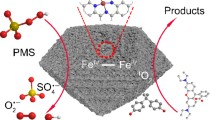
Abstract
Persulfate activation is emerged as an alternative applied in environment remediation, but it is still a great challenge to develop highly active catalysts for efficient degradation of organic pollutants. Herein, a heterogeneous iron-based catalyst with dual-active sites was synthesized by embedding Fe nanoparticles (FeNPs) onto the nitrogen-doped carbon, which was used to activate peroxymonosulfate (PMS) for antibiotics decomposition. The systematic investigation indicated the optimal catalyst exhibited a significant and stable degradation efficiency of sulfamethoxazole (SMX), in which the SMX can be completely removed in 30 min even after 5 cycle tests. Such satisfactory performance was mainly attributed to the successful construction of electron-deficient C centers and electron-rich Fe centers via the short C-Fe bonds. These short C-Fe bonds accelerated electrons to shuttle from SMX molecules to electron-rich Fe centers with a low transmission resistance and short transmission distance, enabling Fe (III) to receive electrons to promote the regeneration of Fe (II) for durable and efficient PMS activation during SMX degradation. Meanwhile, the N-doped defects in the carbon also provided reactive bridges that accelerated the electron transfer between FeNPs and PMS, ensuring the synergistic effects toward Fe (II)/Fe (III) cycle to some extent. The quenching tests and electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) indicated O2·− and 1O2 were the dominant active species during the SMX decomposition. As a result, this work provides an innovative method to construct a high-performance catalyst to active sulfate for organic contaminant degradation.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Ao X, Liu W (2017) Degradation of sulfamethoxazole by medium pressure UV and oxidants: peroxymonosulfate, persulfate, and hydrogen peroxide. Chem Eng J 313:629–637. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.12.089
Bauer I, Knölker H-J (2015) Iron catalysis in organic synthesis. Chem Rev 115:3170–3387. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr500425u
Caltran I, Ayumurti Kukuh F, Rietveld LC, Heijman SGJ (2021) Sulfate precipitation treatment for NOM-rich ion exchange brines. Sep Purif Technol 269:118669. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2021.118669
Chen C, Ma T, Shang Y, Gao B, Jin B, Dan H, Li Q, Yue Q, Li Y, Wang Y, Xu X (2019) In-situ pyrolysis of Enteromorpha as carbocatalyst for catalytic removal of organic contaminants: considering the intrinsic N/Fe in Enteromorpha and non-radical reaction. Appl Catal B 250:382–395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.03.048
Couzi M, Bruneel J-L, Talaga D, Bokobza L (2016) A multi wavelength Raman scattering study of defective graphitic carbon materials: the first order Raman spectra revisited. Carbon 107:388–394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2016.06.017
Dong H, Qiang Z, Hu J, Sans C (2017) Accelerated degradation of iopamidol in iron activated persulfate systems: roles of complexing agents. Chem Eng J 316:288–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.01.099
Fallah S, Mamaghani HR, Yegani R, Hajinajaf N, Pourabbas B (2020) Use of graphene substrates for wastewater treatment of textile industries. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 3:187–193. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-020-00146-4
Fan X, Liu Y, Quan X (2019) A novel reduced graphene oxide/carbon nanotube hollow fiber membrane with high forward osmosis performance. Desalination 451:117–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2018.07.020
Fan M, Pan X, Lin W, Zhang H (2020) Carbon-covered hollow nitrogen-doped carbon nanoparticles and nitrogen-doped carbon-covered hollow carbon nanoparticles for oxygen reduction. ACS Appl Nano Mater 3:3487–3493. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.0c00222
Fang Y, Qian B, Yang Y, Song Y, Yang Z, Li H (2022) Purification of high-arsenic groundwater by magnetic bimetallic MOFs coupled with PMS: balance of catalysis and adsorption and promotion mechanism of PMS. Chem Eng J 432:118669. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.134417
Gonçalves AG, Órfão JJM, Pereira MFR (2013) Ozonation of sulfamethoxazole promoted by MWCNT. Catal Commun 35:82–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catcom.2013.02.012
Hou J, Xu L, Han Y, Tang Y, Wan H, Xu Z, Zheng S (2019) Deactivation and regeneration of carbon nanotubes and nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes in catalytic peroxymonosulfate activation for phenol degradation: variation of surface functionalities. RSC Adv 9:974–983. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ra07696k
Hu S, Hu H, Li W, Ke Y, Li M, Zhao Y (2017) Enhanced sulfamethoxazole degradation in soil by immobilized sulfamethoxazole-degrading microbes on bagasse. RSC Adv 7:55240–55248. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ra10150c
Huang X, Hu Q, Gao L, Hao Q, Wang P, Qin D (2018) Adsorption characteristics of metal-organic framework MIL-101(Cr) towards sulfamethoxazole and its persulfate oxidation regeneration. RSC Adv 8:27623–27630. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ra04789h
Huang C, Qin F, Zhang C, Huang D, Tang L, Yan M, Wang W, Song B, Qin D, Zhou Y, Luo H, Fang G (2022) Effects of heterogeneous metals on the generation of persistent free radicals as critical redox sites in iron-containing biochar for persulfate activation. ACS ES&T Water. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsestwater.2c00299
Jiang Z, Zhao J, Li C, Liao Q, Xiao R, Yang W (2020) Strong synergistic effect of Co3O4 encapsulated in nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes on the nonradical-dominated persulfate activation. Carbon 158:172–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2019.11.066
Jiang J, Wang X, Yue C, Li T, Li M, Li C, Dong S (2022) Nitrogen vacancies induce sustainable redox of iron-cobalt bimetals for efficient peroxymonosulfate activation: dual-path electron transfer. Chem Eng J 427:131702. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.131702
Kaur B, Kuntus L, Tikker P, Kattel E, Trapido M, Dulova N (2019) Photo-induced oxidation of ceftriaxone by persulfate in the presence of iron oxides. Sci Total Environ 676:165–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.04.277
Lai X, Huang N, Pillai SC, Sarmah AK, Li Y, Wang G, Wang H (2022) Formation and transformation of reactive species in the Fe2+/peroxydisulfate/Cl− system. J Environ Manag 316:115219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.115219
Lalas K, Petala A, Frontistis Z, Konstantinou I, Mantzavinos D (2021) Sulfamethoxazole degradation by the CuOx/persulfate system. Catal Today 361:139–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2020.01.047
Lan YK, Chen TC, Tsai HJ, Wu HC, Lin JH, Lin IK, Lee JF, Chen CS (2016) Adsorption behavior and mechanism of antibiotic sulfamethoxazole on carboxylic-functionalized carbon nanofibers-encapsulated Ni magnetic nanoparticles. Langmuir 32:9530–9539. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.6b02904
Li W, Wu X, Li S, Tang W, Chen Y (2018) Magnetic porous Fe3O4/carbon octahedra derived from iron-based metal-organic framework as heterogeneous Fenton-like catalyst. Appl Surf Sci 436:252–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.11.151
Li X, Jia Y, Zhou M, Su X, Sun J (2020) High-efficiency degradation of organic pollutants with Fe, N co-doped biochar catalysts via persulfate activation. J Hazard Mater 397:122764. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122764
Li Y, Ma W, Sun J, Lin M, Niu Y, Yang X, Xu Y (2020b) Electrochemical generation of Fe3C/N-doped graphitic carbon nanozyme for efficient wound healing in vivo. Carbon 159:149–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2019.11.093
Li P, Lin Y, Zhao S, Fu Y, Li W, Chen R, Tian S (2021) Defect-engineered Co3O4 with porous multishelled hollow architecture enables boosted advanced oxidation processes. Appl Catal B Environ 298:120596. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2021.120596
Liang D, Mao J, Liu P, Yan J, Song W (2019) In-situ growth of NCNT and encapsulation of Co9S8/Co as a sustainable multifunctional electrocatalyst. J Colloid Interface Sci 557:291–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2019.09.018
Liu Y, Guo H, Zhang Y, Cheng X, Zhou P, Deng J, Wang J, Li W (2019) Highly efficient removal of trimethoprim based on peroxymonosulfate activation by carbonized resin with Co doping: performance, mechanism and degradation pathway. Chem Eng J 356:717–726. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.09.086
Liu S, Zhang Z, Huang F, Liu Y, Feng L, Jiang J, Zhang L, Qi F, Liu C (2021) Carbonized polyaniline activated peroxymonosulfate (PMS) for phenol degradation: role of PMS adsorption and singlet oxygen generation. Appl Catal B Environ 286:119921. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2021.119921
Luo L, Xu Y, Wang D, Feng W, Qiu X (2022) Tuning active species in n-doped carbon with Fe/Fe(3)C nanoparticles for efficient oxygen reduction reaction. Inorg Chem 61:3166–3175. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.inorgchem.1c03573
Lyu L, Yan D, Yu G, Cao W, Hu C (2018) Efficient destruction of pollutants in water by a dual-reaction-center fenton-like process over carbon nitride compounds-complexed Cu(II)-CuAlO2. Environ Sci Technol 52:4294–4304. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b06545
Ma W, Wang N, Du Y, Tong T, Zhang L, Andrew Lin K-Y, Han X (2019) One-step synthesis of novel Fe3C@nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes/graphene nanosheets for catalytic degradation of Bisphenol A in the presence of peroxymonosulfate. Chem Eng J 356:1022–1031. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.09.093
Martini J, Orge CA, Faria JL, Pereira MFR, Soares OSGP (2019) Catalytic advanced oxidation processes for sulfamethoxazole degradation. Appl Sci 9:2652. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9132652
Meng S, Zhou P, Sun Y, Zhang P, Zhou C, Xiong Z, Zhang H, Liang J, Lai B (2022) Reducing agents enhanced Fenton-like oxidation (Fe(III)/peroxydisulfate): substrate specific reactivity of reactive oxygen species. Water Res 218:118412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2022.118412
Merlen A, Buijnsters J, Pardanaud C (2017) A guide to and review of the use of multiwavelength raman spectroscopy for characterizing defective aromatic carbon solids: from graphene to amorphous carbons. Coatings 7:153. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings7100153
Miao W, Liu Y, Wang D, Du N, Ye Z, Hou Y, Mao S, Ostrikov K (2021) The role of Fe-Nx single-atom catalytic sites in peroxymonosulfate activation: formation of surface-activated complex and non-radical pathways. Chem Eng J 423:130250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.130250
Miao X, Chen X, Wu W, Lin D, Yang K (2022) Intrinsic defects enhanced biochar/peroxydisulfate oxidation capacity through electron-transfer regime. Chem Eng J 438:135606. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.135606
Notini L, Latta DE, Neumann A, Pearce CI, Sassi M, N’Diaye AT, Rosso KM, Scherer MM (2018) The role of defects in Fe(II)–goethite electron transfer. Environ Sci Technol 52:2751–2759. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b05772
Oh W-D, Lim T-T (2019) Design and application of heterogeneous catalysts as peroxydisulfate activator for organics removal: an overview. Chem Eng J 358:110–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.09.203
Oh S-Y, Kim H-W, Park J-M, Park H-S, Yoon C (2009) Oxidation of polyvinyl alcohol by persulfate activated with heat, Fe2+, and zero-valent iron. J Hazard Mater 168:346–351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.02.065
Pang K, Sun W, Ye F, Yang L, Pu M, Yang C, Zhang Q, Niu J (2022) Sulfur-modified chitosan derived N,S-co-doped carbon as a bifunctional material for adsorption and catalytic degradation sulfamethoxazole by persulfate. J Hazard Mater 424:127270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127270
Panjwani MK, Wang Q, Ma Y, Lin Y, Xiao F, Yang S (2021) High degradation efficiency of sulfamethazine with the dual-reaction-center Fe–Mn–SiO2 Fenton-like nanocatalyst in a wide pH range. Environ Sci Nano 8:2204–2213. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1en00253h
Patel M, Kumar R, Kishor K, Mlsna T, Pittman CU, Mohan D (2019) Pharmaceuticals of emerging concern in aquatic systems: chemistry, occurrence, effects, and removal methods. Chem Rev 119:3510–3673. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00299
Pu M, Niu J, Brusseau ML, Sun Y, Zhou C, Deng S, Wan J (2020) Ferrous metal-organic frameworks with strong electron-donating properties for persulfate activation to effectively degrade aqueous sulfamethoxazole. Chem Eng J 394:125044. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.125044
Pu M, Wan J, Zhang F, Brusseau ML, Ye D, Niu J (2021) Insight into degradation mechanism of sulfamethoxazole by metal-organic framework derived novel magnetic Fe@C composite activated persulfate. J Hazard Mater 414:125598. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125598
Rastogi A, Al-Abed SR, Dionysiou DD (2009) Sulfate radical-based ferrous–peroxymonosulfate oxidative system for PCBs degradation in aqueous and sediment systems. Appl Catal B 85:171–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2008.07.010
Rauf M, Zhao Y-D, Wang Y-C, Zheng Y-P, Chen C, Yang X-D, Zhou Z-Y, Sun S-G (2016) Insight into the different ORR catalytic activity of Fe/N/C between acidic and alkaline media: protonation of pyridinic nitrogen. Electrochem Commun 73:71–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elecom.2016.10.016
Ren W, Xiong L, Nie G, Zhang H, Duan X, Wang S (2019) Insights into the electron-transfer regime of peroxydisulfate activation on carbon nanotubes: the role of oxygen functional groups. Environ Sci Technol 54:1267–1275. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.9b06208
Ren W, Nie G, Zhou P, Zhang H, Duan X, Wang S (2020) The intrinsic nature of persulfate activation and n-doping in carbocatalysis. Environ Sci Technol 54:6438–6447. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.0c01161
Shen Y, Martín de Vidales MJ, Gorni G, Gómez-Herrero A, Fernández-Martínez F, Dos santos-García AJ (2022) Enhanced performance and recyclability for peroxymonosulfate activation via g-C3N4 supported CoFe layer double oxide. Chem Eng J 444:136610. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.136610
Sheng B, Yang F, Wang Y, Wang Z, Li Q, Guo Y, Lou X, Liu J (2019) Pivotal roles of MoS2 in boosting catalytic degradation of aqueous organic pollutants by Fe(II)/PMS. Chem Eng J 375:121989. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.121989
Tsuneda T, Taketsugu T (2018) Theoretical investigations on hydrogen peroxide decomposition in aquo. Phys Chem Chem Phys 20:24992–24999. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8cp04299c
Wang J, Wang S (2016) Removal of pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) from wastewater: a review. J Environ Manage 182:620–640. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.07.049
Wang J, Wang S (2018a) Activation of persulfate (PS) and peroxymonosulfate (PMS) and application for the degradation of emerging contaminants. Chem Eng J 334:1502–1517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.11.059
Wang S, Wang J (2018b) Radiation-induced degradation of sulfamethoxazole in the presence of various inorganic anions. Chem Eng J 351:688–696. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.06.137
Wang Y, Guo W, Li X (2018a) Activation of persulfates by ferrocene–MIL-101(Fe) heterogeneous catalyst for degradation of bisphenol A. RSC Adv 8:36477–36483. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ra07007e
Wang Z, Jiang J, Pang S, Zhou Y, Guan C, Gao Y, Li J, Yang Y, Qiu W, Jiang C (2018b) Is sulfate radical really generated from peroxydisulfate activated by iron(II) for environmental decontamination? Environ Sci Technol 52:11276–11284. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.8b02266
Wang M, Cui Y, Cao H, Wei P, Chen C, Li X, Xu J, Sheng G (2021) Activating peroxydisulfate with Co3O4/NiCo2O4 double-shelled nanocages to selectively degrade bisphenol A – a nonradical oxidation process. Appl Catal B Environ 282:119585. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.119585
Wei J, Xiong Z, Ao M, Guo Z, Zhang J, Lai B, Song Y (2022) Selective degradation of sulfamethoxazole by N-doped iron-based carbon activated peroxymonosulfate: collaboration of singlet oxygen and high-valent iron-oxo species. Sep Purif Technol 297:121379. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2022.121379
Weng W, Zhou J, Gu D, Xiao W (2020) Thermoelectrochemical formation of Fe/Fe3C@hollow N-doped carbon in molten salts for enhanced catalysis. J Mater Chem A 8:4800–4806. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0ta00565g
Xiao S, Cheng M, Zhong H, Liu Z, Liu Y, Yang X, Liang Q (2020) Iron-mediated activation of persulfate and peroxymonosulfate in both homogeneous and heterogeneous ways: a review. Chem Eng J 384:123265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.123265
Xie Z, Zhou J, Wang J, François-Xavier CP, Wintgens T (2019) Novel Fenton-like catalyst γ-Cu-Al2O3-Bi12O15Cl6 with electron-poor Cu centre and electron-rich Bi centre for enhancement of phenolic compounds degradation and H2O2 utilization: the synergistic effects of σ-Cu-ligand, dual-reaction centres and oxygen vacancies. Appl Catal B 253:28–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.04.032
Xu Y, Yu Y, Yang Y, Sun T, Dong S, Yang H, Liu Y, Fan X, Song C (2021) Improved separation performance of carbon nanotube hollow fiber membrane by peroxydisulfate activation. Sep Purif Technol 276:119328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2021.119328
Xue Y, Pham NNT, Nam G, Choi J, Ahn Y-Y, Lee H, Jung J, Lee S-G, Lee J (2021) Persulfate activation by ZIF-67-derived cobalt/nitrogen-doped carbon composites: kinetics and mechanisms dependent on persulfate precursor. Chem Eng J 408:127305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.127305
Zhang X, Wang J, Wang Y, Yao Z, Guo W, Xu H, Jiang Z (2023) Boosting electron transport process over multiple channels induced by S-doped carbon and Fe(7)S(8) NPs interface toward high-efficiency antibiotics removal. J Hazard Mater 442:130115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.130115
Zhang X, Yao Z, Zhou Y, Zhang Z, Lu G, Jiang Z (2021) Theoretical guidance for the construction of electron-rich reaction microcenters on C–O–Fe bridges for enhanced Fenton-like degradation of tetracycline hydrochloride. Chem Eng J 411:128535. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.128535
Zhang H, Yan Z, Wan J, Wang Y, Ye G, Huang S, Zeng C, Yi J (2022a) Synthesis of Fe-Nx site-based iron-nitrogen co-doped biochar catalysts for efficient removal of sulfamethoxazole from water by activation of persulfate: electron transfer mechanism of non-free radical degradation. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 654:130174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2022.130174
Zhang X, Yao Z, Wang J, Guo W, Wu X, Jiang Z (2022b) High-capacity NCNT-encapsulated metal NP catalysts on carbonised loofah with dual-reaction centres over C–M bond bridges for Fenton-like degradation of antibiotics. Appl Catal B Environ 307:121205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2022.121205
Zhi K, Li Z, Ma P, Tan Y, Zhou Y, Zhang W, Zhang J (2021) A review of activation persulfate by iron-based catalysts for degrading wastewater. Appl Sci 11:11314. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112311314
Zhong J, Feng Y, Yang B, Xiong Q, Ying G-G (2022) Accelerated degradation of sulfadiazine by nitrogen-doped magnetic biochar-activated persulfate: role of oxygen vacancy. Sep Purif Technol 289:120735. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2022.120735
Zhu K, Bin Q, Shen Y, Huang J, He D, Chen W (2020) In-situ formed N-doped bamboo-like carbon nanotubes encapsulated with Fe nanoparticles supported by biochar as highly efficient catalyst for activation of persulfate (PS) toward degradation of organic pollutants. Chem Eng J 402:126090. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.126090
Zhuang Y, Liu Q, Kong Y, Shen C, Hao H, Dionysiou DD, Shi B (2019a) Enhanced antibiotic removal through a dual-reaction-center Fenton-like process in 3D graphene based hydrogels. Environ Sci Nano 6:388–398. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8en01339j
Zhuang Y, Wang X, Zhang L, Dionysiou DD, Shi B (2019b) Fe-Chelated polymer templated graphene aerogel with enhanced Fenton-like efficiency for water treatment. Environ Sci Nano 6:3232–3241. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9en00924h
Zhuo S-N, Ren H-Y, Cao G-L, Xie G-J, Xing D-F, Ren N-Q, Liu B-F (2022) Highly efficient activation of persulfate by encapsulated nano-Fe0 biochar for acetaminophen degradation: rich electron environment and dominant effect of superoxide radical. Chem Eng J 440:135947. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.135947
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (22076019, 51708085), Xingliao talent program (XLYC2007069), Innovation Funds for Dalian Science and Technology (2021JJ12SN43), the Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province (2021-MS-139) and the Innovation and Entrepreneurship Projects for High-level Talents in Dalian (2019RQ132).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xinfei Fan: conceptualization, investigation, data curation, methodology, visualization, writing—original draft; Na Liu: investigation, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing, software, data curation; Jia Yang: investigation, software, writing—review and editing, data curation; Yueling Yu: writing—review and editing, data curation; Chengwen Song: writing—review and editing, supervision; Yuanlu Xu: writing—review and editing, data curation, supervision; Yanming Liu: writing—review and editing, supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
All authors agree to publication in this journal
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ricardo A. Torres-Palma
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, X., Liu, N., Yang, J. et al. Boosting peroxymonosulfate activation by iron-based dual active site for efficient sulfamethoxazole degradation: synergism of Fe and N-doped carbon. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 71088–71102 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-27391-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-27391-6