Abstract
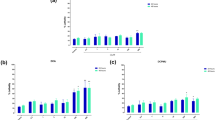
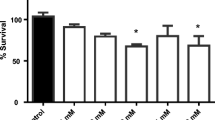
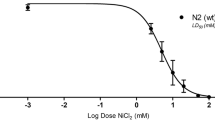
As an emerging flame retardant, organic phosphate flame retardants have been extensively used worldwide. The aim of this study is to determine the effects of TnBP on neurobehavior of Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans) and its mechanisms. L1 larvae of wild-type nematodes (N2) were exposed to TnBP of 0, 0.1, 1, 10, and 20 mg/L for 72 hours. Then, we observed that the body length and body width were inhibited, the head swings were increased, the pump contractions and chemical trend index were reduced, the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) was increased, and the expression of mitochondrial oxidative stress related genes (mev-1 and gas-1) and P38 MAPK signal pathway-related genes (pmk-1, sek-1, and nsy-1) was altered. After reporter gene strains BZ555, DA1240, and EG1285 were exposed to TnBP of 0, 0.1, 1, 10, and 20 mg/L for 72 hours, the synthesis of dopamine, glutamate, and Gamma-Amino Butyric Acid (GABA) was increased. In addition, the pmk-1 mutants (KU25) led to the sensitivity of C. elegans to TnBP in terms of head swings. The results showed that TnBP had harmful effects on the neurobehavior of C. elegans, oxidative stress might be one of the mechanisms of its neurotoxicity, and P38 MAPK signal pathway might play an important regulatory role in this process. The results revealed the potential adverse effects of TnBP on the neurobehavior of C. elegans.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data generated or analyzed and the materials used during this study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abramov AY, Scorziello A, Duchen MR (2007) Three distinct mechanisms generate oxygen free radicals in neurons and contribute to cell death during anoxia and reoxygenation. J Neurosci 27:1129–1138. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4468-06.2007
Adibi JJ, Perera FP, Jedrychowski W, Camann DE, Barr D, Jacek R, Whyatt RM (2003) Prenatal exposures to phthalates among women in New York City and Krakow. Poland Environ Health Perspect 111:1719–1722. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.6235
Andrusiak MG, Jin Y (2016) Context Specificity of stress-activated mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase signaling: the story as told by Caenorhabditis elegans. J Biol Chem 291:7796–7804. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.R115.711101
Blum A et al (2019) Organophosphate ester flame retardants: are they a regrettable substitution for polybrominated diphenyl ethers? Environ Sci Tech Let 6:638–649. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.estlett.9b00582
Carrington CD, Lapadula DM, Othman M, Farr C, Nair RS, Johannsen F, Abou-Donia MB (1990) Assessment of the delayed neurotoxicity of tributyl phosphate, tributoxyethyl phosphate, and dibutylphenyl phosphate. Toxicol Ind Health 6:415–423. https://doi.org/10.1177/074823379000600305
Cequier E, Sakhi AK, Marce RM, Becher G, Thomsen C (2015) Human exposure pathways to organophosphate triesters - a biomonitoring study of mother-child pairs. Environ Int 75:159–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2014.11.009
Chang Y, Cui H, Jiang X, Li M (2020) Comparative assessment of neurotoxicity impacts induced by alkyl tri-n-butyl phosphate and aromatic tricresyl phosphate in PC12 cells. Environ Toxicol 35:1326–1333. https://doi.org/10.1002/tox.22997
CM THOMPSON, JM PRINS, KM GEORGE (2010) Mass spectrometric analyses of organophosphate insecticide oxon protein adducts. Environ Health Persp 118:11–19. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.0900824
Garcia M, Rodriguez I, Cela R (2007) Microwave-assisted extraction of organophosphate flame retardants and plasticizers from indoor dust samples. J Chromatogr A 1152:280–286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2006.11.046
Hammel SC et al (2017) Associations between flame retardant applications in furniture foam, house dust levels, and residents’ serum levels. Environ Int 107:181–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2017.07.015
Hardos JE, Rubenstein M, Pfahler S, Sleight T (2020) Cholinesterase inhibition and exposure to organophosphate esters in aircraft maintenance workers. Aerosp Med Hum Perform 91:710–714. https://doi.org/10.3357/AMHP.5439.2020
Healy CE, Beyrouty PC, Broxup BR (1995) Acute and subchronic neurotoxicity studies with tri-N-butyl phosphate in adult Sprague-Dawley rats. Am Ind Hyg Assoc J 56:349–355. https://doi.org/10.1080/15428119591016962
Hou M, Shi Y, Na G, Cai Y (2021) A review of organophosphate esters in indoor dust, air, hand wipes and silicone wristbands: implications for human exposure. Environ Int 146:106261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2020.106261
Jiang X, Yang Y, Liu P, Li M (2020) Transcriptomics and metabolomics reveal Ca(2+) overload and osmotic imbalance-induced neurotoxicity in earthworms (Eisenia fetida) under tri-n-butyl phosphate exposure. Sci Total Environ 748:142169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142169
Kayser EB, Morgan PG, Hoppel CL, Sedensky MM (2001) Mitochondrial expression and function of GAS-1 in Caenorhabditis elegans. J Biol Chem 276:20551–20558. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M011066200
Kojima H, Takeuchi S, Itoh T, Iida M, Kobayashi S, Yoshida T (2013) In vitro endocrine disruption potential of organophosphate flame retardants via human nuclear receptors. Toxicology 314:76–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2013.09.004
Kucharska A, Cequier E, Thomsen C, Becher G, Covaci A, Voorspoels S (2015) Assessment of human hair as an indicator of exposure to organophosphate flame retardants. Case study on a Norwegian mother-child cohort. Environ Int 83:50–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2015.05.015
Laham S, Szabo J, Long G (1983) Effects of tri-n-butyl phosphate on the peripheral nervous system of the Sprague-Dawley rat. Drug Chem Toxicol 6:363–377. https://doi.org/10.3109/01480548309082716
Larsson K, de Wit CA, Sellstrom U, Sahlstrom L, Lindh CH, Berglund M (2018) Brominated flame retardants and organophosphate esters in preschool dust and children’s hand wipes. Environ Sci Technol 52:4878–4888. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.8b00184
Li J, Zhao L, Letcher RJ, Zhang Y, Jian K, Zhang J, Su G (2019) A review on organophosphate Ester (OPE) flame retardants and plasticizers in foodstuffs: levels, distribution, human dietary exposure, and future directions. Environ Int 127:35–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2019.03.009
Li W, Wang D, Wang D (2018) Regulation of the response of Caenorhabditis elegans to simulated microgravity by P38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling. Sci Rep 8:857. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-19377-z
Lim D, Roh JY, Eom HJ, Choi JY, Hyun J, Choi J (2012) Oxidative stress-related PMK-1 P38 MAPK activation as a mechanism for toxicity of silver nanoparticles to reproduction in the C. elegans Caenorhabditis elegans. Environ Toxicol Chem 31:585–592. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.1706
Liu Q, Tang X, Wang Y, Yang Y, Zhang W, Zhao Y, Zhang X (2019) ROS changes are responsible for tributyl phosphate (TBP)-induced toxicity in the alga Phaeodactylum tricornutum. Aquat Toxicol 208:168–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2019.01.012
Luo Q, Gu L, Wu Z, Shan Y, Wang H, Sun LN (2020) Distribution, source apportionment and ecological risks of organophosphate esters in surface sediments from the Liao River, Northeast China. Chemosphere 250:126297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126297
Ma Y et al (2013) Microwave-assisted extraction combined with gel permeation chromatography and silica gel cleanup followed by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry for the determination of organophosphorus flame retardants and plasticizers in biological samples. Anal Chim Acta 786:47–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2013.04.062
Mao Z, Zheng YL, Zhang YQ (2010) Behavioral impairment and oxidative damage induced by chronic application of nonylphenol. Int J Mol Sci 12:114–127. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms12010114
Mates JM, Segura JA, Alonso FJ, Marquez J (2008) Intracellular redox status and oxidative stress: implications for cell proliferation, apoptosis, and carcinogenesis. Arch Toxicol 82:273–299. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-008-0304-z
Meeker JD, Cooper EM, Stapleton HM, Hauser R (2013) Exploratory analysis of urinary metabolites of phosphorus-containing flame retardants in relation to markers of male reproductive health. Endocr Disruptors (Austin) 1:e26306. https://doi.org/10.4161/endo.26306
Patisaul HB et al (2021) Beyond cholinesterase inhibition: developmental neurotoxicity of organophosphate ester flame retardants and plasticizers. Environ Health Perspect 129:105001. https://doi.org/10.1289/EHP9285
Percy Z et al (2020) Organophosphate esters in a cohort of pregnant women: variability and predictors of exposure. Environ Res 184:109255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2020.109255
Qu M, Li D, Qiu Y, Wang D (2020) Neuronal ERK MAPK signaling in response to low-dose nanopolystyrene exposure by suppressing insulin peptide expression in Caenorhabditis elegans. Sci Total Environ 724:138378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138378
Sanchez AB, Medders KE, Maung R, Sanchez-Pavon P, Ojeda-Juarez D, Kaul M (2016) CXCL12-induced neurotoxicity critically depends on NMDA receptor-gated and L-type Ca(2+) channels upstream of P38 MAPK. J Neuroinflammation 13:252. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-016-0724-2
Schreder ED, Uding N, La Guardia MJ (2016) Inhalation a significant exposure route for chlorinated organophosphate flame retardants. Chemosphere 150:499–504. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.11.084
Sulston JE (1983) Neuronal cell lineages in the C. elegans Caenorhabditis elegans Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol 48. Pt 2:443–452. https://doi.org/10.1101/sqb.1983.048.01.049
Sun L et al (2016a) Developmental exposure of zebrafish larvae to organophosphate flame retardants causes neurotoxicity. Neurotoxicol Teratol 55:16–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ntt.2016.03.003
Sun L et al (2016b) Developmental neurotoxicity of organophosphate flame retardants in early life stages of Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes). Environ Toxicol Chem 35:2931–2940. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.3477
Tang J et al (2022) Neurotoxicity of tris (1,3-dichloroisopropyl) phosphate in Caenorhabditis elegans. Toxicology 474:153211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2022.153211
Valko M, Leibfritz D, Moncol J, Cronin MT, Mazur M, Telser J (2007) Free radicals and antioxidants in normal physiological functions and human disease. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 39:44–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2006.07.001
van der Veen I, de Boer J (2012) Phosphorus flame retardants: properties, production, environmental occurrence, toxicity and analysis. Chemosphere 88:1119–1153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.03.067
Villanueva A, Lozano J, Morales A, Lin X, Deng X, Hengartner MO, Kolesnick RN (2001) jkk-1 and mek-1 regulate body movement coordination and response to heavy metals through jnk-1 in Caenorhabditis elegans. EMBO journal 20:5114–5128. https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/20.18.5114
Wagner EF, Nebreda AR (2009) Signal integration by JNK and P38 MAPK pathways in cancer development. Nat Rev Cancer 9:537–549. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc2694
Wang D (2016) Biological effects, translocation, and metabolism of quantum dots in the C. elegans Caenorhabditis elegans. Toxicol Res (Camb) 5:1003–1011. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6tx00056h
Wang R et al (2015) Occurrence and spatial distribution of organophosphate ester flame retardants and plasticizers in 40 rivers draining into the Bohai Sea, north China. Environ Pollut 198:172–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2014.12.037
Wang X, Zhu Q, Yan X, Wang Y, Liao C, Jiang G (2020) A review of organophosphate flame retardants and plasticizers in the environment: analysis, occurrence and risk assessment. Sci Total Environ 731:139071. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139071
Wu Q, Zhou X, Han X, Zhuo Y, Zhu S, Zhao Y, Wang D (2016) Genome-wide identification and functional analysis of long noncoding RNAs involved in the response to graphene oxide. Biomaterials 102:277–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2016.06.041
Xu Q, Wu D, Dang Y, Yu L, Liu C, Wang J (2017) Reproduction impairment and endocrine disruption in adult zebrafish (Danio rerio) after waterborne exposure to TBOEP. Aquat Toxicol 182:163–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2016.11.019
Yan S, Wang Q, Yang L, Zha J (2020) Comparison of the toxicity effects of tris(1,3-dichloro-2-propyl)phosphate (TDCIPP) with tributyl phosphate (TNBP) reveals the mechanism of the apoptosis pathway in Asian freshwater clams (Corbicula fluminea). Environ Sci Technol 54:6850–6858. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.0c00640
Yang Y, Xiao Y, Chang Y, Cui Y, Klobucar G, Li M (2018) Intestinal damage, neurotoxicity and biochemical responses caused by tris (2-chloroethyl) phosphate and tricresyl phosphate on earthworm. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 158:78–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.04.012
Yin J, Liu R, Jian Z, Yang D, Pu Y, Yin L, Wang D (2018) Di (2-ethylhexyl) phthalate-induced reproductive toxicity involved in dna damage-dependent oocyte apoptosis and oxidative stress in Caenorhabditis elegans. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 163:298–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.07.066
Zhang H et al (2021) Study on the reproductive toxicity and mechanism of tri-n-butyl phosphate (TnBP) in Caenorhabditis elegans. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 227:112896. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112896
Zhao Y, Zhi L, Wu Q, Yu Y, Sun Q, Wang D (2016) P38 MAPK-SKN-1/Nrf signaling cascade is required for intestinal barrier against graphene oxide toxicity in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nanotoxicology 10:1469–1479. https://doi.org/10.1080/17435390.2016.1235738
Funding
The study was supported by the Open Research Fund Program of Key Laboratory of Environmental Medicine Engineering, Ministry of Education (2017EME001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jielin Tang and Jinyan Qin were responsible for coordinating the experiment, analyzing data, and writing articles; Guzailinuer Kuerban, Jiayi Li, and Qinyu Zhou were responsible for determining the theme and implementing the experiment; Hongdan Zhang and Rongli Sun participated in the implementation experiment; Lihong Yin and Yuepu Pu were responsible for revising the article; Juan Zhang was responsible for final revision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This declaration is not applicable.
Consent to participate
This declaration is not applicable.
Consent for publication
The publication of this manuscript has been approved by all co-authors as well as by the responsible authorities explicitly at the institute where the work has been carried out.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ludek Blaha
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Jielin Tang and Jinyan Qin are co-first authors.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, J., Qin, J., Kuerban, G. et al. Effects of tri-n-butyl phosphate (TnBP) on neurobehavior of Caenorhabditis elegans. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 85578–85591 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28015-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28015-9