Abstract
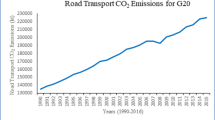
In Europe, there has been a significant shift in the movement of people and things. Nonetheless, despite the fact that transportation is an important component of the supply chain, its environmental consequences pose a severe threat to the ecosystem as a whole. As a result, we intend to explore the relationship between transportation, economy, and CO2 emissions. We used the Static method with Pooled OLS, then tested the Granger causality to validate the use of dynamic approach via the GMM system. The major findings revealed that GDP and trade openness had a considerable impact on CO2 emissions. Although the three modes of transportation have different effects on CO2 emissions, road density has a positive and considerable impact on CO2 emissions. The railway network is inversely connected to CO2 emissions. While the quantity of flight passengers has no substantial effect on emissions. In terms of the impulse response function, there is an initial shock in period 2 for the response of air passengers carried to CO2 emissions, followed by convergence back to zero in period 6, whereas road density has a slight decrease in period 2 with a post shock peak in period 4, followed by convergence back to zero in period 5. The variance decomposition results reveal a little increase until the fifth period for road density, air passengers, and trade openness with coefficients equal to 0.0893, 0.636, and 1.573, respectively, after which these three variables offer decreasing coefficients.

Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The data that support the findings of this study are available on request.
Abbreviations
- CO2 :
-
Carbon dioxide
- GHG:
-
Greenhouse gases
- GLS :
-
Generalized Least Squares
- GMM:
-
Generalized Method of Moments
- LNAIR:
-
Natural Logarithm of Air passengers carried
- LNCO2:
-
Natural Logarithm of CO2 emissions per capita
- LNGDP:
-
Natural Logarithm of Gross Domestic Product
- LNPOP:
-
Natural Logarithm of Population density
- LNRAIL :
-
Natural Logarithm of Railway network length
- LNRE:
-
Natural Logarithm of Renewable Energy
- LNROAD:
-
Natural Logarithm of Road Density
- LNTO:
-
Natural Logarithm of Trade Openness
- LNURBAN:
-
Natural Logarithm of Urbanization Rate
- OLS:
-
Ordinary Least Squares
References
Abdallah KB, Belloumi M, De Wolf D (2013) Indicators for sustainable energy development: A multivariate cointegration and causality analysis from Tunisian road transport sector. Renew Sust Energ Rev 25:34–43
Abdallh AA, Abugamos H (2017) A semi-parametric panel data analysis on the urbanisation-carbon emissions nexus for the MENA countries. Renew Sust Energ Rev 78:1350–1356
Ahmad N, Iqbal A, Mahmood H (2013) CO2 Emission, population and industrial growth linkages in selected South Asian countries: A co-integration analysis. World Appl Sci J 21(4):615–622
Air Transport Action Group (2019) Fact & Figures. Retrieved from. https://www.atag.org/facts-figures.html.
Ajmi AN, Hammoudeh S, Nguyen DK, Sato JR (2015) On the relationships between CO2 emissions, energy consumption and income: the importance of time variation. Energy Econ 49:629–638
Akashi O, Hanaoka T (2012) Technological feasibility and costs of achieving a 50% reduction of global GHG emissions by 2050: mid-and long-term perspectives. Sustain Sci 7:139–156
Alharthi M, Dogan E, Taskin D (2021) Analysis of CO2 emissions and energy consumption by sources in MENA countries: evidence from quantile regressions. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(29):38901–38908
Al-Mulali U, Ozturk I, Lean HH (2015) The influence of economic growth, urbanization, trade openness, financial development, and renewable energy on pollution in Europe. Nat Hazards 79:621–644
Al-Mulali U, Sab CNBC, Fereidouni HG (2012) Exploring the bi-directional long run relationship between urbanization, energy consumption, and carbon dioxide emission. Energy 46(1):156–167
Al-Rawashdeh R, Jaradat AQ, Al-Shboul M (2014) Air pollution and economic growth in MENA countries: testing EKC hypothesis. Environ Res Eng Manage 70(4):54–65
Amankwah-Amoah J (2020) Stepping up and stepping out of COVID-19: New challenges for environmental sustainability policies in the global airline industry. J Clean Prod 271:123000
Ang JB (2007) CO2 emissions, energy consumption, and output in France. Energy Policy 35(10):4772–4778
Arellano M, Bond S (1991) Some tests of specification for panel data: Monte Carlo evidence and an application to employment equations. Rev Econ Stud 58(2):277–297
Arouri MEH, Youssef AB, M'henni, H., & Rault, C. (2012) Energy consumption, economic growth and CO2 emissions in Middle East and North African countries. Energy Policy 45:342–349
Arvin MB, Pradhan RP, Norman NR (2015) Transportation intensity, urbanization, economic growth, and CO2 emissions in the G-20 countries. Util Policy 35:50–66
Awan A, Alnour M, Jahanger A, Onwe JC (2022) Do technological innovation and urbanization mitigate carbon dioxide emissions from the transport sector? Technol Soc 71:102128
Balogh JM, Jámbor A (2017) Determinants of CO2 emission: A global evidence. Int J Energy Econ Policy 7(5):217
Baltagi BH, Feng Q, Kao C (2012) A Lagrange Multiplier test for cross-sectional dependence in a fixed effects panel data model. J Econ 170(1):164–177
Ben Cheikh N, Ben Zaied Y (2021) A new look at carbon dioxide emissions in MENA countries. Clim Chang 166(3):1–22
Blundell R, Bond S (1998) Initial conditions and moment restrictions in dynamic panel data models. J Econ 87(1):115–143
Boonpanya T, Masui T (2021) Assessing the economic and environmental impact of freight transport sectors in Thailand using computable general equilibrium model. J Clean Prod 280:124271
Breusch TS, Pagan AR (1980) The Lagrange multiplier test and its applications to model specification in econometrics. Rev Econ Stud 47(1):239–253
Chandran VGR, Tang CF (2013) The impacts of transport energy consumption, foreign direct investment and income on CO2 emissions in ASEAN-5 economies. Renew Sust Energ Rev 24:445–453
Chang B, Kendall A (2011) Life cycle greenhouse gas assessment of infrastructure construction for California’s high-speed rail system. Transp Res Part D: Transp Environ 16(6):429–434
Clark G (2007) Evolution of the global sustainable consumption and production policy and the United Nations Environment Programme's (UNEP) supporting activities. J Clean Prod 15(6):492–498
Dean JM (2002) Does trade liberalization harm the environment? A new test. Canadian J Econ/Revue canadienne d'économique 35(4):819–842
Dedík M, Čechovič L, Gašparík J (2020) Methodical process for innovative management of the sustainable railway passenger transport. Transport Res Procedia 44:305–312
Destek MA, Balli E, Manga M (2016) The relationship between CO2 emission, energy consumption, urbanization and trade openness for selected CEECs. Res World Econ 7(1):52–58
Dogan E, Seker F (2016) Determinants of CO2 emissions in the European Union: the role of renewable and non-renewable energy. Renew Energy 94:429–439
Dumitrescu EI, Hurlin C (2012) Testing for Granger non-causality in heterogeneous panels. Econ Model 29(4):1450–1460
Erdogan S, Adedoyin FF, Bekun FV, Sarkodie SA (2020) Testing the transport-induced environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis: The role of air and railway transport. J Air Transp Manag 89:101935
Fang Y, Côté RP, Qin R (2007) Industrial sustainability in China: Practice and prospects for eco-industrial development. J Environ Manag 83(3):315–328
Farhani S, Ozturk I (2015) Causal relationship between CO2 emissions, real GDP, energy consumption, financial development, trade openness, and urbanization in Tunisia. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(20):15663–15676
Farhani S, Shahbaz M (2014) What role of renewable and non-renewable electricity consumption and output is needed to initially mitigate CO2 emissions in MENA region? Renew Sust Energ Rev 40:80–90
Forsyth P (2011) Environmental and financial sustainability of air transport: Are they incompatible? J Air Transp Manag 17(1):27–32
Ghazouani A, Xia W, Ben Jebli M, Shahzad U (2020) Exploring the role of carbon taxation policies on CO2 emissions: contextual evidence from tax implementation and non-implementation European Countries. Sustainability 12(20):8680
Gök A, Sodhi N (2021) The environmental impact of governance: a system-generalized method of moments analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(25):32995–33008
González RM, Marrero GA, Rodríguez-López J, Marrero ÁS (2019) Analyzing CO2 emissions from passenger cars in Europe: A dynamic panel data approach. Energy Policy 129:1271–1281
Grossman GM, Krueger AB (1991) Environmental impacts of a North American free trade agreement
Gupta M (2019) Decomposing the Role of Different Factors in CO Emissions Increase in South Asia. Stud Business Econ 14(1):72–86
Hassan SA, Nosheen M (2019) Estimating the Railways Kuznets Curve for high income nations—A GMM approach for three pollution indicators. Energy Rep 5:170–186
Hdom HA, Fuinhas JA (2020) Energy production and trade openness: Assessing economic growth, CO2 emissions and the applicability of the cointegration analysis. Energy Strat Rev 30:100488
Helgeson B, Peter J (2020) The role of electricity in decarbonizing European road transport–Development and assessment of an integrated multi-sectoral model. Appl Energy 262:114365
Herman E (2016) The importance of the manufacturing sector in the Romanian economy. Procedia Technol 22:976–983
Hou L, Wang Y, Zheng Y, Zhang A (2022) The Impact of Vehicle Ownership on Carbon Emissions in the Transportation Sector. Sustainability 14(19):12657
IEA (2023) International Energy Agency: Policies
Iwata H, Okada K, Samreth S (2010) Empirical study on the determinants of CO2 emissions: Evidence from OECD countries. MPRA paper No.21520
Jahanger A, Chishti MZ, Onwe JC, Awan A (2022a) How far renewable energy and globalization are useful to mitigate the environment in Mexico? Application of QARDL and spectral causality analysis. Renew Energy 201:514–525
Jahanger A, Usman M, Balsalobre-Lorente D (2022b) Linking institutional quality to environmental sustainability. Sustain Dev 30(6):1749–1765
Jahanger A, Yu Y, Hossain MR, Murshed M, Balsalobre-Lorente D, Khan U (2022c) Going away or going green in NAFTA nations? Linking natural resources, energy utilization, and environmental sustainability through the lens of the EKC hypothesis. Res Policy 79:103091
Jahanger A, Hossain MR, Onwe JC, Ogwu SO, Awan A, Balsalobre-Lorente D (2023a) Analyzing the N-shaped EKC among top nuclear energy generating nations: A novel dynamic common correlated effects approach. Gondwana Res 116:73–88
Jahanger A, Hossain MR, Usman M, Onwe JC (2023b) Recent scenario and nexus between natural resource dependence, energy use and pollution cycles in BRICS region: Does the mediating role of human capital exist? Res Policy 81:103382
Jahanger A, Ozturk I, Onwe JC, Joseph TE, Hossain MR (2023c) Do technology and renewable energy contribute to energy efficiency and carbon neutrality? Evidence from top ten manufacturing countries. Sustain Energy Technol Assess 56:103084
Jiang T, Yu Y, Jahanger A, Balsalobre-Lorente D (2022) Structural emissions reduction of China's power and heating industry under the goal of" double carbon": A perspective from input-output analysis. Sustain Prod Consump 31:346–356
Juodis A, Karavias Y, Sarafidis V (2021) A homogeneous approach to testing for Granger non-causality in heterogeneous panels. Empir Econ 60(1):93–112
Kasman A, Duman YS (2015) CO2 emissions, economic growth, energy consumption, trade and urbanization in new EU member and candidate countries: a panel data analysis. Econ Model 44:97–103
Kharbach M, Chfadi T (2017) CO2 emissions in Moroccan road transport sector: Divisia, Cointegration, and EKC analyses. Sustain Cities Soc 35:396–401
Krey V, Clarke L (2011) Role of renewable energy in climate mitigation: a synthesis of recent scenarios. Clim Pol 11(4):1131–1158
Liimatainen H, Arvidsson N, Hovi IB, Jensen TC, Nykänen L (2014) Road freight energy efficiency and CO2 emissions in the Nordic countries. Res Transp Bus Manag 12:11–19
Liu J, Yuan C, Hafeez M, Yuan Q (2018) The relationship between environment and logistics performance: Evidence from Asian countries. J Clean Prod 204:282–291
Luderer G, Pietzcker RC, Bertram C, Kriegler E, Meinshausen M, Edenhofer O (2013) Economic mitigation challenges: how further delay closes the door for achieving climate targets. Environ Res Lett 8(3):034033
Luo X, Dong L, Dou Y, Li Y, Liu K, Ren J et al (2017) Factor decomposition analysis and causal mechanism investigation on urban transport CO2 emissions: Comparative study on Shanghai and Tokyo. Energy Policy 107:658–668
Luthra S, Garg D, Haleem A (2016) The impacts of critical success factors for implementing green supply chain management towards sustainability: an empirical investigation of Indian automobile industry. J Clean Prod 121:142–158
Maddala GS, Wu S (1999) A comparative study of unit root tests with panel data and a new simple test. Oxf Bull Econ Stat 61(S1):631–652
Mahmood H, Maalel N, Zarrad O (2019) Trade openness and CO2 emissions:Evidence from Tunisia. Sustainability 11(12):3295
Mallick L, Tandi SM (2015) Energy consumption, economic growth, and CO2 emissions in SAARC countries: Does environmental Kuznets curve exist. Empirical Econometr Quant Econ Lett 4(3):57–69
Mittal N, Bhave AG, Mishra A, Singh R (2016) Impact of human intervention and climate change on natural flow regime. Water Resour Manag 30:685–699
Oh I, Wehrmeyer W, Mulugetta Y (2010) Decomposition analysis and mitigation strategies of CO2 emissions from energy consumption in South Korea. Energy Policy 38(1):364–377
Ouyang X, Shao Q, Zhu X, He Q, Xiang C, Wei G (2019) Environmental regulation, economic growth and air pollution: Panel threshold analysis for OECD countries. Sci Total Environ 657:234–241
Ozturk I, Acaravci A (2010) CO2 emissions, energy consumption and economic growth in Turkey. Renew Sust Energ Rev 14(9):3220–3225
Pao HT, Yu HC, Yang YH (2011) Modeling the CO2 emissions, energy use, and economic growth in Russia. Energy 36(8):5094–5100
Park Y, Meng F, Baloch MA (2018) The effect of ICT, financial development, growth, and trade openness on CO 2 emissions: an empirical analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:30708–30719
Pesaran MH (2004) General diagnostic tests for cross section dependence in panels. University of Cambridge, Faculty of Economics, Cambridge Working Papers in Economics No. 0435
Pesaran MH (2007) A simple panel unit root test in the presence of cross-section dependence. J Appl Econ 22(2):265–312
Peyravi B, Peleckienė V, Vaičiūtė K (2022) Research on the Impact of Motorization Rate and Technological Development on Climate Change in Lithuania in the Context of the European Green Deal. Sustainability 14(18):11610
Pradhan RP (2019) Investigating the causal relationship between transportation infrastructure, financial penetration and economic growth in G-20 countries. Res Transp Econ 78:100766
Pradhan RP, Arvin MB, Nair M (2021) Urbanization, transportation infrastructure, ICT, and economic growth: A temporal causal analysis. Cities 115:103213
Rizet C, Cruz C, de Lapparent M (2014) CO2 emissions of French shippers: The roles of delivery frequency and weight, mode choice, and distance. Res Transp Bus Manag 12:20–28
Rock MT, Angel DP (2007) Grow first, clean up later?: Industrial transformation in East Asia. Environ Sci Policy Sustain Dev 49(4):8–19
Sankaran A, Krishna A, Vadivel A (2021) How does manufacturing output affect export behaviors in emerging market economies? Evidence from a dynamic panel ARDL for ten biggest emerging market economies. Future Business J 7(1):1–10
Schäfer AW, Waitz IA (2014) Air transportation and the environment. Transp Policy 34:1–4
Sebri M, Ben-Salha O (2014) On the causal dynamics between economic growth, renewable energy consumption, CO2 emissions and trade openness: Fresh evidence from BRICS countries. Renew Sust Energ Rev 39:14–23
Sgouridis S, Bonnefoy PA, Hansman RJ (2011) Air transportation in a carbon constrained world: Long-term dynamics of policies and strategies for mitigating the carbon footprint of commercial aviation. Transp Res A Policy Pract 45(10):1077–1091
Shahbaz M, Solarin SA, Mahmood H, Arouri M (2013) Does financial development reduce CO2 emissions in Malaysian economy? A time series analysis. Econ Model 35:145–152
Shahbaz M, Uddin GS, Rehman IU, Imran K (2014) Industrialization, electricity consumption and CO2 emissions in Bangladesh. Renew Sust Energ Rev 31:575–586
Sokolov A, Veselitskaya N, Carabias V, Yildirim O (2019) Scenario-based identification of key factors for smart cities development policies. Technol Forecast Soc Chang 148:119729
Soytas U, Sari R (2009) Energy consumption, economic growth, and carbon emissions: challenges faced by an EU candidate member. Ecol Econ 68(6):1667–1675
Spaargaren G, & Mol AP (2011) Environmental social sciences and sustainable consumption. Encyclopedia of Consumer Culture 538–544
Sun Y, Li H, Andlib Z, Genie MG (2022) How do renewable energy and urbanization cause carbon emissions? Evidence from advanced panel estimation techniques. Renew Energy 185:996–1005
Timilsina GR, Shrestha A (2009) Transport sector CO2 emissions growth in Asia: Underlying factors and policy options. Energy Policy 37(11):4523–4539
Von Blottnitz H, Curran MA (2007) A review of assessments conducted on bio-ethanol as a transportation fuel from a net energy, greenhouse gas, and environmental life cycle perspective. J Clean Prod 15(7):607–619
Yang B, Ali M, Hashmi SH, Jahanger A (2022) Do income inequality and institutional quality affect CO2 emissions in developing economies? Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(28):42720–42741
Yang B, Jahanger A, Khan MA (2020) Does the inflow of remittances and energy consumption increase CO 2 emissions in the era of globalization? A global perspective. Air Qual Atmos Health 13:1313–1328
Yang S, Jahanger A, Hossain MR (2023a) Does China's low-carbon city pilot intervention limit electricity consumption? An analysis of industrial energy efficiency using time-varying DID model. Energy Econ, 106636
Yang S, Jahanger A, Hossain MR (2023b) How effective has the low-carbon city pilot policy been as an environmental intervention in curbing pollution? Evidence from Chinese industrial enterprises. Energy Econ 118:106523
Yang X, Lin S, Li Y, He M (2019) Can high-speed rail reduce environmental pollution? Evidence from China. J Clean Prod 239:118135
Zhang N, Choi Y, Wang W (2019) Does energy research funding work? Evidence from the Natural Science Foundation of China using TEI@ I method. Technol Forecast Soc Chang 144:369–380
Zhang YJ, Da YB (2015) The decomposition of energy-related carbon emission and its decoupling with economic growth in China. Renew Sust Energ Rev 41:1255–1266
Zhu C, Du W (2019) A research on driving factors of carbon emissions of road transportation industry in six Asia-Pacific countries based on the LMDI decomposition method. Energies 12(21):4152
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Imen Ghannouchi, Fedy Ouni, and Foued Aloulou. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Imen Ghannouchi and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Ethics approval was not required for this research.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent to Publish
Not applicable.
Competing Interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: V.V.S.S. Sarma
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ghannouchi, I., Ouni, F. & Aloulou, F. Investigating the impact of transportation system and economic growth on carbon emissions: Application of GMM System for 33 european countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 90656–90674 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28595-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28595-6