Abstract
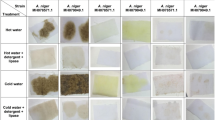
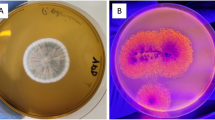
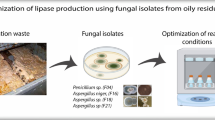
Oils and grease (O&G) have low affinity for water and represent a class of pollutants present in the dairy industry. Enzyme-mediated bioremediation using biocatalysts, such as lipases, has shown promising potential in biotechnology, as they are versatile catalysts with high enantioselectivity and regioselectivity and easy availability, being considered a clean technology (white biotechnology). Specially in the treatment of effluents from dairy industries, these enzymes are of particular importance as they specifically hydrolyze O&G. In this context, the objective of this work is to prospect filamentous fungi with the ability to synthesize lipases for application in a high-fat dairy wastewater environment. We identified and characterized the fungal species Aspergillus sclerotiorum as a good lipase producer. Specifically, we observed highest lipolytic activity (20.72 U g−1) after 96 h of fermentation using sunflower seed as substrate. The fungal solid fermented was used in the bioremediation in dairy effluent to reduce O&G. The experiment was done in kinetic from 24 to 168 h and reduced over 90% of the O&G present in the sample after 168 h. Collectively, our work demonstrated the efficiency and applicability of fungal fermented solids in bioremediation and how this process can contribute to a more sustainable wastewater pretreatment, reducing the generation of effluents produced by dairy industries.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable.
References
Abid M, Sayegh S, Iatsunskyi I, Coy E, Lesage G, Ramanavicius A, Amara ABH, Bechelany M (2022) Design of halloysite-based nanocomposites by electrospinning for water treatment. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 651:129696. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2022.129696
Adulkar TV, Rathod VK (2014) Ultrasound assisted enzymatic pre-treatment of high fat content dairy wastewater, Ultrasound assisted enzymatic pre-treatment of high fat content dairy wastewater. Ultrason. Sonochem 2:1083–1089. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2013.11.017
Ahmad T, Aadil RM, Ahmed H, Rahman UU, Soares BC, Souza SL, Pimentel TC, Scudino H, Guimarães JT, Esmerino EA, Freitas MQ, Almada RB, Vendramel SMR, Silva MC, Cruz AG (2019) Treatment and utilization of dairy industrial waste: a review. Trends Food Sci. Technol 88:361–372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2019.04.003
Akram F, Aqeel A, Shoaib M, Shah FI (2022a) Multifarious revolutionary aspects of microbial keratinases: an efficient green technology for future generation with prospective applications. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res 1-20. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23638-w
Akram F, Mir AS, Roohi A (2022b) An appraisal on prominent industrial and biotechnological applications of bacterial lipases. Mol. Biotechnol 1-23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-022-00592-z
Alberton D, Mitchell DA, Cordova J, Zamora P, Krieger N (2010) Production of a fermented solid containing lipases of Rhizopus microsporus and its application in the pre-hydrolysis of a high-fat dairy wastewater Food Technol. Biotechnol 48:28–35
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer A, Zhang JH, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) gapped blast and psi-blast: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/25.17.3389
Alves AM, Moura RB, Carvalho AKF, Castro HF, Andrade GS (2019) Penicillium citrinum whole-cells catalyst for the treatment of lipid-rich wastewater. Biomass Bioenergy 120:433–438. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2018.12.004
AOAC - Association of Official Analytical Chemists (2005) Official Methods of analysis of AOAC International, 18th edn. AOAC, Washington
Apha A (1995) WPCF, Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. American Public Health Association/American Water Works Association/Water Environment Federation, Washington DC, USA
Apha A (2012) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 22nd edition. Edited by RICE E W, BAIRD R B, EATON A D, CLESCERI L S. American Public Health Association (APHA), American Water Works Association (AWWA) and Water Environment Federation (WEF), Washington, D.C., USA
Asemoloye MD, Marchisio MA (2022) Synthetic Saccharomyces cerevisiae tolerate and degrade highly pollutant complex hydrocarbon mixture. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 241:113768. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2022.113768
Barrios-Gonzáles J (2012) Solid-state fermentation: physiology of solid medium, its molecular basis and applications. Process Biochem 47(2):175–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2011.11.016
Basheer SM, Chellappan S, Beena PS, Sukumaran RK, Elyas K, Chandrasekaran M (2011) Lipase from marine Aspergillus awamori BTMFW032: production, partial purification and application in oil effluent treatment. N Biotechnol 28(6):627–638. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbt.2011.04.007
Bharathi D, Rajalakshmi G (2019) Microbial lipases: an overview of screening, production and purification. Biocat and Agric Biotec 22:101368. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2019.101368
Çakmak M, Aydoğdu H (2021) Screening of microfungi for lipolytic activity and optimization of process parameters in lipase production by solid substrate fermentation using selected microfungi (Penicillium aurantiogriseum). Kuwait J of Sci 48:98–105
Carvalho ACLDM, Fonseca TDS, Mattos MCD, Oliveira MDCFD, Lemos TLGD, Molinari F, Romano D, Serra I (2015) Recent advances in lipase-mediated preparation of pharmaceuticals and their intermediates. Int J Mol Sci 16:29682–29716. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161226191
Carvalho JK, Panatta AS, Silveira MAD, Tav C, Johann S, Rodrigues MLF, Martins CVB (2021) Yeasts isolated from a lotic continental environment in Brazil show potential to produce amylase, cellulase and protease. Biotec Reports 30:e00630. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.btre.2021.e00630
CONAMA - conselho Nacional de Meio Ambiente. Legislação Ambiental Federal, Resolução n° 430, de 13 de maio de 2011. Dispõe sobre a classificação dos corpos de água e diretrizes ambientais para o seu enquadramento, bem como estabelece as condições e padrões de lançamento de efluentes e de outras providências
Dalmau E, Montesinos JL, Lotti M, Casas C (2000) Effect of different carbon sources on lipase production by Candida rugosa. Enzyme Microb Technol 26:657–663. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0141-0229(00)00156-3
de Souza CEC, Ribeiro BD, Coelho MAZ (2019) Characterization and application of Yarrowia lipolytica lipase obtained by solid-state fermentation in the synthesis of different esters used in the food industry. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 189(3):933–959. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-019-03047-5
Deiner K, Bik HM, Mächler E, Seymour M, Lacoursière-Roussel A, Altermatt F, Creer S, Bista I, Lodge BM, Vere N, Pfrender ME (2017) Bernatchez L (2017) Environmental DNA metabarcoding: transforming how we survey animal and plant communities. Mol Ecol 26(21):5872–5895. https://doi.org/10.1111/mec.14350
Fatima S, Faryad A, Ataa A, Joyia FA, Parvaiz A (2020) Microbial lipase production: a deep insight into the recent advances of lipase production and purification techniques. Biotec and App Biochem 68:445–458. https://doi.org/10.1002/bab.2019
Feng K, Huang Z, Peng B, Dai W, Li Y, Zhu X, Chen Y, Tong X, Lan Y, Cao Y (2020) Immobilization of Aspergillus niger lipase onto a novel macroporous acrylic resin: Stable and recyclable biocatalysis for deacidification of high-acid soy sauce residue oil. Biores Tec 298:122553. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.122553
Geoffry K, Achur RN (2018) Screening and production of lipase from fungal organisms. Bioc and Agric Biotec 14:241–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2018.03.009
Giner CR, Forn I, Romac S, Logares R, De Vargas C, Massana R (2016) Environmental sequencing provides reasonable estimates of the relative abundance of specific picoeukaryotes. Appl Environ Microbiol 82(15):4757–4766. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00560-16
Grajales-Hernández DA, Velasco-Lozano S, Armendáriz-Ruiz MA, Rodríguez-González JA, Camacho-Ruíz RM, Asaff-TOrres A, Mateos-Díaz JC (2020) Carrier-bound and carrier-free immobilization of type A feruloyl esterase from Aspergillus niger: searching for an operationally stable heterogeneous biocatalyst for the synthesis of butyl hydroxycinnamates. J Biotechnol 316:6–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2020.04.004
Gurd C, Villa R, Jefferson B (2020) Understanding why fat, oil and grease (FOG) bioremediation can be unsuccessful. J Environ Manage 267:110647. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110647
Hankin L, Anagnostakis SL (1975) The use of solid media for detection of enzyme production by fungi. Mycologia 67(3):597–607. https://doi.org/10.1080/00275514.1975.12019782
Hering D, Borja A, Jones JI, Pont D, Boets P, Bouchez A, Bruce K, Drakare S, Hänflingi B, Kahlert M, Leese F, Meissner K, Mergen P, Reyjol Y, Segurado P, Vogler A, Kelly M (2018) Implementation options for DNA-based identification into ecological status assessment under the European Water Framework Directive. Water Res 138:192–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2018.03.003
Javed S, Azeem F, Hussain S, Rasul I, Sidsique MH, Riaz M, Afzal M, Kouser A, Nadem H (2018) Bacterial lipases: a review on purification and characterization. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 132:23–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2017.07.014
Kapoor M, Gupta MN (2012) Lipase promiscuity and its biochemical applications. Process Biochem 47:555–569. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2012.01.011
Kirk P M, Cannon P F, Minter D W, Stalpers J A (2008) Dictionary of the Fungi. (10thedn). Wallingford, UK
Kreling NE, Simon V, Fagundes VD, Thomé A, Colla LM (2021) Improving the bioremediation and in situ production of biocompounds of a biodiesel-contaminated soil. Environ Manage 68(2):210–225
Ktata A, Krayem N, Aloulou A, Bezzine S, Sayari A, Chamkha M, Karray A (2020) Purification, biochemical and molecular study of lipase producing from a newly thermoalkaliphilic Aeribacillus pallidus for oily wastewater treatment. J Biochem 167(1):89–99. https://doi.org/10.1093/jb/mvz083
Lee LP, Karbul HM, Citartan M, GOpinath SCB (2015) Lipase-secreting Bacillus species in an oil-contaminated habitat: promising strains to alleviate oil pollution. Biomed Res. Int 2015:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/820575
Leite RMVBC, Brighenti AM, Castro C (2005) Girassol no Brasil. Londrina: Embrapa, 641p
Lima RT, Alves AM, De Paula AV, De Castro HF, Andrade GS (2019) Mycelium-bound lipase from Penicillium citrinum as biocatalyst for the hydrolysis of vegetable oils. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 22:101410–101420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2019.101410
Mahmoud GA, Koutb M, Morsy FM, Bagy M (2015) Characterization of lipase enzyme produced by hydrocarbons using fungus Aspergillus terreus. Eur J of Biol Res 5:70–77
Manfrin J, Schwantes D, Gonçalves JRAC, Ferronato MC, Aleixo V, Schiller ADP (2018) Contamination by lead in sediments at Toledo River, hydrographic basin of PARANÁ III. Environ Monit Assess 190(4):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6611-9
Medinger R, Nolte V, Pandey RV, Jost S (2010) Diversity in a hidden world: potential and limitation of next-generation sequencing for surveys of molecular diversity of eukaryotic microorganisms. Mol Ecol 19:32–40. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-294X.2009.04478.x
Mostafa FA, Abd El Aty A, Hamed ER, Eid BM, Ibrahim NA (2016) Enzymatic, kinetic and anti-microbial studies on Aspergillus terreus culture filtrate and Allium cepa seeds extract and their potent applications. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 5:116–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2016.01.005
Oliveira ACD, Watanabe FMF, Rodrigues MLF, Vargas JVC, Mariano AB (2013) Lipase production by endophytic yeast through factorial design. Acad J Microbiol Res 1:16–21
Pereira ADS, Fontes-Sant’Ana GC, Amaral PF (2019) Mango agro-industrial wastes for lipase production from Yarrowia lipolytica and the potential of the fermented solid as a biocatalyst. Food Bioprod Process 115:68–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fbp.2019.02.002
Pintor AMA, Vilar VJP, Botelho CMS, Boaventura RAR (2016) Oil and grease removal from wastewaters: Sorption treatment as an alternative to state-of-the-art technologies. A Critical Review J Chem Eng 297:229–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.03.121
Priji P, Unni KN, Sreedharan S, Binod P, Benjamin S (2014) Production, optimization, and partial purification of lipase from Pseudomonas sp. strain BUP6, a novel rumen bacterium characterized from Malabari goat. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 62:71–78
Rodrigues MLF, Da Silva EA, Borba CE, Oliveira ACD, Kruger C, Raimundo RW, Silva LP, Vanzin M, Stuani BT (2015) Produção de enzimas hidrolíticas pelo fungo endofítico Penicillium sp. Isolado das folhas de Ricinus communis L. Revista Brasileira De Energias Renováveis 4:129–145
Rosa LH, Ogaki MB, Lirio JM, Vieira R, Coria SH, Pinto OHB, Carvalho-Silva M, Transporte P, Rosa CA, Câmera PEAS (2022) Fungal diversity in a sediment core from climate change impacted Boeckella Lake, Hope Bay, north-eastern Antarctic Peninsula assessed using metabarcoding. Extremophiles 26(2):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-022-01264-1
Samson RA, Visagie CM, Houbraken J, Hong SB, Hubka V, Klaassen CHW, Perrone G, Seifert KA, Susca A, Tanney JB, Varga J, Kocsubé S, Szigeti G, Yaguchi T, Frisvad JC (2014) Phylogeny, identification and nomenclature of the genus Aspergillus. Stud Mycol 78:141–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.simyco.2014.07.004
Sattar H, Bibi Z, Kamran A, Aman A, Qader SAU (2019) Degradation of complex casein polymer: production and optimization of a novel serine metalloprotease from Aspergillus niger KIBGE-IB36. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 21:101256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2019.101256
Steudler S, Werner A, Walther T (2019) It is the mix that matters: Substrate-specific enzyme production from filamentous fungi and bacteria through solid-state fermentation. Sol State Ferment 51-81. https://doi.org/10.1007/10_2019_85
Tedersoo L, Sánchez-Ramírez S, Kõljalg U, Bahram M, Döring M, Schigel D, May T, Ryberg M, Abarenkov K (2018) High-level classification of the Fungi and a tool for evolutionary ecological analyses. Fungal Divers 90(1):135–159. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13225-018-0401-0
Thakur V, Tewari R, Sharma R (2014) Evaluation of production parameters for maximum lipase production by P. stutzeri MTCC 5618 and scale-up in bioreactor. Chin J Biol 2014:1–14
Utami TS, Hariyani I, Alamsyah G, Hermansyah H (2017) Production of dry extract extracellular lipase from Aspergillus niger by solid state fermentation method to catalyze biodiesel synthesis. Energy Procedia 136:41–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2017.10.275
Vilela D, Andrade RG, Leite JLB, Hott MC, De Magalhães Junior WCP (2022) Produção de leite no cerrado: conjuntura e análises
Weber AA, Pawlowski J (2013) Can abundance of protists be inferred from sequence data: a case study of Foraminifera. PLoS ONE 8:e56739. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0056739
White TJ, Bruns TD, Lee SB, Taylor JW (1990) Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribossomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In: Gelfand NA, Gelfand J, White TJ (eds) PCR protocols: a guide of methods and applications. Academic Press, San Diego, CA, USA, pp 315–322
Zaitsev SY, Savina A, Zaitsev IS (2019) Biochemical aspects of lipase immobilization at polysaccharides for biotechnology. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 272:102016–102016. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2019.102016
Zulkifli N, Rasit N (2020) Lipase production from solid state fermentation of copra waste associated fungus Aspergillus niger. UMT J Undergrad Res 2:2
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Jéssyca Ketterine Carvalho, Jaíne Daiane de Moura Dickel, Maria Luiza Fernandes Rodrigues, Carlos Augusto Rosa, Susana Johann, and Ana Raquel de Oliveira Santos. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Jaíne Daiane de Moura Rodrigues, Jéssyca Ketterine Carvalho, Maria Luiza Fernandes Rodrigues, Maruhen Amir Datsch Silveira, Paulo Menegotto, Marcia Regina Fagundes-Klen, Cleide Viviane Buzanello-Martins, Rosemeire Aparecida da Silva De Lucca, and Mauricio Ferreira da Rosa, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
We consented.
Consent for publication
We consented.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: George Z. Kyzas
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
de Moura Dickel, J.D., Carvalho, J.K., Silveira, M.A.D. et al. Aspergillus sclerotiorum lipolytic activity and its application in bioremediation of high-fat dairy wastewater environments. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 35517–35527 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-24669-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-24669-z