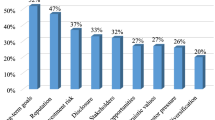
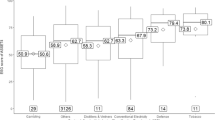
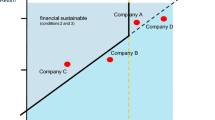
Abstract
This paper uses the sample of all A-share listed companies in China’s securities market except insurance and financial enterprises from 2009 to 2021 to construct a long panel data, and explores whether the environmental investment of enterprises will promote their long-term sustainable development in China’s unique and superior institutional and cultural environment from the perspective of Marxist ecological civilization. On the basis of controlling measurement errors, omitted variables, and endogenous problems of mutual causality to ensure the robustness of the research results, and further distinguishing the heterogeneous effects of environmental investment and sustainable development of enterprises in different degrees of market-oriented environment, the empirical study shows that (1) there is a significant positive relationship between environmental investment and sustainable development of enterprises. That is to say, environmental investment can help enterprises obtain social capital, alleviate resource constraints, enhance their market performance, and thus help their sustainable development in the future; (2) environmental protection investment has a significant positive impact on the sustainable development of enterprises in the mature market environment, while in the relatively backward market environment, environmental protection investment has no significant role in promoting the sustainable development of enterprises. This paper enriches the literature on corporate environmental investment, makes a preliminary test of the implementation effect of sustainable development in China, and provides more detailed empirical evidence for the government to further guide the implementation and implementation of corporate environmental responsibility.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Ahmed Z, Ahmad M, Murshed M et al (2022) How do green energy technology investments, technological innovation, and trade globalization enhance green energy supply and stimulate environmental sustainability in the G7 countries? Gondwana Res 112:105–115
Albarrak MS, Elnahass M, Salama A (2019) The effect of carbon dissemination on cost of equity. Bus Strateg Environ 28(6):1179–1198
Alexopoulos I, Kounetas K, Tzelepis D (2012) Environmental performance and technical efficiency, is there a link?: The case of Greek listed firms. Int J Product Perform Manag 61(1):6–23
Alkaraan F, Albitar K, Hussainey K, Venkatesh VG (2022) Corporate transformation toward industry 4.0 and financial performance: the influence of environmental, social, and governance (ESG). Technol Forecast Soc Chang (175-Feb.)
Baldini M, Maso LD, Liberatore G, Mazzi F, Terzani S (2018) Role of country- and firm-level determinants in environmental, social, and governance disclosure. J Bus Ethics 150(1):79–98
Belin J, Guille M (2008) R&d and innovation in France: what kind of financing for defense enterprises?
Cajias M, Fuerst F, Mcallister P, Nanda A (2014) Do responsible real estate companies outperform their peers? Int J Strateg Prop Manag 18(1):11–27
Chan KS, Dang V, Yan I (2012) Chinese firms’ political connection, ownership, and financing constraints. MPRA Paper 115(2):164–167
Chen YC, Hung M, Wang Y (2017) The effect of mandatory CSR disclosure on firm profitability and social externalities: evidence from China. Soc Sci Electron Publ 65(1):169–190
Cheng B, Ioannou I, Serafeim G (2014) Corporate social responsibility and access to finance. Strateg Manag J 35(1):1–23
Claessens S, Feijen E, Laeven L (2007) Political connections and preferential access to finance: the role of campaign contributions. CEPR Discus Pap 88(3):554–580
Cull R, Li W, Sun B, Xu LC (2015) Government connections and financial constraints: evidence from a large representative sample of Chinese firms. J Corp Finan 32:271–294
Eliwa Y, Aboud A, Saleh A (2019) ESG practices and the cost of debt: evidence from EU countries. Crit Perspect Account 8:1–21
Envelope Z, Envelope J, Envelope A (2022) How do natural resources, digitalization, and institutional governance contribute to ecological sustainability through load capacity factors in highly resource-consuming economies? Resour Policy 79:103068
Ghoul SE, Guedhami O, Kwok C, Mishra DR (2011) Does corporate social responsibility affect the cost of capital? J Bank Finance 35(9):2388–2406
Giese G, Lee LE, Melas D, Nagy Zoltán, Nishikawa L (2019) Foundations of esg investing: how esg affects equity valuation, risk, and performance. J Portf Manag 45(5):69–83
Goss A, Roberts GS (2011) The impact of corporate social responsibility on the cost of bank loans. J Bank Finance 35(7):1794–1810
Hadlock CJ, Pierce JR (2010) New evidence on measuring financial constraints: moving beyond the kz index. Rev Financ Stud 23(5):1909–1940
Hammami A, Zadeh MH (2019) Audit quality, media coverage, environmental, social, and governance disclosure and firm investment efficiency: evidence from Canada. Int J Account Inf Manag 28(1):45–72
Huang Y, Chen C (2022) The spatial spillover and threshold effect of green finance on environmental quality: evidence from China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(12):17487–17498
Klassen, Robert D (2000) Exploring the linkage between investment in manufacturing and environmental technologies. Int J Oper Prod Manag 20(2):127–147
Liu G, Yang Z, Zhang F, Zhang N (2022a) Environmental tax reform and environmental investment: a quasi-natural experiment based on China’s environmental protection tax law. Energy Econ 109:106000
Liu J, Jain V, Sharma P et al (2022b) The role of sustainable development goals to eradicate the multidimensional energy poverty and improve social wellbeing’s. Energ Strat Rev 42:100885
Luo W, Guo X, Zhong S, Wang J (2019) Environmental information disclosure quality, media attention and debt financing costs: evidence from Chinese heavy polluting listed companies. J Clean Prod 231(SEP.10):268–277
Min JH, Kim B, Ha S et al (2015) The relationship between firms’ environmental, social, governance factors and their financial performance: an empirical rationale for creating shared value. Korean Manag Sci Rev 32(1):113–131
Pavelin S, Porter LA (2008) The corporate social performance content of innovation in the U.K. J Bus Ethics 80(4):711–725
Peiris D, Evans J (2010) The relationship between environmental social governance factors and U.S. stock performance. J Invest 19(3):104–112
Satyro WC, De Almeida CMVB, Pinto Jr MJA, Contador JC, Giannetti BF, De Lima AF et al (2022) Industry 4.0 implementation: the relevance of sustainability and the potential social impact in a developing country. J Clean Prod 337
Schuler DA, Cording M (2006) A corporate social performance–corporate financial performance behavioral model for consumers. Acad Manag Rev 31(3):540–558
Serafeim G, Yoon A (2022) Stock price reactions to ESG news: the role of ESG ratings and disagreement. Soc Sci Electron Publ 2:1–31
Shafer M, Szado E (2019) Environmental, social, and governance practices and perceived tail risk. Account Finance 60(4):4195–4224
Sun Y, Chang H, Dinara G et al (2022) Economic performance, investment in energy resources, foreign trade, and natural resources volatility nexus: evidence from China’s provincial data. Renewable Energy 78:102913
Wagner M (2004) The effect of corporate environmental strategy choice and environmental performance on competitiveness and economic performance: an empirical study of EU manufacturing. Eur Manag J 22(5):557–572
Wang X, Hu L, Fan G (2021) Report on China’s Provincial Marketization Index. Social Sciences Academic Press, Beijing
Wei J, Li Y, Liu X et al (2022) Enterprise characteristics and external influencing factors of sustainable innovation: based on China’s innovation survey. J Clean Prod 372:133461
Xu XD, Zeng SX, Zou HL, Shi JJ (2014) The impact of corporate environmental violation on shareholders’ wealth: a perspective taken from media coverage. Bus Strateg Environ 25(2):73–91
Zhang F, Qin X, Liu L (2020) The interaction effect between ESG and green innovation and its impact on firm value from the perspective of information disclosure. Sustainability 12(5):1866
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yong Ye, Yi Yang, and Xiaowei Song: conceptualization, investigation, methodology, formal analysis, and writing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Arshian Sharif
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ye, Y., Yang, Y. & Song, X. Corporate environmental investment and sustainable development: based on the perspective of Marxist ecological civilization. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 89022–89035 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28508-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28508-7