Abstract
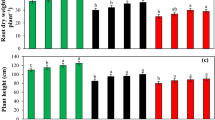
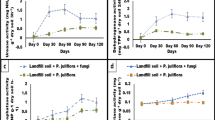
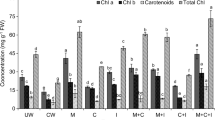
Phytoremediation is one of the best methods for cleaning up natural resources like water because plants are eco-friendly and safe for the ecosystem. Hyperaccumulators, e.g., Solanum nigrum L. and Atriplex lentiformis (Torr.) S. Watson, have been used to remove toxic metals from soil and water through phytoremediation techniques, but it is unknown if they can remove hazardous chemicals such as dinitrophenol (DNP), from wastewater. A hydroponic experiment was conducted to study the efficiency of S. nigrum and A. lentiformis in removing DNP from wastewater. Jasmonic acid (JAC) was applied to the tested plants in two doses, 0.25 and 0.50 mmol, in an effort to better understand how it affects phytoremediation effectiveness. The growth of S. nigrum and A. lentiformis improved significantly (p < 0.05) by the foliar application of JAC. The applications of JAC1 and JAC2 significantly (p < 0.05) increased nutrient uptake and chlorophyll concentrations in S. nigrum and A. lentiformis plants. The foliar spraying of S. nigrum and A. lentiformis with JAC significantly (p < 0.05) increased the antioxidant enzymes activity, i.e., SOD and POD. The levels of osmoregulatory substances like proline and carbohydrates significantly (p < 0.05) increased after JAC was sprayed on S. nigrum and A. lentiformis plants. In the case of S. nigrum, the efficiency of DNP removal varied between 53 and 69%, with an average of 63%, while in the case of A. lentiformis, it varied between 47 and 62%, with an average of 56%. The removal efficiency of DNP reached 67 and 69% when S. nigrum was sprayed with JAC1 and JAC2. When JAC1 and JAC2 were sprayed on A. lentiformis, DNP removal efficiency rose from 47 to 60 and from 47 to 62%, respectively. S. nigrum and A. lentiformis plants can be grown normally and survive in dinitrophenol-contaminated water without showing any toxic symptoms. S. nigrum and A. lentiformis have a powerful antioxidant system and the ability to produce vital compounds that alleviate the stress caused by DNP toxicity. The findings are crucial for cleaning up polluted water and protecting the ecosystem’s health from dangerous pollutants.
Graphical abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas T, Fan R, Hussain S, Sattar A, Khalid S, Butt M, Shahzad U, Atif HM, Batool M, Ullah S, Li Y, Al-Hashimi A, Elshikh M, Al-Yahyai R (2022) Protective effect of jasmonic acid and potassium against cadmium stress in peas (Pisum sativum L.). Saudi J Biol Sci 29(4):2626–2633. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.12.051
Ahmadi F, Karimi K, Struik P (2018) Effect of exogenous application of methyl jasmonate on physiological and biochemical characteristics of Brassica napus L. cv. Talaye under salinity stress. South Afr J Bot 115:5–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajb.2017.11.018
Akhtar N, Syakir Ishak MI, Bhawani SA, Umar K (2021) Various natural and anthropogenic factors responsible for water quality degradation: a review. Water 13(19):2660. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13192660
Alharbi K, Alaklabi A (2022) Alleviation of salinity induced growth and photosynthetic decline in wheat due to biochar and jasmonic acid application involves up-regulation of ascorbate-glutathione pathway, glyoxylase system and secondary metabolite accumulation. Rhizosphere 24:100603. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rhisph.2022.100603
Bates LS, Waldren RP, Teare ID (1973) Rapid determination of free proline for water stress studies. Plant Soil 39:205–207. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00018060
Burt R (2004) Soil survey laboratory methods manual. Soil Survey Investigations Report No. 42, Version 4.0. Natural Resources Conservation Service, United States Department of Agriculture. Accessed 01 June 2020, https://www.nrcs.usda.gov/wps/portal/nrcs/detail/soils/research/guide/?cid=nrcs142p2_054247
Dai H, Wei S, Grzebelus D, Skuza L, Jia J, Hou N (2022) Mechanism exploration of Solanum nigrum L. hyperaccumulating Cd compared to Zn from the perspective of metabolic pathways based on differentially expressed proteins using iTRAQ. J. Hazard Mater 440:129717. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.129717
Ding Z, Alharbi S, Almaroai YA, Eissa MA (2021) Improving quality of metal-contaminated soils by some halophyte and non-halophyte forage plants. Sci Total Environ 764:142885. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142885
Ding Z, Zhao F, Zhu Z, Ali EF, Shaheen SM, Rinklebe J, Eissa MA (2022) Green nanosilica enhanced the salt-tolerance defenses and yield of Williams banana: a field trial for using saline water in low fertile arid soil. Environ Exp Bot 197:104843. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2022.104843
Dou X, Dai H, Skuza L, Wei S (2022) Cadmium removal potential of hyperaccumulator Solanum nigrum L. under two planting modes in three years continuous phytoremediation. Environ Pollut:119493. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2022.119493
Eissa MA (2017) Phytoextraction mechanism of Cd by Atriplex lentiformis using some mobilizing agents. Ecol Eng 108:220–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2017.08.025
Eissa MA, Abeed AH (2019) Growth and biochemical changes in quail bush (Atriplex lentiformis (Torr.) S.Wats) under Cd stress. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:628–635. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3627-1
Eissa MA, Roshdy NMK (2018) Nitrogen fertilization: effect on Cd-phytoextraction by the halophytic plant quail bush [Atriplex lentiformis (Torr.) S. Wats]. South Afr J Bot 115:126–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajb.2018.01.015
Farhangi-Abriz S, Ghassemi-Golezani K (2019) Jasmonates: mechanisms and functions in abiotic stress tolerance of plants. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 20:101210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2019.101210
Glenn EP, Nelson SG, Ambrose B, Martinez R, Soliz D, Pabendinskas V, Hultine K (2012) Comparison of salinity tolerance of three Atriplex spp. in well-watered and drying soils. Environ Exp Bot 83:62–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2012.04.010
Guo W, Nazim H, Liang Z, Yang D (2016) Magnesium deficiency in plants: an urgent problem. Crop J 4(2):83–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cj.2015.11.003
Hanaka A, Nowak A, Ozimek E, Dresler S, Plak A, Sujak A, Strzemski M (2022) Effect of copper stress on Phaseolus coccineus in the presence of exogenous methyl jasmonate and/or Serratia plymuthica from the Spitsbergen soil. J Hazard Mater 439:129232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.129232
Hao G, Xu ZP, Li L (2018) Manipulating extracellular tumour pH: an effective target for cancer therapy. RSC Adv 8(39):22182–22192. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8RA02095G
Hlahla JM, Mafa MS, Van der Merwe R, Alexander O, Duvenhage MM, Kemp G, Moloi MJ (2022) The photosynthetic efficiency and carbohydrates responses of six edamame (Glycine max. L. Merrill) cultivars under drought stress. Plants 11(3):394. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11030394
Jamalian S, Truemper C, Pawelzik E (2020) Jasmonic and abscisic acid contribute to metabolism re-adjustment in strawberry leaves under NaCl stress. Int J Fruit Sci 20(2):S123–S144. https://doi.org/10.1080/15538362.2019.1709112
Jeon MW, Ali MB, Hahn EJ, Paek KY (2006) Photosynthetic pigments, morphology and leaf gas exchange during ex vitro acclimatization of micropropagated CAM Doritaenopsis plantlets under relative humidity and air temperature. Environ Exp Bot 55:183–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2004.10.014
Jones ER, Van Vliet MT, Qadir M, Bierkens MF (2021) Country-level and gridded estimates of wastewater production, collection, treatment and reuse. Earth Syst Sci Data 13(2):237–254. https://doi.org/10.5194/essd-13-237-2021
Kamran M, Wang D, Alhaithloul HAS, Alghanem SM, Aftab T, Xie KZ, Lu YS, Shi CH, Sun J, Gu WJ, Xu PZ, Soliman MH (2021) Jasmonic acid-mediated enhanced regulation of oxidative, glyoxalase defense system and reduced chromium uptake contributes to alleviation of chromium (VI) toxicity in choysum (Brassica parachinensis L.). Ecotox Environ Safe 208:111758. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111758
Kumar KB, Khan PA (1982) Peroxidase and polyphenol oxidase in excised ragi Eleusine coracana (V. PR 202) leaves during senescence. Ind J Exp Biol 20:412–416
Li J, Chang Y, Al-Huqail AA, Ding Z, Al-Harbi MS, Ali EF, Abeed AH, Rekaby SA, Eissa MA, Ghoneim A, Tammam SA (2021) Effect of manure and compost on the phytostabilization potential of heavy metals by the halophytic plant wavy-leaved saltbush. Plants 10(10):2176. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10102176
Lichtenthaler HK (1987) Chlorophylls and carotenoids: pigments of photosynthetic biomembranes. Methods Enzym 148:350–382. https://doi.org/10.1016/0076-6879(87)48036-1
Liu Z, Herman JD, Huang G, Kadir T, Dahlke HE (2021) Identifying climate change impacts on surface water supply in the southern Central Valley, California. Sci Total Environ 759:143429. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143429
Ma T, Sun S, Fu G, Hall JW, Ni Y, He L, Zhou C (2020) Pollution exacerbates China’s water scarcity and its regional inequality. Nat Commun 11(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-14532-5
Malcherek K, Breuer J, Schuphan I, Schmidt B (1998) Metabolism of 4- nitrophenol in aseptically cultivated plants of the species wheat (Triticum aestivum L.), soybean (Glycine max L.), wild oat (Avena fatua L.) and corn cockle (Agrostemma githago L.). J Plant Physiol 153(1–2):192–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0176-1617(98)80065-5
Marschner H (2012) Mineral nutrition of higher plants, third edn. Academic Press, London
Mohammed NA, Abu-Zurayk RA, Hamadneh I, Al-Dujaili AH (2018) Phenol adsorption on biochar prepared from the pine fruit shells: equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamics studies. J Environ Manage 226:377–385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.08.033
Mustafa HM, Hayder G (2021) Recent studies on applications of aquatic weed plants in phytoremediation of wastewater: a review article. Ain Shams Eng J 12(1):355–365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asej.2020.05.009
Nielsen SS (2010) Phenol-sulfuric acid method for total carbohydrates. In: Nielsen SS (ed) Food Analysis Laboratory Manual, Food Science Texts Series. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-1463-7_6
Pan SD, Chen XH, Shen HY, Li XP, Cai MQ, Zhao YG, Jin C (2016) Rapid and effective sample cleanup based on graphene oxide-encapsulated core–shell magnetic microspheres for determination of fifteen trace environmental phenols in seafood by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta 919:34–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2016.02.035
Park SJ, Das GS, Schütt F, Adelung R, Mishra YK, Tripathi KM, Kim T (2019) Visible-light photocatalysis by carbon-nano-onion-functionalized ZnO tetrapods: degradation of 2, 4-dinitrophenol and a plant-model-based ecological assessment. NPG Asia Mater 11(1):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41427-019
Per TS, Khan NA, Masood A, Fatma M (2016) Methyl jasmonate alleviates cadmium-induced photosynthetic damages through increased S-assimilation and glutathione production in mustard. Front Plant Sci 7:1933. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.01933
Raza W, Lee J, Raza N, Luo Y, Kim KH, Yang J (2019) Removal of phenolic compounds from industrial waste water based on membrane-based technologies. J Ind Eng Chem 71:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2018.11.024
Rosa L, Chiarelli DD, Rulli MC, Dell’Angelo J, D’Odorico P (2020) Global agricultural economic water scarcity. Sci Adv 6(18):eaaz6031. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aaz6031
Särkinen T, Kottner S, Stuppy W, Ahmed F, Knapp S (2018) A new commelinid monocot seed fossil from the early Eocene previously identified as Solanaceae. Am J Bot 105(1):95–107. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajb2.1009
Shamsabad MRM, Esmaeilizadeh M, Roosta HR, Dehghani MR, Dąbrowski P, Kalaji HM (2022) The effect of supplementary light on the photosynthetic apparatus of strawberry plants under salinity and alkalinity stress. Sci Rep 12(1):1–15. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-17377-8
Siddiqui M, Mukherjee S, Alamri S, Ali HM, Hasan Z, Kalaji HM (2022) Calcium and jasmonic acid exhibit synergistic effects in mitigating arsenic stress in tomato seedlings accompanied by antioxidative defense, increased nutrient accumulation and upregulation of glyoxalase system. South Afr J Bot 150:14–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajb.2022.06.030
Singh AK, Kim JY, Lee YS (2022a) Phenolic compounds in active packaging and edible films/coatings: natural bioactive molecules and novel packaging ingredients. Molecules 27(21):7513. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27217513
Singh VK, Singh R, Rajput VD, Singh VK (2022b) Halophytes for the sustainable remediation of heavy metal-contaminated sites: recent developments and future perspectives. Chemosphere:137524. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.137524
Sun C, Li C, Wenxiu M, Ma L, Huicheng X, Jingwei X (2022) The photosynthetic physiological response and purification effect of Salix babylonica to 2, 4-dinitrophenol wastewater. Int J Phytorem 24:675–683. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2021.1962799
Talano MA, Busso DC, Paisio CE, González PS, Purro SA, Medina M, Agostini E (2012) Phytoremediation of 2,4-dichlorophenol using wild type and transgenic tobacco plants. Environ Sci Pollut Res 19:2202–2211. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-011-0724-9
Tang S, Wang S, Liu Y, Cong H, Lei A (2018) Electrochemical oxidative C− H amination of phenols: access to triarylamine derivatives. Angew Chem 130(17):4827–4831. https://doi.org/10.1002/ange.201800240
Wang J, Elbagory M, He Y, Zhang X, Hui Y, Eissa MA, Ding Z, El-Nahrawy S, Omara AE, Zoghdan MG (2022) Modeling of p-loss risk and nutrition for mango (Mangifera indica L.) in sandy calcareous soils: a 4-years field trial for sustainable p management. Horticulturae 8:1064. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8111064
Wang J, Song L, Gong X, Xu J, Li M (2020) Functions of jasmonic acid in plant regulation and response to abiotic stress. Int J Mol Sci 21(4):1446. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21041446
Wang P, Farmer ME, Huo X, Jain P, Shen PX, Ishoey M, Yu JQ (2016) Ligand-promoted meta-C–H arylation of anilines, phenols, and heterocycles. J Am Chem Soc 138(29):9269–9276. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.6b04966
Wang YT, Yang CH, Huang KS, Shaw JF (2021) Chlorophyllides: preparation, purification, and application. Biomolecules 11:1115. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11081115
Wei R, Guo Q, Wen H, Liu C, Yang J, Peters M, Wan Y (2016) Fractionation of stable cadmium isotopes in the cadmium tolerant Ricinus communis and hyperaccumulator Solanum nigrum. Sci Rep 6(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep24309
Yang Z, Yang F, Liu JL, Wu HT, Yang H, Shi Y, Chen KM (2021) Heavy metal transporters: functional mechanisms, regulation, and application in phytoremediation. Sci Total Environ 809:15109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.151099
Zahid G, Iftikhar S, Shimira F, Ahmad HM, Kaçar YA (2023) An overview and recent progress of plant growth regulators (PGRs) in the mitigation of abiotic stresses in fruits: a review. Sci Hortic 309:111621. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2022.111621
Zhang LD, Song LY, Dai MJ, Guo ZJ, Wei MY, Li J, Xu CQ, Zhu XY, Zheng HL (2022) Cadmium promotes the absorption of ammonium in hyperaccumulator Solanum nigrum L. mediated by ammonium transporters and aquaporins. Chemosphere 307:136031. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.136031
Zhao R, Cao X, Li X, Li T, Zhang H, Cui X, Cui Z (2023) Ecological toxicity of Cd, Pb, Zn, Hg and regulation mechanism in Solanum nigrum L. Chemosphere 313:137447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.137447
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
Funding
This research was funded by Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University Researchers supporting project number (PNURSP2023R93), Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Arwa Abdulkreem AL-Huqail: conceptualization, methodology, investigation, formal analysis, visualization, and writing original draft.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Elena Maestri
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
AL-Huqail, A.A. Effect of jasmonic acid on the phytoremediation of dinitrophenol from wastewater by Solanum nigrum L. and Atriplex lentiformis (Torr.) S. Watson. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 80144–80153 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28148-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28148-x