Abstract
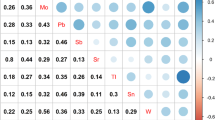
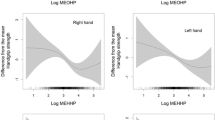
Metallic elements are ubiquitous in the natural environment and always collaborate to affect human health. The relationship of handgrip strength, a marker of functional ability or disability, with metal co-exposure remains vague. In this study, we aimed to investigate the effect of metal co-exposure on sex-specific handgrip strength. A total of 3594 participants (2296 men and 1298 women) aged 21 to 79 years recruited from Tongji Hospital were included in the present study. Urinary concentrations of 21 metals were measured by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer (ICP-MS). We used linear regression, restricted cubic spline (RCS) model, and weighted quantile sum (WQS) regression to evaluate the association of single metal as well as metal mixture with handgrip strength. After adjusting for important confounding factors, the results of linear regression showed that vanadium (V), zinc (Zn), arsenic (As), rubidium (Rb), cadmium (Cd), thallium (Tl), and uranium (U) were adversely associated with handgrip strength in men. The results of RCS showed a non-linear association between selenium (Se), silver (Ag), and nickel (Ni) with handgrip strength in women. The results of WQS regression revealed that metal co-exposure was inversely related to handgrip strength for men (β = -0.65, 95% CI: -0.98, -0.32). Cd was the critical metal in men (weighted 0.33). In conclusion, co-exposure to a higher level of metals is associated with lower handgrip strength, especially among men, and Cd may contribute most to the conjunct risk.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Adedara IA, Fabunmi AT, Ayenitaju FC, Atanda OE, Adebowale AA, Ajayi BO, Owoeye O, Rocha JBT, Farombi EO (2020) Neuroprotective mechanisms of selenium against arsenic-induced behavioral impairments in rats. Neurotoxicology 76:99–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuro.2019.10.009
Alegre-Martinez A, Martinez-Martinez MI, Rubio-Briones J, Cauli O (2022): Plasma Nickel Levels Correlate with Low Muscular Strength and Renal Function Parameters in Patients with Prostate Cancer. Diseases 10 https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases10030039
Anyanwu BO, Ezejiofor AN, Igweze ZN, Orisakwe OE (2018): Heavy Metal Mixture Exposure and Effects in Developing Nations: An Update. Toxics 6 https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics6040065
Azeez IA, Olopade F, Laperchia C, Andrioli A, Scambi I, Onwuka SK, Bentivoglio M, Olopade JO (2016) Regional Myelin and Axon Damage and Neuroinflammation in the Adult Mouse Brain After Long-Term Postnatal Vanadium Exposure. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 75:843–854. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnen/nlw058
Barber DS, Hancock SK, McNally AM, Hinckley J, Binder E, Zimmerman K, Ehrich MF, Jortner BS (2007) Neurological effects of acute uranium exposure with and without stress. Neurotoxicology 28:1110–1119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuro.2007.05.014
Barr DB, Wilder LC, Caudill SP, Gonzalez AJ, Needham LL, Pirkle JL (2005) Urinary creatinine concentrations in the U.S. population: implications for urinary biologic monitoring measurements. Environ Health Perspect 113:192–200. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.7337
Barrientos G, Alves J, Toro V, Robles MC, Munoz D, Maynar M (2020): Association between Trace Elements and Body Composition Parameters in Endurance Runners. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17 https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17186563
Bauer JA, Devick KL, Bobb JF, Coull BA, Bellinger D, Benedetti C, Cagna G, Fedrighi C, Guazzetti S, Oppini M, Placidi D, Webster TF, White RF, Yang Q, Zoni S, Wright RO, Smith DR, Lucchini RG, Claus Henn B (2020) Associations of a Metal Mixture Measured in Multiple Biomarkers with IQ: Evidence from Italian Adolescents Living near Ferroalloy Industry. Environ Health Perspect 128:97002. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp6803
Carrico C, Gennings C, Wheeler DC, Factor-Litvak P (2015) Characterization of Weighted Quantile Sum Regression for Highly Correlated Data in a Risk Analysis Setting. J Agric Biol Environ Stat 20:100–120. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13253-014-0180-3
Celis-Morales CA, Welsh P, Lyall DM, Steell L, Petermann F, Anderson J, Iliodromiti S, Sillars A, Graham N, Mackay DF, Pell JP, Gill JMR, Sattar N, Gray SR (2018): Associations of grip strength with cardiovascular, respiratory, and cancer outcomes and all cause mortality: prospective cohort study of half a million UK Biobank participants. BMJ 361, k1651. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.k1651
Chan J, Lu YC, Yao MM, Kosik RO (2022) Correlation between hand grip strength and regional muscle mass in older Asian adults: an observational study. BMC Geriatr 22:206. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12877-022-02898-8
Charles LE, Burchfiel CM, Fekedulegn D, Kashon ML, Ross GW, Sanderson WT, Petrovitch H (2006) Occupational and other risk factors for hand-grip strength: the Honolulu-Asia Aging Study. Occup Environ Med 63:820–827. https://doi.org/10.1136/oem.2006.027813
Chen CM, Chung MN, Chiu CY, Liu SH, Lan KC (2020): Inorganic Arsenic Exposure Decreases Muscle Mass and Enhances Denervation-Induced Muscle Atrophy in Mice. Molecules 25 https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25133057
Chidi-Ogbolu N, Baar K (2018) Effect of Estrogen on Musculoskeletal Performance and Injury Risk. Front Physiol 9:1834. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2018.01834
Clemens S, Ma JF (2016) Toxic Heavy Metal and Metalloid Accumulation in Crop Plants and Foods. Annu Rev Plant Biol 67:489–512. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-arplant-043015-112301
Derbre F, Gratas-Delamarche A, Gomez-Cabrera MC, Vina J (2014) Inactivity-induced oxidative stress: a central role in age-related sarcopenia? Eur J Sport Sci 14(Suppl 1):S98-108. https://doi.org/10.1080/17461391.2011.654268
Drake PL, Hazelwood KJ (2005) Exposure-related health effects of silver and silver compounds: a review. Ann Occup Hyg 49:575–585. https://doi.org/10.1093/annhyg/mei019
Gade M, Comfort N, Re DB (2021): Sex-specific neurotoxic effects of heavy metal pollutants: Epidemiological, experimental evidence and candidate mechanisms. Environ Res 201, 111558. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.111558
Garcia-Esquinas E, Rodriguez-Artalejo F (2017) Environmental Pollutants, Limitations in Physical Functioning, and Frailty in Older Adults. Curr Environ Health Rep 4:12–20. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40572-017-0128-1
Garcia-Esquinas E, Carrasco-Rios M, Navas-Acien A, Ortola R, Rodriguez-Artalejo F (2020): Cadmium exposure is associated with reduced grip strength in US adults. Environ Res 180, 108819. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2019.108819
Garcia-Esquinas E, Carrasco-Rios M, Ortola R, Sotos Prieto M, Perez-Gomez B, Gutierrez-Gonzalez E, Banegas JR, Queipo R, Olmedo P, Gil F, Tellez-Plaza M, Navas-Acien A, Pastor-Barriuso R, Rodriguez-Artalejo F (2021a): Selenium and impaired physical function in US and Spanish older adults. Redox Biol 38, 101819. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2020.101819
Garcia-Esquinas E, Tellez-Plaza M, Pastor-Barriuso R, Ortola R, Olmedo P, Gil F, Lopez-Garcia E, Navas-Acien A, Rodriguez-Artalejo F (2021b): Blood cadmium and physical function limitations in older adults. Environ Pollut 276, 116748. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.116748
Gbemavo MCJ, Bouchard MF (2021): Concentrations of Lead, Mercury, Selenium, and Manganese in Blood and Hand Grip Strength among Adults Living in the United States (NHANES 2011–2014). Toxics 9 https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics9080189
Genchi G, Carocci A, Lauria G, Sinicropi MS, Catalano A (2020): Nickel: Human Health and Environmental Toxicology. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17 https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17030679
Hariharan S, Dharmaraj S (2020) Selenium and selenoproteins: it’s role in regulation of inflammation. Inflammopharmacology 28:667–695. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-020-00690-x
Heath JC, Banna KM, Reed MN, Pesek EF, Cole N, Li J, Newland MC (2010) Dietary selenium protects against selected signs of aging and methylmercury exposure. Neurotoxicology 31:169–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuro.2010.01.003
Ikeda K, Horie-Inoue K, Inoue S (2019): Functions of estrogen and estrogen receptor signaling on skeletal muscle. The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 191 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsbmb.2019.105375
Javed AA, Mayhew AJ, Shea AK, Raina P (2019): Association Between Hormone Therapy and Muscle Mass in Postmenopausal Women: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Netw Open 2, e1910154. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.10154
Kalita J, Kumar V, Misra UK, Bora HK (2020) Movement Disorder in Copper Toxicity Rat Model: Role of Inflammation and Apoptosis in the Corpus Striatum. Neurotox Res 37:904–912. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-019-00140-9
Khalil N, Faulkner KA, Greenspan SL, Cauley JA, Osteoporotic Fractures in Men Research G (2014): Associations between bone mineral density, grip strength, and lead body burden in older men. J Am Geriatr Soc 62, 141-6https://doi.org/10.1111/jgs.12603
Kim J, Garcia-Esquinas E, Navas-Acien A, Choi YH (2018) Blood and urine cadmium concentrations and walking speed in middle-aged and older U.S. adults. Environ Pollut 232:97–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.09.022
Kim KN, Lee MR, Choi YH, Lee BE, Hong YC (2016) Associations of Blood Cadmium Levels With Depression and Lower Handgrip Strength in a Community-Dwelling Elderly Population: A Repeated-Measures Panel Study. The journals of gerontology. Series a, Biol Sci Med Sci 71:1525–1530. https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/glw119
Krishna S, Dodd CA, Hekmatyar SK, Filipov NM (2014) Brain deposition and neurotoxicity of manganese in adult mice exposed via the drinking water. Arch Toxicol 88:47–64. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-013-1088-3
Lian D, Chen MM, Wu H, Deng S, Hu X (2022): The Role of Oxidative Stress in Skeletal Muscle Myogenesis and Muscle Disease. Antioxidants (Basel) 11 https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11040755
Liu W, Chen R, Song C, Wang C, Chen G, Hao J, Wang Y, Yu C (2021): A Prospective Study of Grip Strength Trajectories and Incident Cardiovascular Disease. Front Cardiovasc Med 8, 705831. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcvm.2021.705831
Meng SJ, Yu LJ (2010) Oxidative stress, molecular inflammation and sarcopenia. Int J Mol Sci 11:1509–1526. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms11041509
Mustapha O, Oke B, Offen N, Siren AL, Olopade J (2014) Neurobehavioral and cytotoxic effects of vanadium during oligodendrocyte maturation: a protective role for erythropoietin. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 38:98–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2014.05.001
Ng SW, Norton EC, Popkin BM (2009) Why have physical activity levels declined among Chinese adults? Findings from the 1991–2006 China Health and Nutrition Surveys. Soc Sci Med 68:1305–1314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socscimed.2009.01.035
Nishikawa H, Shiraki M, Hiramatsu A, Moriya K, Hino K, Nishiguchi S (2016) Japan Society of Hepatology guidelines for sarcopenia in liver disease (1st edition): Recommendation from the working group for creation of sarcopenia assessment criteria. Hepatol Res 46:951–963. https://doi.org/10.1111/hepr.12774
Orndahl G, Rindby A, Selin E (1982) Myotonic dystrophy and selenium. Acta Med Scand 211:493–499. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0954-6820.1982.tb01988.x
Papa V, Wannenes F, Crescioli C, Caporossi D, Lenzi A, Migliaccio S, Di Luigi L (2014) The environmental pollutant cadmium induces homeostasis alteration in muscle cells in vitro. J Endocrinol Invest 37:1073–1080. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-014-0145-y
Perri G, Mendonca N, Jagger C, Walsh J, Eastell R, Mathers JC, Hill TR (2020): Dietary Selenium Intakes and Musculoskeletal Function in Very Old Adults: Analysis of the Newcastle 85+ Study. Nutrients 12 https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12072068
Rantanen T, Guralnik JM, Foley D, Masaki K, Leveille S, Curb JD, White L (1999) Midlife hand grip strength as a predictor of old age disability. JAMA 281:558–560. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.281.6.558
Rantanen T, Harris T, Leveille SG, Visser M, Foley D, Masaki K, Guralnik JM (2000) Muscle strength and body mass index as long-term predictors of mortality in initially healthy men. The journals of gerontology. Series a, Biol Sci Medi Sci 55:M168–M173. https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/55.3.m168
Rederstorff M, Krol A, Lescure A (2006) Understanding the importance of selenium and selenoproteins in muscle function. Cell Mol Life Sci 63:52–59. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-005-5313-y
Renu K, Chakraborty R, Myakala H, Koti R, Famurewa AC, Madhyastha H, Vellingiri B, George A, Valsala Gopalakrishnan A (2021): Molecular mechanism of heavy metals (Lead, Chromium, Arsenic, Mercury, Nickel and Cadmium) - induced hepatotoxicity - A review. Chemosphere 271, 129735. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.129735
Siparsky PN, Kirkendall DT, Garrett WE (2013) Muscle Changes in Aging. Sports Health: A Multidiscip Appr 6:36–40. https://doi.org/10.1177/1941738113502296
Stenholm S, Tiainen K, Rantanen T, Sainio P, Heliovaara M, Impivaara O, Koskinen S (2012) Long-term determinants of muscle strength decline: prospective evidence from the 22-year mini-Finland follow-up survey. J Am Geriatr Soc 60:77–85. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1532-5415.2011.03779.x
Tchounwou PB, Yedjou CG, Patlolla AK, Sutton DJ (2012) Heavy metal toxicity and the environment. Exp Suppl 101:133–164. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-7643-8340-4_6
Tiidus PM (2011) Benefits of Estrogen Replacement for Skeletal Muscle Mass and Function in Post-Menopausal Females: Evidence from Human and Animal Studies. Eur J Med 43:109–114. https://doi.org/10.5152/eajm.2011.24
Walsh JS, Jacques RM, Schomburg L, Hill TR, Mathers JC, Williams GR, Eastell R (2021) Effect of selenium supplementation on musculoskeletal health in older women: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. The Lancet Healthy Longevity 2:e212–e221. https://doi.org/10.1016/s2666-7568(21)00051-9
Wu M, Shu Y, Wang Y (2022) Exposure to mixture of heavy metals and muscle strength in children and adolescents: a population-based study. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19916-2
Wu X, Cobbina SJ, Mao G, Xu H, Zhang Z, Yang L (2016) A review of toxicity and mechanisms of individual and mixtures of heavy metals in the environment. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 23:8244–8259. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6333-x
Yadav RS, Sankhwar ML, Shukla RK, Chandra R, Pant AB, Islam F, Khanna VK (2009) Attenuation of arsenic neurotoxicity by curcumin in rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 240:367–376. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2009.07.017
Yano C, Marcondes M (2005) Cadmium chloride-induced oxidative stress in skeletal muscle cells in vitro. Free Radical Biol Med 39:1378–1384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2005.07.001
Zoroddu MA, Aaseth J, Crisponi G, Medici S, Peana M, Nurchi VM (2019) The essential metals for humans: a brief overview. J Inorg Biochem 195:120–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2019.03.013
Acknowledgements
We thank all the study participants and the staffs of the Tongji Hospital.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82073660, 82003479) and China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2019M662646, 2020T130220).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xiya Qin: formal analysis, writing- original draft, writing- review & editing. Gaojie Fan: data curation, writing- review & editing. Qing Liu: investigation, data curation. Mingyang Wu: conceptualization, data curation. Jianing Bi: investigation, data curation. Qing Fang: investigation, data curation. Zhengce Wan: resource. Yongman Lv: resource. Lulu Song: methodology, funding acquisition, supervision. Youjie Wang: funding acquisition, project administration, supervision, writing- review & editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethics approval
The study protocol was approved by the Ethics Review Board of Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology.
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Lotfi Aleya
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Qin, X., Song, L., Fan, G. et al. Sex-specific associations of single metal and metal mixture with handgrip strength: a cross-sectional study among Chinese adults. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 66585–66597 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-26926-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-26926-1