Abstract
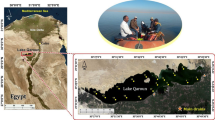
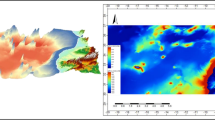
In the face of growing marine pollution, assessment of the sewage outfall discharges is essential as it affects the seawater quality. The study demonstrates sea surface salinity (SSS) variations caused by sewage discharges and links it with tidal characteristics to hypothesize the dynamics of sewage outfall plumes. SSS is estimated using a multilinear regression model based on Landsat-8 (L8) OLI reflectance and in situ SSS data of 2013–2014. Using the validated model, the SSS of the 2018 image is predicted and evidenced by its relationship with colored dissolved organic matter (CDOM). The preliminary results of the hypothesis are encouraging and found that the dispersion patterns of outfall plumes exhibit distinct characteristics depending on the intra-tidal range and hour. The findings indicate a lower SSS in the outfall plume zone than in ambient seawater due to dilution caused by partially treated sewage discharges from diffusers. The plumes observed during the macro tidal range are long and narrowly spread alongshore. In contrast, during the meso and microtidal ranges, the plumes are shorter and are primarily dispersed offshore rather than alongshore. During slack times, low salinity levels are visibly concentrated around outfalls as there is no water movement to disperse the accumulated sewage discharges from diffusers. These observations suggest that slack periods and low-tidal conditions could be significant factors contributing to the accumulation of pollutants in coastal waters. The study further suggests more datasets such as wind speed, wind direction, and density variations are needed to understand the processes influencing the outfall plume dynamics and variation in SSS. The study recommends increasing the treatment capabilities of existing treatment facilities from primary to tertiary treatment levels. Furthermore, it is important to warn and educate the public about the health risks associated with exposure to partially treated sewage that is discharged from outfalls.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed in the current study are available from the Indian National Centre for Ocean Information Services (INCOIS).
References
Abegunrin A, Hepp DA, Mörz T (2020) Correction of water column height variation on 2D grid high-resolution seismic data using dGPS based methodology. Sci Rep 10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-75740-z
Adejumoke I, Babatunde A, Abimbola O et al (2018) Water pollution: effects, prevention, and climatic impact. In: Water Challenges of an Urbanizing World
Ahn YH, Shanmugam P, Moon JE, Ryu JH (2008) Satellite remote sensing of a low-salinity water plume in the East China Sea. Ann Geophys 26:2019–2035. https://doi.org/10.5194/angeo-26-2019-2008
Akdemir T, Dalgic G (2021) The impact of the marine sewage outfalls on the sediment quality: the Black Sea and the Marmara case. Saudi J Biol Sci 28:238–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2020.09.055
Ayad M, Li J, Holt B, Lee C (2020) Analysis and classification of stormwater and wastewater runoff from the Tijuana River using remote sensing imagery. Front Environ Sci 8. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2020.599030
Baban SMJ (1997) Environmental monitoring of estuaries; estimating and mapping various environmental indicators in Breydon Water Estuary, U.K., using Landsat TM Imagery. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 44:589–598. https://doi.org/10.1006/ecss.1996.0142
Bai Y, Pan D, Cai WJ et al (2013) Remote sensing of salinity from satellite-derived CDOM in the Changjiang River dominated East China Sea. J Geophys Res Ocean 118:227–243. https://doi.org/10.1029/2012JC008467
Ballasiotes (2020) Mapping untreated and semi-treated wastewater effluent off the coast of Gaza with Sentinel-1 time series data. M. Sc. Thesis, Oregon State University, USA
Barbier EB (2015) Climate change impacts on rural poverty in low-elevation coastal zones. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 165:A1–A13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2015.05.035
Binding CE, Bowers DG (2003) Measuring the salinity of the Clyde Sea from remotely sensed ocean colour. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 57:605–611. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0272-7714(02)00399-2
Boothroyd JC (1985) Tidal inlets and tidal deltas. In: Coastal Sedimentary Environments, pp 445–532
Burrage DM, Heron ML, Hacker JM et al (2003) Structure and influence of tropical river plumes in the Great Barrier Reef: application and performance of an airborne sea surface salinity mapping system. Remote Sens Environ 85:204–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0034-4257(02)00206-7
Chen S, Hu C (2017) Estimating sea surface salinity in the northern Gulf of Mexico from satellite ocean color measurements. Remote Sens Environ 201:115–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2017.09.004
Cinner J (2000) Socioeconomic influences on coastal resource use in Mahahual, Mexico. Mar Aff Master in:110
CPCB (2013) Performance evaluation of sewage treatment plants under NRCD. Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB), Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate Change, Govt. of India. website: https://cpcb.nic.in/openpdffile.php?id=UmVwb3J0RmlsZXMvMjlfMTQ1ODExMDk5Ml9OZXdJdGVtXzE5NV9TVFBfUkVQT1JULnBkZg==
CPCB (2021) National inventory of sewage treatment plants. Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB), Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate Change, Govt. of India. website: https://cpcb.nic.in/openpdffile.php?id=UmVwb3J0RmlsZXMvMTIyOF8xNjE1MTk2MzIyX21lZGlhcGhvdG85NTY0LnBkZg==
Daqamseh ST, Al-Fugara A, Pradhan B et al (2019) MODIS derived sea surface salinity, temperature, and chlorophyll-a data for potential fish zone mapping: West red sea coastal areas, Saudi Arabia. Sensors (Switzerland) 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19092069
Daqamseh ST, Mansor S, Pradhan B et al (2013) Potential fish habitat mapping using MODIS-derived sea surface salinity, temperature and chlorophyll-a data: South China Sea Coastal areas, Malaysia. Geocarto Int 28:546–560. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2012.730065
Demographia (2021) Demographia World Urban Areas. (17th ed.). website: http://www.demographia.com/db-worldua.pdf
Devlin MJ, Petus C, da Silva E et al (2015) Water quality and river plume monitoring in the Great Barrier Reef: an overview of methods based on ocean colour satellite data. Remote Sens 7:12909–12941. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs71012909
DiGiacomo PM, Washburn L, Holt B, Jones BH (2004) Coastal pollution hazards in southern California observed by SAR imagery: stormwater plumes, wastewater plumes, and natural hydrocarbon seeps. Mar Pollut Bull 49:1013–1024. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2004.07.016
Fu Z, Wu F, Zhang Z et al (2021) Sea surface salinity estimation and spatial-temporal heterogeneity analysis in the gulf of Mexico. Remote Sens 13:1–16. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13050881
GESAMP (2018) Global pollution trends: coastal ecosystem assessment for the past century. GESAMP Rep Stud 106:101
Gierach MM, Holt B, Trinh R et al (2017) Satellite detection of wastewater diversion plumes in Southern California. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 186:171–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2016.10.012
Heckwolf MJ, Peterson A, Jänes H et al (2021) From ecosystems to socio-economic benefits: a systematic review of coastal ecosystem services in the Baltic Sea. Sci Total Environ 755
Hong H, Wu J, Shang S, Hu C (2005) Absorption and fluorescence of chromophoric dissolved organic matter in the Pearl River Estuary, South China. Mar Chem 97:78–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marchem.2005.01.008
Hopkins J, Lucas M, Dufau C et al (2013) Detection and variability of the Congo River plume from satellite derived sea surface temperature, salinity, ocean colour and sea level. Remote Sens Environ 139:365–385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2013.08.015
Inamdar AB, Bhattacharya, Agarwadkar, Azmi A (2011) Methodology Development for Modelling the Propagation of Pollutant Plume & Estimation of Futuristic Impact on Coastal Ecology using Remote Sensing & GIS. 2nd Stage Report of the Project, MMR Environment Improvement Society (MMR-EIS) of the Mumbai Metropolitan Region Development Authority (MMRDA)
Islam MS, Tanaka M (2004) Impacts of pollution on coastal and marine ecosystems including coastal and marine fisheries and approach for management: a review and synthesis. Mar Pollut Bull 48:624–649. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2003.12.004
Jay DA, Pan J, Orton PM, Horner-devine A (2008) Asymmetry of tidal plume fronts in an eastern boundary current regime. J Mar Sys 78:442–459. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmarsys.2008.11.015
Johnson DR, Miller J, Schofield O (2003) Dynamics and optics of the Hudson River outflow plume. J Geophys Res Ocean 108. https://doi.org/10.1029/2002jc001485
Joseph A, Vijaykumar K, Mehra P et al (2009) Observed tides at Mumbai High offshore region near the continental shelf break in the eastern Arabian Sea. Curr Sci 96:1233–1235
Kaisary S, Babu N, Balasubramanian T, et al (2012) Coastal water quality measurements protocol for COMAPS programme. ICMAM Project Directorate, (Ministry of Environment Sciences, India), Govt. of India.1–110
Khorram S (1982) Remote sensing of salinity in the San Francisco Bay Delta. Remote Sens Environ 12:15–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/0034-4257(82)90004-9
Klemas V (2012) Remote sensing of coastal plumes and ocean fronts: overview and case study. J Coast Res 28:1–7. https://doi.org/10.2112/JCOASTRES-D-11-00025.1
Kutser T, Pierson DC, Kallio KY et al (2005) Mapping lake CDOM by satellite remote sensing. 94:535–540. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2004.11.009
Land PE, Shutler JD, Findlay HS et al (2015) Salinity from space unlocks satellite-based assessment of ocean acidification. Environ Sci Technol 49:1987–1994. https://doi.org/10.1021/es504849s
Lavery P, Pattiaratchi C, Wyllie A, Hick P (1993) Water quality monitoring in estuarine waters using the Landsat thematic mapper. Remote Sens Environ 46:268–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/0034-4257(93)90047-2
Liu KJT, Young CC, Wu MC (2007) Evaluation of marine outfall with three-dimensional hydrodynamic and water quality modeling. Environ Model Assess 12:201–211. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10666-006-9068-0
Liu M, Liu X, Liu D et al (2015) Multivariable integration method for estimating sea surface salinity in coastal waters from in situ data and remotely sensed data using random forest algorithm. Comput Geosci 75:44–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2014.10.016
Malačič V (2001) Numerical modelling of the initial spread of sewage from diffusers in the Bay of Piran (northern Adriatic). Ecol Model 138:173–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-3800(00)00401-4
Marghany M, Hashim M (2011) Retrieving seasonal sea surface salinity from MODIS satellite data using a Box-Jenkins algorithm. IEEE Int Geosci Remote Sens Symposium (IGARSS), Vancouver, BC, Canada 24–29. https://doi.org/10.1109/IGARSS.2011.6049526
Marghany M, Hashim M, Cracknell AP (2010) Modelling sea surface salinity from MODIS satellite data. In: Lecture Notes in Computer Science (including subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics). Springer Verlag, pp 545–556
Marley SA, Salgado Kent CP, Erbe C (2017) Occupancy of bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops aduncus) in relation to vessel traffic, dredging, and environmental variables within a highly urbanised estuary. Hydrobiologia 792:243–263. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-016-3061-7
Marmorino GO (2010) Detection of a buoyant coastal wastewater discharge using airborne hyperspectral and infrared imagery. J Appl Remote Sens 4:043502. https://doi.org/10.1117/1.3302630
Medina-Lopez E, Ureña-Fuentes L (2019) High-resolution sea surface temperature and salinity in coastal areas worldwide from raw satellite data. Remote Sens 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11192191
Tchobanoglous G, Burton F, et al. (2013) Plant recycle flow treatment and nutrient recovery. Metcalf and Eddy: Wastewater Engineering (5th ed.). McGraw-Hill, USA
Tchobanoglous G, Burton FL, Stensel HD (1991) Wastewater Engineering: Treatment, Disposal, Reuse (3rd ed.). Metcalf and Eddy: McGraw-Hill, USA
Mohite, Joya (2021) A case study report on waste water management & sewage disposal in Mumbai suburban region. J Emerg Technol Innov Res 8:2349–5162
Morfitt R, Barsi J, Levy R et al (2015) Landsat-8 Operational Land Imager (OLI) radiometric performance on-orbit. Remote Sens 7:2208–2237. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70202208
Moussa H, Benallal MA, Goyet C et al (2015) A comparison of multiple non-linear regression and neural network techniques for sea surface salinity estimation in the tropical Atlantic ocean based on satellite data. ESAIM Proc Surv 49:65–77. https://doi.org/10.1051/proc/201549006
MPCB (2017) Assessment of impact of release of effluents on ecology of inshore and coastal areas of Maharashtra and their management Assessment of impact of release of effluents on ecology of inshore and coastal areas of Maharashtra and their management. Maharashtra Pollution Control Board (MPCB) (NIO/SP- 42/2017 SSP2964). website: https://www.mpcb.gov.in/sites/default/files/focus-area-reports-documents/FINAL_MPCB_PART_A_(Main_Report)_22022019-min_0.pdf
Nicholls RJ, Wong (2007) Coastal systems and low-lying areas. Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, 315–356. https://ro.uow.edu.au/scipapers/164/
Otero P, Ruiz-Villarreal M, Peliz Á (2009) River plume fronts off NW Iberia from satellite observations and model data. ICES J Mar Sci 66:1853–1864. https://doi.org/10.1093/icesjms/fsp156
Palacios SL, Peterson TD, Kudela RM (2009) Development of synthetic salinity from remote sensing for the Columbia River plume. J Geophys Res Ocean 114. https://doi.org/10.1029/2008JC004895
Qing S, Zhang J, Cui T, Bao Y (2013) Retrieval of sea surface salinity with MERIS and MODIS data in the Bohai Sea. Remote Sens Environ 136:117–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2013.04.016
Rajabi-Kiasari S, Hasanlou M (2020) An efficient model for the prediction of SMAP sea surface salinity using machine learning approaches in the Persian Gulf. Int J Remote Sens 41:3221–3242. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431161.2019.1701212
Reul N, Grodsky SA, Arias M et al (2020) Sea surface salinity estimates from spaceborne L-band radiometers: an overview of the first decade of observation (2010–2019). Remote Sens Environ 242:111769. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2020.111769
Satyendra ASK, Vijay R (2023) In-situ drain treatment types and technologies for flowing wastewater: a comprehensive review. Process Saf Environ Prot 170:449–463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2022.12.035
Schott JR, Gerace A, Woodcock CE et al (2016) The impact of improved signal-to-noise ratios on algorithm performance: case studies for Landsat class instruments. Remote Sens Environ 185:37–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2016.04.015
Shirke S, Pinto SM, Kushwaha VK et al (2016) Object-based image analysis for the impact of sewage pollution in Malad Creek, Mumbai, India. Environ Monit Assess 188:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4981-9
Siddorn JR, Bowers DG, Hoguane AM (2001) Detecting the Zambezi River plume using observed optical properties. Mar Pollut Bull 42:942–950. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0025-326X(01)00053-4
Sun D, Su X, Qiu Z et al (2019) Remote sensing estimation of sea surface salinity from GOCI measurements in the southern Yellow Sea. Remote Sens 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11070775
Svejkovsky J, Jones B (2001) Detection of coastal urban stormwater and sewage runoff with synthetic aperture radar satellite imagery. Eos Trans Am Geophys Union 82:621–625
Tate SSC, Peter M (2016) Marine outfalls. In: Springer Handbook of Ocean Engineering, pp 711–740
Thushari GGN, Senevirathna JDM (2020) Plastic pollution in the marine environment. Heliyon 6:e04709. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04709
Towler P, Fishwick M (2018) Reeds Nautical Almanac 2018, EBOOK edn. Bloomsbury Publishing
Trinh RC, Fichot CG, Gierach MM et al (2017) Application of Landsat 8 for monitoring impacts of wastewater discharge on coastal water quality. Front Mar Sci 4. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2017.00329
Urquhart EA, Zaitchik BF, Hoffman MJ et al (2012) Remotely sensed estimates of surface salinity in the Chesapeake Bay: a statistical approach. Remote Sens Environ 123:522–531. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2012.04.008
Vandermeulen RA, Arnone R, Ladner S, Martinolich P (2014) Estimating sea surface salinity in coastal waters of the Gulf of Mexico using visible channels on SNPP-VIIRS. In: Ocean Sensing and Monitoring VI. SPIE, p 911109
Vijay R, Dey J, Sakhre S, Kumar R (2020) Impact of urbanization on creeks of Mumbai, India: a geospatial assessment approach. J Coast Conserv 24. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11852-019-00721-y
Vijay R, Khobragade PJ, Sohony RA (2010) Water quality simulation of sewage impacts on the west coast of Mumbai, India. Water Sci Technol 62:279–287. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2010.237
Vijay R, Kushwaha VK, Pandey N et al (2015) Extent of sewage pollution in coastal environment of Mumbai, India: an object-based image analysis. Water Environ J 29:365–374. https://doi.org/10.1111/wej.12115
Vijay R, Mardikar T, Kumar R (2016) Impact of sewage discharges on coastal water quality of Mumbai, India: present and future scenarios. Environ Monit Assess 188. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5418-9
Wang F, Xu YJ (2008) Development and application of a remote sensing-based salinity prediction model for a large estuarine lake in the US Gulf of Mexico coast. J Hydrol 360:184–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2008.07.036
Wear SL, Acuña V, McDonald R, Font C (2021) Sewage pollution, declining ecosystem health, and cross-sector collaboration. Biol Conserv 255
Webb P (2021) Introduction to Oceanography. website: https://openlibrary-repo.ecampusontario.ca/jspui/handle/123456789/944
Whitfield A, Elliott M (2011) Ecosystem and Biotic classifications of estuaries and coasts. Treatise on Estuarine and Coastal Science 1:99–124
Wong et al. (2007) Modeling of suspended solids and sea surface salinity in Hong Kong using Aqua/MODIS Satellite Images. Korean J Remote Sens 23:161–169
Young NE, Anderson RS, Chignell SM et al (2017) A survival guide to Landsat preprocessing. Ecology 98:920–932. https://doi.org/10.1002/ecy.1730
Zhao J, Temimi M, Ghedira H (2016) Remotely sensed sea surface salinity in the hyper-saline Arabian Gulf: 1 application to Landsat 8 OLI data. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 187:168–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2017.01.008
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to the Director of CSIR – NEERI, Nagpur for providing the necessary infrastructural facility to carry out the research. The Indian National for Ocean Information Services (INCOIS) is acknowledged for providing the salinity data for the research study. The authors are also thankful to Mr. Jaydip Dey and Ms. Shila Waghchaure for their valuable suggestions on remote sensing analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Hanisha Mamidisetti: formal analysis, resources, validation, software, investigation, data curation, writing—original draft, visualization; Ritesh Vijay: conceptualization, writing—review and editing, supervision
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable
Consent to participate
All the authors mentioned in the manuscript have agreed to authorship, read, and approved the manuscript.
Consent for publication
All the authors mentioned in the manuscript have given consent for submission and subsequent publication of the manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Rongrong Wan
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mamidisetti, H., Vijay, R. Dynamics of sewage outfall plumes based on Landsat-8-derived sea surface salinity and tidal characteristics. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 82311–82325 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28137-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28137-0