Abstract
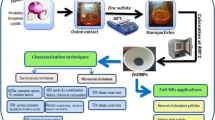
The objective of this study is to investigate the efficiency of two processes for the amoxicillin removal through static (batch) adsorption and photocatalytic degradation onto the prepared samples. Three solid materials as photocatalyst and/or adsorbent were synthesized viz. nanotitanium dioxide (NT) prepared by the sol–gel method, scallop shells-based nanohydroxyapatite (NP), and nanotitanium dioxide/nanohydroxyapatite composite (NTP). The physicochemical and morphological properties of the prepared samples were tested by TGA, XRD, DRS, ATR-FTIR, nitrogen adsorption/desorption isotherm, zeta potential, SEM, and TEM. The major operational conditions were optimized for catalyst or adsorbent mass, pH, shaking time, initial amoxicillin (AMX) concentration, power of UV lamp, and temperature. The results illuminated that NTP achieved the highest adsorption capacity (88.46 mg/g) at 20 ℃ and AMX adsorption onto all the solid materials was well applied by Langmuir, Temkin, pseudo-second order, and Elovich models. The maximum desorption percent (98%) was attained by acetone. The degradation percent of AMX reached 85.3 and 99.5% for NT and NTP, respectively, using 0.9 g/L of catalyst dosage through 90 min. AMX photodegradation onto the catalysts’ surface was well fitted by Langmuir–Hinshelwood, Arrhenius, and Eyring–Polanyi models with endothermic, physical, and nonspontaneous nature of photocatalysis process. NTP acts as a promising adsorbent and photocatalyst for the antibiotics’ removal in wastewater.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Abdelhameed RM, Taha M, Abdel-Gawad H, Emam HE (2022) Purification of soybean oil from diazinon insecticide by iron-based metal organic framework: effect of geometrical shape and simulation study. J Mol Struct 1250:131914. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2021.131914
Ahmed S, Rasul MG, Martens WN et al (2010) Heterogeneous photocatalytic degradation of phenols in wastewater: a review on current status and developments. Desalination 261:3–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2010.04.062
Al-Musawi TJ, Yilmaz M, Ramírez-Coronel AA et al (2022) Degradation of amoxicillin under a UV or visible light photocatalytic treatment process using Fe2O3/bentonite/TiO2: Performance, kinetic, degradation pathway, energy consumption, and toxicology studies. Optik (Stuttg) 272:170230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2022.170230
Alsager OA, Alnajrani MN, Abuelizz HA, Aldaghmani IA (2018) Removal of antibiotics from water and waste milk by ozonation: kinetics, byproducts, and antimicrobial activity. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 158:114–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.04.024
Al-Taweel SS, Saud HR, Kadhum AAH, Takriff MS (2019) The influence of titanium dioxide nanofiller ratio on morphology and surface properties of TiO2/chitosan nanocomposite. Results Phys 13:102296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2019.102296
Anastopoulos I, Pashalidis I, Orfanos AG et al (2020) Removal of caffeine, nicotine and amoxicillin from (waste)waters by various adsorbents. A review. J Environ Manage 261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110236
Awais M, Khursheed S, Tehreem R et al (2022) pH regulated rapid photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue dye via niobium-nitrogen co-doped titanium dioxide nanostructures under sunlight. Appl Catal A Gen 643:118764. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2022.118764
Bergamonti L, Bergonzi C, Graiff C et al (2019) 3D printed chitosan scaffolds: a new TiO2 support for the photocatalytic degradation of amoxicillin in water. Water Res 163:114841. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2019.07.008
Boussatha N, Gilliot M, Ghoualem H, Martin J (2018) Formation of nanogranular ZnO ultrathin films and estimation of their performance for photocatalytic degradation of amoxicillin antibiotic. Mater Res Bull 99:485–490. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2017.11.053
Chahkandi M, Zargazi M (2020) New water based EPD thin BiVO4 film: Effective photocatalytic degradation of amoxicillin antibiotic. J Hazard Mater 389. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121850
Chen H, Shao Y, Xu Z et al (2011) Effective catalytic reduction of Cr(VI) over TiO2 nanotube supported Pd catalysts. Appl Catal B Environ 105:255–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2011.04.004
Cheng D, Ngo HH, Guo W et al (2018) Anaerobic membrane bioreactors for antibiotic wastewater treatment: Performance and membrane fouling issues. Bioresour Technol 267:714–724. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.07.133
Chun SY, Chung WJ, Kim SS et al (2015) Optimization of the TiO2/Ge composition by the response surface method of photocatalytic degradation under ultraviolet-a irradiation and the toxicity reduction of amoxicillin. J Ind Eng Chem 27:291–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2015.01.003
Damiri F, Dobaradaran S, Hashemi S et al (2020) Waste sludge from shipping docks as a catalyst to remove amoxicillin in water with hydrogen peroxide and ultrasound. Ultrason Sonochem 68:105187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2020.105187
de Franco MAE, de Carvalho CB, Bonetto MM et al (2017) Removal of amoxicillin from water by adsorption onto activated carbon in batch process and fixed bed column: Kinetics, isotherms, experimental design and breakthrough curves modelling. J Clean Prod 161:947–956. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.05.197
Dinh TD, Phan MN, Nguyen DT et al (2022) Removal of beta-lactam antibiotic in water environment by adsorption technique using cationic surfactant functionalized nanosilica rice husk. Environ Res 210:112943. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2022.112943
Dou M, Wang J, Gao B et al (2020) Photocatalytic difference of amoxicillin and cefotaxime under visible light by mesoporous g-C3N4: Mechanism, degradation pathway and DFT calculation. Chem Eng J 383:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.123134
Easwaran G, Packialakshmi JS, Syed A et al (2022) Silica nanoparticles derived from Arundo donax L. ash composite with titanium dioxide nanoparticles as an efficient nanocomposite for photocatalytic degradation dye. Chemosphere 307:135951. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.135951
El Azzouzi L, El Aggadi S, Ennouhi M et al (2022) Removal of the amoxicillin antibiotic from aqueous matrices by means of an adsorption process using Kaolinite clay. Sci African 18:e01390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sciaf.2022.e01390
Elmolla ES, Chaudhuri M (2010) Photocatalytic degradation of amoxicillin, ampicillin and cloxacillin antibiotics in aqueous solution using UV/TiO2 and UV/H2O2/TiO2 photocatalysis. Desalination 252:46–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2009.11.003
Firozjaee TT, Mehrdadi N, Baghdadi M, Nabi Bidhendi GRN (2017) The removal of diazinon from aqueous solution by chitosan/carbon nanotube adsorbent. Desalin Water Treat 79:291–300. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2017.20794
Gai H, Wang H, Liu L et al (2021) Potassium and iodide codoped mesoporous titanium dioxide for enhancing photocatalytic degradation of phenolic compounds. Chem Phys Lett 767:138367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cplett.2021.138367
Ganesan K, Jothi VK, Natarajan A et al (2020) Green synthesis of Copper oxide nanoparticles decorated with graphene oxide for anticancer activity and catalytic applications. Arab J Chem 13:6802–6814. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2020.06.033
Gautam S, Sharma C, Purohit SD et al (2021) Gelatin-polycaprolactone-nanohydroxyapatite electrospun nanocomposite scaffold for bone tissue engineering. Mater Sci Eng C 119:111588. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2020.111588
Gharbani P, Mehrizad A, Mosavi SA (2022) Optimization, kinetics and thermodynamics studies for photocatalytic degradation of Methylene Blue using cadmium selenide nanoparticles. npj Clean Water 5. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41545-022-00178-x
Ghasemi Z, Younesi H, Zinatizadeh AA (2016) Kinetics and thermodynamics of photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants in petroleum refinery wastewater over nano-TiO2 supported on Fe-ZSM-5. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 65:357–366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2016.05.039
Guesmi Y, Agougui H, Lafi R et al (2018) Synthesis of hydroxyapatite-sodium alginate via a co-precipitation technique for efficient adsorption of Methylene Blue dye. J Mol Liq 249:912–920. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2017.11.113
Hassan AF, Hrdina R (2018) Chitosan/nanohydroxyapatite composite based scallop shells as an efficient adsorbent for mercuric ions: Static and dynamic adsorption studies. Int J Biol Macromol 109:507–516. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.12.094
Hassan AF, Elhadidy H, Abdel-Mohsen AM (2017) Adsorption and photocatalytic detoxification of diazinon using iron and nanotitania modified activated carbons. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 75:299–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2017.03.026
Hassan AF, El-Naggar GA, Esmail G, Shaltout WA (2023) Efficient adsorption of methylene blue on novel triple-nanocomposites of potassium Kappa-carrageenan, calcium alginate and nanohydroxyapatite obtained from sea scallop shells. Appl Surf Sci Adv 13:100388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsadv.2023.100388
Hu N, Yu J, Hou L et al (2022) Amine-functionalized MOF-derived carbon materials for efficient removal of Congo red dye from aqueous solutions: simulation and adsorption studies. RSC Adv 13:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1039/d2ra06513d
Imanipoor J, Ghafelebashi A, Mohammadi M et al (2021) Fast and effective adsorption of amoxicillin from aqueous solutions by L-methionine modified montmorillonite K10. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 611:125792. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2020.125792
Imanipoor J, Mohammadi M, Dinari M, Ehsani MR (2021b) Adsorption and desorption of amoxicillin antibiotic from water matrices using an effective and recyclable MIL-53(Al) metal-organic framework adsorbent. J Chem Eng Data 66:389–403. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jced.0c00736
Ioannou-Ttofa L, Raj S, Prakash H, Fatta-Kassinos D (2019) Solar photo-Fenton oxidation for the removal of ampicillin, total cultivable and resistant E. coli and ecotoxicity from secondary-treated wastewater effluents. Chem Eng J 355:91–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.08.057
Laksaci H, Belhamdi B, Khelifi O et al (2022) Elimination of amoxicillin by adsorption on coffee waste based activated carbon. J Mol Struct 1274:134500. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2022.134500
Lalliansanga, Tiwari D, Lee SM, Kim DJ (2022) Photocatalytic degradation of amoxicillin and tetracycline by template synthesized nano-structured Ce3+@TiO2 thin film catalyst. Environ Res 210:112914. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2022.112914
Le S, Yang W, Chen G et al (2020) Extensive solar light harvesting by integrating UPCL C-dots with Sn2Ta2O7/SnO2: Highly efficient photocatalytic degradation toward amoxicillin. Environ Pollut 263:114550. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114550
Le TD, Nguyen DT, Nguyen QL et al (2023) Adsorptive removal of dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) using novel nanoparticles based on cationic surfactant-coated titania nanoparticles. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30:42367–42377. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-25312-1
Li J, Cui M (2020) Kinetic study on the sorption and degradation of antibiotics in the estuarine water: an evaluation based on single and multiple reactions. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:42104–42114. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10194-4
Li Y, Shi M, Xia M, Wang F (2021) The enhanced adsorption of ampicillin and amoxicillin on modified montmorillonite with dodecyl dimethyl benzyl ammonium chloride: Experimental study and density functional theory calculation. Adv Powder Technol 32:3465–3475. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2021.08.001
Liu L, Cui W, Lu C et al (2020) Analyzing the adsorptive behavior of Amoxicillin on four Zr-MOFs nanoparticles: Functional groups dependence of adsorption performance and mechanisms. J Environ Manage 268:110630. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110630
Marques Zoccal JV, de Oliveira AF, Silveira Goncalves JA (2010) Synthesis and characterization of TiO2 nanoparticles by the method Pechini. Mater Sci Forum 660–61:6
Mohammed AA, Al-Musawi TJ, Kareem SL et al (2020) Simultaneous adsorption of tetracycline, amoxicillin, and ciprofloxacin by pistachio shell powder coated with zinc oxide nanoparticles. Arab J Chem 13:4629–4643. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2019.10.010
Ngo Thi TD, Nguyen LH, Nguyen XH et al (2022) Enhanced heterogeneous photocatalytic perozone degradation of amoxicillin by ZnO modified TiO2 nanocomposites under visible light irradiation. Mater Sci Semicond Process 142:106456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2022.106456
Nivetha MRS, Kumar JV, Ajarem JS et al (2022) Construction of SnO2/g-C3N4 an effective nanocomposite for photocatalytic degradation of amoxicillin and pharmaceutical effluent. Environ Res 209:112809. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2022.112809
Noviyanti AR, Asyiah EN, Permana MD et al (2022) Preparation of hydroxyapatite-titanium dioxide composite from eggshell by hydrothermal method: characterization and antibacterial activity. Crystals 12:1599. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12111599
Pang YL, Chuo HS, Lim S, Chong WC (2023) Materials Today : Proceedings Photocatalytic degradation of malachite green using titanium dioxide immobilised on oil palm empty fruit bunch derived cellulose. Mater Today Proc 46:2017–2023. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2021.02.684
Pham T-D, Le T-M-A, Pham T-M-Q et al (2021) Synthesis and characterization of novel hybridized CeO2@SiO2 nanoparticles based on rice husk and their application in antibiotic removal. Langmuir 37:2963–2973. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.0c03632
Prabhu SM, Khan A, Hasmath Farzana M et al (2018) Synthesis and characterization of graphene oxide-doped nano-hydroxyapatite and its adsorption performance of toxic diazo dyes from aqueous solution. J Mol Liq 269:746–754. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.08.044
Rajamanickam D, Shanthi M (2016) Photocatalytic degradation of an organic pollutant by zinc oxide – solar process. Arab J Chem 9:S1858–S1868. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2012.05.006
Ren L, Zhou D, Wang J et al (2020) Biomaterial-based flower-like MnO2@ carbon microspheres for rapid adsorption of amoxicillin from wastewater. J Mol Liq 309:113074. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2020.113074
Rodríguez-Chueca J, VarelladellaGiustina S, Rocha J et al (2019) Assessment of full-scale tertiary wastewater treatment by UV-C based-AOPs: removal or persistence of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes? Sci Total Environ 652:1051–1061. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.10.223
Samarghandi MR, Asgari G, Shokoohi R et al (2019) Removing amoxicillin antibiotic from aqueous solutions by Saccharomyces cerevisiae bioadsorbent: kinetic, thermodynamic and isotherm studies. Desalin Water Treat 152:306–315. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2019.23941
Sánchez-Montes I, Fuzer Neto JR, Silva BF et al (2018) Evolution of the antibacterial activity and oxidation intermediates during the electrochemical degradation of norfloxacin in a flow cell with a PTFE-doped β-PbO2 anode: critical comparison to a BDD anode. Electrochim Acta 284:260–270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2018.07.122
Shaltout WA, El-Naggar GA, Esmail G, Hassan AF (2022) Synthesis and characterization of ferric@nanocellulose/nanohydroxyapatite bio-composite based on sea scallop shells and cotton stalks: adsorption of Safranin-O dye. Biomass Convers Biorefinery. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-022-02753-1
Teodoro FS, Elias MMC, Ferreira GMD et al (2018) Synthesis and application of a new carboxylated cellulose derivative. Part III: removal of auramine-O and safranin-T from mono- and bi-component spiked aqueous solutions. J Colloid Interface Sci 512:575–590. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2017.10.083
Tiwari B, Sellamuthu B, Ouarda Y et al (2017) Review on fate and mechanism of removal of pharmaceutical pollutants from wastewater using biological approach. Bioresour Technol 224:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.11.042
Vagropoulou G, Trentsiou M, Georgopoulou A et al (2021) Hybrid chitosan/gelatin/nanohydroxyapatite scaffolds promote odontogenic differentiation of dental pulp stem cells and in vitro biomineralization. Dent Mater 37:e23–e36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dental.2020.09.021
Wang X, Hong S, Lian H et al (2021) Photocatalytic degradation of surface-coated tourmaline-titanium dioxide for self-cleaning of formaldehyde emitted from furniture. J Hazard Mater 420:126565. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126565
Wang Y, Zuo G, Kong J et al (2022) Sheet-on-sheet TiO2/Bi2MoO6 heterostructure for enhanced photocatalytic amoxicillin degradation. J Hazard Mater 421:126634. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126634
Xing Zha S, Zhou Y, Jin X, Chen Z (2013) The removal of amoxicillin from wastewater using organobentonite. J Environ Manage 129:569–576. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2013.08.032
Yeo JYJ, Khaerudini DS, Soetaredjo FE et al (2023) Experimental and modelling study of adsorption isotherms of amoxicillin, ampicillin and doripenem on bentonite-chitosan composite. South African J Chem Eng 43:38–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajce.2022.09.013
Zhang B, Chen J, Wang C et al (2023) Insight into different adsorption behaviors of two fluoroquinolone antibiotics by sediment aggregation fractions. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30:24329–24343. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23947-0
Zhou C, Wang X, Song X et al (2020) Insights into dynamic adsorption of lead by nano-hydroxyapatite prepared with two-stage ultrasound. Chemosphere 253:126661. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126661
Zulmajdi SLN, Zamri NII, Yasin HM et al (2020) Comparative study on the adsorption, kinetics, and thermodynamics of the photocatalytic degradation of six different synthetic dyes on TiO2 nanoparticles. React Kinet Mech Catal 129:519–534. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-019-01701-x
Acknowledgements
All authors acknowledge the Ministry of Higher Education, Research and Innovation, Sultanate of Oman, for financial support. All author also acknowledges the University of Technology and Applied Sciences for supporting the present work.
Funding
This study was funded by Ministry of Higher Education, Research and Innovation of Sultanate of Oman (BFP/RGP/EBR/21/422).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, and analysis were performed by Laila M. Alshandoudi, Asaad F. Hassan, Amal Y. Al Subhi, and Sulaiman A. Al-Isaee. Data collection was performed by Walaa A. Shaltout, and Laila M. Alshandoudi.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable. This study did not involve human participants and/or animals.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: George Z. Kyzas
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Alshandoudi, L.M., Al Subhi, A.Y., Al-Isaee, S.A. et al. Static adsorption and photocatalytic degradation of amoxicillin using titanium dioxide/hydroxyapatite nanoparticles based on sea scallop shells. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 88704–88723 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28530-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28530-9