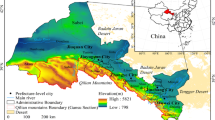
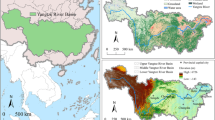
Abstract
In recent years, . the rapid development of the Yangtze River Delta in China has led to increasingly serious regional eco-environmental problems. Therefore, it is of great significance for the construction of ecological civilization to study the ecosystem health in the Yangtze River Delta. In this paper, the assessment framework of “Vigor-Organization-Resilience” was used to assess the ecosystem health index (EHI) of the Yangtze River Delta from 2000 to 2020, and then the spatial autocorrelation method was used to analyze the agglomeration of EHI in 314 counties in this region. Finally, the eXtreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost) model and the SHapley Additive exPlanation (SHAP) model were combined to explore the synergistic impact of EHI driving factors. The results show that (1) from 2000 to 2020, the EHI in the Yangtze River Delta is at the level of ordinary health, and gradually decreased; (2) the EHI has significant spatial positive correlation and aggregation; (3) the driving factors in descending order of importance are urbanization level (UL), precipitation (PRE), PM2.5 (PM), normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI), and temperature (TEMP); and (4) the relationship between UL and EHI is logarithmic; PRE and EHI are quartic polynomial; PM, NDVI, TEMP, and EHI are quadratic polynomial. The results of this paper are of great significance to the management and restoration of the ecosystem in this region








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Bebianno MJ, Pereira CG, Rey F, Cravo A, Duarte D, D’Errico G et al (2015) Integrated approach to assess ecosystem health in harbor areas. Sci Total Environ 514:92–107
Berrios F, Campbell DE, Ortiz M (2018) Emergy-based indicators for evaluating ecosystem health: a case study of three benthic ecosystem networks influenced by coastal upwelling in northern Chile (SE Pacific coast). Ecol Ind 95:379–393
Cda B, Jla B, Yla B, Zlab C, Xna B, Xh C et al (2021) Spatiotemporal dislocation of urbanization and ecological construction increased the ecosystem service supply and demand imbalance - ScienceDirect. J Environ Manag 288:112478
Chen W, Chi G (2022) Urbanization and ecosystem services: the multi-scale spatial spillover effects and spatial variations. Land Use Policy 114:105964
Chen W, Gu T, Zeng J (2022) Urbanisation and ecosystem health in the Middle Reaches of the Yangtze River urban agglomerations, China: a U-curve relationship. J Environ Manage 318:115565
Chen W, Zhang X, Huang Y (2021) Spatial and temporal changes in ecosystem service values in karst areas in southwestern China based on land use changes. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:45724–45738
Chen WX (2022) A multi-scale assessment of ecosystem health based on the pressure-state-response framework: a case in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River urban agglomerations. Chin Environ Sci Pollut earch 29:29202–29219
Cheng X, Chen L, Sun R, Kong P (2018) Land use changes and socio-economic development strongly deteriorate river ecosystem health in one of the largest basins in China. Sci Total Environ 616–617:376–385
Chi Y, Liu D, Xing W, Wang J (2021) Island ecosystem health in the context of human activities with different types and intensities. J Clean Prod 281:125334
Costanza R (2012) Ecosystem health and ecological engineering. Ecol Eng 45:24–29
Das M, Das A, Mandal A (2020) Research note: ecosystem health (EH) assessment of a rapidly urbanizing metropolitan city region of eastern India—a study on Kolkata Metropolitan Area. Landsc Urban Plan 204:103938
Das M, Das A, Pereira P, Mandal A (2021) Exploring the spatio-temporal dynamics of ecosystem health: a study on a rapidly urbanizing metropolitan area of Lower Gangetic Plain. India Ecol Indic 125:107584
Deng M, Chen J, Tao F, Zhu J, Wang M (2022) On the coupling and coordination development between environment and economy: a case study in the Yangtze River Delta of China. Int J Environ Res Public Health 19:586
Ge F, Chen W, Zeng Y, Li J (2021) The nexus between urbanization and traffic accessibility in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River urban agglomerations. Int J Environ Res Public Health 18:3828
Gui K, Che H, Zeng Z, Wang Y, Zhai S, Wang Z et al (2020) Construction of a virtual PM2.5 observation network in China based on high-density surface meteorological observations using the extreme gradient boosting model. Environ Int 141:105801
He J, Pan Z, Liu D, Guo X (2019) Exploring the regional differences of ecosystem health and its driving factors in China. Sci Total Environ 673:553–564
He M, Zeng L, Wu X, Luo J (2019b) The spatial and temporal evolution of logistics enterprises in the Yangtze River Delta. Sustainability 11:5318
Howell PE, Muths E, Hossack BR, Sigafus BH, Chandler RB (2018) Increasing connectivity between metapopulation ecology and landscape ecology. Ecology 99:1119–1128
Li W, Liu C, Su W, Ma X, Zhou H, Wang W et al (2021) Spatiotemporal evaluation of alpine pastoral ecosystem health by using the basic-pressure-state-response framework: a case study of the Gannan region, northwest China. Ecol Ind 129:108000
Li W, Wang Y, Xie S, Cheng X (2021) Coupling coordination analysis and spatiotemporal heterogeneity between urbanization and ecosystem health in Chongqing municipality. Chin Sci Total Environ 791:148311
Li W, Xie S, Wang Y, Huang J, Cheng X (2021) Effects of urban expansion on ecosystem health in Southwest China from a multi-perspective analysis. J Clean Prod 294:126341
Li Y-Y, Dong S-K, Wen L, Wang X-X, Wu Y (2013) Three-dimensional framework of vigor, organization, and resilience (VOR) for assessing rangeland health: a case study from the Alpine Meadow of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, China. Ecohealth 10:423–433
Li Z (2022) Extracting spatial effects from machine learning model using local interpretation method: an example of SHAP and XGBoost. Comput Environ Urban Syst 96:101845
Liu HX, Hua WH, Liu XG (2018) A new indicator for evaluating spatial concentration based on local spatial decompositions of the Gini coefficient. Prof Geogr 70:666–677
Lundberg SM, Lee S-I (2017) A unified approach to interpreting model predictions. In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS’17). Int Conf Neural Inf Proc Syst 30:4768–4777
Luo Q, Zhou J, Li Z, Yu B (2020) Spatial differences of ecosystem services and their driving factors: a comparation analysis among three urban agglomerations in China’s Yangtze River Economic Belt. Sci Total Environ 725:138452
Luo QL, Zhou JF, Zhang Y, Yu BL, Zhu ZB (2022) What is the spatiotemporal relationship between urbanization and ecosystem services? A case from 110 cities in the Yangtze River Economic Belt. China. J Environ Manag 321:115709
Luo Z, Zuo Q, Shao Q (2018) A new framework for assessing river ecosystem health with consideration of human service demand. Sci Total Environ 640–641:442–453
Ou W, Zhang L, Tao Y, Guo J (2018) A land-cover-based approach to assessing the spatio-temporal dynamics of ecosystem health in the Yangtze River Delta region. China Popul Resour Environ 28:84–92
Peng J, Liu Y, Jiansheng H et al (2015) Linking ecosystem services and landscape patterns to assess urban ecosystem health: a case study in Shenzhen City, China. Landsc Urban Plan 143:56–58
Peng J, Liu Y, Li T, Wu J (2017) Regional ecosystem health response to rural land use change: a case study in Lijiang City. Chin Ecol Indic 72:399–410
Peng J, Tian L, Liu Y, Zhao M, Hu Yn WuJ (2017) Ecosystem services response to urbanization in metropolitan areas: thresholds identification. Sci Total Environ 607–608:706–714
Qiao WY, Guan WH, Huang XJ (2021) Assessing the potential impact of land use on carbon storage driven by economic growth: a case study in Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration. Int J Environ Res Public Health 18:11924
Qiao WY, Huang XJ (2022) The impact of land urbanization on ecosystem health in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomerations. China. Cities 130:103981
Ran C, Wang S, Bai X, Tan Q, Wu L, Luo X et al (2021) Evaluation of temporal and spatial changes of global ecosystem health. Land Degrad Dev 32:1500–1512
Shao HM, Long D, He JQ, Zhang L (2022) Evaluation and evolution analysis of water ecosystem service value in the Yangtze River Delta region based on meta-analysis. Front Environ Sci 10:964168
Shaver GR, Canadell J, Chapin FS, Gurevitch J, Harte J, Henry G et al (2000) Global warming and terrestrial ecosystems: a conceptual framework for analysis. Bioscience 50:871–882
Shen W, Zheng ZC, Qin YC, Li Y (2020) Spatiotemporal characteristics and driving force of ecosystem health in an important ecological function region in China. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17:5075
Shu H, Xiao C, Ma T, Sang W (2021) Ecological health assessment of Chinese national parks based on landscape pattern: a case study in Shennongjia National Park. Int J Environ Res Public Health 18:11487
Su MR, Yang ZF, Liu GY, Chen B (2011) Ecosystem health assessment and regulation for urban ecosystems: a case study of the Yangtze River Delta urban cluster. Chin J Environ Inf 18:65–74
Sun B, Tang J, Yu D, Song Z, Wang P (2019) Ecosystem health assessment: a PSR analysis combining AHP and FCE methods for Jiaozhou Bay, China1. Ocean Coast Manag 168:41–50
Sun J, Li YP, Gao PP, Suo C, Xia BC (2018) Analyzing urban ecosystem variation in the City of Dongguan: a stepwise cluster modeling approach. Environ Res 166:276–289
Tang D, Liu X, Zou X (2018) An improved method for integrated ecosystem health assessments based on the structure and function of coastal ecosystems: a case study of the Jiangsu coastal area. China Ecological Indicators 84:82–95
Tao N, Liu D, Wu J (2019) Assessment of forest ecosystem health based on fuzzy evaluation method-a case study of forest ecosystem in Liangshui Natural Reserve. Rev Int De Contaminacion Ambiental 35:159–164
Utkin L, Konstantinov A (2022) Ensembles of random SHAPs. Algorithms 15:431
Wang G (2015) Migration and development: a comparison between the Yangtze River Delta and the Pearl River Delta. Acad Bimest 34:47–58
Wang L, Li Q, Qiu Q, Hou L, Ouyang J, Zeng R et al (2022) Assessing the ecological risk induced by PM2.5 pollution in a fast developing urban agglomeration of southeastern China. J Environ Manag 324:116284
Wang P, Deng X, Zhou H, Qi W (2018) Responses of urban ecosystem health to precipitation extreme: a case study in Beijing and Tianjin. J Clean Prod 177:124–133
Wang YT, Wang YS, Wu ML, Sun CC, Gu JD (2021) Assessing ecological health of mangrove ecosystems along South China Coast by the pressure-state-response (PSR) model. Ecotoxicology 30:622–631
Weihong LI (2009) Ecosystem health assessment in the Tarim River basin by using analytical hierarchy process. Res Sci 31:1535–1544
Weltzin JF, Loik ME, Schwinning S, Williams DG, Fay PA, Haddad BM et al (2003) Assessing the response of terrestrial ecosystems to potential changes in precipitation. Bioscience 53:941–952
Xia C, Zhang A, Wang H, Zhang B, Zhang Y (2019) Bidirectional urban flows in rapidly urbanizing metropolitan areas and their macro and micro impacts on urban growth: a case study of the Yangtze River middle reaches megalopolis. China Land Use Policy 82:158–168
Xiao R, Yu X, Shi R, Zhang Z, Yu W, Li Y et al (2019) Ecosystem health monitoring in the Shanghai-Hangzhou Bay Metropolitan Area: a hidden Markov modeling approach. Environ Int 133:105170
Xiao ZL, Liu R, Gao YH, Yang QY, Chen JL (2022) Spatiotemporal variation characteristics of ecosystem health and its driving mechanism in the mountains of southwest China. J Clean Prod 345:131138
Xu PH, Zhao XC, Li HL (2022) Spatial distribution and influencing factors of ecological efficiency in Yangtze River Delta. Rev Int De Contaminacion Ambiental 38:173–183
Yan Z, Yanfang L, Yang Z, Yi L, Guangxia Z, Yiyun C (2018) On the spatial relationship between ecosystem services and urbanization: a case study in Wuhan, China. Sci Total Environ 637–638:780–790
Yee SH, Paulukonis E, Simmons C, Russell M, Fulford R, Harwell L et al (2021) Projecting effects of land use change on human well-being through changes in ecosystem services. Ecol Model 440:109358
Yin L, Qiu X, Zhao R (2019) Health assessment of the aquatic ecosystem in Aiyi River. Appl Ecol Environ Res 17:10013–10025
Zhang D, Wang XR, Qu LP, Li SC, Lin YP, Yao R et al (2020) Land use/cover predictions incorporating ecological security for the Yangtze River Delta region, China. Ecol Indic 119:106841
Zhang G, Zheng D, Xie L, Zhang X, Wu H, Li S (2021) Mapping changes in the value of ecosystem services in the Yangtze River Middle Reaches Megalopolis. Chin Ecosyst Serv 48:101252
Zhang X, Chen W, Chen Z, Yang F, Meng C, Gou P et al (2022) Construction of cloud-free MODIS-like land surface temperatures coupled with a regional weather research and forecasting (WRF) model. Atmos Environ 283:119190
Zhang X, Gou P, Zhang F, Huang Y, Wang Z, Li G et al (2023) Reconstruction of all-weather land surface temperature based on a combined physical and data-driven model. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-27986-z
Zhang Y, Leung JYS, Zhang Y, Cai Y, Zhang Z, Li K (2021) Agricultural activities compromise ecosystem health and functioning of rivers: insights from multivariate and multimetric analyses of macroinvertebrate assemblages. Environ Pollut 275:116655
Zhao C, Shao N, Yang S, Ren H, Ge Y, Zhang Z et al (2019) Integrated assessment of ecosystem health using multiple indicator species. Ecol Eng 130:157–168
Funding
This research is funded by the National Key R&D Program of China, 2022YFB3903000, 2022YFB3903005, and Li Zhengqiang Expert Workstation of Yunnan Province (202205AF150031).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xuepeng Zhang: methodology, analysis writing, data sources. Peng Gou: methodology, coding. Wei Chen: coding, investigation. Guangchao Li: validation, investigation, coding. Yingshuang Huang: meteorological data. Tianyu Zhou: meteorological data. Yang Liu: investigation. Wei Nie: validation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Thomas Hein
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Gou, P., Chen, W. et al. Spatiotemporal distribution characteristics of ecosystem health and the synergetic impact of its driving factors in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 85184–85197 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28412-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28412-0