Abstract
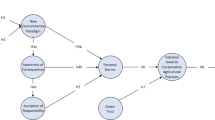
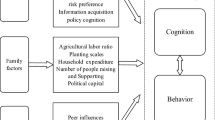
The literature reports that trust in information sources (ISs) is an important determinant of farmers’ adoption of sustainable environmental practices. However, few in-depth studies have focused on the differences in trust among different ISs in heterogeneous farmers’ green behavior. Therefore, it is challenging for heterogeneous farmers to design efficient and differentiated information strategies. This study proposes a benchmark model to explore differences in trust in different ISs in the application of organic fertilizers (OFs) to farmers at different scales. A total of 361 farmers of a geographically indicated agricultural product in China were evaluated to understand their trust in different ISs when adopting OFs. The results identify the differentiation of heterogeneous farmers’ trust in different ISs when considering green practices. Specifically, large-scale farmers’ green behavior is more likely to be influenced by trust in formal ISs (strength–weakness ratio of 1.15 for the effect of two ISs), whereas small-scale farmers’ green behavior is strongly influenced by trust in informal ISs (strength–weakness ratio of 4.62 for the effect of two ISs). This difference was mainly caused by differences in farmers’ information acquisition ability, level of social capital, and preference for social learning. The model and findings of this study can aid policy-makers in designing effective and differentiated information interventions for different types of farmers to maximize their adoption of sustainable environmental practices.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data and materials are available from the authors on request.
References
Aregay FA, Zhao M, Xu T (2018) Knowledge, attitude and behavior of farmers in farmland conservation in China: an application of the structural equation model. J Environ Plan Manag 61(2):249–271
Bagheri A, Bondori A, Allahyari MS, Damalas CA (2019) Modeling farmers’ intention to use pesticides: an expanded version of the theory of planned behavior. J Environ Manage 248:109291
Beckford C, Barker D (2007) The role and value of local knowledge in Jamaican agriculture: adaptation and change in small-scale farming. Geogr J 173:118–128
Blackstock KL, Ingram J, Burton R, Brown KM, Slee B (2010) Understanding and influencing behaviour change by farmers to improve water quality. Sci Total Environ 408(23):5631–5638
Bondori A, Bagheri A, Sookhtanlou M, Allahyari MS, Damalas CA (2018) Pesticide use in cereal production in Moghan Plain, Iran: risk knowledge and farmers’ attitudes. Crop Prot 110:117–124
Bondori A, Bagheri A, Sookhtanlou M, Damalas CA (2021) Modeling farmers’ intention for safe pesticide use: the role of risk perception and use of information sources. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(47):66677–66686
Buck S, Alwang JR (2006) The role of trust in knowledge acquisition: results from field experiments in the Ecuadorian Amazon. In: 2006 Annual meeting, July 23-26, (New Name 2008: Agricultural and Applied Economics Association). American Agricultural Economics Association, Long Beach, CA, pp 1–34
Caffaro F, Roccato M, Cremasco MM, Cavallo E (2019) An ergonomic approach to sustainable development: the role of information environment and social-psychological variables in the adoption of agri-environmental innovations. Sustain Dev 27(6):1049–1062
Caffaro F, Micheletti Cremasco M, Roccato M, Cavallo E (2020) Drivers of farmers’ intention to adopt technological innovations in Italy: the role of information sources, perceived usefulness, and perceived ease of use. J Rural Stud 76:264–271
Cai LM, Wang LP, Ning MX (2022) Farmers’ livelihood differentiation and pesticide application: empirical evidence from a causal mediation analysis. Sustainability 14(14):8502
Chen Y, Fu X, Liu Y (2022) Effect of farmland scale on farmers’ application behavior with organic fertilizer. Int J Environ Res Public Health 19(9):4967
Cruz JL, Albisu LM, Zamorano JP, Sayadi S (2022) Agricultural interactive knowledge models: researchers’ perceptions about farmers’ knowledges and information sources in Spain. J Agric Educ Ext 28(3):325–340
Damalas CA (2021) Farmers’ intention to reduce pesticide use: the role of perceived risk of loss in the model of the planned behavior theory. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(26):35278–35285
Dan V, Osterheider A, Raupp J (2019) The diffusion of innovations in agricultural circles: an explorative study on alternative antimicrobial agents. Sci Commun 41(1):3–37
Daxini A, Ryan M, O’Donoghue C, Barnes AP (2019) Understanding farmers’ intentions to follow a nutrient management plan using the theory of planned behaviour. Land Use Policy 85:428–437
Eanes FR, Singh AS, Bulla BR, Ranjan P, Prokopy LS, Fales M, Wickerham B, Doran PJ (2017) Midwestern US farmers perceive crop advisers as conduits of information on agricultural conservation practices. Environ Manage 60(5):974–988
Fabregas R, Kremer M, Schilbach F (2019) Realizing the potential of digital development: the case of agricultural advice. Science 366(6471):eaay3038
Farani AY, Mohammadi Y, Ghahremani F (2019) Modeling farmers’ responsible environmental attitude and behaviour: a case from Iran. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(27):28146–28161
Fisher M, Holden ST, Thierfelder C, Katengeza SP (2018) Awareness and adoption of conservation agriculture in Malawi: what difference can farmer-to-farmer extension make? Int J Agric Sustain 16(3):310–325
Fisher R (2013) ‘A gentleman’s handshake’: the role of social capital and trust in transforming information into usable knowledge. J Rural Stud 31:13–22
Funing Statistical Bureau (2021) Funing statistical yearbook. http://222.188.117.130:7137/nj/nj2021.pdf
Gao Y, Liu B, Yu L, Yang H, Yin S (2019) Social capital, land tenure and the adoption of green control techniques by family farms: evidence from Shandong and Henan Provinces of China. Land Use Policy 89:104250
Genius M, Koundouri P, Nauges C, Tzouvelekas V (2014) Information transmission in irrigation technology adoption and diffusion: social learning, extension services, and spatial effects. Am J Agric Econ 96(1):328–344
Goodarzi S, Masini A, Aflaki S, Fahimnia B (2021) Right information at the right time: reevaluating the attitude–behavior gap in environmental technology adoption. Int J Prod Econ 242:108278
Gross S, Roosen J (2021) Effects of information on social trust in farmers regarding animal welfare. Int Food Agribusiness Manag Rev 24(1):121–137
Henseler J, Ringle CM, Sarstedt M (2015) A new criterion for assessing discriminant validity in variance-based structural equation modeling. J Acad Mark Sci 43(1):115–135
Henseler J, Ringle CM, Sarstedt M (2016) Testing measurement invariance of composites using partial least squares. Int Mark Rev 33(3):405–431
Imani B, Allahyari MS, Bondori A, Emami N, El Bilali H (2021) Adoption of organic potato production in Ardabil plain, Iran: an application of the extended theory of planned behaviour. Potato Res 64(2):177–195
Jiang L, Zhang J, Wang HH, Zhang L, He K (2018) The impact of psychological factors on farmers’ intentions to reuse agricultural biomass waste for carbon emission abatement. J Clean Prod 189:797–804
Jin G, Deng X, Zhao X, Guo B, Yang J (2018) Spatiotemporal patterns in urbanization efficiency within the Yangtze River Economic Belt between 2005 and 2014. J Geogr Sci 28(8):1113–1126
Kassem HS, Alotaibi BA, Aldosri FO, Muddassir M (2021) Exploring the relationship between information-seeking behavior and adoption of biofertilizers among onion farmers. Agronomy-Basel 11(6):1258
Khataza RRB, Doole GJ, Kragt ME, Hailu A (2018) Information acquisition, learning and the adoption of conservation agriculture in Malawi: a discrete-time duration analysis. Technol Forecast Soc Change 132:299–307
Laepple D, Van Rensburg T (2011) Adoption of organic farming: are there differences between early and late adoption? Ecol Econ 70(7):1406–1414
Laksono P, Irham MJH, Suryantini A (2022) Farmers’ willingness to adopt geographical indication practice in Indonesia: a psycho behavioral analysis. Heliyon 8(8):e10178
Lalani B, Dorward P, Holloway G, Wauters E (2016) Smallholder farmers’ motivations for using Conservation Agriculture and the roles of yield, labour and soil fertility in decision making. Agric Syst 146:80–90
Li B, Shen Y (2021) Effects of land transfer quality on the application of organic fertilizer by large-scale farmers in China. Land Use Policy 100:105124
Li H, Huang D, Ma Q, Qi W, Li H (2019) Factors influencing the technology adoption behaviours of litchi farmers in China. Sustainability 12(1):271
Li J, Feng SY, Luo TY, Guan ZF (2020) What drives the adoption of sustainable production technology? evidence from the large scale farming sector in East China. J Clean Prod 257:120611
Li J, He R, deVoil P, Wan S (2021) Enhancing the application of organic fertilisers by members of agricultural cooperatives. J Environ Manage 293:112901
Li J, Xu F, Yang J (2022b) Improved economic and environmental outcomes from targeted fertilizer policy. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(7):10101–10111
Li X, Wu X (2021) The impact of social norms on rice farmers’ behavior of organic fertilizers application: mediating effect of value perception and moderating effect of education level. Int J Low Carbon Technol 16(4):1492–1503
Li YJ, Qing C, Guo SL, Deng X, Song JH, Xu DD (2022a) Will farmers follow their peers in adopting straw returning? evidence from rural Sichuan Province, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30(8):21169–21185
Lichtenberg E, Zimmerman R (1999) Information and farmers’ attitudes about pesticides, water duality, and related environmental effects. Agr Ecosyst Environ 73(3):227–236
Lu H, Zhang P, Hu H, Xie H, Yu Z, Chen S (2019) Effect of the grain-growing purpose and farm size on the ability of stable land property rights to encourage farmers to apply organic fertilizers. J Environ Manage 251:109621
Ma W, Ma C, Su Y, Nie Z (2017) Organic farming: does acquisition of the farming information influence Chinese apple farmers’ willingness to adopt? China Agric Econ Rev 9(2):211–224
Martini E, Roshetko JM, Paramita E (2016) Can farmer-to-farmer communication boost the dissemination of agroforestry innovations? a case study from Sulawesi. Indonesia. Agrofor Syst 91(5):811–824
Mase AS, Babin NL, Prokopy LS, Genskow KD (2015) Trust in sources of soil and water quality information: implications for environmental outreach and education. J Am Water Resour Assoc 51(6):1656–1666
MNR (Ministry of Natural Resources of China) (2020) The third national land survey. https://www.mnr.gov.cn/zt/td/dscqggtdc/
Ncoyini Z, Savage MJ, Strydom S (2022) Limited access and use of climate information by small-scale sugarcane farmers in South Africa: a case study. Clim Serv 26:100285
Nunes B, Gholami R, Higón DA (2021) Sustainable farming practices, awareness, and behavior in small farms in Brazil. J Glob Inf Manag 29(6):1–23
Pan D (2014) The impact of agricultural extension on farmer nutrient management behavior in Chinese rice production: a household-level analysis. Sustainability 6(10):6644–6665
Pan D, Tang J, Zhang L, He M, Kung C (2021) The impact of farm scale and technology characteristics on the adoption of sustainable manure management technologies: evidence from hog production in China. J Clean Prod 280:124340
Perosa B, Newton P, Carrer MJ (2021) Access to information affects the adoption of integrated systems by farmers in Brazil. Land Use Policy 106:105459
Poncet J, Kuper M, Chiche J (2010) Wandering off the paths of planned innovation: the role of formal and informal intermediaries in a large-scale irrigation scheme in Morocco. Agric Syst 103(4):171–179
Rogers EM, Beal GM (1958) The importance of personal influence in the adoption of technological change. Soc F 36(4):329–335
Rust NA, Stankovics P, Jarvis RM, Morris-Trainor Z, de Vries JR, Ingram J, Mills J, Glikman JA, Parkinson J, Toth Z, Hansda R, McMorran R, Glass J, Reed MS (2022) Have farmers had enough of experts? Environ Manage 69(1):31–44
Sarstedt M, Ringle CM, Cheah JH, Ting HR, Moisescu OI, Radomir L (2020) Structural model robustness checks in PLS-SEM. Tourism Econ 26(4):531–554
Shi ZQ, Deng W, Zhang SY (2018) Spatio-temporal pattern changes of land space in Hengduan Mountains during 1990-2015. J Geogr Sci 28(4):529–542
Simoes ARP, Bueno NP, Almeida FMD, Nicholson CF, dos Reis JD, Leonel FD (2020) Public policies for enhancing diffusion of technology: a network analysis for a dairy farmer community in Minas Gerais. Brazil. Rev Bras Zootecn 49:e20190207
Spurk C, Asule P, Baah-Ofori R, Chikopela L, Diarra B, Koch C (2020) The status of perception, information exposure and knowledge of soil fertility among small-scale farmers in Ghana, Kenya, Mali and Zambia. J Agric Educ Ext 26(2):141–161
Svensson G, Ferro C, Hogevold N, Padin C, Varela JCS, Sarstedt M (2018) Framing the triple bottom line approach: direct and mediation effects between economic, social and environmental elements. J Clean Prod 197:972–991
Tama RAZ, Ying L, Yu M, Hoque MM, Adnan KM, Sarker SA (2021) Assessing farmers’ intention towards conservation agriculture by using the Extended Theory of Planned Behavior. J Environ Manage 280:111654
Taube O, Ranney MA, Henn L, Kaiser FG (2021) Increasing people’s acceptance of anthropogenic climate change with scientific facts: is mechanistic information more effective for environmentalists? J Environ Psychol 73:101549
Tran TA, James H, Nhan DK (2020) Effects of social learning on rural farmers’ adaptive capacity: empirical insights from the Vietnamese Mekong Delta. Soc Nat Resour 33(9):1053–1072
Thu VH, Tran D, Goto D, Kawata K (2020) Does experience sharing affect farmers’ pro-environmental behavior? A randomized controlled trial in Vietnam. World Dev 136:105062
Urbach N, Ahlemann F (2010) Structural equation modeling in information systems research using partial least squares. JITTA 11(2):2
Wang N, Hui H, Liu L, Liu J (2016) Development characteristics and practice of watermelon industry in Funing county Jiangsu province. Chinese Cucurbits and Vegetables 29(6):42–44
Wang X, Zhang J, He K, Li W (2021) Place attachment, environmental cognition and organic fertilizer adoption of farmers: evidence from rural China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(30):41255–41267
Wang Y, Zhu Y, Zhang S, Wang Y (2018) What could promote farmers to replace chemical fertilizers with organic fertilizers? J Clean Prod 199:882–890
Wauters E, Bielders C, Poesen J, Govers G, Mathijs E (2010) Adoption of soil conservation practices in Belgium: an examination of the theory of planned behaviour in the agri-environmental domain. Land Use Policy 27(1):86–94
Wilson TD, Kraft D, Dunn DS (1989) The disruptive effects of explaining attitudes: the moderating effect of knowledge about the attitude object. J Exp Soc Psychol 25(5):379–400
Xie J, Yang G, Guo Z, Wang G (2021) Exploring the influence mechanism of farmers’ organic fertilizer application behaviors based on the normative activation theory. Land 10(11):1111
Yang W, Qi J, Arif M, Liu M, Lu Y (2021) Impact of information acquisition on farmers’ willingness to recycle plastic mulch film residues in China. J Clean Prod 297:126656
Zeweld W, Van Huylenbroeck G, Tesfay G, Speelman S (2017) Smallholder farmers’ behavioural intentions towards sustainable agricultural practices. J Environ Manage 187:71–81
Zhao Q, Pan Y, Xia X (2021) Internet can do help in the reduction of pesticide use by farmers: evidence from rural China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(2):2063–2073
Zhu D, Xie X, Gan Y (2011) Information source and valence: how information credibility influences earthquake risk perception. J Environ Psychol 31(2):129–136
Zhu J, Zheng S, Kaabar MKA, Yue X-G (2022) Online or offline? The impact of environmental knowledge acquisition on environmental behavior of Chinese farmers based on social capital perspective. Front Environ Sci 10:1052797
Funding
This research is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (Grant No. 72171121), Postgraduate Research & Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province (Grant No. KYCX22_0786), and Scientific Research Foundation of Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications (Grant No. NYY222045).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xiaofeng Lv: conceptualization, investigation, analysis, and writing—original draft. Jing Li: conceptualization, methodology, supervision, writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications and Nanjing Agricultural University have no specific policies on the investigation of food supply chains. Our study was approved by Research Ethics Committee of Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications and Research Ethics Committee of Nanjing Agricultural University.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Baojing Gu
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(PDF 140 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lv, X., Li, J. A benchmark model for exploring the differentiation of trust in information sources in heterogeneous farmers’ green behavior. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 69941–69954 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-27340-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-27340-3