Abstract
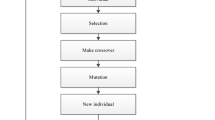
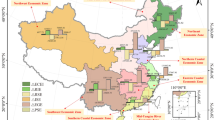
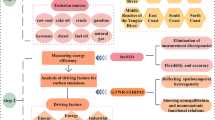
Carbon emission (CE) has led to increasingly severe climate problems. The key to reducing CE is to identify the dominant influencing factors and explore their influence degree. The CE data of 30 provinces from 1997 to 2020 in China were calculated by IPCC method. Based on this, the importance order of six factors included GDP, Industrial Structure (IS), Total Population (TP), Population Structure (PS), Energy Intensity (EI) and Energy Structure (ES) affecting the CE of China’s provinces were obtained by using symbolic regression, then the LMDI and the Tapio models were established to deeply explore the influence degree of different factors on CE. The results showed that the 30 provinces were divided into five categories according to the primary factor, GDP was the most important factor, followed by ES and EI, then IS, and the least TP and PS. The growth of per capita GDP promoted the increase of CE, while reduced EI inhibited the increase of CE. The increase of ES promoted CE in some provinces but inhibited in others. The increase of TP weakly promoted the increase of CE. These results can provide some references for governments to formulate relevant CE reduction policies under dual carbon goal.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Ang BW, Choi KH (1997) Decomposition of aggregate energy and gas emission intensities for industry: A refined divisia index method. Energy J 18:59–74. https://doi.org/10.2307/41322738
Chen C, Bi L (2022) Study on spatio-temporal changes and driving factors of carbon emissions at the building operation stage- A case study of China. Build Environ 219:109147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2022.109147
Du G, Sun C, Ouyang X, Zhang C (2018) A decomposition analysis of energy-related CO2 emissions in Chinese six high-energy intensive industries. J Clean Prod 184:1102–1112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.02.304
Hao J, Gao F, Fang X et al (2022) Multi-factor decomposition and multi-scenario prediction decoupling analysis of China's carbon emission under dual carbon goal. Sci Total Environ 841:156788. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.156788
IPCC (2006) IPCC Guidelines for national greenhouse gas inventories. In: Institute for Global Environmental Strategies (IGES) https://www.ipcc-nggip.iges.or.jp/
IPCC (2021) Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA(in press). https://doi.org/10.1017/9781009157896
Jiang J, Ye B, Xie D, Tang J (2017) Provincial-level carbon emission drivers and emission reduction strategies in China: Combining multi-layer LMDI decomposition with hierarchical clustering. J Clean Prod 169:178–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.03.189
Kabliman E, Kolody AH, Kronsteiner J, Kommenda M, Kronberger G (2021) Application of symbolic regression for constitutive modeling of plastic deformation. Appl Eng Sci 6:100052. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apples.2021.100052
Koza JR (1992) Genetic programming: on the programming of computers by means of natural selection. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA ISBN: 0-262-11170-5
Li J, Ding T (2020) Decomposition of driving factors of China's carbon emission growth. Coal Econ Res 40:47–56. (In Chinese). https://doi.org/10.13202/j.cnki.cer.2020.06.008
Lin B, Tan R (2017) Sustainable development of China's energy intensive industries: From the aspect of carbon dioxide emissions reduction. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 77:386–394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2017.04.042
Lin J (2010) Analysis of inter provincial differences in population urbanization level changes since 2000 — correction and repair based on statistical data. City. Plan Rev 3:9 CNKI:SUN:CSGH.0.2010-03-011
Liu H, Zhang Z (2021) Probing the carbon emissions in 30 regions of China based on symbolic regression and Tapio decoupling. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:2650–2663. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15648-x
Liu L, Fan Y, Wu G, Wei Y (2007) Using LMDI method to analyze the change of China's industrial CO2 emissions from final fuel use: An empirical analysis. Energy Policy 35:5892–5900. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2007.07.010
Luo Y, Long X, Wu C, Zhang J (2017) Decoupling CO2 emissions from economic growth in agricultural sector across 30 Chinese provinces from 1997 to 2014. J Clean Prod 159:220–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.05.076
Liu Z, Guan D, Wei W et al (2015) Reduced carbon emission estimates from fossil fuel combustion and cement production in China. Nature 524:335–338. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14677
Ma L, Guo Q, Li X et al (2022) Drag correlations for flow past monodisperse arrays of spheres and porous spheres based on symbolic regression: Effects of permeability. Chem Eng J 445:136653. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.136653
NBS-a (1998-2021) China Energy Statistical Yearbook. China Statistical Press, Beijing
NBS-b (1998-2021) China Statistical Yearbook. China Statistical Press, Beijing
Neumann P, Cao L, Russo D, Vassiliadis VS, Lapkin AA (2020) A new formulation for symbolic regression to identify physico-chemical laws from experimental data. Chem Eng J 387:123412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.123412
Ouyang X, Lin B (2015) An analysis of the driving forces of energy-related carbon dioxide emissions in China’s industrial sector. Renew Sust Energ Rev 45:838–849. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.02.030
Pan X, Uddin MK, Ai B, Pan X, Saima U (2019) Influential factors of carbon emissions intensity in OECD countries: Evidence from symbolic regression. J Clean Prod 220:1194–1201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.02.195
Quan C, Cheng X, Yu S, Ye X (2020) Analysis on the influencing factors of carbon emission in China's logistics industry based on LMDI method. Sci Total Environ 734:138473. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138473
Qin J, Gong N (2022) The estimation of the carbon dioxide emission and driving factors in China based on machine learning methods. Sustain Prod Consum 33:218–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spc.2022.06.027
Schmidt M, Lipson H (2009) Distilling free-form natural laws from experimental data. Science 324:81–85. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1165893
Shan Y, Huang Q, Guan D et al (2020) China CO2 emission accounts 2016–2017. Sci Data 7:54. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-020-0393-y
Tapio P (2005) Towards a theory of decoupling: degrees of decoupling in the EU and the case of road traffic in Finland between 1970 and 2001. Transp Policy 12:137–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tranpol.2005.01.001
Vladislavleva E, Friedrich T, Neumann F, Wagner M (2013) Predicting the energy output of wind farms based on weather data: Important variables and their correlation. Renew Energy 50:236–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2012.06.036
Wang Q, Zhao M, Li R (2019) Decoupling sectoral economic output from carbon emissions on city level: A comparative study of Beijing and Shanghai, China. J Clean Prod 209:126–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.10.188
Wang W, Zhang M, Zhou M (2011) Using LMDI method to analyze transport sector CO2 emissions in China. Energy 36:5909–5915. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2011.08.031
World Bank (1997-2019) Annual per capita carbon emission. https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/EN.ATM.CO2E.PC?locations=CN.
Wu C, Chou H, Su W (2008) Direct transformation of coordinates for GPS positioning using the techniques of genetic programming and symbolic regression. Eng Appl Artif Intell 21:1347–1359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2008.02.001
Wu Y, Tam V, Shuai C, Shen L, Zhang Y, Liao S (2019) Decoupling China’s economic growth from carbon emissions: empirical studies from 30 Chinese provinces (2001–2015). Sci Total Environ 656:576–588. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.11.384
Xi J (2020) Speech at the climate ambition Summit. Bulletin of the State Council of the people's Republic of China 35:7 (In Chinese)
Xie P, Yang F, Mu Z, Gao S (2020) Influencing factors of the decoupling relationship between CO2 emission and economic development in China’s power industry. Energy 209:118341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2020.118341
Xie J, Zhang L (2022) Machine learning and symbolic regression for adsorption of atmospheric molecules on low-dimensional TiO2. Appl Surf Sci 597:153728. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2022.153728
Yang G, Li W, Wang J, Zhang D (2016) A comparative study on the influential factors of China's provincial energy intensity. Energy Policy 88:74–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2015.10.011
Yang J, Cai W, Ma M, Li L, Liu C, Ma X, Li L, Chen X (2020) Driving forces of China’s CO2 emissions from energy consumption based on Kaya-LMDI methods. Sci Total Environ 711:134569. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134569
Yu S, Zhang Q, Hao J et al (2022) Development of an extended STIRPAT model to assess the driving factors of household carbon dioxide emissions in China. J Environ Manag 325:116502. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.116502
Zhao M, Tan L, Zhang W, Ji M, Liu Y, Yu L (2010) Decomposing the influencing factors of industrial carbon emissions in Shanghai using the LMDI method. Energy 35:2505–2510. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2010.02.049
Funding
This work was supported by the Beijing Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. 3202029).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Chunjing Liu: Writing - original draft, Conceptualization, Software, Writing - review & editing. Weiran Lyu: Material preparation, data collection and analysis. Xuanhao Zang: Writing - review & editing. Fei Zheng: Writing - review & editing. Wenchang Zhao: Writing - review & editing. Qing Xu: Writing - review & editing. Jianyi Lu: Project administration, Writing - review & editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: V.V.S.S. Sarma
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, ., Lyu, W., Zang, X. et al. Exploring the factors effecting on carbon emissions in each province in China: A comprehensive study based on symbolic regression, LMDI and Tapio models. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 87071–87086 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28608-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28608-4