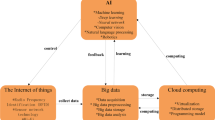
Abstract
Environmental pollution has become a significant concern of nations. International organizations, local authorities, and social activists try to achieve sustainable development goals (SDGs) to protect the environment. However, this cannot be achieved without acknowledging the role of advanced technology applications. Previous studies found a significant relationship between technology and energy resources. But the need to highlight the significance of artificial intelligence (AI) in dealing with inevitable environmental issues still requires more attention. This study aims to analyze the application of AI applications in predicting, developing, and implementing wind and solar energy resources through a bibliometric analysis from 1991 to 2022. It uses bilioshiny of the “bibliometrix 3.0” package of R-programming for influential core aspects and keyword analysis and VOSviewer for co-occurrence analysis. The study provides significant implications for core authors, documents, sources, affiliations, and countries. It also provides keyword analysis and a co-occurrence network to cope with the conceptual integration of the literature. It reports three significant streams of literature in clusters: AI optimization and renewable energy resources; smart renewable energy resource challenges and opportunities; deep learning and machine learning forecasting; and energy efficiency. The findings will uncover the strategic perspective of AI technology for wind and solar energy generation projects.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be provided by the corresponding author upon request.
Abbreviations
- SDGs:
-
Sustainable development goals
- AI:
-
Artificial intelligence
- ML:
-
Machine learning
- DL:
-
Deep learning
- PV:
-
Photovoltaic
- TC:
-
Total citations
- NP:
-
Net production
- ANN:
-
Artificial neural network
- AHP:
-
Analytical hierarchy process
- GIS:
-
Geographical information systems
References
Abualigah L, Zitar RA, Almotairi KH, Hussein AM, Elaziz MA, Nikoo MR, Gandomi AH (2022) Wind, solar, and photovoltaic renewable energy systems with and without energy storage optimization: a survey of advanced machine learning and deep learning techniques. Energies 15:578. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15020578
Adeel M, Mahmood S, Khan KI, Saleem S (2022) Green HR practices and environmental performance: the mediating mechanism of employee outcomes and moderating role of environmental values. Front Environ Sci 10:1793. https://doi.org/10.3389/FENVS.2022.1001100
Al-falahi MDA, Jayasinghe SDG, Enshaei H (2017) A review on recent size optimization methodologies for standalone solar and wind hybrid renewable energy system. Energy Convers Manag 143:252–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2017.04.019
Almalaq A, Alshammarry A, Alanzi B, Alharbi F, Alshudukhi M (2021) Deep learning applied on renewable energy forecasting towards supply-demand matching. In 2021 20th IEEE International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications (ICMLA 2021), pp 1345–1349. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICMLA52953.2021.00218
Amarasinghe PAGM, Abeygunawardane SK (2018) Application of machine learning algorithms for solar power forecasting in Sri Lanka. In: 2018 2nd International Conference on Electrical Engineering (EECon), pp 87–92. https://doi.org/10.1109/EECon.2018.8541017
Atabaki MS, Mohammadi M, Aryanpur V (2022) An integrated simulation-optimization modelling approach for sustainability assessment of electricity generation system. Sustain Energy Technol Assessments 52:102010. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seta.2022.102010
Banu JF, Atul Mahajan R, Sakthi U, Kumar Nassa V, Lakshmi D, Nadanakumar V (2022) Artificial intelligence with attention based BiLSTM for energy storage system in hybrid renewable energy sources. Sustain Energy Technol Assessments 52:102334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seta.2022.102334
Belu R (2009) A project-based power electronics course with an increased content of renewable energy applications. In: 2009 Annual Conference & Exposition ASEE, pp 14–91 https://peer.asee.org/4994
Bermejo JF, Fernández JFG, Polo FO, Márquez AC (2019) A review of the use of artificial neural network models for energy and reliability prediction. A study of the solar PV, hydraulic and wind energy sources. Appl Sci 9:1844. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9091844
Bhoye M, Pandya MH, Valvi S, Trivedi IN, Jangir P, Parmar SA (2016) An emission constraint economic load dispatch problem solution with Microgrid using JAYA algorithm. In 2016 International Conference on Energy Efficient Technologies for Sustainability (ICEETS 2016), pp 497–502. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICEETS.2016.7583805
Chandrasekaran K, Selvaraj J, Amaladoss CR, Veerapan L (2021) Hybrid renewable energy based smart grid system for reactive power management and voltage profile enhancement using artificial neural network. Energy Sources. Part A Recover Util Environ Eff 43:2419–2442. https://doi.org/10.1080/15567036.2021.1902430
Chidzonga RF, Nleya B (2020) Perspectives on impact of high penetration of renewable sources on LV networks. In: 2020 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Big Data, Computing and Data Communication Systems (icABCD 2020), pp 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1109/icABCD49160.2020.9183858
Dagdougui H, Minciardi R, Ouammi A, Robba M, Sacile R (2010) Modelling and control of a hybrid renewable energy system to supply demand of a green-building. In: Proceedings of the iEMSs Fourth Biennial Meeting: International Congress on Environmental Modelling and Software (iEMSs 2010), pp 972–979. http://www.iemss.org/iemss2010/index.php?n=Main.Proceedings
Dagdougui H, Minciardi R, Ouammi A, Robba M, Sacile R (2012) Modeling and optimization of a hybrid system for the energy supply of a “green” building. Energy Convers Manag 64:351–363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2012.05.017
Das DC, Roy AK, Sinha N (2011) PSO based frequency controller for wind-solar-diesel hybrid energy generation/energy storage system. In: 2011 International Conference on Energy, Automation and Signal (ICEAS 2011), pp 458–463. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICEAS.2011.6147150
Das DC, Roy AK, Sinha N (2012) GA based frequency controller for solar thermal-diesel-wind hybrid energy generation/energy storage system. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 43:262–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijepes.2012.05.025
Dawoud SM, Lin X, Okba MI (2018) Hybrid renewable microgrid optimization techniques: a review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 82:2039–2052. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2017.08.007
De Sousa PHF, NMM e N, PPR F, CMS DM (2018) Detection and classification of faults in induction generator applied into wind turbines through a machine learning approach. In: 2018 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), pp 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1109/IJCNN.2018.8489521
Del JS, Casillas-Perez D, Cornejo-Bueno L, Prieto-Godino L, Sanz-Justo J, Casanova-Mateo C, Salcedo-Sanz S (2022) Randomization-based machine learning in renewable energy prediction problems: critical literature review, new results and perspectives. Appl Soft Comput 118:108526. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2022.108526
Devaraj J, Madurai Elavarasan R, Shafiullah GM, Jamal T, Khan I (2021) A holistic review on energy forecasting using big data and deep learning models. Int J Energy Res 45:13489–13530. https://doi.org/10.1002/er.6679
Dogaru DI, Dumitrache I (2019) Cyber security of smart grids in the context of big data and machine learning. In: 2019 22nd International Conference on Control Systems and Computer Science (CSCS 2019), pp 61–67 https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8745044
Güven AF, Yörükeren N, Samy MM (2022) Design optimization of a stand-alone green energy system of university campus based on Jaya-Harmony Search and Ant Colony Optimization algorithms approaches. Energy 253:124089. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2022.124089
Hatata AY, Osman G, Aladl MM (2018) An optimization method for sizing a solar/wind/battery hybrid power system based on the artificial immune system. Sustain Energy Technol Assess 27:83–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seta.2018.03.002
Jia S, Chang J (2009a) Research on multi-agent decision-making model of wind-solar complementary power generation system. Int Conf on Intell Comp Tech Autom ICICTA 2009:7–10. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICICTA.2009.718
Jia S, Chang J (2009b) A multi-agent control method and realization in wind-solar hybrid power generation system. Int Conf on Energy Envir Tech ICEET 2009b: 507–510. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICEET.2009.128
Jiang D, Zhu W, Muthu B, Seetharam TG (2021) Importance of implementing smart renewable energy system using heuristic neural decision support system. Sustain Energy Technol Assessments 45:101185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seta.2021.101185
Kahatapitiya C, Jayasooriya VM, Muthukumaran S (2022) GIS-based weighted overlay model for wind and solar farm locating in Sri Lanka. Environ Sci Pollut Res 0:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11356-022-24595-0/FIGURES/7
Kassem Y, Othman AA (2022) Selection of most relevant input parameters for predicting photovoltaic output power using machine learning and quadratic models. Model Earth Syst Environ 8:4661–4686. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-022-01413-7
Khan KI, Nasir A, Saleem S (2021) Bibliometric analysis of post Covid-19 management strategies and policies in hospitality and tourism. Front Psychol 12:5182. https://doi.org/10.3389/FPSYG.2021.769760
Khan KI, Mata MN, Martins J, Nasir A, Dantas RM, Correia AB, Saghir US (2022a) Impediments of green finance adoption system: Linking economy and environment. Emerg Sci Jour 6:217–237. https://doi.org/10.28991/ESJ-2022-06-02-02
Khan KI, Nasir A, Rashid T (2022b) Green practices: a solution for environmental deregulation and the future of energy efficiency in the Post-COVID-19 era. Front Energy Res 10:458. https://doi.org/10.3389/FENRG.2022.878670/BIBTEX
Khare CJ, Verma HK, Khare V (2021) Optimal power generation and power flow control using artificial intelligence techniques. Renew Energy Sys Modell Optimiz Control 47:607–631. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-820004-9.00028-0
Khatib T, Mohamed A, Sopian K (2013) A review of photovoltaic systems size optimization techniques. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 22:454–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2013.02.023
Khosravi A, Koury RNN, Machado L, Pabon JJG (2018a) Prediction of hourly solar radiation in Abu Musa Island using machine learning algorithms. J Clean Prod 176:63–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.12.065
Khosravi A, Nunes RO, Assad MEH, Machado L (2018b) Comparison of artificial intelligence methods in estimation of daily global solar radiation. J Clean Prod 194:342–358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.05.147
Koc A, Turk S, Şahin G (2019) Multi-criteria of wind-solar site selection problem using a GIS-AHP-based approach with an application in Igdir Province/Turkey. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:32298–32310. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11356-019-06260-1/TABLES/10
Lian J, Zhang Y, Ma C, Yang Y, Chaima E (2019) A review on recent sizing methodologies of hybrid renewable energy systems. Energy Convers Manag 199:112027. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2019.112027
Nasir A, Shaukat K, Hameed I, Luo S, Mahboob T, Iqbal F (2020) A bibliometric analysis of Corona pandemic in social sciences: a review of influential aspects and conceptual structure. IEEE Access 8:133377–133402. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3008733
Nasir A, Shaukat K, Khan KI, Hameed IA, Alam TM, Luo S (2021a) Trends and directions of financial technology (Fintech) in society and environment: a bibliometric study. Appl Sci 11:10353. https://doi.org/10.3390/APP112110353
Nasir A, Shaukat K, Khan KI, Hameed IA, Alam TM, Luo S (2021b) What is core and what future holds for blockchain technologies and cryptocurrencies: a bibliometric analysis. IEEE Access 9:989–1004. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3046931
Oyekale J, Petrollese M, Tola V, Cau G (2020) Impacts of renewable energy resources on effectiveness of grid-integrated systems: succinct review of current challenges and potential solution strategies. Energies 13:4856. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13184856
Paliwal NK (2020) A day-ahead optimal scheduling operation of battery energy storage with constraints in hybrid power system. Procedia Comput Sci:167, 2140–2152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2020.03.263
Panagopoulos AA, Chalkiadakis G, Koutroulis E (2012) Predicting the power output of distributed renewable energy resources within a broad geographical region. In 20th European Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Including Prestigious Applications of Artificial Intelligence (PAIS-2012), pp 981–986. https://doi.org/10.3233/978-1-61499-098-7-981
Patel D, Patel S, Patel P, Shah M (2022) Solar radiation and solar energy estimation using ANN and Fuzzy logic concept: a comprehensive and systematic study. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:32428–32442. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11356-022-19185-Z/TABLES/4
Paterakis NG, Mocanu E, Gibescu M, Stappers B, Van Alst W (2017) Deep learning versus traditional machine learning methods for aggregated energy demand prediction. 2017 IEEE PES Innov Smart Grid Tech Conf Europ. ISGT-Europe 2017:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1109/ISGTEurope.2017.8260289
Queen HJ, Jayakumar J, Deepika TJ, Moses Babu KVSM, Thota SP (2021) Machine learning-based predictive techno-economic analysis of power system. IEEE Access 9:123504–123516. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3110774
Rangel-Martinez D, Nigam KDP, Ricardez-Sandoval LA (2021) Machine learning on sustainable energy: a review and outlook on renewable energy systems, catalysis, smart grid and energy storage. Chem Eng Res Des 174:414–441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2021.08.013
Saini VK, Mathur F, Gupta V, Kumar R (2020) Predictive analysis of traditional, deep learning and ensemble learning approach for short-term wind speed forecasting, 2020 IEEE International Conference on Computing, Power and Communication Technologies (GUCON), pp 783–788. https://doi.org/10.1109/GUCON48875.2020.9231081
Singh R, Memon SA, Shaikh R, Upadhyay DS (2022) A review of artificial intelligence applied for the solution of issues in the extensive adaption of solar and wind energy. Int J Ambient Energy 43:7419–7436. https://doi.org/10.1080/01430750.2022.2063384
Sinha S, Chandel SS (2015) Review of recent trends in optimization techniques for solar photovoltaic-wind based hybrid energy systems. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 50:755–769. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.05.040
Trivedi IN, Thesiya DK, Esmat A, Jangir P (2015) A multiple environment dispatch problem solution using ant colony optimization for micro-grids. In: 2015 IEEE International Conference on Power and Advanced Control. Engineering (ICPACE 2015), pp 109–115. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICPACE.2015.7274927
Tyralis H, Papacharalampous G (2021) Boosting algorithms in energy research: a systematic review. Neural Comput Appl 33:14101–14117. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-021-05995-8
Vyas S, Kumar R, Kavasseri R (2017) Data analytics and computational methods for anti-islanding of renewable energy based Distributed Generators in power grids. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 69:493–502. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2016.11.116
Wu C, Wang AC, Ding W, Guo H, Wang ZL (2019) Triboelectric nanogenerator: a foundation of the energy for the new era. Adv Energy Mater 9:1802906. https://doi.org/10.1002/aenm.201802906
Zafar SS, Fiaz M, Ikram A, Khan KI, Qamar UM (2021) Barriers involve in the energy efficiency in the manufacturing industries of Pakistan. Int J Energy Econ Policy 11:293–299. https://doi.org/10.32479/IJEEP.7599
Zahraee SM, KhalajiAssadi M, Saidur R (2016) Application of artificial intelligence methods for hybrid energy system optimization. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 66:617–630. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2016.08.028
Zeng J, Qiao W (2013) Short-term solar power prediction using a support vector machine. Renew Energy 52:118–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2012.10.009
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Both authors equally contributed to the manuscript. Further, both have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, K.I., Nasir, A. Application of artificial intelligence in solar and wind energy resources: a strategy to deal with environmental pollution. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 64845–64859 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-27038-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-27038-6