Abstract
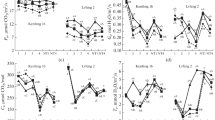
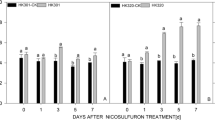
Starch is an important reserve of sugar, and starch-sugar conversion in plants plays an important role in the response of plants to various abiotic stresses. Nicosulfuron is a post-emergence herbicide commonly applied to maize fields. However, it is unclear how sucrose and starch in sweet corn are converted to accommodate nicosulfuron stress. Field and pot experiments were conducted to study the effects of nicosulfuron on the sugar metabolism enzymes, starch metabolism enzymes, non-enzyme substances, and expression of key enzyme genes in leaves and roots of sweet maize seedlings. Accordingly, this research compared the responses of the sister lines HK301 and HK320, which are nicosulfuron tolerant and sensitive, respectively. Under nicosulfuron stress, compared with HK301 seedlings, the accumulation of stem and root dry matter of HK320 seedlings was significantly reduced, resulting in a lower root-to-shoot ratio. Compared with HK320 seedlings, nicosulfuron stress significantly increased the sucrose, soluble sugar, and starch contents in HK301 leaves and roots. This may be related to the enhanced carbohydrate metabolism under nicosulfuron stress, including significant changes in sugar metabolism enzyme activity and the levels of SPS and SuSys expression. Further, under nicosulfuron stress, sucrose transporter genes (SUC 1, SUC 2, SWEET 13a, and SWEET 13b) in the leaves and roots of HK301 seedlings were significantly upregulated. Our results emphasize that changes in sugar distribution, metabolism, and transport can improve the adaptability of sweet maize to nicosulfuron stress.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Supporting data are available as electronic supplementary material. Additional information would be provided upon request.
References
Ayre BG (2011) Membrane-transport systems for sucrose in relation to whole-plant carbon partitioning. Mol Plant 4:377–394. https://doi.org/10.1093/mp/ssr014
Chen S, Hajirezaei M, Bornke F (2005) Differential expression of sucrose-phosphate synthase isoenzymes in tobacco reflects their functional specialization during dark governed starch mobilization in source leaves. Plant Physiol 139:1163–1174. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.105.069468
Chen LQ, Qu XQ, Hou BH, Sosso D, Osorio S, Fernie AR, Frommer WB (2012b) Sucrose efflux mediated by SWEET proteins as a key step for phloem transport. Science 335:207–211. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1213351
Chen T, Pei H, Zhang Y, Qian Q (2012a) Seasonal changes in non-structural carbohydrates and sucrose metabolism enzymes in two Sabina species. Acta Physiol Plant 34:173–180. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-011-0815-8
Choudhury B, Mitra S, Biswas AK (2010) Regulation of sugar metabolism in rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings under arsenate toxicity and its improvement by phosphate. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 16:59–68. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-010-0008-8
Du YL, Zhao Q, Chen LR, Yao XD, Zhang W, Zhang B, Xie FT (2020) Effect of drought stress on sugar metabolism in leaves and roots of soybean seedlings. Plant Physiol Biochem 146:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2019.11.003
Dong SY, Becklesa DM (2019) Dynamic changes in the starch-sugar interconversion with in plant source and sink tissues promote a better abiotic stress response. J Plant Physiol 234–235:80–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2019.01.007
Durand M, Porcheron B, Hennion N, Maurousset L, Lemoine R, Pourtau N (2016) Water deficit enhances C export to the roots in Arabidopsis thaliana plants with contribution of sucrose transporters in both shoot and roots. Plant Physiol 170:1460–1479. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.15.01926
Erice G, Louahlia S, Irigoyen JJ, Sanchez-Diaz M, Avice JC (2010) Biomass partitioning, morphology and water status of four alfalfa genotypes submitted to progressive drought and subsequent recovery. J Plant Physiol 167(2):114–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2009.07.016
Ferguson JE, Rhodes AM, Dickinson DB (1990) The genetic of sugary enhancer (se), an independent modifier of sweet corn (su). Heredity 69(6):377–380. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.jhered.a108976
Gottwald JR, Krysan PJ, Young JC, Evert RF, Sussman MR (2000) Genetic evidence for the in plant a role of phloem-specific plasma membrane sucrose transporters. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:13979–13984. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.250473797
Jha AB, Dubey RS (2004) Carbohydrate metabolism in growing rice seedlings under arsenic toxicity. J Plant Physiol 161:867–872. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2004.01.004
Jha AB, Dubey RS (2005) Effect of arsenic on behaviour of enzymes of sugar metabolism in germinating rice seeds. Acta Physiol Plant 27:341–347. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-005-0010-x
Higuchi K, Kanai M, Tsuchiya M, Ishii H, Shibuya N, Fujita N, Nakamura Y, Suzui N, Fujimaki S, Miwa E (2015) Common reed accumulates starch in its stem by metabolic adaptation under Cd stress conditions. Front Plant Sci 6:138. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2015.00138
Kaplan F, Sung DY, Guy CL (2006) Roles of β-amylase and starch breakdown during temperatures stress. Physiol Plant 126:120–128. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.2006.00604.x
Kuai J, Liu Z, Wang Y, Meng Y, Chen B, Zhao W, Zhou Z, Oosterhuis DM (2014) Waterlogging during flowering and boll forming stages affects sucrose metabolism in the leaves subtending the cotton boll and its relationship with boll weight. Plant Sci 223:79–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2014.03.010
Hummel I, Pantin F, Sulpice R, Piques M, Rolland G, Dauzat M, Christophe A, Pervent M, Bouteillé M, Stitt M (2010) Arabidopsis plants acclimate to water deficit at low cost through changes of carbon usage: an integrated perspective using growth, metabolite, enzyme, and gene expression analysis. Plant Physiol 154:357–372. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.110.157008
Hu MY, Shi ZG, Xu P, Li H, Zhang ZB (2015) Wheat acclimate to water deficit by modifying carbohydrates metabolism, water use efficiency, and growth. Braz J Bot 38:505–515. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40415-015-0169-3
Lemoine R, La Camera S, Atanassova R, Dédaldéchamp F, Allario T, Pourtau N, Bonnemain JL, Laloi M, Coutos-Thévenot P, Maurousset L (2013) Source-to-sink transport of sugar and regulation by environmental factors. Front Plant Sci 4:272. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2013.00272
Li X, Jiang H, Liu F, Cai J, Dai T, Cao W, Jiang D (2013) Induction of chilling tolerance in wheat during germination by pre-soaking seed with nitric oxide and gibberellin. Plant Growth Regul 71:31–40. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-013-9805-8
Li X, Riaz M, Song B, Liu H (2022) Exogenous salicylic acid alleviates fomesafen toxicity by improving photosynthetic characteristics and antioxidant defense system in sugar beet. Ecotoxico Environ Safety 238:113587. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2022.113628
Liu HS, Li FM, Xu H (2004) Deficiency of water can enhance root respiration rate of drought-sensitive but not drought-tolerant spring wheat. Agric Water Manag 64:41–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-3774(03)00143-4
Liu J, Ma Y, Lv F, Chen J, Zhou Z, Wang Y, Abudurezike A, Oosterhuis DM (2013) Changes of sucrose metabolism in leaf subtending to cotton boll under cool temperature due to late planting. Field Crop Res 144:200–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2013.02.003
Liu XM, Bi B, Xu X, Li BH, Tian SG, Wang JP, Zhang H, Wang GQ, Han YJ, McElroy JS (2019) Rapid identification of a candidate nicosulfuron sensitivity gene (Nss) in maize (Zea mays L.) via combining bulked segregant analysis and RNA-seq. Theor Appl Genet 132:1351–1361. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-019-03282-8
Muller B, Pantin F, Génard M, Turc O, Freixes S, Piques M, Gibon Y (2011) Water deficits uncouple growth from photosynthesis, increase C content, and modify the relationships between C and growth in sink organs. J Exp Bot 62:1715–1729. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erq438
Robinson DK, Monks DW, Burton JD (1996) Safening influence of LAB 145 138 on nicosulfuron, terbufos, and bentazon interactions in sweet corn. Weed Sci 44:339–344
Ruan YL, Jin Y, Yang YJ, Li GJ, Boyer JS (2010) Sugar input, metabolism, and signaling mediated by invertase: roles in development, yield potential, and response to drought and heat. Mol Plant 3:942–955. https://doi.org/10.1093/mp/ssq044
Ruan YL (2012) Signaling role of sucrose metabolism in development. Mol Plant 5:763–765. https://doi.org/10.1093/mp/sss046
Samanta S, Singh A, Banerjee A, Roychoudhury A (2020) Exogenous supplementation of melatonin alters representative organic acids and enzymes of respiratory cycle as well as sugar metabolism during arsenic stress in two contrasting indica rice cultivars. J Biotechnology 324:220–232
Sauer N (2007) Molecular physiology of higher plant sucrose transporters. FEBS Lett 581(12):2309–2317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2007.03.048
Scofield GN, Ruuska SA, Aoki N, Lewis DC, Tabe LM, Jenkins CLD (2009) Starch storage in the stems of wheat plants: localization and temporal changes. Ann Bot 103:859–868. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcp010
Smith AM, Stitt M (2007) Coordination of carbon supply and plant growth. Plant Cell Environ 30:1126–1149. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.2007.01708.x
Sree KS, Keresztes A, Mueller-Roeber B, Brandt R, Eberius M, Fischer W, Appenroth KJ (2015) Phytotoxicity of cobalt ions on the duckweed Lemna minor-morphology, ion uptake, and starch accumulation. Chemosphere 131:149–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.03.008
Stein O, Granot D (2019) An overview of sucrose synthases in plants. Front Plant Sci 10:95. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.00095
Thitisaksakul M, Arias MC, Dong SY, Beckles DM (2017) Overexpression of GSK3-like Kinase 5 (OsGSK5) in rice (Oryza sativa) enhances salinity tolerance in part via preferential carbon allocation to root starch. Funct Plant Biol 44(7):705–719. https://doi.org/10.1071/FP16424
Verma AK, Upadhyay SK, Verma PC, Solomon S, Singh SB (2010) Functional analysis of sucrose phosphate synthase (SPS) and sucrose synthase (SS) in sugarcane (Saccharum) cultivars. Plant Biol 13:325–332. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1438-8677.2010.00379.x
Wang J, Zhong XM, Lv XL, Shi ZS, Li FH (2018a) Photosynthesis and physiology responses of paired near-isogenic lines in waxy maize (Zea mays L.) to nicosulfuron. Photosynthetica 56:1059–1068. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11099-018-0816-6
Wang J, Zhong XM, Li FH, Shi ZS (2018b) Effects of nicosulfuron on growth, oxidative damage, and ascobate-glutathione pathway in paired nearly isogenic lines of waxy maize (Zea mays L.). Pestic Biochem Phys 145:108–117. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2105-0
Wang J, Gao H, Guo ZQ, Meng YY, Yang M, Li XL, Yang Q (2021) Adaptation responses in C4 photosynthesis of sweet maize (Zea mays L.) exposed to nicosulfuron. Ecotoxicol Environmen Saf 214:112096. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112096
Wang L, Riaz M, Song B, Song X, Huang W, Bai X, Zhao X (2022) Study on phytotoxicity evaluation and physiological properties of nicosulfuron on sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.). Front. Plant Sci 13:998867. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2022.998867
Williams BJ, Harvey RG (2000) Effect of nicosulfuron timing onwild-proso millet (Panicum miliaceum) control in sweet corn (Zea mays L.). Weed Technol 14(2):377–382. https://doi.org/10.1614/0890-037X(2000)014[0377:EONTOW]2.0.CO;2
Wright T, Bascomb N, Sturner S, Penner D (2017) Biochemical mechanism and molecular basis for ALS-inhibiting herbicide resistance in sugarbeet (Beta vulgaris) somatic cell selections. Weed Sci 1:13–23. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0043174500090111
Wu ZX, Xu NW, Yang M, Li XL, Han JL, Lin XH, Yang Q, Lv GH (2022) Responses of photosynthesis, antioxidant enzymes, and related gene expression to nicosulfuron stress in sweet maize (Zea mays L.). Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(25):37248–37265. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-18641-0
Xu W, Cui K, Xu A, Nie L, Huang J, Peng S (2015) Drought stress condition increases root to shoot ratio via alteration of carbohydrate partitioning and enzymatic activity in rice seedlings. Acta Physiol Plant 37:9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-014-1760-0
Zhao H, Su T, Huo L, Wei H, Jiang Y, Xu L, Ma F (2015) Unveiling the mechanism of melatonin impacts on maize seedling growth: sugar metabolism as a case. J Pineal Res 59:255–266. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12258
Zhang J, Zeng B, Mao Y, Kong X, Wang X, Yang Y, Zhang J, Xu J, Rengel Z, Chen Q (2017) Melatonin alleviates aluminium toxicity through modulating antioxidative enzymes and enhancing organic acid anion exudation in soybean. Funct Plant Biol 44:961. https://doi.org/10.1071/FP17003
Zhou X, Zhang Y, Deng J, Jiang Z, He Z, Zou Z (2019) Effects of melatonin on the sugar metabolism and antioxidative response to excess nitrate stress in lettuce seedlings. IOP Conf Ser: Earth Environ Sci 358:02208. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/358/2/022085
Funding
This work was supported by Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province of China (C2022407026 and C2019407095), Key Research and Development Plan of Hebei Province (22326501D), Doctoral Initiation Fund of Hebei Normal University of Science and Technology (2022YB011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jian Wang: investigation, methodology, data curation, funding acquisition, writing—original draft. Qing Yang: data curation, formal analysis. Jinling Han: conceptualization, validation, writing—review and editing. Zidian He: conceptualization, investigation, funding acquisition. Min Yang: writing—review and editing. Xiuping Wang: investigation, methodology, writing—review and editing. Xiaohu Lin: conceptualization, methodology, writing—review and editing, supervision. All the authors agree that the description of the individual contributions presented above is accurate and appropriate.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This work is original and has not been published elsewhere in any form or language. The manuscript has been submitted to this journal solely for consideration
Consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publish
Not applicable
Competing interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Gangrong Shi
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Yang, Q., Han, J. et al. Effect of nicosulfuron on dynamic changes in the starch-sugar interconversion in sweet maize (Zea mays L.). Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 59606–59620 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-26766-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-26766-z