Abstract
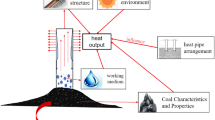
Spontaneous combustion gangue hill has attracted great attention due to serious environmental pollution and terrible geological disasters. However, the rich thermal resources inside are often ignored. In order to control the spontaneous combustion of gangue hill and utilize the internal waste heat resources, this project studied the combined treatment effect of 821 gravity heat pipes, laid 47 sets of temperature monitoring devices, evaluated the storage of waste heat resources, and proposed different waste heat utilization methods. The results show that (1) the positions of spontaneous combustion are all located on the windward slope. The highest temperature is in the range of 6 ~ 12 m underground, exceeding 700 ℃. (2) The single-tube experiment of gravity heat pipe shows that the effective temperature control radius is 2 m. The cooling effect is obvious in the range of 3 ~ 5 m underground. However, the temperature rises at the depth of 1 m underground. (3) After 90 days of treatment of the gravity heat pipe group, the temperature at the depths of 3 m, 4 m, 5 m, and 6 m in the high-temperature zone dropped by 56 ℃, 66 ℃, 63 ℃, and 42 ℃, respectively. The maximum temperature drop exceeds 160 ℃. The average temperature drop in the middle- and low-temperature areas is between 9 and 21 °C. (4) The concentration of harmful gases (CO, SO2, and H2S) decreases by more than 90%. The hazard level is greatly reduced. (5) The amount of waste heat resources contained within 10 m of the spontaneous combustion gangue hill is 7.83E13J. Waste heat resources can be used for indoor heating and greenhouse cultivation. And, under the temperature difference of 50 °C, 100 °C, and 150 °C, the electric energy generated by the heat through the thermoelectric conversion device in the high-temperature zone of the gangue hill is 4056.8 kWh, 7468.2 kWh, and 10,603 kWh, respectively.




















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Arat H, Arslan O, Ercetin U, Akbulut A (2021) A comprehensive numerical investigation of unsteady-state two-phase flow in gravity assisted heat pipe enclosure. Thermal Science and Engineering Progress 25:100993
Brown CS (2022) Regional geothermal resource assessment of hot dry rocks in Northern England using 3D geological and thermal models. Geothermics 105:102503
Carlson GA, Granoff B (1991) Modeling of coal structure by using computer-aided molecular design. Coal Science II. ACS Symposium Series, Washington, pp 159–170
Chaudhry HN, Hughes BR, Ghani SA (2012) A review of heat pipe systems for heat recovery and renewable energy applications. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 16:2249–2259
Deng J, Zhou F, Shi B, Torero JL, Qi H, Liu P, Ge S, Wang Z, Chen C (2020) Waste heat recovery, utilization and evaluation of coalfield fire applying heat pipe combined thermoelectric generator in Xinjiang, China. Energy 207:118303
Deng J, Ge S, Qi H, Zhou F, Shi B (2021) Underground coal fire emission of spontaneous combustion, Sandaoba coalfield in Xinjiang, China: investigation and analysis. Sci Total Environ 777:146080
Fu L, Wen D, Feng Q, Zhang S, Ma X, Zhang L, Shao W (2022) Methods for geothermal resource assessment of hot dry rock: A case study in the Gonghe Basin, China. Energy Explor Exploit 40:1268–1286
Huang W, Cen J, Chen J, Cao W, Li Z, Li F, Jiang F (2022a) Heat extraction from hot dry rock by super-long gravity heat pipe: A field test. Energy 247:123492
Huang W, Chen J, Cen J, Cao W, Li Z, Li F, Jiang F (2022b) Heat extraction from hot dry rock by super-long gravity heat pipe: Effect of key parameters. Energy 248:123527
Huang Z, Le T, Zhang Y, Gao Y, Li J, Li Z, Ma Z (2019) Development and performance study of a novel physicochemical composite inhibitor for the prevention of coal gangue spontaneous combustion. Fire Mater 44:76–89
Jang J-C, Chi R-G, Rhi S-H, Lee K-B, Hwang H-C, Lee J-S, Lee W-H (2015) Heat Pipe-assisted thermoelectric power generation technology for waste heat recovery. J Electron Mater 44:2039–2047
Jodeiri Shokri B, Doulati Ardejani F, Ramazi H, Moradzadeh A (2016) Predicting pyrite oxidation and multi-component reactive transport processes from an abandoned coal waste pile by comparing 2D numerical modeling and 3D geo-electrical inversion. Int J Coal Geol 164:13–24
Jouhara H, Chauhan A, Nannou T, Almahmoud S, Delpech B, Wrobel LC (2017) Heat pipe based systems - advances and applications. Energy 128:729–754
Li A, Chen C, Chen J, Lei P, Zhang Y (2021a) Experimental investigation of temperature distribution and spontaneous combustion tendency of coal gangue stockpiles in storage. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 28:34489–34500
Li A, Lei P, Chen C, Xu T (2021b) A simplified model for SO2 generation during spontaneous combustion of coal gangue. Energy Eng 118:1469–1482
Li B, Deng J, Xiao Y, Zhai X, Shu C-M, Gao W (2018) Heat transfer capacity of heat pipes: an application in coalfield wildfire in China. Heat Mass Transf 54:1755–1766
Li B, Liu G, Gao W, Cong H-Y, Bi M-S, Ma L, Deng J, Shu C-M (2020a) Study of combustion behaviour and kinetics modelling of Chinese Gongwusu coal gangue: model-fitting and model-free approaches. Fuel 268:117284
Li B, Wang JH, Bi MS, Gao W, Shu CM (2020b) Experimental study of thermophysical properties of coal gangue at initial stage of spontaneous combustion. J Hazard Mater 400:123251
Li J, Wang J (2019) Comprehensive utilization and environmental risks of coal gangue: a review. J Clean Prod 239:117946
Liu Z-h, Zheng B-c, Wang Q, Li S-S (2015) Study on the thermal storage performance of a gravity-assisted heat-pipe thermal storage unit with granular high-temperature phase-change materials. Energy 81:754–765
Naghavi MS, Ong KS, Badruddin IA, Mehrali M, Metselaar HSC (2017) Thermal performance of a compact design heat pipe solar collector with latent heat storage in charging/discharging modes. Energy 127:101–115
Querol X, Izquierdo M, Monfort E, Alvarez E, Font O, Moreno T, Alastuey A, Zhuang X, Lu W, Wang Y (2008) Environmental characterization of burnt coal gangue banks at Yangquan, Shanxi Province, China. Int J Coal Geol 75:93–104
Robertson WJ, Kinnunen PH-M, Plumb JJ, Franzmann PD, Puhakka JA, Gibson JAE, Nichols PD (1999) Moderately thermophilic iron oxidising bacteria isolated from a pyritic coal deposit showing spontaneous combustion. Miner Eng 15:815–822
Su H, Zhou F, Qi H, Li J (2017) Design for thermoelectric power generation using subsurface coal fires. Energy 140:929–940
Su H, Qi H, Liu P, Li J (2018) Experimental investigation on heat extraction using a two-phase closed thermosyphon for thermoelectric power generation. Energy Sour Part A: Recovery Util Environ Effects 40:1485–1490
Taraba B, Michalec Z, Michalcová V, Blejchař T, Bojko M, Kozubková M (2014) CFD simulations of the effect of wind on the spontaneous heating of coal stockpiles. Fuel 118:107–112
Wang B, Liu X, Zhang J, Cheng F (2018) Pyrolysis behavior of corncob and coal gangue with modified medical stone and HZSM-5 based additives. Fuel 211:816–826
Wang C-P, Bai Z-J, Xiao Y, Deng J, Shu C-M (2020a) Effects of FeS2 on the process of coal spontaneous combustion at low temperatures. Process Saf Environ Prot 142:165–173
Wang C-P, Zhao X-Y, Bai Z-J, Deng J, Shu C-M, Zhang M (2021a) Comprehensive index evaluation of the spontaneous combustion capability of different ranks of coal. Fuel 291:120087
Wang H, Tan B, Zhang X (2020b) Research on the technology of detection and risk assessment of fire areas in gangue hills. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 27:38776–38787
Wang H, Fang X, Du F, Tan B, Zhang L, Li Y, Xu C (2021b) Three-dimensional distribution and oxidation degree analysis of coal gangue dump fire area: A case study. Sci Total Environ 772:145606
Wang K, Tang H, Wang F, Miao Y, Liu D (2019) Research on complex air leakage method to prevent coal spontaneous combustion in longwall goaf. PLoS ONE 14:e0213101
Wu Y, Yu X, Hu S, Shao H, Liao Q, Fan Y (2019) Experimental study of the effects of stacking modes on the spontaneous combustion of coal gangue. Process Saf Environ Prot 123:39–47
Xiao Y, Zhong K-Q, Tian J-Y, Yin L, Tian Y, Shu C-M (2021) Thermal extraction from a low-temperature stage of coal pile spontaneous combustion by two-phase closed thermosyphon. J Therm Anal Calorim 144:587–597
Yang N, Zhang Y, Niu J (2021) Temperature field distribution and deep temperature fitting of spontaneous gangue hill in Yinying Coal Mine. Mining Safety & Environmental Protection 48(04):3–27
Yu F, Qi J, Zhang M, Lai Y, Yao X, Liu Y, Wu G (2016) Cooling performance of two-phase closed thermosyphons installed at a highway embankment in permafrost regions. Appl Therm Eng 98:220–227
Zhang Y-Y, Guo Y-X, Cheng F-Q, Yan K-Z, Cao Y (2015) Investigation of combustion characteristics and kinetics of coal gangue with different feedstock properties by thermogravimetric analysis. Thermochim Acta 614:137–148.
Zhai X, Wu S, Wang K, Drebenstedt C, Zhao J (2017) Environment influences and extinguish technology of spontaneous combustion of coal gangue heap of Baijigou coal mine in China. Energy Procedia 136:66–72
Zhang J, Liang Y, Ren T, Wang Z, Wang G (2016) Transient CFD modelling of low-temperature spontaneous heating behaviour in multiple coal stockpiles with wind forced convection. Fuel Process Technol 149:55–74
Funding
This research was funded by Shanxi Basic Research Program Project (202203021211127); No.1 Institute of Geology and Mineral resources of Shandong Province (2022DY09).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xueyu Zhou: Investigation, Writing–original draft, data analysis, Writing–review & editing, Writing–Revised draft. Liangliang Guo: Methodology, Investigation, Writing–original draft, data analysis, Investigation, Funding acquisition, Writing–Revised draft. Yongbo Zhang: Supervision, Conceptualization, Investigation, Resources, Writing–original draft, Writing–review & editing. Ke Chang: Investigation, Writing–original draft, Writing–review & editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This research was approved by Institute of Geology and Mineral resources of Shandong Province.
Consent to participate
Entrusted by the governance of Yangquan Coal Industry Co., Ltd., we have carried out research on spontaneous combustion governance and waste heat utilization of gangue mountains.
Consent to publish
All co-authors (Xueyu Zhou, Liangliang Guo, Yongbo Zhang, Ke Chang) have agreed to publish this paper.
Competing Interest
The authors declare no known competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Shimin Liu
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, X., Guo, L., Zhang, Y. et al. Ignition control and waste heat assessment of spontaneous combustion gangue hill by gravity heat pipe group: a case study in Shanxi Province, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 59262–59281 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-26713-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-26713-y