wu Y, Liu Y, Li X, Wang X, Chen P (2021c) A fractal analysis of radon migration in discrete fracture network model. Chemosphere 266:129010. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.129010
Ferry C, Richon P, Beneito A, Robé MC (2001) Radon exhalation from uranium mill tailings: experimental validation of a 1-D model. J Environ Radioact 54(1):99–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0265-931X(00)00169-7
Ferry C, Richon P, Beneito A, Robé MC (2002) Evaluation of the effect of a cover layer on radon exhalation from uranium mill tailings: transient radon flux analysis. J Environ Radioact 63(1):49–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0265-931X(02)00015-2
Fleischer RL, Mogro-Campero A (1978) Mapping of integrated radon emanation for detection of long-distance migration of gases within the Earth: techniques and principles. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 83(B7):3539–3549. https://doi.org/10.1029/jb083ib07p03539
Fleischer L, Mogro-Campero A (1979) Radon enhancements in the earth: evidence for intermittent upflows? Geophys Res Lett 6(5)
Fleischer RL, Mogro-Campero A (1981) Radon transport in the earth: a tool for uranium exploration and earthquake prediction. Nucl Tracks 5:377. https://doi.org/10.1016/0191-278X(81)90338-3
Fleischer RL, Hart HR, Mogro-Campero A (1980) Radon emanation over an ore body: search for long-distance transport of radon. Nucl Instruments Methods 173(1):169–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/0029-554X(80)90584-4
Fournier F, Groetz JE, Jacob M, Crolet JM, Lettner JM (2005) Simulation of radon transport through building materials: influence of the water content on radon exhalation rate. Transp Porous Media 59(2):197–214. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-004-1489-0
Fujioka Y (2012) PIV measurement of separated flow using micro bubbles as tracers. Adv Exp Mech 5:25–30
Gee GW, Kincaid CT, Lenhard RJ, Simmons CS (1991) Recent studies of flow and transport in the vadose zone. Rev Geophys 29(S1):227–239. https://doi.org/10.1002/rog.1991.29.s1.227
Ghanbarian B, Perfect E, Liu HH (2019) A geometrical aperture-width relationship for rock fractures. Fractals 27(1):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218348X19400024
Ghasemian S, Ahmadzadegan A, Chatzis I (2019) Bubble migration velocity in a uniform pore network. Transp Porous Media 129(3):811–836. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-019-01307-w
Gimbun J, Rielly CD, Nagy ZK (2009) Modelling of mass transfer in gas-liquid stirred tanks agitated by Rushton turbine and CD-6 impeller: a scale-up study. Chem Eng Res Des 87(4):437–451. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2008.12.017
Glamheden R, Hansen LM, Fredriksson A, Bergkvist L, Markström I, and Elfström M (2007) Mechanical modelling of the Singö deformation zone R-07-06 Site Descriptive Modelling Forsmark Forsmark Stage 2.1.
Goldenberg LC, Hutcheon I, Wardlaw N (1989) Experiments on transport of hydrophobic particles and gas bubbles in porous media. Transp Porous Media 4(2):129–145. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00134994
Gregorič A, Vaupotič J, Gabrovšek F (2013) Reasons for large fluctuation of radon and CO2 levels in a dead-end passage of a karst cave (Postojna Cave, Slovenia). Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci 13(2):287–297. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-13-287-2013
Gudmundsson A (1983) Stress estimates from the length/width ratios of fractures. J Struct Geol 5(6):623–626. https://doi.org/10.1016/0191-8141(83)90075-5
Guerra M, Etiope G (1999) Effects of gas-water partitioning, stripping and channelling processes on radon and helium gas distribution in fault areas. Geochem J 33(3):141–151. https://doi.org/10.2343/geochemj.33.141
Gundersen LCS, Wanty RB (1991) Field studies of radon in rocks, soils, and water. In: US Geological Survey Bulletin, vol 1971
Haggerty R, Gorelick SM (1995) Multiple-rate mass transfer for modeling diffusion and surface reactions in media with pore-scale heterogeneity. Water Resour Res 31(10):2383–2400. https://doi.org/10.1029/95WR10583
Haghi AH, Chalaturnyk R, Talman S (2019) Stress-dependent pore deformation effects on multiphase flow properties of porous media. Sci Rep 9(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-51263-0
Hammond DE, Simpson HJ, Mathieu G (1977) Radon 222 distribution and transport across the sediment-water interface in the Hudson River estuary. J Geophys Res 82(27):3913–3920. https://doi.org/10.1029/jc082i027p03913
Harris LD (1981) Fracture systems in the Eastern overthrust belt.
Haustein UF (2021) Silica-induced scleroderma in miners in former uranium ore mining (Wismut AG). Hautarzt 72(7):644–646. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00105-021-04791-8
Heinicke J, Koch U (2000) Slug flow - a possible explanation for hydrogeochemical earthquake precursors at Bad Brambach, Germany. Pure Appl Geophys 157(10):1621–1641. https://doi.org/10.1007/pl00001053
Heinicke J, Koch U, Martinelli G (1995) CO2 and radon measurements in the Vogtland Area (Germany) - A contribution to earthquake prediction research. Geophys Res Lett 22(7):771–774. https://doi.org/10.1029/94GL03074
Hoek E, Martin CD (2014) Fracture initiation and propagation in intact rock - a review. J Rock Mech Geotech Eng 6(4):287–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2014.06.001
Hovland M, Judd AG, Burke RA Jr (1993) The global flux of methane from shallow submarine sediments. Chemosphere 26(1–4):559–577
Hu X, Song X, Wu K, Shi Y, Li G (2021) Effect of proppant treatment on heat extraction performance in enhanced geothermal system. J Pet Sci Eng 207:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2021.109094
Huang F, Yao C, Zhang X, Wu L, Shao Y, Zhou C (2021) Effects of fracture parameters and roughness on heat-flow coupling in rock masses with two-dimensional fracture networks. Energy Sci Eng 9(8):1216–1231. https://doi.org/10.1002/ese3.885
Huang D, Liu Y, Liu Y, Song Y, Hong C, Li X (2022) Identification of sources with abnormal radon exhalation rates based on radon concentrations in underground environments. Sci Total Environ 807:150800. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.150800
Ishimori Y, Lange K, Martin P, Mayya YS, and Phaneuf M (2013) Measurement and calculation of radon releases from NORM residues In BiD (Vol. 31, Issue 474). https://doi.org/10.1344/bid2014.31.10
Italiano F, Martelli M, Martmelli G, Nuccio PM (2000) Geochemical evidence of melt intrusions along lithospheric faults of the Southern Apennines, Italy’ Geodynamic and seismogenic implications. J Geophys Res 105(B6):13,569–13,578
Iwata D, Nagahama H, Muto J, Yasuoka Y (2018) Non-parametric detection of atmospheric radon concentration anomalies related to earthquakes. Sci Rep 8(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-31341-5
Jackson CRM, Parman SW, Kelley SP, Cooper RF (2013) Noble gas transport into the mantle facilitated by high solubility in amphibole. Nat Geosci 6(7):562–565. https://doi.org/10.1038/ngeo1851
Javadi M, Sharifzadeh M, Shahriar K, Sayadi S (2014) Numerical modeling of hydraulic confinement around crude oil storage cavern in fractured rocks: direct application of DFN concept. Proceedings of the World Tunnel Congress 2014 – Tunnels for a Better Life
Jiang T, Cao J, Wu Z, Wu Y, Zeng J, Wang Z (2019) A TEM study of particles carried by ascending gas flows from the Bairendaba lead-zinc deposit, Inner Mongolia, China. Ore Geol Rev 105:18–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2018.12.010
Jing L (2003) A review of techniques, advances and outstanding issues in numerical modelling for rock mechanics and rock engineering. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 40(3):283–353. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1365-1609(03)00013-3
Jodar J, Medina A, Carrera J (2009) Gas tracer transport through a heterogeneous fracture zone under two phase flow conditions: model development and parameter sensitivity. Adv Water Resour 32(3):315–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2008.10.008
Joshi JB, Nandakumar K, Patwardhan AW, Nayak AK, Pareek V, Gumulya M, Wu C, Minocha N, Pal E, Kumar M, Bhusare V, Tiwari S, Lote D, Mali C, Kulkarni A, Tamhankar S (2019) Computational fluid dynamics. In: Advances of computational fluid dynamics in nuclear reactor design and safety assessment. Elsevier Ltd, pp 21–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-102337-2.00002-X
Juanes R, Meng Y, Primkulov BK (2020) Multiphase flow and granular mechanics. Phys Rev Fluids 5(11):110516. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevFluids.5.110516
Kar A, Chatterjee S, Ghosh D (2019) Multifractal detrended cross correlation analysis of land-surface temperature anomalies and soil radon concentration. Phys A Stat Mech Appl 521:236–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physa.2019.01.056
Kelly-reif K, Sandler DP, Shore D, Schubauer- MK, Troester MA, Nylander-french L, David B (2021) Radon and cancer mortality among underground uranium miners in the Příbram region of the Czech Republic. Am J Ind Med 63(10):859–867. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajim.23167.Radon
Kerrich R (1986) Fluid infiltration into fault zones: chemical, isotopic, and mechanical effects. Pure Appl Geophys 124(1–2):225–268. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00875727
Kerrick DM, Michael AM, Seward TM, Caldeira K (1995) Convective hydrothermal CO 2 emission from high heat flow regions. Chem Geol 121:285–293
Kim JG, Deo MD (2000) Finite element, discrete-fracture model for multiphase flow in porous media. AIChE J 46(6):1120–1130. https://doi.org/10.1002/aic.690460604
Kim TH, Schechter DS (2009) Estimation of fracture porosity of naturally fractured reservoirs with no matrix porosity using fractal discrete fracture networks. SPE Reserv Eval Eng 12(2):232–242. https://doi.org/10.2118/110720-PA
King C (1967) Radon emanation on San Andreas Fault. Angew Chem Int Ed 6(11):951–952 5–48
Kostakis K, Harrison JP (1999) Numerical analysis of gas-bubble flow in water-filled natural fractures. Comput Geol 24(1):3–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0266-352X(98)00027-5
Koukoulis A, Karageorgiou DE (2017) Radon: geoinformation for the planning of urban – suburban regions. the Case of Nafplion City, Greece. Bull Geol Soc Greece 43(3):1457. https://doi.org/10.12681/bgsg.11320
Kristiansson K, Malmqvist L (1982) Evidence for nondiffusive transport of 22286 Rn in the ground and a new physical model for the transport. Geophysics 47(10):1444–1452. https://doi.org/10.1190/1.1441293
Kristiansson K, Malmqvist L (1987) Trace elements in the geogas and their relation to bedrock composition. Geoexploration 24(6):517–534. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-7142(87)90019-6
Kumar A, Chauhan RP (2014) Active and passive measurements of radon diffusion coefficient from building construction materials. Environ Earth Sci 72(1):251–257. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-013-2951-5
Kuo MCT, Fan K, Kuochen H, Chen W (2006) A mechanism for anomalous decline in radon precursory to an earthquake. Ground Water 44(5):642–647. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6584.2006.00219.x
Lallier F, Caumon G, Borgomano J, Viseur S, Fournier F, Antoine C, Gentilhomme T (2012) Relevance of the stochastic stratigraphic well correlation approach for the study of complex carbonate settings: application to the Malampaya buildup (Offshore Palawan, Philippines). Geol Soc Spec Pub 370(1):265–275. https://doi.org/10.1144/SP370.12
Lau YM, Deen NG, Kuipers JAM (2013) Development of an image measurement technique for size distribution in dense bubbly flows. Chem Eng Sci 94:20–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2013.02.043
Law RM, Steele LP, Krummel PB, Zahorowski W (2010) Synoptic variations in atmospheric CO2 at Cape Grim: a model intercomparison. Tellus Ser B Chem Phys Meteorol 62(5):810–820. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0889.2010.00470.x
Lecomte JF (2014) ICRP draft publication on “radiological protection against radon exposure”. Radiat Prot Dosim 160(1–3):4–7. https://doi.org/10.1093/rpd/ncu105
Lee IH, Ni CF (2015) Fracture-based modeling of complex flow and CO2 migration in three-dimensional fractured rocks. Comput Geosci 81:64–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2015.04.012
Lee CC, Lee CH, Yeh HF, Lin HI (2011) Modeling spatial fracture intensity as a control on flow in fractured rock. Environ Earth Sci 63(6):1199–1211. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-010-0794-x
Legrand M, Nogueira J, Rodriguez PA, Lecuona A, Jimenez R (2017) Generation and droplet size distribution of tracer particles for PIV measurements in air, using propylene glycol/water solution. Exp Thermal Fluid Sci 81:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expthermflusci.2016.09.015
Lei Q, Latham JP, Tsang CF (2017) The use of discrete fracture networks for modelling coupled geomechanical and hydrological behaviour of fractured rocks. Comput Geol 85:151–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2016.12.024
Li YH, Liu JP, Zhao XD, Yang YJ (2010) Experimental studies of the change of spatial correlation length of acoustic emission events during rock fracture process. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 47:1254–1262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2010.08.002
Li H, Lou J, Shang Z, Tang H (2013) Simulation of bubbly flow in a vertical pipe using discrete phase model. Int J Aerosp Light Struct 3(2):291. https://doi.org/10.3850/s2010428613000688
Liang K, Hong C, Luo J, Liu P, Zhao T, Zhou Z, Zeng Z, Liu Y (2022) Radon attenuation characteristics of compacted soil layer for uranium mill tailings pond subjected to drying-wetting cycles. Sci Total Environ 851:158184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.158184
Lide DR (2007) CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics. In: Internet Version 2007, 87th edn. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-2860(92)85083-s
Lipsey LC, van Wees JD, Pluymaekers MPD (2015) Numerical modelling of thermal convection related to fracture permeability - implications for geothermal exploration and basin modelling. First EAGE TNO Workshop 17:12454. https://doi.org/10.3997/2214-4609.201412330
Liu Z, Zheng Y (2006) PIV study of bubble rising behavior. Powder Technol 168(1):10–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2006.05.020
Liu R, Jiang Y, Li B, Wang X (2015) A fractal model for characterizing fluid flow in fractured rock masses based on randomly distributed rock fracture networks. Comput Geol 65:45–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2014.11.004
Liu J, Zhou XC, Chen W, Hong X (2019) Breach discharge estimates and surface velocity measurements for an earth dam failure process due to overtopping based on the LS-PIV method. Arab J Sci Eng 44(1):329–339. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-018-3310-3
Liu L, Liu Y, Yao J, Huang Z (2020a) Efficient coupled multiphase-flow and geomechanics modeling of well performance and stress evolution in shale-gas reservoirs considering dynamic fracture properties. SPE J 25(3):1523–1542. https://doi.org/10.2118/200496-PA
Liu ZX, Han KW, Yang S, Liu YX (2020b) Fractal evolution mechanism of rock fracture in undersea metal mining. J Central South Univ 27(4):1320–1333. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-020-4369-z
Lochard J (2015) Application of the Commission’s recommendations: the 2013–2017 Committee 4 programme of work. Ann ICRP 44:33–46. https://doi.org/10.1177/0146645315578779
Loeckle F (2021) Terrestrial photogrammetry: a method to gather data on fractures for DFN modelling from exposed rock surfaces. Saf Nucl Waste Disposal 1:61–62. https://doi.org/10.5194/sand-1-61-2021
Long JCS, Remer JS, Wilson CR, Witherspoon PA (1982) Porous media equivalents for networks of discontinuous fractures. Water Resour Res 18(3):645–658. https://doi.org/10.1029/WR018i003p00645
Long JCS, Gilmour P, Witherspoon PA (1985) A model for steady fluid flow in random three-dimensional networks of disc-shaped fractures. Water Resour Res 21(8):1105–1115. https://doi.org/10.1029/WR021i008p01105
Lou W, Zhu M (2013) Numerical simulation of gas and liquid two-phase flow in gas-stirred systems based on Euler-Euler approach. Metall Mater Trans B Process Metall Mater Process Sci 44(5):1251–1263. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-013-9897-6
Lu M, Lu J, Zhang Y, Tryggvason G (2019a) Numerical study of thermocapillary migration of a bubble in a channel with an obstruction. Phys Fluids 31(6). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5094033
Lu M, Ye R, Wang Z, Wang X (2019b) Geogas prospecting for buried deposits under loess overburden: taking Shenjiayao gold deposit as an example. J Geochem Explor 197:122–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2018.11.015
Luo H, Tang D, Yan Q, He W, Xu H (2012) Radioactive elements in natural gas: a case study on distribution of gaseous 222radon and its origin mechanism. Nat Hazards 63(2):647–657. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-012-0171-z
Ma Y, Bringemeier D, Scheuermann A, Molebatsi T, and Li L (2012) Fault and fracture zone detection based on soil gas mapping and gamma ray survey at the extension site of an open pit coal mine. Proceedings of the 2012 Coal Operators’ Conference, February 2019, 18–20.
Mahabadi N, and van Paassen LA (2020) Pore scale study of gas bubble nucleation and migration in porous media. http://arxiv.org/abs/2006.06851
Mahabadi N, Zheng X, Yun TS, van Paassen L, Jang J (2018) Gas bubble migration and trapping in porous media: pore-scale simulation. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 123(2):1060–1071. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017JB015331
Mahmoodi M, Rezaei N, Zendehboudi S, Heagle D (2020) Fluid dynamic modeling of multiphase flow in heterogeneous porous media with matrix, fracture, and skin. J Hydrol 583:124510. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.124510
Malmqvist L, Kristiansson K (1985) A physical mechanism for the release of free gases in the lithosphere. Geoexploration 23(4):447–453. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-7142(85)90072-9
Malmqvist L, Kristiansson K, Kristiansson P (1999) Geogas prospecting - an ideal industrial application of PIXE. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res Sect B 150(1–4):484–490. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-583X(98)01044-1
Mandelbrot BB, Wheeler JA (1983) The fractal geometry of nature. Am J Phys 51(3):286–287. https://doi.org/10.1119/1.13295
Martinelli G, Ferrari G (1991) Earthquake forerunners in a selected area of Northern Italy: recent developments in automatic geochemical monitoring. Tectonophysics 193(4):397–410. https://doi.org/10.1016/0040-1951(91)90348-V
Marzocchi W, Lombardi AM, Casarotti E (2014) The establishment of an operational earthquake forecasting system in Italy. Seismol Res Lett 85(5):961–969. https://doi.org/10.1785/0220130219
Matthews A, Fouillac C, Hill R, O’Nions RK, Oxburgh ER (1987) Mantle-derived volatiles in continental crust: the Massif Central of France. Earth Planet Sci Lett 85(1–3):117–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/0012-821X(87)90026-4
Mattia M, Tuccimei P, Soligo M, Carusi C (2020) Radon as a natural tracer for monitoring napl groundwater contamination. Water 12(12):1–11. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123327
Mazraehli M, Zare S (2020) An application of uncertainty analysis to rock mass properties characterization at porphyry copper mines. Bull Eng Geol Environ 79(7):3721–3739. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-020-01758-2
Mcdermott E (1940) Geochemical Exploration (Soil Analysis ) The newly developed method of geochemical exploration will un- doubtedly play an important role in exploration for oil and gas fields. There has been a tendency in this country among the explorers for oil and gas. 24(5):859–881
Meslin P-Y, Adler PM, Sabroux J-C (2010) Diffusive transport of gases in wet porous media. Application to Radon. Soil Sci Soc Am J 74(6):1871–1885. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2009.0474
Mezon C, Mourzenko VV, Thovert JF, Antoine R, Fontaine F, Finizola A, Adler PM (2018) Thermal convection in three-dimensional fractured porous media. Phys Rev E 97(1). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.97.013106
Miao T, Yu B, Duan Y, Fang Q (2015) A fractal analysis of permeability for fractured rocks. Int J Heat Mass Transf 81:75–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2014.10.010
Miklyaev PS, Petrova TB, Marennyy AM, Shchitov DV, Sidyakin PA, Murzabekov M, Lopatin MN (2020) High seasonal variations of the radon exhalation from soil surface in the fault zones (Baikal and North Caucasus regions). J Environ Radioact 219:106271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvrad.2020.106271
Miklyaev PS, Petrova TB, Shchitov DV, Sidyakin PA, Murzabekov M, Marennyy AM, Nefedov NA, Sapozhnikov YA (2021) The results of long-term simultaneous measurements of radon exhalation rate, radon concentrations in soil gas and groundwater in the fault zone. Appl Radiat Isot 167:109460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apradiso.2020.109460
Moein A, Javad M, Valley B, Evans KF (2019) Scaling of fracture patterns in three deep boreholes and implications for constraining fractal discrete fracture network models. Rock Mech Rock Eng 52(6):1723–1743. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-019-1739-7
Mogro-Campero A, Fleischer RL (1977) Subterrestrial fluid convection: a hypothesis for long-distance migration of radon within the earth. Earth Planet Sci Lett 34(2):321–325. https://doi.org/10.1016/0012-821X(77)90017-6
Moldrup P, Olesen T, Komatsu T, Schjønning P, Rolston DE (2001) Tortuosity, diffusivity, and permeability in the soil liquid and gaseous phases tortuosity phenomena of pore space influence the transport of. Soil Sci Soc Am J 65:613–623
Moörner NA, Etiope G (2002) Carbon degassing from the lithosphere. Glob Planet Chang 33(1–2):185–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-8181(02)00070-X
Murgan I, Bunea F, Ciocan GD (2017) Experimental PIV and LIF characterization of a bubble column flow. Flow Meas Instrum 54:224–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.flowmeasinst.2017.02.004
Nachshon U, Weisbrod N, Dragila MI, Ganot Y (2016) The importance of advective fluxes to gas transport across the earth-atmosphere interface: the role of thermal convection, vol 11. Intech, p 13 https://www.intechopen.com/books/advanced-biometric-technologies/liveness-detection-in-biometrics
Nazaroff WW (1992) Radon transport from soil to air. Rev Geophys 30(2):137–160. https://doi.org/10.1029/92RG00055
Neuman SP (1995) On advective transport in fractal permeability and velocity fields. Water Resour Res 31(6):1455–1460. https://doi.org/10.1029/95WR00426
Nielson DL (1978) Radon emanometry as a geothermal exploration technique; theory and an example from Roosevelt Hot Springs KGRA, Utah.
Nielson KK, Rogers VC (1982) A Mathematical Model for Radon Diffusion in Earthen Materials, p 44
Nielson KK, Rogers VC, Gee GW (1988a) Diffusion of radon through soils: a pore distribution model. Soil Sci Soc Am J 52(3):898–899. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1988.03615995005200030058x
Nielson KK, Rogers VC, Gee GW (1988b) Reply to “Comments on ‘Diffusion of Radon Through Soils: A Pore Distribution Model’”. Soil Sci Soc Am J 52(3):898–899. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1988.03615995005200030058x
Nikolopoulos D, Petraki E, Vogiannis E, Chaldeos Y, Yannakopoulos P, Kottou S, Nomicos C, Stonham J (2014) Traces of self-organisation and long-range memory in variations of environmental radon in soil: comparative results from monitoring in Lesvos Island and Ileia (Greece). J Radioanal Nucl Chem 299(1):203–219. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-013-2764-8
Oldenburg CM, Lewicki JL, Dobeck L, Spangler L (2010) Modeling gas transport in the shallow subsurface during the ZERT CO2 release test. Transp Porous Media 82(1):77–92. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-009-9361-x
Omori Y, Yasuoka Y, Nagahama H, Kawada Y, Ishikawa T, Tokonami S, Shinogi M (2007) Anomalous radon emanation linked to preseismic electromagnetic phenomena. Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci 7(5):629–635. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-7-629-2007
Orabi M (2020) Simplified theoretical approaches to calculate radon concentrations in walls and ground. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 324(2):569–578. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-020-07121-9
Osborn SG, Vengosh A, Warner NR, Jackson RB (2011) Methane contamination of drinking water accompanying gas-well drilling and hydraulic fracturing. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108(20):8172–8176. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1100682108
Ozel A, Fede P, Simonin O (2013) Development of filtered Euler-Euler two-phase model for circulating fluidised bed: high resolution simulation, formulation and a priori analyses. Int J Multiph Flow 55:43–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmultiphaseflow.2013.04.002
Pang C, Tan W, Sha E, Tao Y, Liu L (2012) Simulating multiphase flow in a two-stage pusher centrifuge using computational fluid dynamics. Front Chem Sci Eng 6(3):329–338. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11705-012-1205-5
Parsons RW (1966) Permeability of idealized fractured rock. Soc Pet Eng J 6(2):126–136. https://doi.org/10.2118/1289-pa
Pasala SM, Forster CB, Deo M, Evans JP (2013) Simulation of the impact of faults on CO2 injection into sandstone reservoirs. Geofluids 13(3):344–358. https://doi.org/10.1111/gfl.12029
Patterson JW, Driesner T (2021) Elastic and thermoelastic effects on thermal water convection in fracture zones. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 126(2). https://doi.org/10.1029/2020JB020940
Peng X, Liu Z, Yao L, Xie Q, Wan F (2012) Research status and influencing factors for the radon emanation of uranium tailings impoundment. Adv Mater Res 356–360:1679–1683. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.356-360.1679
Peters A, Lantermann U (2019) Simulation of an internal nozzle flow using an Euler-Lagrange method. In: Proceedings of the 10th International Symposium on Cavitation (CAV2018), pp 925–929. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.861851_ch176
Phillips T, Kampman N, Bisdom K, Forbes Inskip ND, den Hartog SAM, Cnudde V, Busch A (2020) Controls on the intrinsic flow properties of mudrock fractures: a review of their importance in subsurface storage. Earth Sci Rev 211:103390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2020.103390
Planinić J, Radolić V, Vuković B (2004) Radon as an earthquake precursor. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res Sect A 530(3):568–574. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nima.2004.04.209
Poirier DR, Geiger GH (2016) Fick’s law and diffusivity of materials (Smithell’s Ch. 12). In: Transport Phenomena in Materials Processing, pp 419–461
Povolny A, Batsaikhan M, Ihara T, Takahashi H, Kikura H (2019) Bubble size measurement by the ultrasonic pulse echo with tracking technique. J Flow Control Meas Vis 7(1):11–27. https://doi.org/10.4236/jfcmv.2019.71002
Qadir S, Hussain A, Ahsan M (2019) A computational fluid dynamics approach for the modeling of gas separation in membrane modules. Processes 7(7). https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7070420
Qinbin L, Yaxin Y, Ye Z, Xinmin W, Yongming Z, Baiyu Z (2018) Application and current status of geogas prospecting in concealed uranium deposits exploration. Adv Earth Sci 33(1):75–84
Raffel M, Willert C, Kompenhans J (1998) Particle image velocimetry: a practical guide
Rama, Moore WS (1984) Mechanism of transport of U-Th series radioisotopes from solids into ground water. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 48(2):395–399. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-7037(84)90261-8
Rasmussen TC (1991) Steady fluid flow and travel times in partially saturated fractures using a discrete air-water interface. Water Resour Res 27(1):67–76
Rasmussen TC, Evans DD (1993) Water infiltration into exposed fractured rock surfaces. Soil Sci Soc Am J 57(2):324–329. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1993.03615995005700020006x
Ratnayake SY (2021) Assessment of the fate and behavior of naturally occurring thorium and uranium in the environment of central Sri Lanka, p 233
Riccardi G, De Bernardis E (2018) Dynamics of a spherical bubble rising in gravity, subject to traveling pressure disturbance. Commun Appl Ind Math 9(1):149–158. https://doi.org/10.2478/caim-2018-0020
Robinson PC, and Rae J (1984) Connectivity, flow and transport in network models of fractured media Ph. D. dis(May), 1 v. (various pagings).
Rodrigo-Naharro J, Quindós LS, Clemente-Jul C, Mohamud AH, Pérez del Villar L (2017) CO2 degassing from a Spanish natural analogue for CO2 storage and leakage: implications on 222Rn mobility. Appl Geochem 84:297–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2017.07.008
Rodríguez-Ocampo PE, Ring M, Hernández-Fontes JV, Alcérreca-Huerta JC, Mendoza E, Silva R (2020) CFD simulations of multiphase flows: interaction of miscible liquids with different temperatures. Water 12(9). https://doi.org/10.3390/W12092581
Rogers VC, Nielson KK (1991a) Correlations for predicting air permeabilities and 222rn diffusion coefficients of soils. Health Phys 61(2):225–230. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004032-199108000-00006
Rogers VC, Nielson KK (1991b) Multiphase radon generation and transport in porous materials. Health Phys 60(6):807–815. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004032-199106000-00006
Rutqvist J, Stephansson O (2003) The role of hydrochemical coupling in fractured rock engineering. Hydrogeol J 11(1):7–40. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-002-0241-5
Saâdi Z (2014) ON the air-filled effective porosity parameter of rogers and Nielson’s (1991) BULK radon diffusion coefficient in unsaturated soils. Health Phys 106(5):598–607. https://doi.org/10.1097/HP.0000000000000034
Sahoo BK, Mayya YS (2010) Agricultural and forest meteorology two dimensional diffusion theory of trace gas emission into soil chambers for flux measurements. Agric For Meteorol 150(9):1211–1224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2010.05.009
Saunders DF, Burson KR, Thompson CK (1999) Model for hydrocarbon microseepage and related near-surface alterations. AAPG Bull 83(1):170–185. https://doi.org/10.1306/00aa9a34-1730-11d7-8645000102c1865d
Schery SD, Gaeddert DH, Wilkening MH (1982) Transport of radon from fractured rock. J Geophys Res 87(B4):2969–2976. https://doi.org/10.1029/JB087iB04p02969
Schery SD, Petschek AG (1983) Exhalation of radon and thoron: the question of the effect of thermal gradients in soil. Earth Planet Sci Lett 64(1):56–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/0012-821X(83)90052-3
Schubert M, Paschke A, Lau S, Geyer W, Knöller K (2007) Radon as a naturally occurring tracer for the assessment of residual NAPL contamination of aquifers. Environ Pollut 145(3):920–927. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2006.04.029
Scibek J (2020) Multidisciplinary database of permeability of fault zones and surrounding protolith rocks at world-wide sites. Sci Data 7(1):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-020-0435-5
Sethy NK, Jha VN, Sutar AK, Rath P, Sahoo SK, Ravi PM, Tripathi RM (2014) Assessment of naturally occurring radioactive materials in the surface soil of uranium mining area of Jharkhand, India. J Geochem Explor 142:29–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2013.11.009
Shackelford CD, Collins F (2013) Geoenvironmental Engineering. In: Reference Module in Earth Systems and Environmental Sciences. Elsevier Inc. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-409548-9.05424-5
Shi P, Rzehak R (2020) Solid-liquid flow in stirred tanks: Euler-Euler/RANS modeling. Chem Eng Sci 227:115875. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2020.115875
Silverman MP (2017) Analysis of residence time in the measurement of radon activity by passive diffusion in an open volume: a micro-statistical approach. World J Nucl Sci Technol 7(4):252–273. https://doi.org/10.4236/wjnst.2017.74020
Sjoblom R, Hermansson H, Akerblom G (1995) Geogas in crystalline bedrock and its potential significance for disposal of nuclear waste. 353:477–484
Smeraglia L, Mercuri M, Tavani S, Pignalosa A, Kettermann M, Billi A, Carminati E (2021) 3D Discrete Fracture Network (DFN) models of damage zone fluid corridors within a reservoir-scale normal fault in carbonates: multiscale approach using field data and UAV imagery. Mar Pet Geol 126:104902. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2021.104902
Sobakin PI, Chevychelov AP, Dyachkovskii AP (2011) Radon migration in landscapes of the Elkon Uranium Ore region, Southern Yakutia. Russ J Ecol 42(3):252–255. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1067413611030167
Steinitz G, Kotlarsky P, Piatibratova O (2018) Radon signals in geological (natural) geogas and in a simultaneous enhanced confined mode simulation experiment. Proc R Soc A Math Phy Eng Sci 474(2216). https://doi.org/10.1098/rspa.2017.0787
Sterczyńska M, Jakubowski M (2017) Research on particles’ velocity distribution in a whirlpool separator using the PIV method of measurement. Int J Food Eng 13(6). https://doi.org/10.1515/ijfe-2016-0316
Subramaniam S (2012) Lagrangian–Eulerian methods for multiphase flows. Prog Energy Combust Sci 1:75
Sun J, Schechter D (2015) Optimization-based unstructured meshing algorithms for simulation of hydraulically and naturally fractured reservoirs with variable distribution of fracture aperture, spacing, length, and strike. SPE Reserv Eval Eng 18(4):463–480. https://doi.org/10.2118/170703-PA
Sungkorn R, Derksen JJ, Khinast JG (2012) Euler–Lagrange modeling of a gas–liquid stirred reactor with consideration of bubble breakage and coalescence. AIChE J 59(4):215–228. https://doi.org/10.1002/aic.12690
Tanner AB (1968) Radon migration in the ground: a review.
Tanner AB (1978) Radon migration in the ground: a supplementary review.
Taylor SFR, Brittle SA, Desai P, Jacquemin J, Hardacre C, Zimmerman WA (2017) Factors affecting bubble size in ionic liquids. Phys Chem Chem Phys 19(22):14306–14318. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7cp01725a
Thordarson W (1965) Perched ground water in zeolitized-bedded tuff, rainier mesa and vicinity,Nevada Test Site, Nevada.
Tirmarche M (2018) Cancer risk following alpha-emitter exposure. Ann ICRP 47(3–4):115–125. https://doi.org/10.1177/0146645318756247
Toutain JP, Baubron JC (1999) Gas geochemistry and seismotectonics: a review. Tectonophysics 304(1–2):1–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-1951(98)00295-9
Tran LK, Matthai SK (2021) Simulation of the infiltration of fractured rock in the unsaturated zone. Appl Sci 11(19). https://doi.org/10.3390/app11199148
Tran LK, Kim JC, Matthäi SK (2020) Simulation of two-phase flow in porous media with sharp material discontinuities. Adv Water Resour 142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2020.103636
Trique M, Richon P, Perrier F, Avouac JP, Sabroux JC (1999) Radon emanation and electric potential variations associated with transient deformation near reservoir lakes. Nature 399(6732):137–141. https://doi.org/10.1038/20161
Tryggvason G, Dabiri S, Aboulhasanzadeh B, Lu J (2013) Multiscale considerations in direct numerical simulations of multiphase flows. Phys Fluids 25(3). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4793543
UNSCEAR (1988) UNSCEAR Report (1988) Sources, Effects and Risks of Ionising RadiationUnited Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic.
UNSCEAR (2000) Sources and effects of ionizing radiation Volume I: source. In: United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation: Vol. I
Van De Ven CJC, Mumford KG (2020) Intermediate-scale laboratory investigation of stray gas migration impacts: transient gas flow and surface expression. Environ Sci Technol 54(19):12493–12501. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.0c03530
Vañó E, Miller CJ, Rehani MM, Kang K, Rosenstein M, Ortiz-López P, Mattsson S, Padovani R, and Rogers A (2014) Radiological protection against radon exposure (Annals of the ICRP) In Protection, International Commission on Radiological (Vol. 43, Issue 3). www.icrp.org
Varhegyi A, Baranyi I, Somogyi G (1986) A model for the vertical subsurface radon transport in “geogas” microbubbles. Geophys Trans 32(3):235–253
Vàrhegyi A, Hakl J, Monnin M, Morin JP, Seidel JL (1992) Experimental study of radon transport in water as test for a transportation microbubble model. J Appl Geophys 29(1):37–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/0926-9851(92)90011-9
Viswanathan HS, Hyman JD, Karra S, O’Malley D, Srinivasan S, Hagberg A, Srinivasan G (2018) Advancing graph-based algorithms for predicting flow and transport in fractured rock. Water Resour Res 54(9):6085–6099. https://doi.org/10.1029/2017WR022368
Wang JSY, Narasimhan TN (1985) Hydrologic mechanisms governing fluid flow in a partially saturated, fractured, porous medium. Water Resour Res 21(12):1861–1874. https://doi.org/10.1029/WR021i012p01861
Wang H, Xu W, Shao J, Skoczylas F (2014) The gas permeability properties of low-permeability rock in the process of triaxial compression test. Mater Lett 116:386–388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2013.11.061
Wang P, Yang T, Xu T, Cai M, Li C (2016) Numerical analysis on scale effect of elasticity, strength and failure patterns of jointed rock masses. Geosci J 20(4):539–549. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12303-015-0070-x
Wang F, Jiao L, Lian P, Zeng J (2019a) Apparent gas permeability, intrinsic permeability and liquid permeability of fractal porous media: carbonate rock study with experiments and mathematical modelling. J Pet Sci Eng 173:1304–1315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2018.10.095
Wang Q, Laubach SE, Ramos MJ (2019b) Quantified fracture (joint) clustering in Archean basement, Wyoming: application of normalized correlation count method. Pet Geosci Quant 25:415–428
Wang X, Jiang Y, Liu R, Li B, Wang Z (2020) A numerical study of equivalent permeability of 2D fractal rock fracture networks. Fractals 28(1):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218348X20500140
Wang Y, Wang L, Bai Y, Wang Z, Hu J, Hu D, Wang Y, Hu S (2021) Assessment of geothermal resources in the north jiangsu basin, east china, using monte carlo simulation. Energies 14(2). https://doi.org/10.3390/en14020259
Wanninkhof R, Mulholland PJ, Elwood JW (1990) Gas exchange rates for a first-order stream determined with deliberate and natural tracers. Water Resour Res 26(7):1621–1630. https://doi.org/10.1029/WR026i007p01621
Weber A, Bart H-J (2018) Flow simulation in a 2D bubble column with the Euler-lagrange and Euler-euler method. Open Chem Eng J 12(1):1–13. https://doi.org/10.2174/1874123101812010001
Wei Y, Chen J (2021) DFNSC: a particle tracking discrete fracture network simulator considering successive spatial correlation. Comput Geol 135:104156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2021.104156
Woith H, Barbosa S, Gajewski C, Steinitz G, Piatibratova O, Malik U, Zschau J (2011) Periodic and transient radon variations at the Tiberias hot spring, Israel during 2000-2005. Geochem J 45(6):473–482. https://doi.org/10.2343/geochemj.1.0147
Xu C, Fidelibus C, Dowd P, Wang Z, Tian Z (2018) An iterative procedure for the simulation of the steady-state fluid flow in rock fracture networks. Eng Geol 242:160–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2018.06.005
Xue D, Lu L, Zhou J, Lu L, Liu Y (2021) Cluster modeling of the short-range correlation of acoustically emitted scattering signals. Int J Coal Sci Technol 8(4):575–589. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40789-020-00357-6
Yan G, Li Z, Bore T, Torres SAG, Scheuermann A, Li L (2021) Discovery of dynamic two-phase flow in porous media using two-dimensional multiphase lattice boltzmann simulation. Energies 14(13):1–22. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14134044
Ye R, Zhang B, Wang Y (2015) Mechanism of the migration of gold in desert regolith cover over a concealed gold deposit. Geochem Explor Environ Anal 15(1):62–71. https://doi.org/10.1144/geochem2013-228
Ye YJ, Wu WH, Huang CH (2019) Theoretical study of the exhalation of radon from a circular tubular cover layer. Indian J Phys 93(5):667–672. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-018-1327-9
Yu Q, Xu Z, Zhao J, Zhang M, Ma X (2020) PIV-based acoustic pressure measurements of a single bubble near the elastic boundary. Micromachines 11(7). https://doi.org/10.3390/MI11070637
Yuce G, Fu CC, D’Alessandro W, Gulbay AH, Lai CW, Bellomo S, Yang TF, Italiano F, Walia V (2017) Geochemical characteristics of soil radon and carbon dioxide within the Dead Sea Fault and Karasu Fault in the Amik Basin (Hatay), Turkey. Chem Geol 469:129–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2017.01.003
Zahorowski W, Chambers SD, Henderson-Sellers A (2004) Ground based radon-222 observations and their application to atmospheric studies. J Environ Radioact 76(1–2):3–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvrad.2004.03.033
Zhang X, Dong H, Bao D, Huang Y, Zhang X, Zhang S (2014) Effect of small amount of water on CO2 bubble behavior in ionic liquid systems. Ind Eng Chem Res 53(1):428–439. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie4020827
Zhang L, Cui C, Ma X, Sun Z, Liu F, Zhang K (2019a) A fractal discrete fracture network model for history matching of naturally fractured reservoirs. Fractals 27(1):1–15. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218348X19400085
Zhang Y, Tang Z, Duan W, Si M (2019b) Multiphase flow law and well control risk analysis in deep water gas hydrate horizontal well while drilling. IOP Conf Ser Earth Environ Sci 300(2). https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/300/2/022142
Zhang X, Wang J, Wan D (2020) Euler-Lagrange study of bubble drag reduction in turbulent channel flow and boundary layer flow. Phys Fluids 32(2). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5141608
Zhou Z, Tao S, Xu F, Dawson R (2003) A physical-mathematical model for the transport of heavy metals and toxic matter from point sources by geogas microbubbles. Ecol Model 161(1–2):139–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-3800(02)00322-8
Zielinski JM, Carr Z, Krewski D, Repacholi M (2006) World health organization’s international radon project. J Toxicol Environ Health A 69(7–8):759–769. https://doi.org/10.1080/15287390500261299
Zou X, Hu W, Song H, Chen B (2021) The visual measurement of velocity profile distribution in silt carrying flow by using ultrasound PIV and iterative multi-grid deformation technique. Appl Sci 11(15). https://doi.org/10.3390/app11156952
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank the assistance provided in the laboratory.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant numbers 11705083), Foundation project in the field of Equipment Advance Research (grant number 80927015101), Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province (grant number 2019JJ50488), and Science and Technology Innovation Project of Hengyang (grant number 202105006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Writing: Xiaojie Chen; literature collection: Yong Liu; visualization: Yourui Jiang; conceptualization: Shengyang Feng. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Georg Steinhauser
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, ., Liu, Y., Jiang, Y. et al. Radon transport carried by geogas: prediction model. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 86656–86675 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28616-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28616-4