Abstract
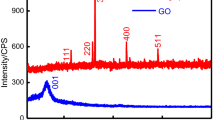
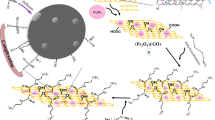
The current study involves the removal of Pb(II) ions from an aqueous solution using GO/Mn-Fe hybrids in a fixed bed column study. The capability of the hybrid in the Pb removal was examined using a continuous flow fixed bed column which revealed that the hybrid had the maximum adsorption capacity of 172.768 mg/g at a flow rate of 2 mL/min, bed height of 1 cm, and influent concentration of 200 mg/L. The breakthrough curves obtained from the experiments were examined using three different models, i.e., Bohart-Adams model, Thomas Model, and Yoon-Nelson model, wherein all the models showed high correlation coefficient values. Three consecutive adsorption–desorption cycles in the column yielded regeneration efficiencies of 91.71%, 88.31%, and 85.41%. The column life factor indicated that the fixed bed would have enough capacity to avoid a zero breakthrough time for up to 9 cycles, implying that GO/Mn-Fe could be used as a cheap and efficient adsorbent in the removal of Pb(II) from contaminated water. The adsorption mechanism was postulated based on the characterization of the spent adsorbent by FTIR and SEM. The phenomenon of the adsorption process can be described in accordance with the surface complex formation theory, which suggests that an increase in pH decreases the competition between metal ions and protons, favoring metal ion adsorption. The toxicity of the synthesized hybrid was evaluated on HeLa cells and compared to the toxicity of GO. Increasing the concentration of GO/Mn-Fe hybrid from 50 to 250 g/mL resulted in a decrease in cell viability from 91.90 to 56.52%, whereas increasing the concentration of GO resulted in a decrease in cell viability from 61.59 to 37.19%. The study clearly demonstrates the use of GO/Mn-Fe hybrid as an adsorbent for efficient sequestration of Pb(II) ions with lower environmental toxicity.














Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available within the submitted manuscript.
References
Aksu Z, Gönen F (2004) Biosorption of phenol by immobilized activated sludge in a continuous packed bed: prediction of breakthrough curves. Process Biochem 39:599–613. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-9592(03)00132-8
Bolisetty S, Peydayesh M, Mezzenga R (2019) Sustainable technologies for water purification from heavy metals: review and analysis. Chem Soc Rev 48:463–487. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8cs00493e
Carolin CF, Kumar PS, Saravanan A, Joshiba GJ, Naushad M (2017) Efficient techniques for the removal of toxic heavy metals from aquatic environment: a review. J Environ Chem Eng 5:2782–2799. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2017.05.029
de Franco MAE, de Carvalho CB, Bonetto MM, de Soares R, P., Féris, L.A., (2017) Removal of amoxicillin from water by adsorption onto activated carbon in batch process and fixed bed column: kinetics, isotherms, experimental design and breakthrough curves modelling. J Clean Prod 161:947–956. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.05.197
Dreyer DR, Park S, Bielawski CW, Ruoff RS (2010) The chemistry of graphene oxide. Chem Soc Rev 39:228–240. https://doi.org/10.1039/b917103g
Dreyer DR, Todd AD, Bielawski CW (2014) Harnessing the chemistry of graphene oxide. Chem Soc Rev 43:5288–5301. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4cs00060a
He X, Qiu X, Hu C, Liu Y (2018) Treatment of heavy metal ions in wastewater using layered double hydroxides: a review. J Dispersion Sci Technol 39:792–801. https://doi.org/10.1080/01932691.2017.1392318
Jang J, Lee DS (2016) Enhanced adsorption of cesium on PVA-alginate encapsulated Prussian blue-graphene oxide hydrogel beads in a fixed-bed column system. Biores Technol 218:294–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.06.100
Jawed, A., Saxena, V., Pandey, L.M., 2020. Engineered nanomaterials and their surface functionalization for the removal of heavy metals: a review. Journal of Water Process Engineering 33, 101009. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2019.101009
Kumar U, Bandyopadhyay M (2006) Fixed bed column study for Cd(II) removal from wastewater using treated rice husk. J Hazard Mater 129:253–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.08.038
Li B, Jin X, Lin J, Chen Z (2018) Green reduction of graphene oxide by sugarcane bagasse extract and its application for the removal of cadmium in aqueous solution. J Clean Prod 189:128–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.04.018
Li L, Fan L, Sun M, Qiu H, Li X, Duan H, Luo C (2013) Adsorbent for chromium removal based on graphene oxide functionalized with magnetic cyclodextrin-chitosan. Colloids Surf, B 107:76–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2013.01.074
Li X, Wang Z, Li Q, Ma J, Zhu M (2015) Preparation, characterization, and application of mesoporous silica-grafted graphene oxide for highly selective lead adsorption. Chem Eng J 273:630–637. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.03.104
Ma Z, Zhao D, Chang Y, Xing S, Wu Y, Gao Y (2013) Synthesis of MnFe2O4@Mn-Co oxide core-shell nanoparticles and their excellent performance for heavy metal removal. Dalton Trans 42:14261–14267. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3dt51310f
Mohan S, Singh DK, Kumar V, Hasan SH (2017a) Modelling of fixed bed column containing graphene oxide decorated by MgO nanocubes as adsorbent for lead(II) removal from water. J Water Process Eng 17:216–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2017.03.009
Mohan S, Singh DK, Kumar V, Hasan SH (2017b) Effective removal of fluoride ions by rGO/ZrO2 nanocomposite from aqueous solution: fixed bed column adsorption modelling and its adsorption mechanism. J Fluorine Chem 194:40–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfluchem.2016.12.014
Patel H (2019) Fixed-bed column adsorption study: a comprehensive review. Appl Water Sci 9:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-019-0927-7
Peng W, Li H, Liu Y, Song S (2017) A review on heavy metal ions adsorption from water by graphene oxide and its composites. J Mol Liq 230:496–504. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2017.01.064
Rahman Z, Singh VP (2019) The relative impact of toxic heavy metals (THMs) (arsenic (As), cadmium (Cd), chromium (Cr)(VI), mercury (Hg), and lead (Pb)) on the total environment: an overview. Environ Monit Assess 191. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7528-7
Rathour RKS, Bhattacharya J (2018) A green approach for single-pot synthesis of graphene oxide and its composite with Mn3O4. Appl Surf Sci 437:41–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.12.139
Rathour RKS, Bhattacharya J, Mukherjee A (2020) Selective and multicycle removal of Cr(VI) by graphene oxide–EDTA composite: insight into the removal mechanism and ionic interference in binary and ternary associations. Environ Technol Innov 19, 100851. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2020.100851
Rozhina E, Batasheva S, Miftakhova R, Yan X, Vikulina A, Volodkin D, Fakhrullin R (2021) Comparative cytotoxicity of kaolinite, halloysite, multiwalled carbon nanotubes and graphene oxide. Appl Clay Sci 205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2021.106041
Samuel MS, Selvarajan E, Subramaniam K, Mathimani T, Seethappan S, Pugazhendhi A (2020) Synthesized β-cyclodextrin modified graphene oxide (β-CD-GO) composite for adsorption of cadmium and their toxicity profile in cervical cancer (HeLa) cell lines. Process Biochem 93:28–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2020.02.014
Samuel MS, Shah SS, Bhattacharya J, Subramaniam K, Pradeep Singh ND (2018) Adsorption of Pb(II) from aqueous solution using a magnetic chitosan/graphene oxide composite and its toxicity studies. Int J Biol Macromol 115:1142–1150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.04.185
Volesky B, Weber J, Park JM (2003) Continuous-flow metal biosorption in a regenerable Sargassum column. Water Res 37:297–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(02)00282-8
Wang J, Chen Z, Chen B (2014) Adsorption of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by graphene and graphene oxide nanosheets. Environ Sci Technol 48:4817–4825. https://doi.org/10.1021/es405227u
Yang X, Wan Y, Zheng Y, He F, Yu Z, Huang J, Wang H, Ok YS, Jiang Y, Gao B (2019) Surface functional groups of carbon-based adsorbents and their roles in the removal of heavy metals from aqueous solutions: a critical review. Chem Eng J 366:608–621. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.02.119
Zhang G, Liu H, Liu R, Qu J (2009) Removal of phosphate from water by a Fe-Mn binary oxide adsorbent. J Colloid Interface Sci 335:168–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2009.03.019
Funding
All authors thank the School of Environmental Science and Engineering, Department of Civil Engineering and CRF IIT Kharagpur, for providing the infrastructure and instrumentation facilities. S Raj, H Singh, and A Hansda would like to acknowledge the MHRD, New Delhi, for providing financial assistance during the course of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Sankalp Raj: conceptualization, methodology, software, data analysis, writing – original draft, investigation.
Hemant Singh: data analysis, assistance to the investigation.
Arman Hansda: writing – original draft, data analysis, assistance to the investigation.
Ritobrata Goswami: supervision, writing – review and editing.
Jayanta Bhattacharya: supervision, writing – review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Tito Roberto Cadaval Jr
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Raj, S., Singh, H., Hansda, A.K. et al. Performance and cell toxicity studies for the use of graphene oxide-bimetallic oxide hybrids in the absorptive removal of Pb(II) from wastewater: fixed-bed column study with regeneration. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 124950–124963 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-25825-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-25825-9