Abstract
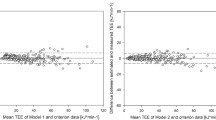
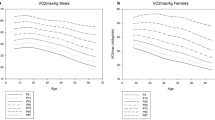
Existing equations to estimate ventilation (VE) may not represent the Chinese population. The objective is to develop regression equations to predict the basal metabolic rate (BMR) for ventilation estimation. 80 participants underwent the incremental tests on a bicycle ergometer, wearing a fitted facial mask with an airflow sensor connected to the cardiopulmonary gas analyzer, where the energy expenditure, metabolic factors and VE were monitored simultaneously. Linear regression models were established between BMR and body weight, which were used to estimate energy expenditure and VE. Extrapolation of the regression model was evaluated by the five-fold cross-validation. And we also assessed the inhaled load of air pollutants in subgroups at the same exposure levels. Regression models for males and females were BMR (kJ/d) = 107.58 × weight (kg)-172.61 and BMR (kJ/d) = 105.61 × weight (kg)-26.94, respectively. The model showed good fitness between the measured and predicted VE. Differences between the measured and predicted VE of this model are smaller than that of other models. There were significant differences in inhaled load participants in the same exposure concentrations. The regression model showed that weight and BMR are highly correlated and can be used to estimate individual VE.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors declare that the data and materials will be available to readers upon request.
References
Ainsworth BE, Haskell WL, Whitt MC et al (2000) Compendium of physical activities: an update of activity codes and MET intensities. Med Sci Sports Exerc 32(Supplement):S498–S516. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005768-200009001-00009
Allan M, Richardson GM, Jones-Otazo H (2008) Probability density functions describing 24-hour inhalation rates for use in human health risk assessments: An update and comparison. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 14(2):372–391. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807030801934796
Bowes HM, Burdon CA, Taylor NAS (2021) The scaling of human basal and resting metabolic rates. Eur J Appl Physiol 121(2020):193–208. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-020-04515-1
Brochu P, Ducré-Robitaille J-F, Brodeur J (2006) Physiological daily inhalation rates for free-Living individuals aged 1 month to 96 years, using data from doubly labeled water measurements: a proposal for air quality criteria, standard calculations and health risk assessment. Hum Ecol Risk Assess Int J 12(4):675–701. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807030600801550
Brook RD (2008) Cardiovascular effects of air pollution. Clin Sci 115(6):175–187. https://doi.org/10.1042/CS20070444
Brunekreef B, Holgate ST (2002) Air pollution and health. Lancet 360(2022):1233–1242. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(02)11274-8
Burnett RT, Pope CA, Ezzati M et al (2014) An integrated risk function for estimating the global burden of disease attributable to ambient fine particulate matter exposure. Environ Health Perspect 122(4):397–403. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.1307049
China E (2016) Ambient air quality standards. GB 3095–2012. Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China. Available at: https://www.mee.gov.cn/ywgz/fgbz/bz/bzwb/dqhjbh/dqhjzlbz/201203/t20120302_224165.shtml. Accessed 14 Nov 2022
China S (2018) Screening for overweight and obesity among school-age children and adolescents. WS/T 586–2018. Available at: http://www.nhc.gov.cn/wjw/pqt/201803/a7962d1ac01647b9837110bfd2d69b26.shtml. Accessed 27 Apr 2023
Cozza IC, Zanetta DMT, Fernandes FLA et al (2015) An approach to using heart rate monitoring to estimate the ventilation and load of air pollution exposure. Sci Total Environ 520(2015):160–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.03.049
Curtis L, Rea W, Smith-Willis P et al (2006) Adverse health effects of outdoor air pollutants. Environ Int 32(2006):815–830. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2006.03.012
Dons E, Laeremans M, Orjuela JP et al (2017) Wearable sensors for personal monitoring and estimation of inhaled traffic-related air pollution: evaluation of methods. Environ Sci Technol 51(3):1859–1867. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b05782
Duan X, Zhao X, Wang B et al (2015) Highlights of the Chinese Exposure Factors Handbook (Adults). China Science Press, Beijing. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-803125-4.00006-7
Good N, Carpenter T, Anderson GB et al (2019) Development and validation of models to predict personal ventilation rate for air pollution research. J Eposure Sci Environ Epidemiol 29(2018):568–577. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41370-018-0067-4
Guo Q, Zhao Y, Shao J et al (2021) Using heart rate to estimate the minute ventilation and inhaled load of air pollutants. Sci Total Environ 763(2021):143011. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143011
Harms CA (2006) Does gender affect pulmonary function and exercise capacity? Respir Physiol Neurobiol 151(2006):124–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resp.2005.10.010
Haslam DW, James WPT (2005) Obesity. The Lancet 366(9492):1197–1209. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(05)67483-1
Henry CJK (2005) Basal metabolic rate studies in humans: measurement and development of new equations. Public Health Nutr 8(7A):1133–1152. https://doi.org/10.1079/PHN2005801
Layton DW (1993) Metabolically consistent breathing rates for use in dose assessments. Health Phys 64(1):23–36. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004032-199301000-00003
Mack SM, Madl AK, Pinkerton KE (2011) Respiratory health effects of exposure to ambient particulate matter and bioaerosols. Compr Physiol 10(1):1–20. https://doi.org/10.1002/cphy
Marmett B, Carvalho RB, Dorneles GP et al (2020) Air pollution inhalation during acute exercise is dependent of the body mass index and ventilation of young men. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(2020):39019–39028. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10019-4
Mermier CM, Samet JM, Lambert WE et al (1993) Evaluation of the relationship between heart rate and ventilation for epidemiologic studies. Arch Environ Health 48(4):263–269. https://doi.org/10.1080/00039896.1993.9940371
Nwokoro C, Ewin C, Harrison C et al (2012) Cycling to work in London and inhaled dose of black carbon. Eur Respir J 40:1091–1097. https://doi.org/10.1183/09031936.00195711
O’Donoghue RT, Gill LW, McKevitt RJ et al (2007) Exposure to hydrocarbon concentrations while commuting or exercising in Dublin. Environ Int 33(2007):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2006.05.005
Ramos CA, Reis JF, Almeida T et al (2015) Estimating the inhaled dose of pollutants during indoor physical activity. Sci Total Environ 527–528(2015):111–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.04.120
Samet JM, Lambert WE, James DS, et al (1993) Assessment of heart rate as a predictor of ventilation. Research Report 59:19–55. Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8216970/. Accessed 27 Apr 2023
Schofield WN (1985) Predicting basal metabolic rate, new standards and review of previous work. Hum Nutr Clin Nutr 39(Suppl 1):5–41. https://doi.org/10.2307/41448805
Sheppard L, Burnett RT, Szpiro AA et al (2012) Confounding and exposure measurement error in air pollution epidemiology. Air Qual Atmos Health 5(2012):203–216. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-011-0140-9
Soares MJ, Francis DG, Shetty PS (1993) Predictive equations for basal metabolic rates of Indian males. Eur J Clin Nutr 47(6):389–394. Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8365380/. Accessed 27 Apr 2023
U.S. EPA (2009) Metabolically derived human ventilation rates: a revised based upon oxygen consumption rates, vol 2. EPA/600/R-06/129F. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC, p 3
U.S. EPA (2011) Exposure factors handbook, 2011 edn, vol 6. EPA/600/R-090/052F. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC, pp 40–42
Yang X, Li M, Mao D et al (2010) Basal energy expenditure in southern Chinese healthy adults: measurement and development of a new equation. Br J Nutr 104(2010):1817–1823. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114510002795
Yin P, Brauer M, Cohen AJ et al (2020) The effect of air pollution on deaths, disease burden, and life expectancy across China and its provinces, 1990–2017: an analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet Planetary Health 4(2020):E386–E398. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2542-5196(20)30161-3
Zhang JJ, Lioy PJ (2002) Human exposure assessment in air pollution systems. Sci World J 2(2002):497–513. https://doi.org/10.1100/tsw.2002.119
Zhang Z, Guo C, Lau AKH et al (2018) Long-term exposure to fine particulate matter, blood pressure, and incident hypertension in Taiwanese adults. Environ Health Perspect 126:017008. https://doi.org/10.1289/EHP2466
Zhou M, Wang H, Zeng X et al (2019) Mortality, morbidity, and risk factors in China and its provinces, 1990–2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. The Lancet 394:1145–1158. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(19)30427-1
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation [grant numbers 41977374].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yuchen Zhao: Formal analysis, Methodology, Investigation, Data Writing—original draft, Visualization. Qian Guo: Methodology, Investigation, Writing—review & editing. Jing Shao: Methodology, Writing—review & editing. Ping Liu: Methodology, Writing—review & editing. Qirong Wang: Methodology, Writing—review & editing. Zongshuang Wang: Writing—review & editing. Xiaoli Duan: Conceptualization, Methodology, Investigation, Data curation, Writing—review & editing, Supervision, Project administration, Funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Ethics Committee of Research Projects Analysis of the People's Liberation Army of China Strategic Support Force Characteristic Medical Center (K2019-082).
Consent to participate
Written informed consent was provided by all participants.
Consent to publish
All authors agree with publication in this journal.
Competing interests
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Lotfi Aleya
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Y., Guo, Q., Shao, J. et al. Using energy expenditure to estimate the minute ventilation and inhaled load of air pollutants: a pilot survey in young Chinese adults. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 93892–93899 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28038-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28038-2