Abstract
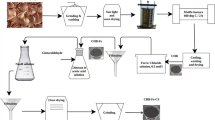
A group of Bacillus sp. was extracted from monosodium glutamate wastewater. Lignocellulose/montmorillonite composite was selected as the carrier. Lignocellulose/montmorillonite composite immobilized Bacillus sp./calcium alginate microspheres were prepared by immobilized microorganism techniques. The microspheres were used to treat monosodium glutamate wastewater with significantly reduced ammonia nitrogen (NH3-N) and chemical oxygen demand (COD) concentrations. The optimum preparation conditions of microspheres in the treatment of NH3-N and COD of monosodium glutamate wastewater were studied. The concentration of sodium alginate was 2.0 wt%, lignocellulose/montmorillonite was 0.06 wt%, Bacillus sp. was 1.0 wt%, CaCl2 solution was 2.0 wt%, coagulation time was 12 h, and the removal capacities of NH3-N and COD were 44832 and 78345 mg/L, respectively. The surface structure, element content, functional group change, and crystal structure of the microspheres were characterized by SEM, EDS, and other methods. The results showed that the -COOH in lignocellulose/montmorillonite and the -OH in the Bacillus sp. form intermolecular hydrogen bonds. The Si–O and Al-O bonds in lignocellulose/montmorillonite reacted with sodium ions in sodium alginate. New crystal structures appear inside the material after crosslinking, and the microspheres was formed. Thus, the study has shown that the microspheres were successfully prepared and contributes to the treatment of NH3-N and COD in monosodium glutamate wastewater. This work can provide an interesting strategy for the removal of COD and NH3-N in industrial wastewater by reasonably combining bio-physicochemical processes.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Alekseeva OV, Noskov AV, Titov VA, Nikitin D, Choukourov A, Agafonov AV (2021) Adsorption performance of the polystyrene/montmorillonite composites: effect of plasma treatment. Chem Eng Process 167:108505. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cep.2021.108505
Chen L, Qin J, Zhao Q, Ye Z (2022) Treatment of dairy wastewater by immobilized microbial technology using polyurethane foam as carrier. Bioresour Technol 347:126430. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.126430
Chul-Hwi P, Jin-Sook L, Duck-Hyun N, Yoon-sun B, In-Ho J (2008) A study on the operating condition for carbon-nitrogen removal in wastewater and sludge reduction using PVA-GEL immobilized microorganism. Water Pract Technol 3(2):1–9. https://doi.org/10.2166/wpt.2008.026
Hossain MF, Paul TC, Khan MNI, Islam S, Bala P (2021) Magnetic and dielectric properties of ZnFe2O4/nanoclay composites synthesized via sol-gel autocombustion. Mater Chem Phys 271:124914. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2021.124914
Huo Q, Li R, Chen C, Wang C, Long T, Liu X (2022) Study on potential microbial community to the waste water treatment from bauxite desilication process. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30(6):15438–15453. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23150-1
Jiang Y, Yang F, Dai M, Ali I, Shen X, Hou X, Naz I (2022) Application of microbial immobilization technology for remediation of Cr(VI) contamination: a review. Chemosphere 286:131721. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131721
Khalid S, Iqbal A, Javed A, Rashid J, Ul HI, Barakat MAE, Kumar R (2022) Analysis of diesel hydrocarbon decomposition using efficient indigenous bacterial isolate: bacterial growth and biodegradation kinetics. Korean J Chem Eng 39(11):3074–3082. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-022-1229-6
Li L, Zhang M, Jiang W, Yang P (2022a) Study on the efficacy of sodium alginate gel particles immobilized microorganism SBBR for wastewater treatment. J Environ Chem Eng 10(2):107134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2022.107134
Li X, Sun X, Zhou X, He Z, Lin K, Chen X, Jiang G (2022b) Fabrication of immobilized algal-bacterial beads and its application in synthetic mariculture tail water treatment. Process Saf Environ Prot 166:158–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2022.08.005
Malovanyy M, Masikevych A, Masikevych Y, Blyzniuk M, Tymchuk I, Zhuk V, Vlasyk L (2022) Use of microbiocenosis immobilized on carrer in technologies of biological treatment of surface and wastewater. Ecol Eng 23(9):34–43. https://doi.org/10.12911/22998993/151146
Qiu B, Shao Q, Shi J, Yang C, Chu H (2022) Application of biochar for the adsorption of organic pollutants from wastewater: modification strategies, mechanisms and challenges. Sep Purif 300:121925. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2022.121925
Ren J, Li X, Zhang W, Li Z, Wang Q, Li S, Li H (2022) Evaluation of application potential of dye-decolorizing peroxidase from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens in bioremediation of paper and pulp mill effluent. Front Microbiol 13:1031853. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2022.1031853
Rivero CW, Britos CN, Lozano ME, Sinisterra JV, Trelles JA (2021) Green biosynthesis of floxuridine by immobilized microorganisms. FEMS Microbiol. Lett 331(1):31–36. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.2012.02547
Selepe TN, Akanbi R, Maliehe TS, Moganedi K, Masoko P (2022) Flocculating activity of a bioflocculant from Bacillus megaterium BMBF in treatment of domestic and coal mine wastewater. Appl Sci 12(16):8312. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12168312
Song W, Huang T, Zuo H, Deng D, Tang C (2022) Application of microbial immobilization on chitosan composite membrane for manganese removal in water treatment. Polymer 243:124531. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2022.124531
Strong PJ, Burgess JE (2008) Treatment methods for wine-related and distillery wastewaters: a review. Bioremediat J 12(2):70–87. https://doi.org/10.1080/10889860802060063
Wang Y, Su J, Ali A, Chang Q, Bai Y, Gao Z (2022) Enhanced nitrate, manganese, and phenol removal by polyvinyl alcohol/sodium alginate with biochar gel beads immobilized bioreactor: performance, mechanism, and bacterial diversity. Bioresour Technol 348:126818. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2022.126818
Wu C, Zhi D, Yao B, Zhou Y, Yang Y, Zhou Y (2022) Immobilization of microbes on biochar for water and soil remediation: a review. Environ Res 212:113226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2022.113226
Yu W, Xinyu X (2022) Application of immobilized microorganism technology in water environment treatment. FSST 4(2):63–66. https://doi.org/10.25236/FSST.2022.040211
Yuniati MD, Rachmawati V, Nurjayati R, Marganingrum D, Lisdiana A, Noviardi RRW, Purwoko W (2022) COD removal of batik wastewater using microbial immobilization system for agricultural purposes. IOP Conf Ser Earth Environ Sci 1059(1):12032. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/1059/1/012032
Zhao B, Liu Z, Liu X, Shi Q, Liu Y, Wang L (2022) Study on treatment of high concentration monosodium glutamate wastewater with LNC/MMT nanocomposite. Modern Chemical Industry 42(07):152–157. https://doi.org/10.16606/j.cnki.issn0253-4320.2022.07.030. (In Chinese)
Zhao F, Zhang H, Yan P, Chen Y, Wu Q, Fang M.,... Gong Z (2021) Synthesis of coimmobilized microorganisms for the removal of cadmium from cadmium-contaminated rice flour. Food Sci Nutr 9(8):4509-4516. https://doi.org/10.1002/fsn3.2427
Funding
The authors received financial support from the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region Science and Technology Department Project (2019GG018), the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region Natural Science Foundation Project (2021MS02024), and the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region Science and Technology Department Project (2021GG0213).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Bai-Yun Zhao: conceptualization, investigation, methodology, data curation, writing — original draft, writing — review and editing. Xiao-Kai Liu: conceptualization, formal analysis, writing — review and editing. Xi-lin Li: conceptualization, investigation, writing — review and editing. Li-Juan Zhou: conceptualization, writing — review and editing. Li Wang: conceptualization, investigation, methodology, validation, writing — review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
In this paper, it will not cause harm to organisms.
Consent to participate
In this paper, biological experiments are not involved.
Consent for publication
The authors agree to publish the article to the journal Environmental Science and Pollution Research.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Angeles Blanco
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, BY., Liu, XK., Li, XL. et al. Effect of lignocellulose/montmorillonite immobilized Bacillus sp. on monosodium glutamate wastewater. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 83260–83269 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28230-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28230-4