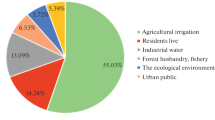
Abstract
Water environmental carrying capacity (WECC) is an important indicator for assessing the coordination between the water environment and the social-economic-resources and environment subsystems. In this study, to determine the WECC of Changsha-Zhuzhou-Xiangtan urban agglomeration in Xiang River Basin, a three-level index system was established using an analytic hierarchy process. Because the previous evaluation system lacked continuous indicators, the results could not reflect the differences of WECC within the administrative units, thus, this study selected 4 continuous indicators, and finally an evaluation index system including 15 indicators was established. Based on the TOPSIS model and logistic regression model, the current situation and change trend of WECC in the study area were obtained in ArcGIS. The results showed that the comprehensive WECC in this region was inferior in 2020, particularly in urban concentrated areas, and it was extremely uneven in spatial distribution. The WECC decreased significantly from 2011 to 2014 and gradually improved from 2014 to 2020. According to the prediction results, the WECC will increase in the future, with an average value of 0.54 in 2025 and 0.60 in 2035. This study will have important guiding implications for the protection and improvement of the water environment in the study area and related areas.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All the data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this article.
References
Baccour S, Albiac J, Kahil T, Esteban E, Crespo D, Dinar A (2021) Hydroeconomic modeling for assessing water scarcity and agricultural pollution abatement policies in the Ebro River Basin, Spain. J Clean Prod 327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.129459
Chen L, Zhang AA (2022) Evaluation and influencing factors of water resources and social economy in the Yellow River Basin. Water Resour Prot 1–14. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/32.1356.TV.20220624.1733.004.html
Chen MX, Xiong GY, Zhang JP, Li L, Wang JH (2019) Comprehensive evaluation of water quality in Xiangjiang River Basin from multi-dimensional perspective and its spatial-temporal evolution analysis. Environ Eng (Beijing, China) 37(10):83–90+104. https://doi.org/10.13205/j.hjgc.201910014
Chen PY (2021) Effects of the entropy weight on TOPSIS. Expert Syst Appl 168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2020.114186
Chen WT, Zheng MX, Xia Q, Su J, Xi BD, Xiang W, Yu MD, Fu XM (2022) System dynamics simulation and control strategy of water environment carrying capacity in Baiyangdian Basin based on industry refinement and multifactor constraint. Resour Environ Yangtze Val. 31(2):345–357. https://doi.org/10.11870/cjlyzyyhj202202009
Dai J, Qi J, Chi JJ, Chen SQ, Yang J, Ju LP, Chen B (2010) Integrated water resource security evaluation of Beijing based on GRA and TOPSIS. Front Earth Sci-Prc 4(3):357–362. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11707-010-0120-7
Daly HE (1995) Carrying capacity and ecological economics. Bioscience 45(9):610–629. https://doi.org/10.2307/1312765
Delgado A, Fernandez A, Lozano E, Miguel D, Leon F, Arteta J, Carbajal C (2021) Applying grey systems and inverse distance weighted method to assess water quality from a river. Int J Adv Comput Sci 12(11):614–622. https://doi.org/10.14569/IJACSA.2021.0121170
Du XQ, He LY, Yao HY, Ren SR, Qiao QT (2022) Evaluation of the coupling coordination development of water resources, socio-economy and eco-environment in northern China in recent 15 years. China Rur Water Hydrop 476(06):66–75
Fu JY, Zang CF, Zhang JM (2020) Economic and resource and environmental carrying capacity trade-off analysis in the Haihe River basin in China. J Clean Prod 270:13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122271
Gong L, Jin C (2009) Fuzzy comprehensive evaluation for carrying capacity of regional water resources. Water Resour Manag 23(12):2505–2513. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-008-9393-y
Gundogdu FK, Kahraman C (2019) Spherical fuzzy sets and spherical fuzzy TOPSIS method. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 36(1):337–352. https://doi.org/10.3233/jifs-181401
Guo XJ, He Q, Zhang DM, Xu JF, He J (2012) Application of subjective and objective methods in weights determination of synthetic evaluation of science and technology. Sci Technol Manag Res 32(20):64–67+71. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1000-7695.2012.20.015
Hastoyuando E, Brontowiyono W, Hasanah NAI (2020) Environmental carrying capacity analysis based on water resources (case study of east Subrabaya area). Civ Environ Eng 16(2):229–237. https://doi.org/10.2478/cee-2020-0022
He WJ, Meng X, Kong Y, Zhang XY (2022) Evaluation and driving factors of water environmental carrying capacity in the Yangtze River Economic Belt from the perspective of spatial-temporal heterogeneity. Water Resour Prot 1–12. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/32.1356.tv.20220612.1428.004.html
Hu YC, Tai QG, Cui C, Li QJ, Cui YP, An GC (2020) Weather forecasting model of pomegranate fruit cracking: based on logistic regression method. Chin Agr Sci Bull 36(01):117–121
Jiang Y, Guo QJ, Deng YN (2022) Research progress in the distribution of heavy metals in sediments and soils in the Yangtze River Basin. Chin J Ecol 41(4):804–812. https://doi.org/10.13292/j.1000-4890.202203.006
Jin CL, Guan QY, Gong L, Zhou Y, Ji ZT (2022) Evaluation of regional water environmental carrying capacity and diagnosis of obstacle factors based on UMT model. Water 14(17):2621. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14172621
Jing CG (2019) Water environment change and comprehensive evaluation analysis in Tao River Basin. Ground Water 41(02):62–63+97. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1004-1184.2019.02.021
Joseph J, Parameswaran G (2006) Dependence of groundwater quality on rainfall. Asian J Chem 18(1):485–490
Kai XL, Qiu XC, Wang Y, Zhang WJ, Yin J (2020) The water environment carrying capacity of the Aiyi River based on artificial neural networks. Pol J Environ Stud 29(1):131–139. https://doi.org/10.15244/pjoes/100669
Kong Y, He WJ, Yuan L, Zhang ZF, Gao X, Zhao YE, Degefu DM (2021) Decoupling economic growth from water consumption in the Yangtze River Economic Belt. China. Ecol Indic 123:107344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.107344
Li A, Yuan Q, Strokal M, Kroeze C, Ma L, Liu Y (2021) Equality in river pollution control in China. Sci Total Environ 777. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146105
Li XM, Ma Y, Sun YH, Gong HL, Li XJ (2013) Flood hazard assessment in Pakistan at grid scale. J Geo-Inf Sci 15(2):314–320. https://doi.org/10.3724/SP.J.1047.2013.00314
Li XY, Li Z, Bao YY, Li L, Li YP (2019) Assessment of seawater quality spatial distribution based on inverse distance weighted interpolation. Environ monit China 35(06):70–77. https://doi.org/10.19316/j.issn.1002-6002.2019.06.10
Li Z, Chen Y, Pan JW (2020) Domestic river basin legislative practice and its enlightenment to the formulation of the Yangtze River Protection Law. Water Resour Develop Res 20(08):5–10+21. https://doi.org/10.13928/j.cnki.wrdr.2020.08.002
Li ZY (2018) Research of GDP distribution pattern based on spatial statistical clustering analysis and GIS. Geomat Spatial Inform Technol 41(09):171–173+177
Liu D, Liu CL, Fu Q, Li TX, Khan MI, Cui S, Faiz MA (2018a) Projection pursuit evaluation model of regional surface water environment based on improved chicken swarm optimization algorithm. Water Resour Manag 32(4):1325–1342. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-017-1872-6
Liu SH, Li Y, Ge YX, Geng XY (2022) Analysis on the impact of river basin ecological compensation policy on water environment pollution. Sustainability 14(21):13774. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142113774
Liu YY, Mao DH, Yang JL, Qian Z (2018b) Analysis on the water quality change characteristics and influencing factors of the Xiangjiang River Mainstream from 1990 to 2016. J Glaciol Geo 40(04):820–827
Long X, Wu SG, Wang JY, Wu PZ, Wang Z (2022) Urban water environment carrying capacity based on VPOSR-coefficient of variation-grey correlation model: a case of Beijing. China. Ecol Indic 138:108863. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.108863
Lv HJ, Wang Y, Li DY, Liu CY (2003) The application of backward cloud in qualitative evaluation. Chin J Comp 08:1009–1014
Malin F (2013) Growing water scarcity in agriculture: future challenge to global water security. Philosophical transactions. Philos T R Soc A 371(2002). https://doi.org/10.1098/rsta.2012.0410
Meissner S (2021) The impact of metal mining on global water stress and regional carrying capacities-a GIS-based water impact assessment. Resources-Basel 10(12):120. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources10120120
Mikulic J, Kozic I, Kresic D (2015) Weighting indicators of tourism sustainability: a critical note. Ecol Indic 48:312–314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2014.08.026
Mishra AR, Bullet PR, Pandey K (2022) Fermatean fuzzy CRITIC-EDAS approach for the selection of sustainable third-party reverse logistics providers using improved generalized score function. J Amb Intel and Hum Comp 13(1):295–311. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-021-02902-w
Ou ZH, Zhu ZP (2014) The dynamic study on the efficiency of regional independent innovation based on dynamic evaluation method on the overall maximum sum of deviation square. Chin J Manag Sci 22(S1):782–787. https://doi.org/10.16381/j.cnki.issn1003-207x.2014.s1.082
Ouma KO, Shane A, Syampungani S (2022) Aquatic ecological risk of heavy-metal pollution associated with degraded mining landscapes of the Southern Africa River Basins: a review. Minerals 12(2):225. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12020225
Peng SQ, Zhang KJ, Peng YH, Fan L (2020) Study on water environmental carrying capacity of Changsha-Zhuzhou-Xiangtan urban agglomeration. J Anhui Agr Univ 47(05):763–769. https://doi.org/10.13610/j.cnki.1672-352x.20201113.004
Peng T, Deng HW (2020) Comprehensive evaluation on water resource carrying capacity based on DPESBR framework: a case study in Guiyang, southwest China. J Clean Prod 268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122235
Prato T (2009) Fuzzy adaptive management of social and ecological carrying capacities for protected areas. J Environ Manag 90(8):2551–2557. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2009.01.015
Rostamzadeh R, KeshavarzGhorabaee M, Govindan K, Esmaeili A, Nobar HBK (2018) Evaluation of sustainable supply chain risk management using an integrated fuzzy TOPSIS- CRITIC approach. J Clean Prod 175:651–669. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.12.071
Song FY, Lin KR, He YH, Li WJ, Zhang Y (2020) Assessment of water environmental carrying capacity in the Pearl River Delta region with considering weight incertainty: based on game theoty and cloud model. Water Resour Hydropower Eng 51(11):145–154. https://doi.org/10.13928/j.cnki.wrahe.2020.11.018
Sun G, Xu DL, Zhou Y, Ren X (2017) Water quality evaluation of Kui River Based on particle swarm optimization and sum of squared deviations. Water Resour Develop Res 17(03):58–62. https://doi.org/10.13928/j.cnki.wrdr.2017.03.016
Tu Y, Chen K, Wang HY, Li ZM (2020) Regional water resources security evaluation based on a hybrid fuzzy BWM-TOPSIS Method. Int J Env Res Pub He 17(14):4987. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17144987
Wang CJ, Zhao D, Wang BQ, Feng T, Zhang W, Dong MF (2022a) Study on coordinated development and spatio-temporal evolution of water environment based on DPSIR theory. J Xi’an Univ Archit Technol 54(03):466–474. https://doi.org/10.15986/j.1006-7930.2022.03.018
Wang HD, Xu YH, Sulong RS, Ma HL, Wu LF (2021a) Comprehensive evaluation of water carrying capacity in Hebei Province, China on principal component analysis. Front Envi Sci-Switz 9. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2021.761058
Wang XY, Zhang SL, Liu L (2021b) Fuzzy comprehensive evaluation of water environmental carrying capacity based on AHP-Entropy method. Environ Sci Technol 44(09):206–212. https://doi.org/10.19672/j.cnki.1003-6504.0922.21.338
Wang XY, Liu L, Zhang SL, Gao C (2022b) Dynamic simulation and comprehensive evaluation of the water resources carrying capacity in Guangzhou city, China. Ecol Indic 135:13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.108528
Wang YS, Min XT, Wang C, Xia CQ, Zhu Q (2022c) Multi-source remote sensing soil moisture data analysis over the Xiang River basin based on EnKF. Sci Soil Water Conserv 20(02):40–48. https://doi.org/10.16843/j.sswc.2022.02.006
Wu B, Shi P-l, Jing X-h, Li X-s (2006) Water conservation capacity and its value evaluation of vegetation types in eastern Daxing’anling Mountain forest area. Forest Res 19(6):706–712
Wu SZ, Chen Y (2013) Strengthening the construction of river basin protection system and promoting good water body protection – interpretation of “Good lake ecological environment protection plan (2011–2020).” Environ Prot 41(11):13–16. https://doi.org/10.14026/j.cnki.0253-9705.2013.11.010
Wu Y, Ma ZY, Li X, Sun L, Sun SH, Jia RB (2021) Assessment of water resources carrying capacity based on fuzzy comprehensive evaluation - case study of Jinan, China. Water Supply 21(2):513–524. https://doi.org/10.2166/ws.2020.335
Xiao R (2021) Value expression and function construction of river basin protection legislation in China: take the Yangtze River Protection Law as the analysis object. Resour Environ Yangtze Basin 30(12):3017–3028
Xu ZQ, Liu XY, Deng QY, Yan BF, Xiao SH, Sun C (2020) Scenario analysis and forecasts of water environmental carrying capacity in Nanjing city. J Environ Eng Technol 10(03):494–503. https://doi.org/10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20190168
Ye Q, Li SW, Zhang YH, Shu XW, Ni DP (2011) Cloud model and application overview. Comput Eng Des 32(12):4198–4201. https://doi.org/10.16208/j.issn1000-7024.2011.12.033
Yuan L, Yang DQ, Wu X, He WJ, Kong Y, Ramsey TS, Degefu DM (2023) Development of multidimensional water poverty in the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. J Environ Manag 325:116608. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.116608
Zeng Z, Luo W-G, Wang Z, Yi F-C (2021) Water pollution and its causes in the Tuojiang River Basin, China: an artificial neural network analysis. Sustainability 13(2):792. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13020792
Zhang YJ, Yue Q, Wang T, Zhu Y, Li Y (2021a) Evaluation and early warning of water environment carrying capacity in Liaoning province based on control unit: a case study in Zhaosutai river Tieling city control unit. Ecol Indic 124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.107392
Zhang YT, Wang JY, Qi DM, Liu W, Tian ZH (2021b) Comprehensive evaluation of water environmental carrying capacity of Chengdu rivers based on DCSM framework. Acta Sci Circumst 41(9):3825–3833. https://doi.org/10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2021.0013
Zhou K (2022) Comprehensive evaluation on water resources carrying capacity based on improved AGA-AHP method. Appl Water Sci 12(5):103. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-022-01626-2
Zhu Y (2020) Construction of index system for water environmental carrying capacity based on “Three Waters” connotation: taking Liaohe River Basin as an example. J Environ Eng Technol 10(6):1029–1035. https://doi.org/10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20200124
Zhu YM, Huang WB, Chen SJ, Ma GW (2020) Application of logistic regression model in runoff wetness-dryness prediction. Water Resour Power 38(12):16–19+23
Zhu X, Zhu Y, Zhai YB, He J (2011) Assessment of the ecological security of water environment in Changsha-Zhuzhou-Xiangtan District. J Hunan Univ (Nat Sci) 38(1):72–77
Funding
This research was supported by the program of the National Science Foundation of China (Grant no. 51874352).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Peng Wang: conceptualization, methodology, software, investigation, data curation, formal analysis, and writing — original draft. Hongwei Deng: validation, formal analysis, visualization, software, and writing — review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Xianliang Yi
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, P., Deng, H. Research on regional water environmental carrying capacity based on GIS and TOPSIS comprehensive evaluation model. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 57728–57746 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-26574-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-26574-5