Abstract
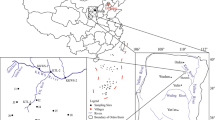
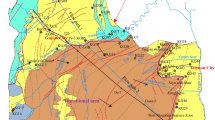
Acid mine drainage (AMD) is considered one of the serious environmental issues in the mining area. Understanding the key processes and pathways of hydrogeochemical evolution is critical for the effective control of AMD pollution. Hydrogeochemical analysis along with environmental isotope tracing was utilized to provide information regarding the hydrogeochemical process of groundwater pollution by using the multi-aquifer of abandoned Dashu pyrite in Southwest China as an example. Using the deuterium excess parameter d of groundwater and the results of 2H, 18O, and T analysis, the water–rock interaction intensity was determined. The distribution characteristics of d-T revealed that the groundwater primarily originated from the Quaternary reservoir platform groundwater and that there was a close hydraulic connection among the aquifers. The results of ion analysis and sulfur isotope tracing indicated that the sulfur in groundwater was primarily derived from gypsum dissolution, whereas the sulfur in mine water was primarily derived from pyrite oxidation. The results of the hydrogeochemical inversion indicated that mining activities altered the water level and flow conditions, promoted water–rock interactions, altered the hydrogeochemical process, and caused aquifer and mine water cross-contamination. The findings provide theoretical guidance for identifying the pollution sources and critical hydrogeochemical processes that affect groundwater in depleted mining areas of multi-aquifers and also provide technical support for developing water source control and prevention techniques.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during the course of this investigation are included in this article and its supporting materials.
References
Aubertin M, Bussière B, Pabst T, James M, Mbonimpa M (2016) Review of the reclamation techniques for acid-generating mine wastes upon closure of disposal sites. Geo-Chicago 270:343–357
Argamasilla M, Barberá J A, Andreo B (2017) Factors controlling groundwater salinization and hydrogeochemical processes in coastal aquifers from southern Spain[J]. Science of the Total Environment 580:50–68
Banks D, Boyce AJ, Burnside NM, Janson E, Roqueñi Gutierrez N (2020) On the common occurrence of sulphate with elevated δ34S in European mine waters: sulphides, evaporites or seawater. Int J Coal Geol 232:103619
Carreira PM, Marques JM, Nunes D (2014) Source of groundwater salinity in coastline aquifers based on environmental isotopes (Portugal): natural vs. human interference a review and reinterpretation. Appl Geochem 41:163–175
Chandrasekar T, Sabarathinam C, Nadesan D, Rajendiran T, Panda BB, Keesari T et al (2019) Geochemical (process based) characterization of groundwater along the kt boundary of south India. Chem Erde 79:62–77
Chen L, Xie W, Feng X, Zhang N, Yin X (2017) Formation of hydrochemical composition and spatiotemporal evolution mechanism under mining-induced disturbance in the Linhuan coal-mining district. Arab J Geosci 10(3):57
Chen L, Xu D, Yin X, Xie W, Zeng W (2017) Analysis of groundwater chemistry and its controlling factors in concealed coal mining area of North China: a case study of main aquifer inrush in Suxian Mining area. J China Coal Soc 42(4):996–1004 (China)
Christopher HG, Allison B, Simon RP, Thomas HH (2013) Using stable isotopes (S, O) of sulfate to track local contamination of the Madison karst aquifer, Montana, from abandoned coal mine drainage. Appl Geochem 31:228–238
Craig H (1961) Standard for reporting concentrations of deuterium and oxygen-18 in natural waters. Science 133:1833–1834
Dogramaci S, McLeanb L, Skrzypek G (2017) Hydrochemical and stable isotope indicators of pyrite oxidation in carbonate-rich environment: the Hamersley Basin, Western Australia. J Hydrol 545:288–298
Esmaeil G, Mostafa R, Mojtaba GM, Aziz RC (2021) Saltwater intrusion in drinking water wells of Kordkuy, Iran: an integrated quantitative and graphical study. Environ Earth Sci 80:520
Gammons CH, Brown A, Poulson SR, Henderson TH (2013) Using stable isotopes(S, O) of sulfate to track local contamination of the Madison karst aquifer, Montana, from abandoned coal mine drainage. Appl Geochem 31:228–238
Han Y, Wang G, Cravotta CA, Hu W, Bian Y, Zhang Z, Liu Y (2013) Hydro-geochemical evolution of Ordovician limestone groundwater in Yanzhou, North China. Hydrol Process 27:2247–2257
He J, Ma J, Zhao W, Sun S (2015) Groundwater evolution and recharge determination of the Quaternary aquifer in the Shule River basin, Northwest China. Hydrogeol J 23(8):1745–1759
Huang B, Liu J, Li N, Zhao X (2017) Framework of the theory and technology for mine closure. J China Univ MinTechnol 46(4):715–729,747. (China)
Jeong SW, Wu YH, Cho YC, Ji SW (2018) Flow behavior and mobility of contaminated waste rock materials in the abandoned Imgi mine in Korea. Geomorphology 301:79–91
Jiang C, Gao X, Zhang S, Li C, Wang W (2020) Occurrence and environmental impact of coal mine goaf water in karst areas in China. J Clean Prod 275:123813
Ledesma-Ruiz R, Pasten-Zapata E, Parra R, Harter T, Mahlknecht J (2015) Investigation of the geochemical evolution of groundwater under agricultural land: a case study in northeastern Mexico. J Hydrol 521:410–423
Li B, Liu G, Nie Y, Ye Z, Yang Z, Yin G (2020) Hydrochemical characteristics and environmental isotope analysis of typical abandoned pyrite in Southwest China. Environ Sci Technol 43(10):10–17 (China)
Li B, Liu G, Nie Y, Ye Z (2021) Causes and effects of a water spill from the underground pit of the Dashu Pyrite mine, Southern Sichuan Basin, Southwest China. Mine Water Environ 40:864–876
Li B, Zheng LF, Liu G et al (2023) Identification of the sources of mine drainage in a multi-aquifer area: a case study of the abandoned Dashu pyrite mine in Southwest China. Hydrogeol J 31:387–400
Liang Y, Gao X, Zhao C, Tang C, Shen H, Wang Z (2018) Review: characterization, evolution, and environmental issues of karst water systems in northern China. Hydrogeol J 26(5):1371–1385
Liu J, Zhao Y, Wang D, Liu A (1997) Time-space distribution of stable isotopes of atmospheric precipitation in China. Investig Sci Technol 3:34–39 (China)
Liu P, Nils H, Carsten D, Sun Y, Xu Z (2017) Hydro-geochemical paths of multi-layer groundwater system in coal mining regions using multivariate statistics and geochemical modeling approaches. Sci Total Environ 601–602(Dec. 1):1–14
Liu P, Yang M, Sun Y (2019) Hydro-geochemical processes of the deep ordovician groundwater in a coal mining area, Xuzhou, China. Hydrogeol J 27:2231–2244
Malov AI, Tokarev IV (2019) Using stable isotopes to characterize the conditions of groundwater formation on the eastern slope of the Baltic Shield (NW Russia). J Hydrol 578:124–130
Migaszewski ZM, Gałuszka A, Dołe˛gowska S (2018) Stable isotope geochemistry of acid mine drainage from the Wisniowka area (south-central Poland). Appl Geochem 95:45–56
Morán-Ramírez J, Ledesma-Ruiz R, Mahlknecht J, Ramos-Leal JA (2016) Rockwater interactions and pollution processes in the volcanic aquifer system of Guadalajara, Mexico, using inverse geochemical modeling. Appl Geochem 68:79–94
Omiyama S, Igarashi T, Tabelin CB, Tangviroon P, Ii H (2019) Acid mine drainage sources and hydrogeochemistry at the Yatani mine, Yamagata, Japan: a geochemical and isotopic study. J Contam Hydrol 225:103502
Park I, Tabelin CB, Jeon S, Li X, Seno K, Ito M, Hiroyoshi N (2019) A review of recent strategies for acid mine drainage prevention and mine tailings recycling. Chemosphere 219:588–606
Qian J, Peng Y, Zhao W, Ma L, He X, Lu Y (2018) Hydrochemical processes and evolution of karst ground-water in the northeastern Huaibei Plain, China. Hydrogeol J 26:1721–1729
Ramesh BK, Vanitha S (2021) Hydrogeochemical and geospatial analysis of water quality for domestic and irrigation purposes in Padmana-bhapuram, Kanyakumari District, India. Arab J Geosci 14:2012
Ren K, Zeng J, Liang J, Yuan D, Pan X (2020) Impacts of acid mine drainage on karst aquifers: evidence from hydrogeochemistry, stable sulfur and oxygen isotopes. Sci Total Environ 761(11):143223
Sako A, Bamba O, Gordie A (2016) Hydrogeochemical processes controlling groundwater quality around Bomboré gold mineralized zone, central Burkina Faso. J Geochem Explor 170:58–71
Seibert S, Descourvieres C, Skrzypek G, Deng HL, Prommer H (2017) Model-based analysis of δ34S signatures to trace sedimentary pyrite oxidation during managed aquifer recharge in a heterogeneous aquifer. J Hydrol 548:368–381
Shingo T, Toshifumi I, Carlito B, Pawit T, Hiroyuki I (2019) Acid mine drainage sources and hydrogeochemistry at the yatani mine, Yamagata, Japan: a geochemical and isotopic study. J Contam Hydrol 225:103502
Sparks JM, Crowley BE, Rutherford MG, Jaggernauth D (2019) Coastal proximity, orientation, and precipitation amount drive spatial variability in δ34S values on the Caribbean island of Trinidad. Appl Geochem 108:104372
Sun J, Yoshio T, William HJ, Strosnider TK, Wu P, Gao X (2019) Tracing and quantifying contributions of end members to karst water at a coalfield in Southwest China. Chemosphere 234:777–788
Tarasenko IA, Zinkov AV, Vakh EA, Vetoshkina AV, Strelnikova AB (2016) Groundwater composition fluctuation within technogenic zones (case study: flooded coal mines in Primorsky Krai, Russia. Iop Conf 33(1):12–13
Voutsis N, Kelepertzis E, Tziritis E, Kelepertsis A (2015) Assessing the hydrogeochemistry of groundwaters in ophiolite areas of Euboea Island, Greece, using multivariate statistical methods[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration 159:79–92
Wu Q, Li S (2018) Positive and negative environmental effects of closed mines and its countermeasures. J China Coal Soc 43(1):21–32
Yang X, Hu J, Liu J, Luo Z, Zhang Y, Liu F, Zhao Z, Li Y (2018) Hydrogeochemical characteristics and formation mechanism of groundwater in Xianghualing mining area, Hunan Province. Acta Sci Circumstantiae 38(7):2575–2585 (China)
Yang Z, Huang P, Ding F (2020) Groundwater hydro-geochemical mechanisms and the connectivity of multilayer aquifers in a coal mining region. Mine Water Environ 39(4):808–822
Yeh HF, Lee JW (2018) Stable hydrogen and oxygen isotopes for groundwater sources of Penghu islands, Taiwan. Geosciences 8(84):1–8
Zhang Q, Zhou J, Lin S, Wei D, Zhang L, Yuan L (2015) Characteristics and causes of groundwater pollution after Hongshan-Zhaili mine coal closure in Zibo. Saf Environ Eng 22(6):23–28
Zhang H, Xu G, Zhan H, Chen X, Liu M, Wang M (2020) Identification of hydrogeochemical processes and transport paths of a multi-aquifer system in closed mining regions. J Hydrol 589(2):125344
Zheng L, Chen X, Dong X, Wei X, Jiang C, Tang Q (2019) Using δ34S–SO4 and δ18O–SO4 to trace the sources of sulfate in different types of surface water from the Linhuan coal-mining subsidence area of Huaibei, China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 18:231–240
Zhou JW, Zhang YP, Zhou AG, Liu CF, Cai HS, Liu YD (2016) Application of hydrochemistry and stable isotopes (δ34S, δ18O and δ37Cl) to trace natural and anthropogenic influences on the quality of groundwater in the piedmont region, Shijiazhuang, China. Appl Geochem 71:63–72
Funding
This work was conducted as part of the State Key Laboratory of Geohazard Prevention and Geoenvironment Protection free exploration project (SKLGP2019Z008), the Sichuan Province Science and Technology Plan projects that focus on research and development program (2020YFS0339), the State Environmental Protection Key Laboratory of Synergetic Control and Joint Remediation for Soil & Water Pollution open fund (GHBK-2020–018), Scientific research and innovation Team project of Chengdu Normal University (CSCXTD2020A04), and the state environmental protection special fund for support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CC proposed the study’s concept and collaborated with other co-authors on the writing and discussion of the findings. LB was responsible for measuring relevant experimental data. LG and DY organized the article. ZM revised grammatical specifications and examined experimental data. WX completed the analysis of microbial data. The final manuscript was reviewed and endorsed by all authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Xianliang Yi
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, C., Li, B., Zhu, M. et al. Multi-isotope identification of key hydrogeochemical processes and pollution pathways of groundwater in abandoned mining areas in Southwest China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 78198–78215 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-27607-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-27607-9