Abstract
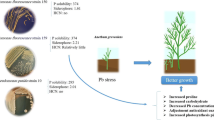
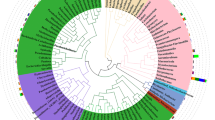
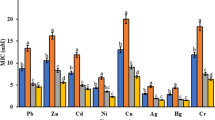
Metal-immobilizing bacteria play a critical role in metal accumulation in vegetables. However, little is known concerning the mechanisms involved in bacteria-induced reduced metal availability and uptake in vegetables. In this study, the impacts of metal-immobilizing Pseudomonas taiwanensis WRS8 on the plant biomass, Cd and Pb availability and uptake in two coriander (Coriandrum sativum L.) cultivars, and bacterial community structure were investigated in the polluted soil. Strain WRS8 increased the biomass of two coriander cultivars by 25–48% and reduced Cd and Pb contents in the edible tissues by 40–59% and available Cd and Pb contents in the rhizosphere soils by 11.1–15.2%, compared with the controls. Strain WRS8 significantly increased the pH values and relative abundances of the dominant populations of Sphingomonas, Pseudomonas, Gaiellales, Streptomyces, Frankiales, Bradyrhizobium, and Luteimonas, while strain WRS8 significantly decreased the relative abundances of the dominant populations of Gemmatimonadaceae, Nitrospira, Haliangium, Paenibacillus, Massilia, Bryobacter, and Rokubacteriales and the rare bacterial populations of Enterorhabdus, Roseburia, Luteibacter, and Planifilum in the rhizosphere soils, compared with the controls. Significantly negative correlations were observed between the available metal concentrations and the abundances of Pseudomonas, Luteimonas, Frankiales, and Planifilum. These results implied that strain WRS8 could affect the abundances of the dominant and rare bacterial populations involved in metal immobilization, resulting in increased pH values and decreased metal availability and uptake in the vegetables in the contaminated soil.
Graphical Abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used in the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abbasi S, Kafi SA, Karimi E, Sadeghi A (2022) Streptomyces consortium improved quality attributes of bell pepper fruits, induced plant defense priming, and changed microbial communities of rhizosphere under commercial greenhouse conditions. Rhizosphere 23:100570
Abou-Aly HE, Youssef AM, Tewfike TA, El-Alkshar EA, El-Meihy RM (2021) Reduction of heavy metals bioaccumulation in sorghum and its rhizosphere by heavy metals-tolerant bacterial consortium. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 31:101911
Altunta OA (2019) A comparative study on the effects of different conventional, organic and bio-fertilizers on broccoli yield and quality. Appl Ecol Env Res 16:1959–1623
Antoniadis V, Shaheen SM, Levizou E, Shahid M, Niazi NK, Vithanag M, Yong SO (2019) A critical prospective analysis of the potential toxicity of trace element regulation limits in soils worldwide: are they protective concerning health risk assessment? A review. Environ Int 127:819–847
Chen ZQ, Liu QZ, Chen SN, Zhang SJ, Wang M, MujtabaMunir MA, Feng Y, He ZL, Yang XE (2022) Roles of exogenous plant growth regulators on phytoextraction of Cd/Pb/Zn by Sedum alfredii Hance in contaminated soils. Environ Pollut 293:118510
Cheng C, Luo WW, Wang QX, He LY, Sheng XF (2020) Combined biochar and metal-immobilizing bacteria reduces edible tissue metal uptake in vegetables by increasing amorphous Fe oxides and abundance of Fe- and Mn-oxidising Leptothrix species. Ecotoxi Environ Safe 206:111189
Cheng C, Wang Q, Wang QX, He LY, Sheng XF (2021a) Wheat-associated Pseudomonas taiwanensis WRS8 reduces cadmium uptake by increasing root surface cadmium adsorption and decreasing cadmium uptake and transport related gene expression in wheat. Environ Pollut 268:115850
Cheng C, Wang R, Sun LJ, He LY, Sheng XF (2021) Cadmium-resistant and arginine decarboxylase-producing endophytic Sphingomonas sp. C40 decreases cadmium accumulation in host rice (Oryza sativa Cliangyou 513). Chemosphere 275:130109
Chodak M, Gołębiewski M, Morawska-Płoskonka J, Kuduk K, Niklińska M (2013) Diversity of microorganisms from forest soils differently polluted with heavy metals. Appl Soil Ecol 64:7–14
Du M, Zheng MG, Liu AF, Wang L, Pan X, Liu J, Ran XB (2022) Effects of emerging contaminants and heavy metals on variation in bacterial communities in estuarine sediments. Sci Total Environ 832:155118
Etesami H (2018) Bacterial mediated alleviation of heavy metal stress and decreased accumulation of metals in plant tissues: mechanisms and future prospects. Ecotoxicol Environ Safe 147:175–191
Fakhar A, Gul B, Gurmani AR, Khan SM, Ali S, Sultan T, Chaudhary HJ, Mazhar Rafique M, Rizwan M (2022) Heavy metal remediation and resistance mechanism of Aeromonas, Bacillus, and Pseudomonas: a review. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 52:1868–1914
Fatemi H, Esmaielpour B, Sefidkon F, Soltani AA, Nematollahzadeh A (2020) How mycorrhiza symbiosis helps coriander (Coriandrum sativum L.) plants grow better under contaminated soil? J Plant Nutrition 13:2040–2053
Feng NX, Liang QF, Feng YX, Xiang L, Wong MH (2020) Improving yield and quality of vegetable grown in PAEs-contaminated soils by using novel bioorganic fertilizer. Sci Total Environ 739:139883
Gantait S, Sharangi AB, Mahanta M (2022) Agri-biotechnology of coriander (Coriandrum sativum L.): an inclusive appraisal. Appl Microbiol Biot 106:951–969
Ge YY, Ge ZB, Zheng JW, Sheng XF, He LY (2022) Biofilm-overproducing Bacillus subtilis B12∆Ywcc decreases Cd uptake in Chinese cabbage through increasing Cd-immobilizing related gene abundance and root surface colonization. J Environ Sci 120:84–93
Ghosh PK, Maiti TK, Pramanik K, Ghosh SK, Mitra S, De TK (2018) The role of arsenic resistant Bacillus aryabhattai MCC3374 in promotion of rice seedlings growth and alleviation of arsenic phytotoxicity. Chemosphere 211:407–419
Guo JK, Muhammad H, Lv X, Wei T, Ren XH, Jia HL, Atif S, Hua L (2020) Prospects and applications of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria to mitigate soil metal contamination: A review. Chemosphere 246:125823
Han H, Wang X, Yao L, Chen Z (2020) Lettuce-derived rhizosphere polyamine-producing bacteria and their potential to reduce Cd and Pb accumulation in lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.). Environ Exp Bot 178:104161
Li XY, Li ZG, Lin CJ, Bi XY, Liu JL, Feng XB, Zhang H, Chen J, Wu TT (2018) Health risks of heavy metal exposure through vegetable consumption near a large-scale Pb/Zn smelter in central China. Ecotox Environ Safe 161:99–110
Li XQ, Meng DL, Li J, Yin HQ, Liu HW, Liu XD, Cheng C, Xiao YH, Liu ZH, Yan ML (2017) Response of soil microbial communities and microbial interactions to long-term heavy metal contamination. Environ Pollut 231:908–917
Li CC, Quan Q, Gan YD, Dong JY, Fang LH, Wang LF, Liu J (2020) Effects of heavy metals on microbial communities in sediments and establishment of bioindicators based on microbial taxa and function for environmental monitoring and management. Sci Total Environ 749:141555
Lv P, Wei ZM, Yu ZM, Zhang JZ, Wang LM (2019) Heavy metal contamination in soils of greenhouse vegetable production systems in a cold region of China. Int J Agric Biol Eng 12:98–102
Mitra S, Pramanik K, Ghosh PK, Soren T, Sarkar A, Dey RS, Pandey S, Maiti TK (2018) Characterization of Cd-resistant Klebsiella michiganensis MCC3089 and its potential for rice seedling growth promotion under Cd stress. Microbiol Res 210:12–25
Nedelescu M, Baconi D, Neagoe A, Iordache V, Stan M, Constantinescu P, Ciobanu AM, Vardavas AI, Vinceti M, Tsatsakis AM (2017) Environmental metal contamination and health impact assessment in two industrial regions of Romania. Sci Total Environ 580:984–995
Pal AK, Chakraborty A, Sengupta C (2022) Differential effects of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria on chilli (Capsicum annuum L.) seedling under cadmium and lead stress. Plant Sci Today 5:182–190
Petrovic B, Sękara A, Pokluda R (2020) Biofertilizers enhance quality of onion. Agronomy 10:1937
Punjee P, Siripornadulsil W, Siripornadulsil S (2018) Reduction of cadmium uptake in rice endophytically colonized with the cadmium-tolerant bacterium Cupriavidus taiwanensis KKU2500-3. Can J Microbiol 64:131–145
Renu S, Sarim KM, Singh DP, Sahu U, Bhoyar MS, Sahu A, Kaur B, Gupta A, Mandal A, Thakur JK, Manna MC, Saxena AK (2022) Deciphering cadmium (Cd) tolerance in newly isolated bacterial strain, Ochrobactrum intermedium BB12, and its role in alleviation of Cd stress in Spinach plant (Spinacia oleracea L.). Front Microbiol 12:758144
Sardar R, Ahmed S, Akbar M, Yasin NA, Li GH (2022) Alleviation of cadmium phytotoxicity in triacontanol treated Coriandrum sativum L. by modulation of physiochemical attributes, oxidative stress biomarkers and antioxidative system. Chemosphere 295:133924
Wang XY, Cai DB, Ji MF, Chen ZJ, Yao LG, Han H (2022) Isolation of heavy metal-immobilizing and plant growth-promoting bacteria and their potential in reducing Cd and Pb uptake in water spinach. Sci Total Environ 819:153242
Wang Q, Zhang WJ, He LY, Sheng XF (2018) Increased biomass and quality and reduced heavy metal accumulation of edible tissues of vegetables in the presence of Cd-tolerant and immobilizing Bacillus megaterium H3. Ecotox Environ Safe 148:269–274
Wei JN, Liu ZH, Zhao YP, Zhao LL, Xue TK, Lan QK (2019) Phytochemical and bioactive profile of Coriandrum sativum L. Food Chem 286:260–267
Wei T, Liu X, Dong MF, Lv X, Hua L, Jia HL, Ren XH, Yu SH, Guo JK, Li YT (2021) Rhizosphere iron and manganese-oxidizing bacteria stimulate root iron plaque formation and regulate Cd uptake of rice plants (Oryza sativa L.). J Environ Manag 278:111533
Wen K, Li XG, Huang R, Nian H (2022) Application of exogenous glutathione decreases chromium translocation and alleviates its toxicity in soybean (Glycine max L.). Ecotox Environ Safe 234:113405
Xie LL, Yin CY (2022) Seasonal variations of soil fungal diversity and communities in subalpine coniferous and broadleaved forests. Sci Total Environ 846:157049
Xiong ZH, Zheng JW, Sun HR, Hu JW, Sheng XF, He LY (2022) Biofilm-overproducing Bacillus amyloliquefaciens P29 sinR decreases Pb availability and uptake in lettuce in Pb-polluted soil. J Environ Manag 302:114016
Xu ZH, Zhang RF, Wang DD, Qiu MH, Feng HD, Zhang N, Shen QR (2014) Enhanced control of cucumber wilt disease by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens SQR9 by altering the regulation of its DegU phosphorylation. Appl Environ Microbiol 80:2941–2950
Zeb A, Liu WT, Meng LZ, Lian J, Wang Q, Lian YH, Chen CH, Wu J (2021) Effects of polyester microfibers (PMFs) and cadmium on lettuce (Lactuca sativa) and the rhizospheric microbial communities: a study involving physio-biochemical properties and metabolomic profiles. J Hazard Mater 424:127405
Zeng XY, Li SW, Leng Y, Kang XH (2020) Structural and functional responses of bacterial and fungal communities to multiple heavy metal exposure in arid loess. Sci Total Environ 723:138081
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41977199) and the Social Development Program of Jiangsu Province (BE2016744).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yanyan Ge: investigation, formal analysis, methodology, writing—original draft. Zhenyu Wen: investigation, methodology, formal analysis. Linyan He: formal analysis. Xiafang Sheng: conceptualization, formal analysis, writing—review & editing, supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Diane Purchase
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• Strain WRS8 reduced Cd and Pb uptake in coriander cultivars in metal-polluted soil.
• Coriander Cd and Pb contents treated with strain WRS8 met the metal limit standard.
• WRS8 increased soil dominant bacterial group abundances and rare group compositions.
• Group abundances induced by WRS8 were negative correlations to metal availability.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ge, Y., Wen, Z., He, L. et al. Metal-immobilizing Pseudomonas taiwanensis WRS8 reduces heavy metal accumulation in Coriandrum sativum by changing the metal immobilization–related bacterial population abundances. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 76911–76922 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-27967-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-27967-2