Abstract
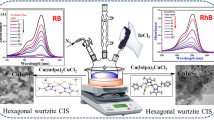
Colloidal route synthesis of quaternary compound CZTS (Cu2ZnSnS4) has been anticipated with an inimitable combination of coordinating ligands and solvents using the hot injection technique. CZTS is recognized as one of the worthiest materials for photo-voltaic/catalytic applications due to its exclusive properties (viz., non-toxic, economical, direct bandgap, high absorbance coefficient, etc.). This paper demonstrates the formation of crystalline, single-phased, monodispersed, and electrically passivated CZTS nanoparticles using a distinctive combination of ligands viz. oleic acid (OA)-trioctylphosphine (TOP) and butylamine (BA)-trioctylphosphine (TOP). Detailed optical, structural, and electrochemical studies were done for all CZTS nanoparticles, and the most efficient composition was found using ligands butylamine and TOP. CZTS nanocrystals were rendered hydrophilic via surface-ligand engineering, which was used for photocatalysis studies of organic pollutants. Malachite green (MG) and rhodamine 6G (Rh) for water remediation have great commercial prospects. The unique selling proposition of this work is the rapid synthesis time (~ 45 min) of colloidal CZTS nanocrystals, cost-effective ligand-exchange process, and negligible material wastage (~ 200 µl per 10 ml of pollutant) during photocatalytic experiments.
Graphical Abstract














Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All the necessary data and materials information have been already explained in this article.
References
Ahmed S, Reuter KB, Gunawan O, Guo L, Romankiw LT, Deligianni HJAEM (2012) A high efficiency electrodeposited Cu2ZnSnS4 solar cell. 2(2):253–259
Alzahrani S, Mohammad AW (2014) Challenges and trends in membrane technology implementation for produced water treatment: a review. J Water Process Eng 4:107–133
Ansari MZ, Faraz M, Munjal S, Kumar V, Khare N (2017) Highly dispersible and uniform size Cu2ZnSnS4 nanoparticles for photocatalytic application. Adv Powder Technol 28(9):2402–2409
Arthur JD, Langhus BG, Patel C (2005) Technical summary of oil & gas produced water treatment technologies. All Consulting, LLC, Tulsa, OK
Baibakov M, Patra S, Claude J-B, Moreau A, Lumeau J, Wenger JJAn (2019) Extending single-molecule forster resonance energy transfer (FRET) range beyond 10 nanometers in zero-mode waveguides. 13(7):8469–8480
Bard AJ, Faulkner LR (2001) Fundamentals and applications. Electrochem Methods 2(482):580–632
Chanturiya VA, Krasavtseva EA, Makarov DVJS (2022) Electrochemistry of Sulfides: Process and Environmental Aspects. 14(18):11285
Chen Y, Liu Y, Xie X, Li C, Si Y, Zhang M, Yan QJJoMSMiE (2019) Synthesis flower-like BiVO4/BiOI core/shell heterostructure photocatalyst for tetracycline degradation under visible-light irradiation. 30(10):9311–9321
Currier JM, Holland JM, Drescher K, Foy D (2015) Initial psychometric evaluation of the Moral Injury Questionnaire—Military version. Clin Psychol Psychother 22(1):54–63
Danish M, Muneer MJCI (2021) Facile synthesis of highly efficient Co@ ZnSQDs/g-C3N4/MWCNT nanocomposites and their photocatalytic potential for the degradation of RhB dye: Efficiency, degradation kinetics, and mechanism pathway. 47(9):13043–13056
Danish MSS, Estrella LL, Alemaida IMA, Lisin A, Moiseev N, Ahmadi M, Nazari M, Wali M, Zaheb H, Senjyu T (2021) Photocatalytic applications of metal oxides for sustainable environmental remediation. Metals 11(1):80
Dilsaver PS, Reichert MD, Hallmark BL, Thompson MJ, Vela J (2014) Cu2ZnSnS4–Au heterostructures: toward greener chalcogenide-based photocatalysts. J Phys Chem C 118(36):21226–21234
Dores R, Hussain A, Katebah M, Adham S (2012) Using advanced water treatment technologies to treat produced water from the petroleum industry, SPE International Production and Operations Conference & Exhibition. OnePetro
Fakhru’l-Razi A, Pendashteh A, Abdullah LC, Biak DRA, Madaeni SS, Abidin ZZ (2009) Review of technologies for oil and gas produced water treatment. J Hazardous Mater 170(2–3):530–551
Hevekerl H, Spielmann T, Chmyrov A, Widengren JJTjopcB (2011) Forster resonance energy transfer beyond 10 nm: exploiting the triplet state kinetics of organic fluorophores. 115(45):13360–13370
Hood SN, Walsh A, Persson C, Iordanidou K, Huang D, Kumar M, Jehl Z, Courel M, Lauwaert J, Lee SJJoPE (2019) Status of materials and device modelling for kesterite solar cells. 1(4):042004
Hou X, Li Y, Yan J-J, Wang C-W (2014) Highly efficient photocatalysis of p-type Cu2ZnSnS4 under visible-light illumination. Mater Res Bull 60:628–633
Hunge Y, Yadav A, Liu S, Mathe V (2019) Sonochemical synthesis of CZTS photocatalyst for photocatalytic degradation of phthalic acid. Ultrason Sonochem 56:284–289
Igunnu ET, Chen GZ (2014) Produced water treatment technologies. Int J Low-Carbon Technol 9(3):157–177
Jain S, Singh D, Vijayan N, Sharma SN (2018) Time-controlled synthesis mechanism analysis of kesterite-phased Cu 2 ZnSnS 4 nanorods via colloidal route. Appl Nanosci 8(3):435–446
Jenkins R, Snyder RL (1996) Introduction to X-ray powder diffractometry
Kang C-C, Chen H-F, Yu T-C, Lin T-C (2013) Aqueous synthesis of wurtzite Cu2ZnSnS4 nanocrystals. Mater Lett 96:24–26
Kannan A, Manjulavalli T, Chandrasekaran JJPE (2016) Influence of solvent on the properties of CZTS nanoparticles. 141:15-22
Kush P, Deori K, Kumar A, Deka S (2015) Efficient hydrogen/oxygen evolution and photocatalytic dye degradation and reduction of aqueous Cr (VI) by surfactant free hydrophilic Cu 2 ZnSnS 4 nanoparticles. J Mater Chem A 3(15):8098–8106
Lee SL, Chang C-J (2019) Recent progress on metal sulfide composite nanomaterials for photocatalytic hydrogen production. Catalysts 9(5):457
Li J, Shen J, Li Z, Li X, Sun Z, Hu Z, Huang S (2013) Wet chemical route to the synthesis of kesterite Cu2ZnSnS4 nanocrystals and their applications in lithium ion batteries. Mater Lett 92:330–333
Lin L, Jiang W, Chen L, Xu P, Wang H (2020) Treatment of produced water with photocatalysis: recent advances, affecting factors and future research prospects. Catalysts 10(8):924
Liu W, Guo B, Wu X, Zhang F, Mak C, Wong K (2013) Facile hydrothermal synthesis of hydrotropic Cu 2 ZnSnS 4 nanocrystal quantum dots: band-gap engineering and phonon confinement effect. J Mater Chem A 1(9):3182–3186
Loeb SK, Alvarez PJ, Brame JA, Cates EL, Choi W, Crittenden J, Dionysiou DD, Li Q, Li-Puma G, Quan X (2018) The technology horizon for photocatalytic water treatment: sunrise or sunset? ACS Publications
Ma R, Sun J, Li DH, Wei JJJIJoHE (2020) Review of synergistic photo-thermo-catalysis: Mechanisms, materials and applications. 45(55):30288–30324
Mahjoubi S, Bitri N, Abaab M, Ly I (2018) Effect of copper concentration on the characteristics of Cu2ZnSnS4 (CZTS) thin films. Mater Lett 216:154–157
Munirasu S, Haija MA, Banat F (2016) Use of membrane technology for oil field and refinery produced water treatment—a review. Process Saf Environ Prot 100:183–202
Nhalil H, Han D, Du M-H, Chen S, Antonio D, Gofryk K, Saparov B (2018) Optoelectronic properties of candidate photovoltaic Cu2PbSiS4, Ag2PbGeS4 and KAg2SbS4 semiconductors. J Alloy Compd 746:405–412
Orazem ME, Tribollet B (2008) Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. New Jersey, 383–389
Otowa T, Tanibata R, Itoh M (1993) Production and adsorption characteristics of MAXSORB: high-surface-area active carbon. Gas Sep Purif 7(4):241–245
Pahang F, Parvin P, Ghafoori-Fard H, Bavali A, Moafi AJOC (2020) Fluorescence properties of methylene blue molecules coupled with metal oxide nanoparticles. 3(3):688-697
Patel JB, Tiwana P, Seidler N, Morse GE, Lozman OR, Johnston MB, Herz LMJAam, interfaces (2019) Effect of ultraviolet radiation on organic photovoltaic materials and devices. 11(24):21543–21551
Peng H, Guo JJECL (2020) Removal of chromium from wastewater by membrane filtration, chemical precipitation, ion exchange, adsorption electrocoagulation, electrochemical reduction, electrodialysis, electrodeionization, photocatalysis and nanotechnology: a review. 18(6):2055–2068
Persson CJJoAP (2010) Electronic and optical properties of Cu 2 ZnSnS 4 and Cu 2 ZnSnSe 4. 107(5):053710
Phaltane SA, Vanalakar S, Bhat T, Patil P, Sartale S, Kadam L (2017) Photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue by hydrothermally synthesized CZTS nanoparticles. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 28(11):8186–8191
Rajesh G, Muthukumarasamy N, Subramanian E, Venkatraman M, Agilan S, Ragavendran V, Thambidurai M, Velumani S, Yi J, Velauthapillai D (2015) Solution-based synthesis of high yield CZTS (Cu2ZnSnS4) spherical quantum dots. Superlattices Microstruct 77:305–312
Rasheed T, Bilal M, Nabeel F, Adeel M, Iqbal HMJEi (2019) Environmentally-related contaminants of high concern: potential sources and analytical modalities for detection, quantification, and treatment. 122:52–66
Roelofs KE, GuoQ, Subramoney S, Caspar JVJJoMCA (2014) Investigation of local compositional uniformity in Cu 2 ZnSn (S, Se) 4 thin film solar cells prepared from nanoparticle inks. 2(33):13464–13470
Sakr ME, Abou Kana MT, Abdel Fattah GJL (2014) Fluorescence enhancement monitoring of pyrromethene laser dyes by metallic Ag nanoparticles. 29(7):938–944
Scragg JJ (2011) Copper zinc tin sulfide thin films for photovoltaics: synthesis and characterisation by electrochemical methods. Springer Science & Business Media
Sekar RB, Periasamy AJTJocb (2003) Fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) microscopy imaging of live cell protein localizations. 160(5):629
Semalti P, Sharma V, Sharma SNJJoM (2021) A novel method of water remediation of organic pollutants and industrial wastes by solution-route processed CZTS nanocrystals. 7(5):904–919
Sharma SN, Kumar U, Singh V, Mehta B, Kakkar R (2010) Surface modification of CdSe quantum dots for biosensing applications: role of ligands. Thin Solid Films 519(3):1202–1212
Si KJ, Chen Y, Shi Q, Cheng W (2018) Nanoparticle superlattices: the roles of soft ligands. Advanced Science 5(1):1700179
Singh A, Gupta G, Vijayan N, Sharma SN (2018) Precursor ratio optimizations for the synthesis of colloidal CZTS nanoparticles for photocatalytic degradation of malachite green. J Phys Chem Solids 122:8–18
Su Z, Sun K, Han Z, Cui H, Liu F, Lai Y, Li J, Hao X, Liu Y, Green MA (2014) Fabrication of Cu 2 ZnSnS 4 solar cells with 51% efficiency via thermal decomposition and reaction using a non-toxic sol–gel route. J Mater Chem A 2(2):500–509
Thomas AN, Root RA, Lantz RC, Sáez AE, Chorover JJG (2018) Oxidative weathering decreases bioaccessibility of toxic metal (loid) s in PM10 emissions from sulfide mine tailings. 2(4):118–138
Tovmachenko OG, Graf C, van den Heuvel DJ, van Blaaderen A, Gerritsen HCJAm (2006) Fluorescence enhancement by metal‐core/silica‐shell nanoparticles. 18(1):91–95
Tsang CHA, Li K, Zeng Y, Zhao W, Zhang T, Zhan Y, Xie R, Leung DY, Huang H (2019) Titanium oxide based photocatalytic materials development and their role of in the air pollutants degradation: Overview and forecast. Environ Int 125:200–228
Vanalakar S, Agwane G, Gang M, Patil P, Kim J, Kim J (2015) A mild hydrothermal route to synthesis of CZTS nanoparticle inks for solar cell applications. physica status solidi (c) 12(6):500–503
Wang J, Zhang P, Song X, Gao LJRa (2014a) Surfactant-free hydrothermal synthesis of Cu 2 ZnSnS 4 (CZTS) nanocrystals with photocatalytic properties. 4(53):27805–27810
Wang X, Kou D-X, Zhou W-H, Zhou Z-J, Wu S-X, Cao X (2014b) Cu 2 ZnSnSe 4 nanocrystals capped with S 2− by ligand exchange: utilizing energy level alignment for efficiently reducing carrier rec ombination. Nanoscale Res Lett 9(1):1–7
Wei X, Zhu G, Fang J, Chen J (2013) Synthesis, characterization, and photocatalysis of well-dispersible phase-pure anatase TiO2 nanoparticles. Int J Photoenergy 2013.
Xu X, Sun Y, Fan Z, Zhao D, Xiong S, Zhang B, Zhou S, Liu G (2018) Mechanisms for· O2-and· OH production on flowerlike BiVO4 photocatalysis based on electron spin resonance. Front Chem 6:64
Yang S, Prendergast D, Neaton JBJNl (2012) Tuning semiconductor band edge energies for solar photocatalysis via surface ligand passivation. 12(1):383–388
Yoshida T, Yamaguchi A, Umezawa N, Miyauchi MJTJoPCC (2018) Photocatalytic CO2 reduction using a pristine Cu2ZnSnS4 film electrode under visible light irradiation. 122(38):21695–21702
Yu X, Shavel A, An X, Luo Z, Ibáñez M, Cabot AJJotACS (2014) Cu2ZnSnS4-Pt and Cu2ZnSnS4-Au heterostructured nanoparticles for photocatalytic water splitting and pollutant degradation. 136(26):9236–9239
Yuan X-ZR, Song C, Wang H, Zhang J (2009) Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy in PEM fuel cells: fundamentals and applications. Springer Science & Business Media
Zhou Y-L, Zhou W-H, Du Y-F, Li M, Wu S-X (2011) Sphere-like kesterite Cu2ZnSnS4 nanoparticles synthesized by a facile solvothermal method. Mater Lett 65(11):1535–1537
Zhou Z, Zhang P, Lin Y, Ashalley E, Ji H, Wu J, Li H, Wang Z (2014) Microwave fabrication of Cu 2 ZnSnS 4 nanoparticle and its visible light photocatalytic properties. Nanoscale Res Lett 9(1):1–6
Acknowledgements
The author (PS) sincerely acknowledges the National Physical Laboratory (NPL), Council of Scientific & Industrial Research (CSIR) and AcSIR for providing the necessary facilities to carry out the experimental work, and also thanks CSIR for providing Research Fellowship (#31/001(0521)/2018-EMR-I)
Funding
Funding was provided by the CSIR-Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (#31/001(0521)/2018-EMR-I).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Pooja Semalti: conceptualization, original draft, methodology, investigation, data curation.
Meenakshi Devi, P. Prathap, Naval Kishor Upadhyay, Vikash Sharma: resources and software.
Shailesh Narain Sharma: supervision; validation; visualization; review; and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the Doctoral Advisory Committee of CSIR-National Physical Laboratory, Delhi, India.
Consent to participate
Authors gives their full consent to participate.
Consent to publish
Authors give their full consent to publish without any conflict.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: George Z. Kyzas
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Synopsis: Production in each stage produces hazardous biproducts which mainly cause pollution, affecting human health. Present work highlights the degradation of hazardous water pollutants containing chemical dyes and toxic pollutants, using ligand-assisted non-toxic and cost-effective Cu2ZnSnS4 nanoparticles.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Semalti, P., Sharma, V., Devi, M. et al. Surface engineering of colloidal quaternary chalcogenide Cu2ZnSnS4 nanocrystals: a potential low-cost photocatalyst for water remediation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 79774–79788 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-26603-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-26603-3