Abstract
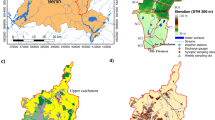
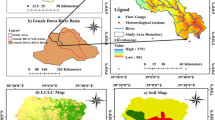
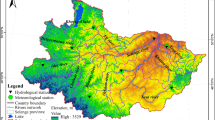
Despite the significant impacts of natural factors such as rainfall, topography, soil type, and river network as well as agricultural activities on the environmental water quality, little is known about the influence of their temporal and spatial variations in a fluvial-lacustrine watershed. In this study, a whole process accounting method based the export coefficient model (WP-ECM) was first developed to quantify how natural factors and agricultural activities distribution influenced water quality. A case study was performed in a typical fluvial-lacustrine area — Dongting basin, China. The simulated results indicated that the natural factors can promote and inhibit the migration and transformation of agricultural pollutants generated from the watershed and the spatial distribution of the natural factors displayed high variability. It should be priority to monitor the areas with greater natural impact in the basin. Moreover, the cultivated land area and the number of pig-breeding were positively correlated with the pollutant discharge. From the perspective of the spatial distribution of comprehensive influence, the comprehensive high-impact areas are mainly distributed in the Dongting Lake district in 2005–2010 and in Xiang River watershed in 2010–2020. A key strategy for controlling or reducing the cultivated land area and the intensity of livestock breeding in these high-impacts areas is recommended to reduce the impact of the environmental water quality for the entire basin.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Alvarez-Cabria M, Barquin J, Penas FJ (2016) Moedeling the spatial and seasonal variability of water quality for entire river networks: relationships between natural and anthropogenic factors. Sci Total Environ 545–546:152–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.12.109
Athira RP (2021) Calibration of hydrological models considering process interdependence: a case study of SWAT model. Environ Model Softw 144:105131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2021.105131
Bajracharya AR, Bajracharya SR, Shrestha AB, Maharjan SB (2018) Climate change impact assessment on the hydrological regime of the Kaligandaki basin, Nepal. Sci Total Environ 625:837–848. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.12.332
Bao L, Li X, Cheng P (2018) Phosphorus retention along a typical urban landscape river with a series of rubber dams. J Environ Manag 228:55–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j,jenvman.2018.09.019
Billen G, Thieu V, Garnier J, Silvestre M (2009) Modeling the N cascade in regional watersheds: the case study of the Seine, Somme and Scheldt river. Agric Ecosyst Environ 133:234–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2009.04.018
Burke M, Shahabi M, Xu Y, Zheng H, Zhang X, Vanlooy J (2018) Identifying the driving factors of water quality in a sub-watershed of the Republican River basin, Kansas USA. Int J Environ Res Public Health 15(5):1041. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15051041
Byrne P, Onnis P, Runkel RL, Frau I, Lynch SFL, Edwards P (2020) Critical shifts in trace metal transport and remediation performance under future low river flows. Environ Sci Technol 54(24):15742–15750. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.0c04016
Cai YP, Rong QQ, Yang ZF, Yue WC, Qian T (2018) An export coefficient based inexact fuzzy bi-level multi-objective programming model for the management of agricultural nonpoint source pollution under uncertainty. J Hydrol 557:713–725. https://doi.org/10.1016/j,jhydrol.2017.12.067
Caletka M, Sulc Michalkova M, Karasek P et al (2020) Improvement of SCS-CN initial abstraction coefficient in the Czech Republic: a study of five catchments. Water 12(7). https://doi.org/10.3390/w12071964
Carpenter SR, Caraco NF, Correll DL, Howarth RW, Sharpley AN, Smith VH (1998) Nonpoint pollution of surface waters with phosphorus and nitrogen. Ecol Appl 8:559–568. https://doi.org/10.1890/1051-0761(1998)008[0559:DPOSWW]2.0.CO;2
Chen BH, Chang SX, Lam SK, Erisman JW, Gu BJ (2017) Land use mediates riverine nitrogen export under the dominant influence of human activities. Environ Res Lett 12:094018. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/aa84bc
Chen L, Wang YW, Yang N, Zhu KH, Yan XM, Bai ZH, Zhai LM, Shen ZY (2023) Improving crop-livestock integration in China using numerical experiments at catchment and regional scales. Agric Ecosyst Environ 341:108192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2022.108192
Cheng X, Chen L, Sun R, Jing Y (2019) Identification of regional water resource stress based on water quantity and quality: a case study in a rapid urbanization region of China. J Clean Prod 209:216–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.10.175
Cheng JR, Gong YM, Zhu DZ, Xiao M, Zhang ZZ, Bi JP, Wang K (2021) Modeling the sources and retention of phosphorus nutrient in a coastal river system in China using SWAT. J Environ Manag 278:111556. https://doi.org/10.1016/j,jenvman.2020.111556
Ding XW, Shen ZY, Hong Q, Yang ZF (2010) Development and test of the export coefficient model in the Upper Reach of the Yangtze River. J Hydrol 383:233–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydrol.2009.12.039
Ding XW, Hou BD, Xue Y, Jiang GH (2017) Long-term effects of ecological factors on nonpoint source pollution in the upper reach of the yangtze river. J Environ Inf 30(1):17–28. https://doi.org/10.3808/jei.201700370
Epele LB, Manzo LM, Grech MG, Macchi P, Claverie A, Lagomarsino L, Miserendino ML (2018) Disentangling natural and anthropogenic inflences on Patagonian pond water quality. Sci Total Environ 613–614:866–876. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.09.147
Feng Y, Zheng BH, Jia HF, Peng JY, Zhou XY (2021) Influence of social and economic development on water quality in Dongting Lake. Ecol Ind 131:108220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.108220/
Foley JA, Ramankutty N, Brauman KA, Cassidy ES, Gerber JS, Johnston M, Mueller ND, Connell O, Ray C, West DK, Balzer PC, Bennett C, Carpenter EM, Hill SR, Monfreda J, Polasky C, Rockstrom S, Sheehan J, Siebert J, Tilman S, Zaks D (2011) Solutions for a cultivated planet. Nature 478(337):342. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature10452
Follett RF, Keeney DR, Cruse RM (1991) Managing nitrogen for groundwater quality and farm profitability: overview and introduction. ASA, CSSA, and SSSA Books, Madison, WI, U.S. https://doi.org/10.2136/1991.managingnitrogen.cl
Garnett T, Appleby MC, Balmford A, Bateman IJ, Benton TG, Bloomer P, Burlingame B, Dawkins M, Dolan L, Fraser D, Herrero M, Hoffmann I, Smith P, Thornton PK, Toulmin C, Vermeulen SJ, Godfray HCJ (2013) Sustainable intensification in a agriculture: premises and policies. Science 341:33–34. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1234485
Geng MM, Wang KL, Yang N, Li F, Zou YA, Chen XS, Deng ZM, Xie YH (2021) Evaluation and variation trends analysis of water quality in response to water regime changes in a typical river-connected lake (Dongting Lake), China. Environ Pollut 268:115761. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115761
Grizzetti B, Passy P, Billen G, Bouraoui F, Garnier J, Lassaletta L (2015) The role of water nitrogen retention in integrated nutrient management: assessment in a large basin using different modeling approaches. Environ Res Lett 10:065008. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/10/6/065008
Guo YZ, Wang XY, Melching C, Nan Z (2022) Identification method and application of critical load contribution areas based on river retention effect. J Environ Manag 305:114314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.114314
Hailu KA, Andreas K (2015) Predicting the spatial distribution of soil erodibility factor using USLE nomograph in an agricultural watershed, Ethiopia. Int Soil Water Conserv Res 3:282–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j,iswcr.2015.11.002
Han L, Huang MS, Ma MH, Wei JB, Hu W, Chouhan S (2018) Evaluating source and processing of nonpoint source nitrate in a small suburban watershed in China. J Hydrol 559:661–668. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydrol.2017.04.057
Han Q, Tong R, Sun WC, Zhao Y, Yu JS, Wang GQ, Shrestha S, Jin YL (2020) Anthropogenic influences on the water quality of the Baiyangdian Lake in North China over the last decade. Sci Total Environ 701:134929. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134929
Howarth R, Chan F, Conley DJ, Garnier J, Doney SC, Marino R, Billen G (2011) Coupled biogeochemical cycles: eutrophication and hypoxia in temperate estuaries and coastal marine ecosystems. Front Ecol Environ 9:18–26. https://doi.org/10.1890/100008
Hua LL, Li WC, Zhai LM, Yen H, Lei QL, Liu HB, Ren TZ, Xia Y, Zhang FL, Fan XP (2019) An innovative approach to identifying agricultural pollution sources and loads by using nutrient export coefficients in watershed modeling. J Hydrol 571:322–331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydrol.2019.01.043
Johnes PJ (1996) Evaluation and management of the impact of land use change on the nitrogen and phosphorus load delivered to surface waters: the export coefficient modeling approach. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1694(95)02951-6
Jordan TE, Correll DL, Weller DE (1998) Relating nutrient discharges from watersheds to land use and streamflow variability. Water Resour Res 33:2579–2590. https://doi.org/10.1029/97WR02005
Jung JW, Yoon KS, Choi DH, Lim SS, Choi WJ, Choi SM, Lim BJ (2012) Water management practices and SCS curve numbers of paddy fields equipped with surface drainage pipes. Agric, Water Manag 110:78–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2012.03.014
Karaburun A (2010) Estimation of C factor for soil erosion modeling using NDVI in Buyukcekmece watershed. Ozean J Applied Sci 3:77–85. https://doi.org/10.1007/S1266-5-012-2086-0
Kiese R, Heinzeller C, Werner C, Wochele S, Grote R, Butterbach Bahl K (2011) Quantification of nitrate leaching form German forest ecosystems by use of a process oriented biogeochemical model. Environ Pollut 159:3204–3214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2011.05.004
Li SL, Xu S, Wang TJ, Yue FJ, Peng T, Zhong J, Wang LC, Chen JA, Wang SJ, Chen X, Liu CQ (2020) Effects of agricultural activities coupled with karst structures on riverine biogeochemical cycles and environmental quality in the karst region. Agric Ecosyst Environ 303:107120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2020.107120
Li HC, Guan QY, Sun YF, Wang QZ, Liang LS, Ma YR, Du QQ (2022) Spatiotemporal analysis of the quantitative attribution of soil water erosion in the upper reaches of the Yellow River Basin based on the RUSLE-TLSD model. Catena 212:106081. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2022.106081
Liu QQ, Singh VP (2004) Effect of microtopography, slope length and gradient, and vegetative cover on overland flow through simulation. J Hydrol Eng 9:375–382. https://doi.org/10.1016/(ASCE)1084-0699(2004)9:5(375)
Mainali J, Chang H (2018) Landscape and anthropogenic factors affecting spatial patterns of water quality trends in a large river basin, South Korea. J Hydrol 564:26–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydrol.2018.06.074
Miralha L, Muenich RL, Scavia D, Wells K, Steiner AL, Kalcic M et al (2021) Bias correction of climate model outputs influences watershed model nutrient load predictions. Sci Total Environ 759:143039. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143039
Mishra SK, Sahu RK, Eldho TI et al (2006) An improved la S relation incorporating antecedent moisture in SCS-CN methodology. Water Resour Manag 20:643–660. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-005-9000-4
Peterson BJ, Wollheim MW, Mulholland PJ, Webster JR, Meyer JL, Tank JL, Marti E, Bowden WB, Valett HM, Hershey AE, McDowell WH, Dodds WK, Hamilton SK, Gregory S, Morrall DD (2001) Control of nitrogen export from watersheds by headwater streams. Science 292:86–90. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1056874
Pijl A, Reuter IEIH, Quarella F, Vogel TA, Tarolli P (2020) GIS-based soil erosion modelling under various steep-slope vineyard practices. Catena 193:104604. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2020.104604
Qu YB, Zhang QQ, Zhan LY, Jiang GH, Si HY (2022) Understanding the nonpoint source pollution loads’ spatiotemporal dynamic response to intensive land use in rural China. J Environ Manag 315:115066. https://doi.org/10.1016/j,jenvman.2022.115066
Rao PZ, Wang SR, Wang A, Yang DW, Tang LH (2022) Spatiotemporal characteristics of nonpoint source nutrient loads and their impact on river water quality in Yancheng city, China, simulated by an improved export coefficient model coupled with grid-based runoff calculations. Ecol Ind 142:109188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.109188
Rodrigues M, Rosa A, Cravo A, Jacob J, Fortunato A (2021) Effects of climate change and anthropogenic pressures in the water quality of a coastal lagoon (Ria Formosa, Portugal). Sci Total Environ 780:146311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146311
Schoumans OF, Chardon WJ, Bechmann ME, Gascuel-Odoux C, Hofman G, Kronvang B, Rubaek GH, Ulen B, Dorioz JM (2014) Mitigation options to reduce phosphorus losses from the agricultural sector and improve surface water quality: a review. Sci Total Environ 468–469:1255–1266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.08.061
Seitzinger SP, Styles RV, Boyer EW, Alexander RB, Billen G, Howarth RW, Mayer B, Van Breemen N (2002) Nitrogen retention in rivers: model development and application to watersheds in the northeastern USA. Biogeochemistry 57:199–237. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015745629794
Shrestha NK, Rudra RP, Daggupati P, Goel PK, Shukla R (2021) A comparative evaluation of the continuous and event-based modelling approaches for identifying critical source areas for sediment and phosphorus losses. J Environ Manage 277:111427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111427
Sinha E, Michalak AM (2016) Precipitation dominates interannual variability of riverine nitrogen loading across the continental United States. Environ Sci Technol 50:12874–12884. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b04455
Udayakumara EPN, Dias BARH, Jayawardana JMCK, Malavipathirana S, Dissanayake DATWK (2021) Effects of soil erosion on water quality: a case study from Uma Oya Catchment, Sri Lanka. D. R. and Sustain. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-323-85195-4.00029-9
Van RRD, Hamilton ME, Hickey RJ (2001) Estimating the LS factor for RUSLE through iterative slope length processing of digital elevation data within Arclnfo gird. Cartography 30:27–35. https://doi.org/10.1080/00690805.2001.9714133
Vareker V, Yadav V, Karmakar S (2021) Rationalization of water quality monitoring locations under spatiotemporal heterogeneity of diffuse pollution using seasonal export coefficient. J Environ Manag 277:11342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j,jenvman.2020.111342
Wang Y, Liang J, Yang J, Ma X, Li X, Wu J, Yang G, Ren G, Feng Y (2019) Analysis of the environmental behavior of farmers for non-point source pollution control and management: an integration of the theory of planned behavior and the protection motivation theory. J Environ Manage 237:15–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.02.070
Wang WZ, Chen L, Shen ZY (2020) Dynamic export coefficient model for evaluating the effects of environmental changes on non-point source pollution. Sci Total Environ 747:141164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141164
Wang YX, Liu GH, Zhao ZH, Wu CS, Yu BW (2021) Using soil erosion to locate nonpoint source pollution risks in costal zones: a case study in the Yellow River Delta. China. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envplo.2021.117117
Wang ZJ, Yue FJ, Wang YC, Qin CQ, Ding H, Xue LL, Li SL (2022) The effect of heavy rainfall events on nitrogen patterns in agricultural surface and underground streams and the implications for karst water quality protection. Agric, Water Manag 266:107600. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2022.107600
Wischmeier WH, Johnson CB, Cross BV (1971) Soil erodibility nomograph for farmland and construction sites. J Soil Water Conserv 26:189–193. https://doi.org/10.2307/3896643
Xiong FY, Chen YS, Zhang SH, Xu YX, Lu Y, Qu X, Gao WQ, Wu XH, Xin W, Gang DD, Lin LS (2022) Land use, hydrology, and climate influence water quality of China’s largest river. J Environ Manag 318:115581. https://doi.org/10.1016/j,jenvman.2022.115581
Yin GY, Liu LM, Jiang XL (2017) The sustainable arable land use pattern under the tradeoff of agricultural production, economic development, and ecological protection: an analysis of Dongting Lake basin, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:25329–25345. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0132-x
Yu YW, Mei XF, Dai ZJ, Gao JJ, Li JB, Wang J, Lou YY (2018) Hydromorphological processes of Dongting Lake in China between 1951 and 2014. J Hydrol 562:254–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j,jhydrol.2018.05.015
Zhang J, Guo QJ, Du CJ, Wei RF (2022a) Quantifying the effect of anthropogenic activities on water quality change in the Yangtze River from 1981 to 2019. J Clean Prod 363:132415. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.132415
Zhang XQ, Chen P, Dai SN, Han YH (2022b) Analysis of non-point source nitrogen pollution in watersheds based on SWAT model. Ecol Ind 138:108881. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.108881
Zhou Y, Xu JF, Yin W, Ai L, Fang NF, Tan WF, Yan FL, Shi ZH (2017) Hydrological and environmental controls of the stream nitrate concentration and flux in a small agricultural watershed. J Hydrol 545:335–366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydrol.2016.12.015
Zhou WJ, Zhu ZH, Xie YL, Cai YP (2021) Impacts of rainfall spatial and temporal variability on runoff quality and quantity at the watershed scale. J Hydrol 603:127057. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydrol.2021.127057
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Hunan Province Ecological Environment Monitoring Center and the State Environmental Protection Scientific Observation and Research Station for Lake Dongting for the water quality data in the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Project (No. 2021YFC3201003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yu Feng: conceptualization, methodology, investigation, data curation, writing — original draft, writing — review and editing, visualization, project administration. Binghui Zheng: resources, supervision. Haifeng Jia: reviewing and editing. Bing-bing Song: data curation. Yang Liu: writing — reviewing and editing. Jun-ping Bi: resources.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The work did not involve human participants and/or animals. To the best of our knowledge and belief, this manuscript has not been considered for publication elsewhere.
Consent to participate
All the authors approved to participate.
Consent for publication
The authors have reviewed the manuscript and approved it for publication.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Xianliang Yi
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, Y., Zheng, BH., Jia, HF. et al. The impacts of spatio-temporal variation of natural and agricultural influences on the environmental water quality in a fluvial-lacustrine watershed in China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 76387–76404 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-27978-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-27978-z