Abstract
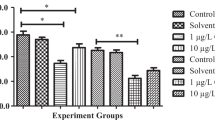
Pyrethroids are among the most widely used insecticides. Permethrin and tetramethrin, which are synthetic pyrethroids, are generally used to control insects in agricultural areas and household applications. Due to broad use areas, they contaminate aquatic ecosystems and cause adverse effects to the non-target aquatic organisms. Even though permethrin and tetramethrin are known to alter the oxidative stress parameters of in vivo aquatic animal model organisms, there are limited studies in vitro. This study aims to determine the adverse effects of permethrin and tetramethrin in the in vitro models of freshwater mussels exposed to 1 mg/L, 10 μg/L, 100 ng/L and 1 ng/L concentrations of chemicals for 24 h. For this purpose, reduced glutathione activities were evaluated as biomarkers of the primary gill and digestive gland cell cultures. In both cell cultures, reduced glutathione values increased in the exposed groups, compared to the control group. Even though the results showed that reduced glutathione activities had not significantly changed concentration-dependently (p > 0.05), significant differences were observed in the reduced glutathione activities of both cell cultures (p < 0.05). This study showed that permethrin and tetramethrin had highly toxic effects in the in vitro models of mussels even at low concentrations.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amin KA, Hashem KS (2012) Deltamethrin-induced oxidative stress and biochemical changes in tissues and blood of catfish (Clarias gariepinus): antioxidant defense and role of alpha-tocopherol. BMC Vet Res 8:45. https://doi.org/10.1186/1746-6148-8-45
Arrighetti F, Ambrosio E, Astiz M, Capítulo AR, Lavarías S (2018) Differential response between histological and biochemical biomarkers in the apple snail Pomacea canaliculata (Gasteropoda: Amullariidae) exposed to cypermethrin. Aquat Toxicol 194:140–151
Arslan A, Günal AÇ (2021) Synthetic pyrethroid toxicity in aquatic organisms. In: Amutkan Mutlu D (ed) Recent biological studies, 1st edn. IKSAD Publications, Ankara, Turkey, pp 25–46
Arslan P (2021) Determination of the oxidative stress effect of chlorpyrifos etyhl on the in vitro models of the freshwater organisms. Future Biochem Bioscience 3(2):50–55. https://doi.org/10.48086/ASD0031
Arslan P, Yurdakok-Dikmen B, Kuzukiran O, Ozeren SC, Filazi A (2021a) Effects of acetamiprid and flumethrin on Unio sp. primary cells. Biologia 76:1359–1365. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-021-00692-2
Arslan P, Yurdakok-Dikmen B, Ozeren SC, Kuzukıran O, Filazi A (2021b) In vitro effects of erythromycin and florfenicol on primary cell lines of Unio crassus and Cyprinus carpio. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:48408–48416. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14139-3
Balbi T, Ciacci C, Grasselli E, Smerilli A, Voci A, Canesi L (2017) Utilization of Mytilus digestive gland cells for the in vitro screening of potential metabolic disruptors in aquatic invertebrates. Comp Biochem Physiol Part C: Toxicol Pharmacol 191:26–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2016.08.009
Bao W, Liu B, Simonsen DW, Lehmler H-J (2020) Association between exposure to pyrethroid insecticides and risk of all-cause and cause-specific mortality in the general us adult population. JAMA Intern Med 180(3):367–374
Bast A, Haenen GRMM (1990) Regulation of lipid peroxidation by glutathione and lipoic acid: involvement of liver microsomal vitamin E free radical reductase. In: Emerit I, Packer L, Auclair C (eds) Antioxidants in therapy and preventive medicine. Advances in experimental medicine and biology, vol 264. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4684-5730-8_15
Bat L, Arıcı E, Öztekin A, Yardım Ö, Üstün F (2018) Use of the Mediterranean mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis Lamarck, 1819 from Sinop coasts of the Black Sea as bio-monitor. Int J Mar Sci 8(5):44–47
Birben E, Sahiner UM, Sackesen C, Erzurum S, Kalayci O (2012) Oxidative stress and antioxidant defense. World Allergy Organ J 5:9–19
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Brown LR, Gray RH, Hughes RM, Meador MR (2005) Introduction to effects of urbanization on stream ecosystems. In American Fisheries Society Symposium. 47(1-8)
Bury NR, Schnell S, Hogstrand C (2014) Gill cell culture systems as models for aquatic environmental monitoring. J Exp Biol 217(5):639–650
De A, Bose R, Kumar A, Mozumdar S (2014) Worldwide pesticide use. In: Targeted delivery of pesticides using biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles. Springer, Berlin, pp 5–6
Ellman GL (1959) Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys 82(1):70–77
Faedmaleki F, Shirazi HF, Salarian AA, Ahmadi Ashtiani H, Rastegar H (2014) Toxicity effect of silver nanoparticles on mice liver primary cell culture and HepG2 cell line. IJPR. 13(1):235–242
Febrer-Serra M, Lassnig N, Colomar V, Picó G, Tejada S, Sureda A, Pinya S (2023) Oxidative stress and behavioral responses of moorish geckos (Tarentola mauritanica) submitted to the presence of an introduced potential predator (Hemorrhois hippocrepis). Sci Total Environ 855:158864
Gómez-Mendikute A, Elizondo M, Venier P, Cajaraville MP (2005) Characterization of mussel gill cells in vivo and in vitro. Cell Tissue Res 321:131–140. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-005-1093-9
Günal AÇ, Tunca SK, Arslan P, Gül G, Sepici Dinçel A (2021) How does sublethal permethrin effect non-target aquatic organisms? Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:52405–52417. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14475-4
Heckmann LH, Friberg N, Ravn HW (2005) Relationship between biochemical biomarkers and pre-copulatory behaviour and mortality in Gammarus pulex following pulse-exposure to lambda-cyhalothrin. Pest Manag Sci 61(7):627–635
Kaviraj A, Gupta A (2014) Biomarkers of type II synthetic pyrethroid pesticides in freshwater fish. Biomed Res Int 2014:928063. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/928063
Khabib MNH, Sivasanku Y, Lee HB, Kumar S, Kue CS (2022) Alternative animal models in predictive toxicology. Toxicology 465:153053
Khazri A, Sellami B, Hanachi A, Dellali M, Eljarrat E, Beyrem H, Mahmoudi E (2016) Neurotoxicity and oxidative stress induced by permethrin in gills of the freshwater mussel Unio ravoisieri. Chem Ecol 33(1):88–101
Köprücü K, Yonar SM, Şeker E (2010) Effects of cypermethrin on antioxidant status, oxidative stress biomarkers, behavior, and mortality in the freshwater mussel Unio elongatulus eucirrus. Fish Sci 76:1007–1013
Le Pennec G, Le Pennec M (2001) Acinar primary cell culture from the digestive gland of Pecten maximus (L.): an original model for ecotoxicological purposes. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol. 259(2):171–187
Mendis JC, Tennakoon TK, Jayasinghe CD (2018) Zebrafish embryo toxicity of a binary mixture of pyrethroid insecticides: d-tetramethrin and cyphenothrin. J Toxicol 2018:4182694. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/4182694
Narahashi T (1971) Mode of action of pyrethroids. Bull World Health Organ 44(1-2-3):337
National Center for Biotechnology Information (2022a) PubChem compound summary for CID 40326, permethrin. Retrieved February 18, 2022 from https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Permethrin
National Center for Biotechnology Information (2022b) PubChem compound summary for CID 83975, tetramethrin. Retrieved February 18, 2022 from https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Tetramethrin.
Oehlmann J, Schulte-Oehlmann U (2003) Molluscs as bioindicators. In: Trace metals and other contaminants in the environment, vol 6. Elsevier, pp 577–635. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0927-5215(03)80147-9
Parolini M, Quinn B, Binelli A, Provini A (2011) Cytotoxicity assessment of four pharmaceutical compounds on the zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha) haemocytes, gill and digestive gland primary cell cultures. Chemosphere 84(1):91–100
Passos LC, Ricupero M, Gugliuzzo A, Soares MA, Desneux N, Carvalho GA, Zappala L, Biondi A (2022) Does the dose make the poison? Neurotoxic insecticides impair predator orientation and reproduction even at low concentrations. Pest Manage Sci 78(4):1698–1706. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.6789
Patetsini E, Dimitriadis VK, Kaloyianni M (2013) Biomarkers in marine mussels, Mytilus galloprovincialis, exposed to environmentally relevant levels of the pesticides, chlorpyrifos and penoxsulam. Aquat Toxicol 126:338–345
Rios-Fuster B, Alomar C, Capó X, González GP, Martínez RMG, Rojas DLS, Silva M, Hernando PF, Sole M, Freitas R, Deudero S (2022) Assessment of the impact of aquaculture facilities on transplanted mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis): integrating plasticizers and physiological analyses as a biomonitoring strategy. J Hazard Mater 424:127264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127264
Robertson JD, Orrenius S (2002) Role of mitochondria in toxic cell death. Toxicology 181:491–496
Sharma A, Kumar V, Shahzad B, Tanveer M, Sidhu GPS, Handa N, Kohli SK, Yadav P, Bali AS, Parihar RD, Dar OI, Singh K, Jasrotia S, Bakshi P, Ramakrishnan M, Kumar S, Bhardwaj R, Thukral AK (2019) Worldwide pesticide usage and its impacts on ecosystem. SN Appl Sci 1:1446. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-019-1485-1
Stehle S, Schulz R (2015) Agricultural insecticides threaten surface waters at the global scale. PNAS 112(18):5750–5755
Stott LC, Schnell S, Hogstrand C, Owen SF, Bury NR (2015) A primary fish gill cell culture model to assess pharmaceutical uptake and efflux: evidence for passive and facilitated transport. Aquat Toxicol 159:127–137
Sumudumali RGI, Jayawardana JMCK (2021) A review of biological monitoring of aquatic ecosystems approaches: with special reference to macroinvertebrates and pesticide pollution. Environ Manage 67:263–276. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00267-020-01423-0
Tsaboula A, Menexes G, Papadakis EN, Vryzas Z, Kotopoulou A, Kintzikoglou K, Papadopoulou-Mourkidou E (2019) Assessment and management of pesticide pollution at a river basin level part II: optimization of pesticide monitoring networks on surface aquatic ecosystems by data analysis methods. Sci Total Environ. 653:1612–1622. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.10.270
Vais H, Williamson MS, Devonshire AL, Usherwood PN (2001) The molecular interactions of pyrethroid insecticides with insect and mammalian sodium channels. Pest Manag Sci 57(10):877–888
Wei G, Yang Z, Cui B, Li B, Chen H, Bai J, Dong S (2009) Impact of dam construction on water quality and water self-purification capacity of the Lancang River, China. Water Resour Manag 23(9):1763–1780
Weston DP, Poynton HC, Wellborn GA, Lydy MJ, Blalock BJ, Sepulveda MS, Colbourne JK (2013) Multiple origins of pyrethroid insecticide resistance across the species complex of a nontarget aquatic crustacean, Hyalella azteca. PNAS 110(41):16532–16537
Wongmaneepratip W, Leong M, Yang H (2022) Quantification and risk assessment of pyrethroid residues in seafood based on nanoparticle-extraction approach. Food Control. 133:108612
Xie W, Zhao J, Zhu X, Chen S, Yang X (2022) Pyrethroid bioaccumulation in wild fish linked to geographic distribution and feeding habit. J Hazard Mater 430:128470
Yoloğlu E (2019) Alterations in some biochemical responses of freshwater mussels in acute imidacloprid exposure. ADYUSCI 9(2):213–229
Yurdakök-Dikmen B, Arslan P, Kuzukıran Ö, Filazi A, Erkoç F (2018b) Unio sp. primary cell culture potential in ecotoxicology research. Toxin Rev 37(1):75–81
Yurdakök-Dikmen B, Vejselova D, Kutlu HM, Filazi A, Erkoç F (2018a) Effects of synthetic pyrethroids on RTG-2 cells. Toxin Rev 37(4):304–312
Zhang ZY, Yu XY, Wang DL, Yan HJ, Liu XJ (2010) Acute toxicity to zebrafish of two organophosphates and four pyrethroids and their binary mixtures. Pest Manag Sci 66(1):84–89. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.1834
Acknowledgements
Special thanks to Prof. Dr. A. Çağlan Günal for providing permethrin and tetramethrin and to Prof. Dr. Aylin Sepici-Dinçel for providing the Ellman’s reagent.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Funding
This study was funded partly by Çankırı Karatekin University Science Research Projects (Grand number FF210621B12).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PA designed the study, made the experiments and wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Bruno Nunes
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Arslan, P. Pyrethroid-induced oxidative stress and biochemical changes in the primary mussel cell cultures. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 48484–48490 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-25845-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-25845-5