Abstract
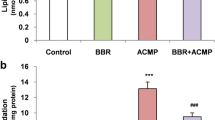
The widespread application of organophosphorus (OP) pesticides can affect the environment as well as the animal and human health. Chlorpyrifos (CPF) is a broad-spectrum OP pesticide used in agriculture and can cause several toxic effects in which oxidative stresses and inflammation play a key role. This study aimed to evaluate the protective activity of betulinic acid (BA), an antioxidant and anti-inflammatory pentacyclic triterpene, against CPF cardiotoxicity in rats. The rats were divided into four groups. CPF (10 mg/kg) and BA (25 mg/kg) were orally administered for 28 days, and blood and heart samples were collected. CPF-administered rats showed an increase in serum cardiac troponin I (cTnI), creatine kinase (CK)-MB, and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), accompanied with multiple myocardial tissue alterations. Lipid peroxidation (LPO), nitric oxide (NO), nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-κB), interleukin (IL)-6, IL-1β, and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α were increased, and antioxidant were decrease in CPF-administered rats. BA ameliorated cardiac function markers and tissue injury, decreased LPO, NO, NF-κB, and proinflammatory cytokines, and increased antioxidants. In addition, BA decreased proapoptosis markers, and increased B-cell lymphoma (Bcl)-2, IL-10, Nrf2, and HO-1 in the heart of CPF-treated rats. In conclusion, BA protected against cardiotoxicity in CPF-administered rats by mitigating oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis, and enhanced Nrf2 and antioxidants.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article.
References
Abd El-Twab SM, Hozayen WG, Hussein OE (2016) Mahmoud AM (2016): 18beta-Glycyrrhetinic acid protects against methotrexate-induced kidney injury by up-regulating the Nrf2/ARE/HO-1 pathway and endogenous antioxidants. Ren Fail 8:1–12
Abd El-Twab SM, Hussein OE, Hozayen WG, Bin-Jumah M, Mahmoud AM (2019) Chicoric acid prevents methotrexate-induced kidney injury by suppressing NF-κB/NLRP3 inflammasome activation and up-regulating Nrf2/ARE/HO-1 signaling. Inflammation research. Official J Eur Histamine Res Soc ... [et al.] 68:511–523
Abukhalil MH, Althunibat OY, Aladaileh SH, Al-Amarat W, Obeidat HM, Al-khawalde AA-mA, Hussein OE, Alfwuaires MA, Algefare AI, Alanazi KM, Al-Swailmi FK, Arab HH, Mahmoud AM (2021): Galangin attenuates diabetic cardiomyopathy through modulating oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis in rats. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 138,111410
Abraham NG, Lutton JD, Levere RD (1985) Heme metabolism and erythropoiesis in abnormal iron states: role of delta-aminolevulinic acid synthase and heme oxygenase. Exp Hematol 13:838–843
Adeleke GE, Adaramoye OA (2017) Betulinic acid protects against N-nitrosodimethylamine-induced redox imbalance in testes of rats. Redox Report 22:556–562
Aebi H (1984) [13] Catalase in vitro, Methods in Enzymology. Academic Press, pp 121–126
Alamgir Zaman Chowdhury M, Fakhruddin ANM, Nazrul Islam M, Moniruzzaman M, Gan SH, Khorshed Alam M (2013) Detection of the residues of nineteen pesticides in fresh vegetable samples using gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. Food Control 34:457–465
Alanazi AM, Fadda L, Alhusaini A, Ahmad R, Hasan IH, Mahmoud AM (2020) Liposomal resveratrol and/or carvedilol attenuate doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by modulating inflammation, oxidative stress and S100A1 in rats. Antioxidants 9:159
Allam MAM, Khowailed AA, Elattar S, Mahmoud AM (2022): Umbelliferone ameliorates oxidative stress and testicular injury, improves steroidogenesis and upregulates peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma in type 2 diabetic rats. J Pharm Pharmacol 74,573–584
Alotaibi MF, Al-Joufi F, Abou Seif HS, Alzoghaibi MA, Djouhri L, Ahmeda AF, Mahmoud AM (2020): Umbelliferone Inhibits Spermatogenic Defects and Testicular Injury in Lead- Intoxicated Rats by Suppressing Oxidative Stress and Inflammation, and Improving Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling. Drug Des Devel Ther 14,4003–4019
Antar SA, Abdo W, Taha RS, Farage AE, El-Moselhy LE, Amer ME, Abdel Monsef AS, Abdel Hamid AM, Kamel EM, Ahmeda AF, Mahmoud AM (2022): Telmisartan attenuates diabetic nephropathy by mitigating oxidative stress and inflammation, and upregulating Nrf2/HO-1 signaling in diabetic rats. Life Sci 291,120260
Auten RL, Davis JM (2009) Oxygen toxicity and reactive oxygen species: the devil is in the details. Pediatric Research 66:121–127
Bai Y-Y, Yan D, Zhou H-Y, Li W-X, Lou Y-Y, Zhou X-R, Qian L-B, Xiao C (2020) Betulinic acid attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced vascular hyporeactivity in the rat aorta by modulating Nrf2 antioxidative function. Inflammopharmacology 28:165–174
Cai Z, Yan L-J (2013) Protein oxidative modifications: beneficial roles in disease and health. J Biochemical Pharmacol Res 1:15
Costa JF, Barbosa-Filho JM, Maia GL, Guimarães ET, Meira CS, Ribeiro-dos-Santos R, de Carvalho LC, Soares MB (2014) Potent anti-inflammatory activity of betulinic acid treatment in a model of lethal endotoxemia. Int Immunopharmacol 23:469–474
de Sá MS, Costa JF, Krettli AU, Zalis MG, Maia GL, Sette IM, Câmara Cde A, Filho JM, Giulietti-Harley AM, Ribeiro Dos Santos R, Soares MB (2009) Antimalarial activity of betulinic acid and derivatives in vitro against Plasmodium falciparum and in vivo in P. berghei-infected mice. Parasitol Res 105:275–279
Georgiadis N, Tsarouhas K, Tsitsimpikou C, Vardavas A, Rezaee R, Germanakis I, Tsatsakis A, Stagos D, Kouretas D (2018) Pesticides and cardiotoxicity. Where do we stand? Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 353:1–14
Green DR (1998) Apoptotic pathways: the roads to ruin. Cell 94:695–698
Green LC, Wagner DA, Glogowski J, Skipper PL, Wishnok JS, Tannenbaum SR (1982) Analysis of nitrate, nitrite, and [15N]nitrate in biological fluids. Anal Biochem 126:131–138
Griffith OW (1980) Determination of glutathione and glutathione disulfide using glutathione reductase and 2-vinylpyridine. Anal Biochem 106:207–212
Has AL, Alotaibi MF, Bin-Jumah M, Elgebaly H, Mahmoud AM (2019) Olea europaea leaf extract up-regulates Nrf2/ARE/HO-1 signaling and attenuates cyclophosphamide-induced oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis in rat kidney. Biomed Pharmacother = Biomed Pharmacother 111:676–685
Hassanein EHM, Abd El-Ghafar OAM, Ahmed MA, Sayed AM, Gad-Elrab WM, Ajarem JS, Allam AA, Mahmoud AM (2020) Edaravone and acetovanillone upregulate Nrf2 and PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling and prevent cyclophosphamide cardiotoxicity in rats. Drug Des, Devel Ther 14:5275–5288
Huang L, Zhu L, Ou Z, Ma C, Kong L, Huang Y, Chen Y, Zhao H, Wen L, Wu J, Yuan Z, Yi J (2021) Betulinic acid protects against renal damage by attenuation of oxidative stress and inflammation via Nrf2 signaling pathway in T-2 toxin-induced mice. Int Immunopharmacol 101:108210
Huang Y, Zhu Z, Luo C, Ma C, Zhu L, Kong L, Li R, Wu J, Yuan Z, Yi J (2022) Betulinic acid attenuates cognitive dysfunction, oxidative stress, and inflammation in a model of T-2 toxin-induced brain damage. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:52098–52110
Ibrahim KA, Khwanes SA, El-Desouky MA, Elhakim HKA (2019) Propolis relieves the cardiotoxicity of chlorpyrifos in diabetic rats via alleviations of paraoxonase-1 and xanthine oxidase genes expression. Pestic Biochem Physiol 159:127–135
Jafari Hajati R, Payamnoor V, Ahmadian Chashmi N, Ghasemi Bezdi K (2018) Improved accumulation of betulin and betulinic acid in cell suspension culture of Betula pendula roth by abiotic and biotic elicitors. Prep Biochem Biotechnol 48:867–876
Jennes L (2013) Chapter 7 — Immunohistochemical detection of neuropeptides/transmitters in mammalian brain. In: Conn PM (ed) Methods in Cell Biology. Academic Press, pp 123–147
Jiang W, Li X, Dong S, Zhou W (2021) Betulinic acid in the treatment of tumour diseases: application and research progress. Biomed Pharmacother = Biomed Pharmacother 142:111990
Khalaf HA, El-Mansy AAE-R (2019) The possible alleviating effect of saffron on chlorpyrifos experimentally induced cardiotoxicity: histological, immunohistochemical and biochemical study. Acta Histochemica 121:472–483
Liu M, Grigoryev DN, Crow MT, Haas M, Yamamoto M, Reddy SP, Rabb H (2009) Transcription factor Nrf2 is protective during ischemic and nephrotoxic acute kidney injury in mice. Kidney Int 76:277–285
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001): Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 25(4):402–408
Mahmoud AM, Hussein OE, Abd El-Twab SM, Hozayen WG (2019) Ferulic acid protects against methotrexate nephrotoxicity via activation of Nrf2/ARE/HO-1 signaling and PPARγ, and suppression of NF-κB/NLRP3 inflammasome axis. Food Funct 10:4593–4607
Nandi NK, Vyas A, Akhtar MJ, Kumar B (2022) The growing concern of chlorpyrifos exposures on human and environmental health. Pestic Biochem Physiol 185:105138
Nigam PK (2007) Biochemical markers of myocardial injury. Indian J Clin Biochem 22:10–17
Nishikimi M, Rao NA, Yagi K (1972) The occurrence of superoxide anion in the reaction of reduced phenazine methosulfate and molecular oxygen. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 46:849–854
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K (1979) Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 95:351–358
Oliveira-Costa JF, Meira CS, Neves M, Dos Reis B, Soares MBP (2022) Anti-inflammatory activities of betulinic acid: a review. Front Pharmacol 13:883857
Ou Z, Zhu L, Huang C, Ma C, Kong L, Lin X, Gao X, Huang L, Wen L, Liang Z, Yuan Z, Wu J, Yi J (2021) Betulinic acid attenuates cyclophosphamide-induced intestinal mucosa injury by inhibiting the NF-κB/MAPK signalling pathways and activating the Nrf2 signalling pathway. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 225:112746
Pacher P, Beckman JS, Liaudet L (2007) Nitric oxide and peroxynitrite in health and disease. Physiol Rev 87:315–424
Paglia DE, Valentine WN (1967) Studies on the quantitative and qualitative characterization of erythrocyte glutathione peroxidase. J Lab Clin Med 70:158–169
Peter JV, Sudarsan TI, Moran JL (2014) Clinical features of organophosphate poisoning: a review of different classification systems and approaches. Indian J Crit Care Med : Peer-Rev, Off Publ Indian Soc Crit Care Med 18:735–745
Ramadan SA, Kamel EM, Ewais MA, Khowailed AA, Hassanein EHM, Mahmoud AM (2023): Flavonoids of Haloxylon salicornicum (Rimth) prevent cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury by modulating oxidative stress, inflammation, Nrf2, and SIRT1. Environ sci Pollut Research, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-25694-2
Redza-Dutordoir M, Averill-Bates DA (2016) Activation of apoptosis signalling pathways by reactive oxygen species. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular. Cell Res 1863:2977–2992
Rodrigues NR, Batista JES, de Souza LR, Martins IK, Macedo GE, da Cruz LC, da Costa Silva DG, Pinho AI, Coutinho HDM, Wallau GL, Posser T, Franco JL (2019) Activation of p38MAPK and NRF2 signaling pathways in the toxicity induced by chlorpyrifos in Drosophila melanogaster: Protective effects of Psidium guajava pomífera L. (Myrtaceae) hydroalcoholic extract. Arab J Chem 12:3490–3502
Saoudi M, Badraoui R, Rahmouni F, Jamoussi K, El Feki A (2021) Antioxidant and protective effects of Artemisia campestris essential oil against chlorpyrifos-induced kidney and liver injuries in rats. Front Physiol 12:618582
Sarawi WS, Alhusaini AM, Fadda LM, Alomar HA, Albaker AB, Aljrboa AS, Alotaibi AM, Hasan IH, Mahmoud AM (2021) Nano-curcumin prevents cardiac injury, oxidative stress and inflammation, and modulates TLR4/NF-κB and MAPK signaling in copper sulfate-intoxicated rats. Antioxidants 10:1414
Sharma S, Chadha P (2016) Induction of neurotoxicity by organophosphate pesticide chlorpyrifos and modulating role of cow urine. SpringerPlus 5:1–7
Shi Y, Chen J, Weng C, Chen R, Zheng Y, Chen Q, Tang H (2003) Identification of the protein-protein contact site and interaction mode of human VDAC1 with Bcl-2 family proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 305:989–996
Suratman S, Edwards JW, Babina K (2015) Organophosphate pesticides exposure among farmworkers: pathways and risk of adverse health effects. Rev Environ Health 30:65–79
Sylla B, Lavoie S, Legault J, Gauthier C, Pichette A (2019) Synthesis, cytotoxicity and anti-inflammatory activity of rhamnose-containing ursolic and betulinic acid saponins. RSC Adv 9:39743–39757
ur Rahman HU, Asghar W, Nazir W, Sandhu MA, Ahmed A, Khalid N (2021) A comprehensive review on chlorpyrifos toxicity with special reference to endocrine disruption: evidence of mechanisms, exposures and mitigation strategies. Sci Total Environ 755:142649
Wardyn JD, Ponsford AH, Sanderson CM (2015) Dissecting molecular cross-talk between Nrf2 and NF-κB response pathways. Biochem Soc Trans 43:621–626
Weis GCC, Assmann CE, Mostardeiro VB, Alves AO, da Rosa JR, Pillat MM, de Andrade CM, Schetinger MRC, Morsch VMM, da Cruz IBM, Costabeber IH (2021) Chlorpyrifos pesticide promotes oxidative stress and increases inflammatory states in BV-2 microglial cells: A role in neuroinflammation. Chemosphere 278:130417
Yi J, Zhu R, Wu J, Wu J, Tan Z (2015) Ameliorative effect of betulinic acid on oxidative damage and apoptosis in the splenocytes of dexamethasone treated mice. Int Immunopharmacol 27:85–94
Zhang J, Almoallim HS, Ali Alharbi S, Yang B (2021) Anti-atherosclerotic activity of Betulinic acid loaded polyvinyl alcohol/methylacrylate grafted Lignin polymer in high fat diet induced atherosclerosis model rats. Arab J Chem 14:102934
Zhao MW, Yang P, Zhao LL (2019) Chlorpyrifos activates cell pyroptosis and increases susceptibility on oxidative stress-induced toxicity by miR-181/SIRT1/PGC-1α/Nrf2 signaling pathway in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells. Environ Toxicol 34:699–707
Zhu L, Yi X, Zhao J, Yuan Z, Wen L, Pozniak B, Obminska-Mrukowicz B, Tian Y, Tan Z, Wu J, Yi J (2018) Betulinic acid attenuates dexamethasone-induced oxidative damage through the JNK-P38 MAPK signaling pathway in mice. Biomed Pharmacother 103:499–508
Zhu L, Yi X, Ma C, Luo C, Kong L, Lin X, Gao X, Yuan Z, Wen L, Li R, Wu J, Yi J (2020) Betulinic acid attenuates oxidative stress in the thymus induced by acute exposure to T-2 toxin via regulation of the MAPK/Nrf2 signaling pathway. Toxins 12:540
Albasher G, Almeer R, Al-Otibi FO, Al-Kubaisi N, Mahmoud AM (2019) Ameliorative effect of beta vulgaris root extract on chlorpyrifos-induced oxidative stress, inflammation and liver injury in rats. Biomolecules 9
Bancroft JD, Gamble M (2008) Theory and practice of histological techniques. Elsevier health sciences
Satta S, Mahmoud AM, Wilkinson FL, Yvonne Alexander M, White SJ (2017) The role of Nrf2 in cardiovascular function and disease. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2017
Uchendu C, Ambali SF, Ayo JO (2012) The organophosphate, chlorpyrifos, oxidative stress and the role of some antioxidants: a review
Wielgomas B, Krechniak J (2007) Effect of α-cypermethrin and chlorpyrifos in a 28-day study on free radical parameters and cholinesterase activity in Wistar rats. Pol J Environ Stud 16
Yang Y, Wei S, Zhang B, Li W (2021) Recent progress in environmental toxins-induced cardiotoxicity and protective potential of natural products. Front Pharmacol 12
Yoon JJ, Son CO, Kim HY, Han BH, Lee YJ, Lee HS, Kang DG (2020) Betulinic acid protects DOX-triggered cardiomyocyte hypertrophy response through the GATA-4/calcineurin/NFAT pathway. Molecules 26
Acknowledgements
The author thanks Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, for supporting this work through the Researchers Supporting Project Number (PNURSP2023R381).
Funding
Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University Researchers Supporting Project Number (PNURSP2023R381), Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Not applicable.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The experiment was conducted according to the guidelines of the National Institutes of Health (NIH publication No. 85–23, revised 2011) and was approved by the Research Ethics Committee at Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University (IRB approval number: HAP-01-R-059).
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Alruhaimi, R.S. Betulinic acid protects against cardiotoxicity of the organophosphorus pesticide chlorpyrifos by suppressing oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis in rats. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 51180–51190 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-25917-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-25917-6