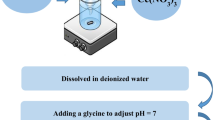
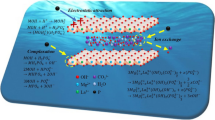
Abstract
La-based adsorbents are widely used for controlling phosphate concentration in water bodies. In order to explore the effect of different B-site metals regulating La-based perovskites on phosphate adsorption, three La-based perovskites (LaBO3, B = Fe, Al, and Mn) were prepared using the citric acid sol–gel method. Adsorption experiments showed that LaFeO3 exhibited the highest adsorption capacity for phosphate, which was 2.7 and 5 times higher than those of LaAlO3 and LaMnO3, respectively. The characterization results demonstrated that LaFeO3 has dispersed particles exhibiting larger pore size and more pores than LaAlO3 and LaMnO3. Spectroscopy analysis and density functional theory calculation results showed that different B-positions cause a change in the type of perovskite crystals. Among them, the differences between lattice oxygen consumption ratio, zeta potential and adsorption energy are the main reasons for the differences in adsorption capacity. In addition, the adsorption of phosphate by La-based perovskites were well fitted with Langmuir isotherm and pursues the pseudo-second-order kinetic models. The maximum adsorption capacities were 33.51, 12.31 and 6.61 mg/g for LaFeO3, LaAlO3 and LaMnO3, respectively. The adsorption mechanism was mainly based on inner-sphere complexation and electrostatic attraction. This study provides an explanation for the influence of different B sites on phosphate adsorption by perovskite.
Graphical Abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data used to support the findings of this study are included within the article.
References
Akhade SA, Kitchin JR (2012) Effects of strain, d-band filling, and oxidation state on the surface electronic structure and reactivity of 3d perovskite surfaces. J Chem Phys 137. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4746117
Bacelo H, Pintor AMA, Santos SCR et al (2020) Performance and prospects of different adsorbents for phosphorus uptake and recovery from water. Chem Eng J 381:122566. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.122566
Borgohain X, Boruah A, Sarma GK, Rashid MH (2020) Rapid and extremely high adsorption performance of porous MgO nanostructures for fluoride removal from water. J Mol Liq 305:112799. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2020.112799
Delmastro A, Mazza D, Ronchetti S et al (2001) Synthesis and characterization of non-stoichiometric LaFeO3 perovskite. Mater Sci Eng B Solid-State Mater Adv Technol 79:140–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-5107(00)00570-5
Du CM, Yu YH, Jiang LD, Yu JK (2022) Efficient extraction of phosphate from dephosphorization slag by hydrochloric acid leaching. J Clean Prod 332:130087. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.130087
Feng Y, Luo Y, He Q et al (2021) Performance and mechanism of a biochar-based Ca-La composite for the adsorption of phosphate from water. J Environ Chem Eng 9:105267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.105267
Gürses A, Hassani A, Kranşan M et al (2014) Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution using by untreated lignite as potential low-cost adsorbent: Kinetic, thermodynamic and equilibrium approach. J Water Process Eng 2:10–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2014.03.002
Hassani A, Eghbali P, Mahdipour F, et al (2023) Insights into the synergistic role of photocatalytic activation of peroxymonosulfate by UVA-LED irradiation over CoFe2O4-rGO nanocomposite towards effective Bisphenol A degradation: Performance, mineralization, and activation mechanism. Chem Eng J 453. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.139556
He Y, Li Z, Xue M et al (2022) Enhanced adsorption performance of subordinate magnesium sites in pinhole magnesium oxide nanosheets with rich oxygen vacancies. Environ Funct Mater 1:105–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.efmat.2022.04.002
He J, Xu Y, Wang W, et al (2020) Ce(III) nanocomposites by partial thermal decomposition of Ce-MOF for effective phosphate adsorption in a wide pH range. Chem Eng J 379. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.122431
Huang T, Su Z, Dai Y, Zhou L (2021a) Enhancement of the heterogeneous adsorption and incorporation of uraniumVI caused by the intercalation of β-cyclodextrin into the green rust. Environ Pollut 290:118002. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.118002
Huang T, Zhang SW, Zhou L, Liu LF (2021b) Electrokinetics couples with the adsorption of activated carbon-supported hydroxycarbonate green rust that enhances the removal of Sr cations from the stock solution in batch and column. Sep Purif Technol 265:118531. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2021.118531
Huang T, Pan L, Dong J et al (2022a) A comprehensive investigation of zeolite-rich tuff functionalized with 3-mercaptopropionic acid intercalated green rust for the efficient removal of HgII and CrVI in a binary system. J Environ Manage 324:116344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.116344
Huang T, Song D, Zhou L et al (2022b) Non-thermal plasma irradiated polyaluminum chloride for the heterogeneous adsorption enhancement of Cs+ and Sr2+ in a binary system. J Hazard Mater 424:127441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127441
Huang T, Song D, Yang C, Zhang SW (2023) Nonthermal plasma-irradiated polyvalent ferromanganese binary hydro(oxide) for the removal of uranyl ions from wastewater. Environ Res 217:114911. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2022.114911
Karim AV, Hassani A, Eghbali P, Nidheesh PV (2022) Nanostructured modified layered double hydroxides (LDHs)-based catalysts: A review on synthesis, characterization, and applications in water remediation by advanced oxidation processes. Curr Opin Solid State Mater Sci 26:100965. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cossms.2021.100965
Kim K, Kim D, Kim T et al (2019) Synthesis of mesoporous lanthanum hydroxide with enhanced adsorption performance for phosphate removal. RSC Adv 9:15257–15264. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ra00895k
Lai L, Xie Q, Chi L et al (2016) Adsorption of phosphate from water by easily separable Fe3O4@SiO2 core/shell magnetic nanoparticles functionalized with hydrous lanthanum oxide. J Colloid Interface Sci 465:76–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2015.11.043
Li R, Wang JJ, Zhou B et al (2016) Enhancing phosphate adsorption by Mg/Al layered double hydroxide functionalized biochar with different Mg/Al ratios. Sci Total Environ 559:121–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.03.151
Li R, Wang JJ, Zhou B et al (2017) Simultaneous capture removal of phosphate, ammonium and organic substances by MgO impregnated biochar and its potential use in swine wastewater treatment. J Clean Prod 147:96–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.01.069
Li T, Liao T, Su X et al (2018) Preparation of cobalt-containing spinel oxides as novel adsorbents for efficient phosphate removal. Environ Sci Water Res Technol 4:1671–1684. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ew00517f
Li S, Guo M, Wang X, Gao K (2020) Fabrication and photocatalytic activity of LaFeO3 ribbon-like nanofibers. J Chinese Chem Soc 67:990–997. https://doi.org/10.1002/jccs.201900431
Li M, Luo Y, Zhao D et al (2022) Different La/Fe oxide composites for efficient phosphate removal from wastewater: Properties and mechanisms. J Environ Chem Eng 10:107329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2022.107329
Lin J, Zhao Y, Zhan Y, Wang Y (2020) Control of internal phosphorus release from sediments using magnetic lanthanum/iron-modified bentonite as active capping material. Environ Pollut 264:114809. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114809
Liu R, Chi L, Wang X et al (2018) Review of metal (hydr)oxide and other adsorptive materials for phosphate removal from water. J Environ Chem Eng 6:5269–5286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2018.08.008
Liu X, Shen F, Qi X (2019) Adsorption recovery of phosphate from aqueous solution by CaO-biochar composites prepared from eggshell and rice straw. Sci Total Environ 666:694–702. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.02.227
Liu X, Yuan Z, Liu X et al (2020) Historic Trends and Future Prospects of Waste Generation and Recycling in China’s Phosphorus Cycle. Environ Sci Technol 54:5131–5139. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.9b05120
Liu B, Liu Z, Wu H et al (2021a) Insight into simultaneous selective removal of nitrogen and phosphorus species by lanthanum-modified porous polymer: Performance, mechanism and application. Chem Eng J 415:129026. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.129026
Liu H, Shan J, Chen Z, Lichtfouse E (2021b) Efficient recovery of phosphate from simulated urine by Mg/Fe bimetallic oxide modified biochar as a potential resource. Sci Total Environ 784:147546. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.147546
Liu LY, Zhang CH, Chen SR et al (2022a) Phosphate adsorption characteristics of La(OH)3-modified, canna-derived biochar. Chemosphere 286:131773. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131773
Liu S, Zhao S, Fan F et al (2022b) Magnetically separable and recyclable lanthanum/iron co-modified attapulgite: A sustainable option to efficiently control phosphate loading. J Clean Prod 348:131294. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.131294
Luo W, Huang Q, Zhang X et al (2020) Lanthanum/Gemini surfactant-modified montmorillonite for simultaneous removal of phosphate and nitrate from aqueous solution. J Water Process Eng 33:101036. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2019.101036
Luo Y, Xie K, Feng Y et al (2021) Colloids and Surfaces A : Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects Synthesis of a La ( OH ) 3 nanorod / walnut shell biochar composite for reclaiming phosphate from aqueous solutions. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem Eng Asp 610:125736
Makita Y, Sonoda A, Sugiura Y et al (2019) Preparation and phosphate adsorptive properties of metal oxide-loaded granular activated carbon and pumice stone. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem Eng Asp 582:123881. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2019.123881
Penninger MW, Kim CH, Thompson LT, Schneider WF (2015) DFT Analysis of NO Oxidation Intermediates on Undoped and Doped LaCoO3 Perovskite. J Phys Chem C 119:20488–20494. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.5b06351
Qiu H, Liang C, Zhang X et al (2015) Fabrication of a Biomass-Based Hydrous Zirconium Oxide Nanocomposite for Preferable Phosphate Removal and Recovery. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:20835–20844. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b06098
Rashid M, Price NT, Gracia Pinilla MÁ, O’Shea KE (2017) Effective removal of phosphate from aqueous solution using humic acid coated magnetite nanoparticles. Water Res 123:353–360. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.06.085
Santos AG, Leite JO, Souza MJB et al (2018) Effect of the metal type in perovskites prepared by modified proteic method in dye adsorption from aqueous medium. Ceram Int 44:5743–5750. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.12.232
Shi W, Fu Y, Jiang W et al (2019) Enhanced phosphate removal by zeolite loaded with Mg–Al–La ternary (hydr)oxides from aqueous solutions: Performance and mechanism. Chem Eng J 357:33–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.08.003
Song Q, Huang S, Xu L, et al (2020) Synthesis of magnetite/lanthanum hydroxide composite and magnetite/aluminum hydroxide composite for removal of phosphate. Sci Total Environ 723. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137838
Sun X, Jiang D, Zhang L et al (2017) Enhanced Nitrogen Photofixation over LaFeO3 via Acid Treatment. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 5:9965–9971. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.7b01912
Tang Q, Shi C, Shi W et al (2019) Preferable phosphate removal by nano-La(III) hydroxides modified mesoporous rice husk biochars: Role of the host pore structure and point of zero charge. Sci Total Environ 662:511–520. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.01.159
Trazzi PA, Leahy JJ, Hayes MHB, Kwapinski W (2016) Adsorption and desorption of phosphate on biochars. J Environ Chem Eng 4:37–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2015.11.005
Tuan VN, Dinh TD, Zhang W et al (2021) A smart diagnostic tool based on deep kernel learning for on-site determination of phosphate, calcium, and magnesium concentration in a hydroponic system. RSC Adv 11:11177–11191. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1ra00140j
Wang J, Wu L, Li J et al (2018) Simultaneous and efficient removal of fluoride and phosphate by Fe-La composite: Adsorption kinetics and mechanism. J Alloys Compd 753:422–432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.04.177
Wang H, Han H, Sun E et al (2019) Production of Aryl Oxygen-Containing Compounds by the Pyrolysis of Bagasse Alkali Lignin Catalyzed by LaM0.2Fe0.8O3 (M = Fe, Cu, Al, Ti). Energy Fuels 33:8596–8605. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.energyfuels.9b00755
Wang Y, Li J, Yuan Y et al (2021) La(OH)3 loaded magnetic nanocomposites derived from sugarcane bagasse cellulose for phosphate adsorption: Characterization, performance and mechanism. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem Eng Asp 626:127060. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2021.127060
Wu K, Li Y, Liu T et al (2019a) The simultaneous adsorption of nitrate and phosphate by an organic-modified aluminum-manganese bimetal oxide: Adsorption properties and mechanisms. Appl Surf Sci 478:539–551. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.01.194
Wu Y, Li X, Yang Q et al (2019b) Hydrated lanthanum oxide-modified diatomite as highly efficient adsorbent for low-concentration phosphate removal from secondary effluents. J Environ Manag 231:370–379. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.10.059
Xiang F, Chen X, Yu J et al (2018) Synthesis of three-dimensionally ordered porous perovskite type LaMnO3 for Al-air battery. J Mater Sci Technol 34:1532–1537. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2018.01.010
Xiang C, Wang H, Ji Q et al (2019) Tracking Internal Electron Shuttle Using X-ray Spectroscopies in La/Zr Hydroxide for Reconciliation of Charge-Transfer Interaction and Coordination toward Phosphate. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11:24699–24706. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b05397
Xiao G, Qiao W, Zhang L et al (2021) Study on Hydrogen Production Catalytic Materials for Perovskite Methanol Steam Reforming. Acta Chim Sin 79:100–107. https://doi.org/10.6023/A20080374
Xie J, Wang Z, Lu S et al (2014) Removal and recovery of phosphate from water by lanthanum hydroxide materials. Chem Eng J 254:163–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.05.113
Yao X, Liu J, Wang W (2018) Influence of B-site transition metal on NO oxidation over LaBO3 (B=Mn, Fe and Co) perovskite catalysts. AIP Adv 8. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5051785
Yu J, Xiang C, Zhang G et al (2019) Activation of Lattice Oxygen in LaFe (Oxy)hydroxides for Efficient Phosphorus Removal. Environ Sci Technol 53:9073–9080. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.9b01939
Zhang L, Jin SW, Wang Y, Ji J (2018) Phosphate adsorption from aqueous solution by lanthanum–iron hydroxide loaded with expanded graphite. Environ Technol (united Kingdom) 39:997–1006. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2017.1317843
Zhang X, Chu W, Bai H, Liang S (2022) LaAlO3: a new high-temperature negative temperature coefficient thermistor. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 33:12093–12103. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-08169-x
Zheng D, Yao R, Sun C et al (2021) Highly Efficient Low-Concentration Phosphate Removal from Effluents by Recoverable La(OH)3/Foamed Nickel Adsorbent. ACS Omega 6:5399–5407. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.0c05489
Zhou A, Zhu C, Chen W et al (2018) Phosphorus recovery from water by lanthanum hydroxide embedded interpenetrating network poly (vinyl alcohol)/sodium alginate hydrogel beads. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem Eng Asp 554:237–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2018.05.086
Zhou Y, Lü Z, Li J et al (2021) The electronic properties and structural stability of LaFeO3 oxide by niobium doping: A density functional theory study. Int J Hydrogen Energy 46:9193–9198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.12.202
Acknowledgements
The author thanks the the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2017YFD0800403), Yunnan Fundamental Research Projects (202101AT070002), Central Public-interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund (Y2022PT06, Y2021XC18), Major Science and Technology Special Plan of Yunnan Province (202102AE090011), and Erhai Watershed Ecological Environment Quality Testing Engineering Research Center of Yunnan Provincial Universities (DXDGCZX02).
Funding
This research was financially supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2017YFD0800403), Yunnan Fundamental Research Projects (202101AT070002), Central Public-interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund (Y2022PT06, Y2021XC18), Major Science and Technology Special Plan of Yunnan Province (202102AE090011), and Erhai Watershed Ecological Environment Quality Testing Engineering Research Center of Yunnan Provincial Universities (DXDGCZX02).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Changbin Guo: Visualization, Methodology, Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing-original draft preparation. Mengmeng Li: Investigation, Conceptualization, Methodology, Data curation, Formal analysis. Menghan Feng: Visualization, Investigation, Formal analysis. Mingyao Yuan: Methodology, Software. Shangkai Qiu: Editing. Lisheng Zhang: Software. Weilin Fu: Conceptualization. Jien Zhou: Conceptualization. Keqiang Zhang: Writing-review & editing. Yanli Luo: Writing-review & editing.Feng Wang: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Writing-review & editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publication
All authors allow the publication of the paper.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: George Z. Kyzas
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, C., Li, M., Feng, M. et al. B-site metal modulation of phosphate adsorption properties and mechanism of LaBO3 (B = Fe, Al and Mn) perovskites. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 66638–66650 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-27284-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-27284-8