Abstract
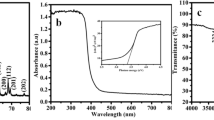
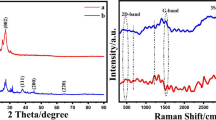
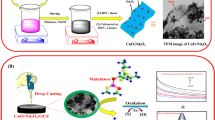
Clioquinol (CLQ) is one of the most toxic halogenated neurodegenerative drugs, and its synaptic plasticity effect directly affects human health and the environment. Cupric oxide (CuO) is an ideal electrocatalyst owing to its earth-abundance, non-toxic nature, and cost-effectiveness. Since phenolate oxygen and pyridine nitrogen in CLQ act as an electron donor and pave the way for detection with Cu2+ ions in the CuO. Designing the architecture of CuO with a multi-walled carbon nanotube (MWCNT) is a sensible strategy to improve the electrochemical activity of the developed sensor. Inspired by the bio-synthesis and green processing, we have demonstrated the in-situ synthesis of CuO nanosphere-decorated MWCNT by Chenopodium album leaf extract through a sonochemical approach and explored its electrochemical sensing performance toward CLQ. The physical comprehensive characterization of prepared nanocomposite was investigated by various microscopic and spectroscopic techniques. For comparison studies, the CuO nanosphere was prepared by the same preparation process without MWCNT. Based on the physical characterization outcomes, the morphological nature of CuO was observed to be a sphere-like structure, which was decorated on the MWCNT with an average crystallite size of 16 nm (± 1 nm). Based on the electrochemical studies, the fabricated nanocomposite exhibits a wider linear range of 0.025–1375 μM, with a minimum detection limit of 4.59 nM L–1 toward CLQ. The viability examination on the biological matrix obtained considerable spike recoveries.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available upon request.
References
Aminuzzaman M, Kei LM, Liang WH (2017) Green synthesis of copper oxide (CuO) nanoparticles using banana peel extract and their photocatalytic activities. AIP Conf Proc 1828:020016. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4979387
Anandalakshmi K (2021) Green Synthesis, characterization and antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles using Chenopodium album leaf extract. Indian J Pure Appl Phys 59:456–461
Barani M, Sabir F, Rahdar A et al (2020) Nanotreatment and nanodiagnosis of prostate cancer: recent updates. Nanomater 10:1696. https://doi.org/10.3390/NANO10091696
Bareggi SR, Cornelli U (2012) Clioquinol: review of its mechanisms of action and clinical uses in neurodegenerative disorders. CNS Neurosci Ther 18:41–46. https://doi.org/10.1111/J.1755-5949.2010.00231.X
Batool M, Nazar MF, Awan A et al (2021) Bismuth-based heterojunction nanocomposites for photocatalysis and heavy metal detection applications. Nano-Struct Nano-Objects 27:100762. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.NANOSO.2021.100762
Belal F, Sharaf El-Din MK, El EN, Saad S (2013) A validated liquid chromatographic method for the simultaneous determination of betamethasone valerate and clioquinol in creams using time programmed UV detection. Anal Methods 5:6767–6773. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3AY41138A
Benvenisti-Zarom L, Chen J, Regan RF (2005) The oxidative neurotoxicity of clioquinol. Neuropharmacology 49:687–694. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.NEUROPHARM.2005.04.023
Breadmore MC, Grochocki W, Kalsoom U et al (2019) Recent advances in enhancing the sensitivity of electrophoresis and electrochromatography in capillaries and microchips (2016–2018). Electrophoresis 40:17–39. https://doi.org/10.1002/ELPS.201800384
Chand Mali S, Raj S, Trivedi R (2019) Biosynthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles using Enicostemma axillare (Lam.) leaf extract. Biochem Biophys Reports 20:100699. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BBREP.2019.100699
Chen D, Cui QC, Yang H et al (2007) Clioquinol, a therapeutic agent for Alzheimer’s disease, has proteasome-inhibitory, androgen receptor–suppressing, apoptosis-inducing, and antitumor activities in human prostate cancer cells and xenografts. Cancer Res 67:1636–1644. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-3546
Chen M, Tao T, Zhang L et al (2013) Highly conductive and stretchable polymer composites based on graphene/MWCNT network. Chem Commun 49:1612–1614. https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CC38290C
Cuong HN, Pansambal S, Ghotekar S et al (2022) New frontiers in the plant extract mediated biosynthesis of copper oxide (CuO) nanoparticles and their potential applications: a review. Environ Res 203:111858. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENVRES.2021.111858
D. Schimmer A (2011) Clioquinol – a novel copper-dependent and independent proteasome inhibitor. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 11:325–331
Degen PH, Schneider W, Vuillard P et al (1976) The determination of clioquinol in biological materials by extractive alkylation and gas-liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A 117:407–413. https://doi.org/10.1016/0021-9673(76)80018-0
Dhineshbabu NR, Rajendran V, Nithyavathy N, Vetumperumal R (2016) Study of structural and optical properties of cupric oxide nanoparticles. Appl Nanosci 6:933–939. https://doi.org/10.1007/S13204-015-0499-2
Ding WQ, Lin B, Vaught JL et al (2005) Anticancer activity of the antibiotic clioquinol. Cancer Res 65:3389–3395. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-3577
Dwivedi AD, Gopal K (2010) Biosynthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles using Chenopodium album leaf extract. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem Eng Asp 369:27–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.COLSURFA.2010.07.020
Gangula A, Podila R, Ramakrishna M et al (2011) Catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol using biogenic gold and silver nanoparticles derived from Breynia rhamnoides. Langmuir 27:15268–15274. https://doi.org/10.1021/LA2034559
Hajnorouzi A (2020) Two ultrasonic applications for the synthesis of nanostructured copper oxide (II). Ultrason Sonochem 64:105020. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ULTSONCH.2020.105020
Jahan S, Azad T, Ayub A et al (2019) Ameliorating potency of Chenopodium album Linn. and vitamin C against mercuric chloride-induced oxidative stress in testes of Sprague Dawley rats. Environ Health Prev Med 24:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1186/S12199-019-0820-X
Ji HF, Shen L, Zhang HY (2005) β-Lactam antibiotics are multipotent agents to combat neurological diseases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 333:661–663. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BBRC.2005.05.014
Karthik R, Vinoth Kumar J, Chen SM et al (2017) Investigation on the electrocatalytic determination and photocatalytic degradation of neurotoxicity drug clioquinol by Sn(MoO4)2 nanoplates. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:26582–26592. https://doi.org/10.1021/ACSAMI.7B06851/SUPPL_FILE/AM7B06851_SI_001.PDF
Kawamura K, Kuroda Y, Sogo M et al (2014) Superoxide dismutase as a target of clioquinol-induced neurotoxicity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 452:181–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BBRC.2014.04.067
Kokulnathan T, Wang TJ (2019) Synthesis and characterization of 3D flower-like nickel oxide entrapped on boron doped carbon nitride nanocomposite: an efficient catalyst for the electrochemical detection of nitrofurantoin. Compos Part B Eng 174:106914. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.COMPOSITESB.2019.106914
Kokulnathan T, Raja N, Chen S-M et al (2017) Chitosan stabilized multi-walled carbon nanotubes for electrochemical determination of dihydroxybenzene isomers. J Electrochem Soc 164:H958–H966. https://doi.org/10.1149/2.1571713JES/XML
Kokulnathan T, Sakthi Priya T, Wang TJ (2019) Surface engineering three-dimensional flowerlike cerium vanadate nanostructures used as electrocatalysts: real time monitoring of clioquinol in biological samples. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 7:16121–16130. https://doi.org/10.1021/ACSSUSCHEMENG.9B02891/SUPPL_FILE/SC9B02891_SI_001.PDF
Kokulnathan T, Rajagopal V, Wang TJ et al (2021a) Electrochemical behavior of three-dimensional cobalt manganate with flowerlike structures for effective roxarsone sensing. Inorg Chem 60:17986–17996. https://doi.org/10.1021/ACS.INORGCHEM.1C02583
Kokulnathan T, Wang TJ, Kumar EA et al (2021c) An electrochemical platform based on yttrium oxide/boron nitride nanocomposite for the detection of dopamine. Sensors Actuators B Chem 349:130787. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SNB.2021.130787
Kokulnathan T, Wang TJ, Kumar EA, Liu ZY (2021d) Zinc manganate: synthesis, characterization, and electrochemical application toward flufenamic acid detection. Inorg Chem 60:4723–4732. https://doi.org/10.1021/ACS.INORGCHEM.0C03672
Kokulnathan T, Wang T-J, Ashok Kumar E, Ahmed F (2021b) Construction of nickel cobalt-layered double hydroxide/functionalized–halloysite nanotubes composite for electrochemical detection of organophosphate insecticide. Chem Eng J 133639. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CEJ.2021.133639
Kokulnathan T, Sriram B, Pandiyarajan S, et al (2022) Introduction to biowaste-derived materials. Biomass‐Derived Carbon Mater 27–61. https://doi.org/10.1002/9783527832903.CH2
Koventhan C, Pandiyarajan S, Chen SM (2022) Simple sonochemical synthesis of flake-ball shaped bismuth vanadate for voltammetric detection of furazolidone. J Alloys Compd 895:162315. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JALLCOM.2021.162315
Li Y, Cheng C, Yang YP et al (2019) A novel electrochemical sensor based on CuO/H-C3N4/rGO nanocomposite for efficient electrochemical sensing nitrite. J Alloys Compd 798:764–772. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JALLCOM.2019.05.137
Manjari G, Saran S, Arun T et al (2017) Catalytic and recyclability properties of phytogenic copper oxide nanoparticles derived from Aglaia elaeagnoidea flower extract. J Saudi Chem Soc 21:610–618. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JSCS.2017.02.004
Mao X, Li X, Sprangers R et al (2008) Clioquinol inhibits the proteasome and displays preclinical activity in leukemia and myeloma. Leuk 23:585–590. https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2008.232
Masjedi-Arani M, Salavati-Niasari M (2016) A simple sonochemical approach for synthesis and characterization of Zn2SiO4 nanostructures. Ultrason Sonochem 29:226–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ULTSONCH.2015.09.020
Nagajyothi PC, Muthuraman P, Sreekanth TVM et al (2017) Green synthesis: in-vitro anticancer activity of copper oxide nanoparticles against human cervical carcinoma cells. Arab J Chem 10:215–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ARABJC.2016.01.011
Najeeb J, Farwa U, Ishaque F et al (2022) Surfactant stabilized gold nanomaterials for environmental sensing applications – a review. Environ Res 208:112644. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENVRES.2021.112644
Pandiyarajan S, Ganesan M, Liao AH et al (2021a) Ultrasonic-assisted supercritical-CO2 electrodeposition of Zn-Co film for high-performance corrosion inhibition: a greener approach. Ultrason Sonochem 72:105463. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ULTSONCH.2021.105463
Pandiyarajan S, Hsiao PJ, Liao AH et al (2021c) Influence of ultrasonic combined supercritical-CO2 electrodeposition process on copper film fabrication: electrochemical evaluation. Ultrason Sonochem 74:105555. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ULTSONCH.2021.105555
Pandiyarajan S, Srinivasan R, Manickaraj SSM et al (2022) Robust fabrication of silver pyro-vanadates via sonochemical approach for advanced energy storage application. J Alloys Compd 893:162268. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JALLCOM.2021.162268
Pandiyarajan S, Manickaraj SSM, Liao A-H et al (2023) Coherent construction of recovered γ-Al2O3 embedded N-doped activated carbon by supercritical-CO2 pathway: robust hybrid electrode material for energy storage device. J Alloys Compd 936:168213. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JALLCOM.2022.168213
Pandiyarajan S, Manickaraj SSM, Liao AH et al (2023) Recovery of Al2O3 from hazardous Al waste as a reinforcement particle for high-performance Ni/Al2O3 corrosion resistance coating via ultrasonic-aided supercritical-CO2 electrodeposition. Chemosphere 313:137626. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CHEMOSPHERE.2022.137626
Pandiyarajan S, Hsiao PJ, Liao AH, et al (2021b) High-performance polyvinylpyrrolidone capped copper coatings via ultrasonic-assisted supercritical-CO2 electrodeposition: electrochemical evaluation. Surf Coatings Technol 409. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SURFCOAT.2021.126926
Pandiyarajan S, Liu ZC, Liao AH, et al (2021d) High-performance anti-corrosion behavior of graphene oxide decorated nickel coating by novel ultrasonic-assisted supercritical-CO2 electrodeposition approach. Electrochim Acta 387. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ELECTACTA.2021.138543
Patel VK, Bhattacharya S (2013) High-performance nanothermite composites based on aloe-vera-directed CuO nanorods. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5:13364–13374. https://doi.org/10.1021/AM404308S
Pollet BG, Ashokkumar M (2019) Introduction to ultrasound, sonochemistry and sonoelectrochemistry, Springer Nature Swi…. Springer International Publishing, Cham
Pourmadadi M, Rajabzadeh-Khosroshahi M, Tabar FS et al (2022a) Two-dimensional graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4) nanosheets and their derivatives for diagnosis and detection applications. J Funct Biomater 13:204. https://doi.org/10.3390/JFB13040204
Pourmadadi M, Yazdian F, Ghorbanian S et al (2022b) Construction of aptamer-based nanobiosensor for breast cancer biomarkers detection utilizing g-C3N4/magnetic nano-structure. Biosens 12:921. https://doi.org/10.3390/BIOS12110921
Pourmadadi M, Rahmani E, Rajabzadeh-Khosroshahi M et al (2023) Properties and application of carbon quantum dots (CQDs) in biosensors for disease detection: a comprehensive review. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 80:104156. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JDDST.2023.104156
Qi JQ, Tian HY, Li LT, Chan HLW (2007) Fabrication of CuO nanoparticle interlinked microsphere cages by solution method. Nanoscale Res Lett 2:107–111. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11671-007-9039-7/METRICS
Rizwan K, Rahdar A, Bilal M, Iqbal HMN (2022) MXene-based electrochemical and biosensing platforms to detect toxic elements and pesticides pollutants from environmental matrices. Chemosphere 291:132820. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CHEMOSPHERE.2021.132820
Rothstein JD, Patel S, Regan MR et al (2005) β-Lactam antibiotics offer neuroprotection by increasing glutamate transporter expression. Nat 2004 433(7021):73–77. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature03180
Sakthinathan S, Kokulnathan T, Chen S-M et al (2019) Simple sonochemical synthesis of cupric oxide sphere decorated reduced graphene oxide composite for the electrochemical detection of flutamide drug in biological samples. J Electrochem Soc 166:B68–B75. https://doi.org/10.1149/2.0561902JES/XML
Shekh MI, Amirian J, Du B et al (2020) Electrospun ferric ceria nanofibers blended with MWCNTs for high-performance electrochemical detection of uric acid. Ceram Int 46:9050–9064. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CERAMINT.2019.12.153
Sivasankarapillai VS, Somakumar AK, Joseph J et al (2020) Cancer theranostic applications of MXene nanomaterials: recent updates. Nano-Struc Nano-Objects 22:100457. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.NANOSO.2020.100457
Sriram B, Baby JN, Wang SF et al (2020) Cobalt molybdate nanorods decorated on boron-doped graphitic carbon nitride sheets for electrochemical sensing of furazolidone. Microchim Acta 187:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00604-020-04590-3
Sriram B, Baby JN, Hsu Y-F et al (2021a) Zirconium phosphate supported on g-C3N4 nanocomposite for sensitive detection of nitrite. J Electrochem Soc 168:087502. https://doi.org/10.1149/1945-7111/AC1707
Sriram B, Baby JN, Wang SF et al (2021b) Surface engineering of three-dimensional-like hybrid AB2O4 (AB = Zn Co, and Mn) wrapped on sulfur-doped reduced graphene oxide: investigation of the role of an electrocatalyst for clioquinol detection. ACS Appl Electron Mater 3:362–372. https://doi.org/10.1021/ACSAELM.0C00906
Tan X, Yue X, Yuan M et al (2020) Solid-state microwave synthesis CuO/CNT: a high-performance electrode material for supercapacitors. NANO 15:2050102. https://doi.org/10.1142/S1793292020501027
Vats T, Gogoi R, Gaur P et al (2017) Pristine graphene-copper(II) oxide nanocatalyst: a novel and green approach in CuAAC reactions. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 5:7632–7641. https://doi.org/10.1021/ACSSUSCHEMENG.7B00960/
Vijayaraghavan K, Ashokkumar T (2017) Plant-mediated biosynthesis of metallic nanoparticles: a review of literature, factors affecting synthesis, characterization techniques and applications. J Environ Chem Eng 5:4866–4883. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JECE.2017.09.026
Wang W, Zhou Q, Fei X et al (2010) Synthesis of CuO nano- and micro-structures and their Raman spectroscopic studies. CrystEngComm 12:2232–2237. https://doi.org/10.1039/B919043K
Wang J, Chang Y, Zhang P et al (2015) Cu2+-mediated fluorescence switching of gold nanoclusters for the selective detection of clioquinol. Analyst 140:8194–8200. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5AN01975C
Yang Z, Shen J, Li J et al (2013) An ultrasensitive streptavidin-functionalized carbon nanotubes platform for chemiluminescent immunoassay. Anal Chim Acta 774:85–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ACA.2013.02.041
Zedan AF, Mohamed AT, El-Shall MS et al (2018) Tailoring the reducibility and catalytic activity of CuO nanoparticles for low temperature CO oxidation. RSC Adv 8:19499–19511. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8RA03623C
Zhan Y, Bai J, Guo F et al (2021) Facile synthesis of biomass-derived porous carbons incorporated with CuO nanoparticles as promising electrode materials for high-performance supercapacitor applications. J Alloys Compd 885:161014. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JALLCOM.2021.161014
Zhao J, Fan Z (2020) Using zinc ion-enhanced fluorescence of sulfur quantum dots to improve the detection of the zinc(II)-binding antifungal drug clioquinol. Microchim Acta 187:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00604-019-4020-6
Acknowledgements
The authors express sincere gratitude to Professor C.Y. Lee and his research team at the Department of Mechanical Engineering and Professor Sheng Tung Huang and his research team at the Department of Chemical Engineering, National Taipei University of Technology, for providing technical support. The authors acknowledged the management of Bishop Heber College (Autonomous), Tiruchirappalli -620 017, Tamil Nadu, India for the constant encouragement and facilities rendered by means of Material Chemistry Lab, PG and Research Department of Chemistry and DST-FIST Instrumentation Centre (HAIF) for Scientific Instrumentation.
Funding
This work was supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST), Taiwan, under contract number MOST 111–2628-E-027–004-MY3.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Sabarison Pandiyarajan: study’s conception, design, and first draft of the manuscript written.
Gurunathan Velayutham: material design and data curation.
Ai-Ho Liao: resource and formal analysis.
Shobana Sebastin Mary Manickaraj: software handle, data curation, and formal analysis.
Balaji Ramachandran: data curation and formal analysis.
Kuo-Yu Lee: resource and formal analysis.
Ho-Chiao Chuang: resource, supervision, formal analysis, and fund acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
All authors have agreed to participate in this work.
Consent for publication
All authors have approved and agreed to publish the work in the Environmental Science and Pollution Research.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: George Z. Kyzas
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Pandiyarajan, S., Velayutham, G., Liao, AH. et al. A biogenesis construction of CuO@MWCNT via Chenopodium album extract: an effective electrocatalyst for synaptic plasticity neurodegenerative drug pollutant detection. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 79744–79757 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-25629-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-25629-x