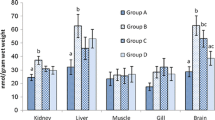
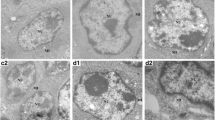
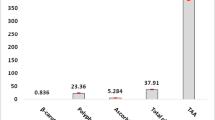
Abstract
Lead is one of the major pollutants that is harmful to both animals and humans. It is found in every aspect of the environment such as the air, water, and soil. This pollutant affects both wild and domestic birds. Naringin has an active principle called flavonoid that has been found to have medicinal properties, mostly because of its antioxidant and metal chelating properties. This study was carried out to investigate the protective effect of naringin as an antioxidant against lead-induced anemia, cardio and nephrotoxicity, and hypertension. This study also aimed at elucidating the use of naringin as a heavy metal binder in poultry feed. Thirty-six cockerel chicks were used for this study, and randomly grouped into six groups per group; group A served as the control, group B received Pb-only (300 ppm), group C (Pb and naringin; 80 mg/kg), group D (Pb and naringin; 160 mg/kg), group E (naringin 80 mg/kg), and group F (naringin 160 mg/kg), respectively, for 8 weeks. Lead (Pb) was administered via drinking water, while naringin was administered via oral gavage. Lead acetate intoxication precipitated anemia as indicated by significant reductions in the values of PCV, RBC, and Hb concentration in lead-treated chicks when compared with the controls. Also, lead administration induced hypertension together with increased oxidative stress, depletion of the antioxidant defense system, reduced nitric oxide production, and an increase in high blood pressure. Immunohistochemistry indicated high expressions of cardiac troponin, renal angiotensin-converting enzymes, and renal neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin. Treatment with naringin corrected anemia, reduced oxidative stress, improved antioxidant system, reduced high blood pressure, and offered protection against lead acetate-induced cardio-renal dysfunction in cockerel chicks. We recommend that naringin should be incorporated poultry feeds as a metal binder.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on request.
Abbreviations
- IHC:
-
Immunohistochemistry
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- GPx:
-
Glutathione peroxidase
- GSH:
-
Reduced glutathione
- GST:
-
Gluthaione S-transferase
- NO:
-
Nitric oxide
- MPO:
-
Myeloperoxidase
- MDA:
-
Malondialdhyde
- H2O2 :
-
Hydrogen peroxide
- EDC:
-
Endocrine-disrupting chemical
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- NF-κβ:
-
Nuclear factor kappa
- TP:
-
Total protein
- RBC:
-
Red blood cell
- WBC:
-
White blood cell
- Hb:
-
Hemoglobulin
- ALA:
-
Aminolaevulinic acid
- PCV:
-
Packed cell volume
- NGAL:
-
Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin
- ACE:
-
Angiotensin-converting enzyme
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor alpha
- HTN:
-
Hypertension
- BUN:
-
Blood urea nitrogen
- Pb:
-
Lead
- ECG:
-
Electrocardiogram
- ANOVA:
-
Analysis of variance
- GSSG:
-
Oxidized glutathione
- TBA:
-
Thiobarbituric acid
- CDNB:
-
1, 2-Dichloro-2, 4-dinitrobenzene
- δ-ALAD:
-
Delta-aminolaevulinic acid dehydratase
References
Ahmad A, Dempsey SK, Daneva Z, Azam M, Li N, Li P, Ritter JK (2018) Role of nitric oxide in the cardiovascular and renal systems. Int J Mol Sci 19:2605
Ajarem JS, Hegazy AK, Allam GA, Allam AA, Maodaa SN, Mahmoud AM (2021) Effect of visnagin on altered steroidogenesis and spermatogenesis, and testicular injury induced by the heavy metal lead. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen 24(6):758–766
Akinlolu AA, Ameen MO, Oyewopo AO, Kadir RE, Ahialaka O, Tijani S, Ogungbesan O, Bebeyi R, Adebayo S, Amoo T, Abdulazeez M (2021) Anticancer effects of Morinda lucida and Annona muricata on immunomodulations of melatonin, tumor necrosis factor-alpha and p53 concentrations in lead acetate-induced toxicity in rats. Int J Health Sci (qassim) 15(4):20–28
Alam MA, Kauter K, Brown L (2013) Naringin improves diet-induced cardiovascular dysfunction and obesity in high carbohydrate, high fat diet-fed rats. Nutrients 5(3):637–650
Al-Brakati A, Alsharif KF, Alzahrani KJ, Kabrah S, Al-Amer O, Oyouni AA, Habotta OA, Lokman MS, Bauomy AA, Kassab RB, Abdel Moneim AE (2021) Using green biosynthesized lycopene-coated selenium nanoparticles to rescue renal damage in glycerol-induced acute kidney injury in rats. Int J Nanomedicine 16:4335–4349
Amini N, Sarkaki A, Dianat M, Mard SA, Ahangarpour A, Badavi M (2019) Protective effects of naringin and trimetazidine on remote effect of acute renal injury on oxidative stress and myocardial injury through Nrf-2 regulation. Pharm Rep 71(6):1059–1066
Azab FE (2021) Ameliorative effect of kiwifruit (Actinidia deliciosa) against lead-induced oxidative stress in Wistar albino rats. Pak J Biol Sci 24(5):599–611
Baranowska M, Koziara Z, Suliborska K, Chrzanowski W, Wormstone M, Namieśnik J, Bartoszek A (2021) Interactions between polyphenolic antioxidants quercetin and naringenin dictate the distinctive redox-related chemical and biological behaviour of their mixtures. Sci Rep 11(1):12282
Barthold SW, Bayne AK, Davis MA (2011) Animal care and use program. In: Ballinger MB (ed) Guide for the care and use of laboratory animals: National Research Council. National Academy Press, Washington, pp 11–20
Beutler E, Duron O, Kelly MB (1963) Improved method for determination of blood glutathione reduced. J Lab Clin Med 61:882–888
Broseghini-Filho GB, Almenara CC, Vassallo DV, Padilha AS (2016) Blood pressure decreases following lead treatment cessation: highest NO bioavailability involved. Biol Trace Elem Res 170(2):410–414
Chanet A, Milenkovic D, Deval C, Potier M, Constans J, Mazur A, BennetauPelissero C, Morand C, Bérard AM (2012) Naringin, the major grapefruit flavonoid, specifically affects atherosclerosis development in diet-induced hypercholesterolemia in mice. J Nutr Biochem 23:469–477
D’souza HS, Menezes G, Thuppil V (2021) Ameliorative effects of nutritional minerals on lead-induced hematological alterations in male Wistar albino rats. Drug Chem Toxicol 1:1–5
De’Moura Magalhães BAB, Rodrigues LF, De’Oliveira TF, Vassallo DV, Simões MR (2021) Lead and mercury 28-day exposure at small concentrations reduces smooth muscle relaxation by decreasing cGMP. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 413(15):115405
Deng M, Jia X, Dong L, Liu L, Huang F, Chi J, Ma Q, Zhao D, Zhang M, Zhang R (2022) Structural elucidation of flavonoids from Shatianyu (Citrus grandis L. Osbeck) pulp and screening of key antioxidant components. Food Chem 366:130605
Descalzo E, Camarero PR, Sánchez-Barbudo IS, Martinez-Haro M, Ortiz-Santaliestra ME, Moreno-Opo R, Mateo R (2021) Integrating active and passive monitoring to assess sublethal effects and mortality from lead poisoning in birds of prey. Sci Total Environ 750:142260
Ellman GL (1959) Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys 82(1):70–77
Eum KD, Nie LH, Schwartz J, Vokonas PS, Sparrow D, Hu H, Weisskopf MG (2011) Prospective cohort study of lead exposure and electrocardiographic conduction disturbances in the Department of Veterans Affairs Normative Aging Study. Environ Health Perspect 119(7):940–944
Fakunle PB, Ajibade AJ, Oyewo EB, Hannah AO (2013) A study of some effects of aqueous extract of neem (Azadiractha indica) leaves on the lead acetate induced neurotoxicity in the superior colliculus of adult Wistar rats (Rattus norvegicus). Br J Pharm Res 3(2):217–231
Fleiss JL, Levin B, Paik MC (2003) Statistical methods for rates and proportions, 3rd edn. John Wiley & Sons, New York, pp 598–626
Gadde R, Betharia S (2021) N, N′ bis-(2-mercaptoethyl) isophthalamide (NBMI) exerts neuroprotection against lead-induced toxicity in U-87 MG cells. Arch Toxicol 95(8):2643–2657
Gagan F, Deepesh G, Archana T (2012) Toxicity of lead: a review with recent updates. Interdiscip Toxicol 5(2):47–58
Gargouri M, Akrouti A, Magné C, El Feki A, Soussi A (2020) Protective effects of spirulina against hemato-biochemical alterations, nephrotoxicity, and DNA damage upon lead exposition. Hum Exp Toxicol 39(6):855–869
Golden NH, Warner SE, Coffey MJ (2016) A review and assessment of spent lead ammunition and its exposure and effects to scavenging birds in the United States. In W. de Voogt (eds.) Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 237:123–191
González F, Camacho M, Tiburón NP, Peña MZ, Rueda LR, Luzardo OP (2019) Suitability of anodic stripping voltammetry for routine analysis of venous blood from raptors. Environ Toxicol Chem 38(4):737–747
Gornal AG, Bardawill JC, David MM (1949) Determination of serum proteins by means of Biuret reaction. J Biol Chem 177:751–766
Habig WH, Pabst MJ, Jakpoby WB (1974) Glutathione transferase, a first enzymatic step in mercapturic acid formation. J Biol Chem 249:7130–7139
Haig SM, D’Elia J, Eagles-Smith C, Fair JM, Gervais J, Herring G, Rivers JW, Schulz JH (2014) The persistent problem of lead poisoning in birds from ammunition and fishing tackle. The Condor: Ornithol Appl 116:408–428
Hassan RA, Hozayen WG, Abo Sree HT, Al-Muzafar HM, Amin KA, Ahmed OM (2021) Naringin and hesperidin counteract diclofenac-induced hepatotoxicity in male Wistar rats via their antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antiapoptotic activities. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2021:9990091
Herring G, Eagles-Smith CA, Varland DE (2018) Mercury and lead exposure in avian scavengers from the Pacific Northwest suggest risks to California condors: implications for reintroduction and recovery. Environ Pollut 243(Pt A):610–619
Hossain MA, Mostofa M, Alam MN, Sultana MR, Rahman MM (2014) The ameliorating effects of garlic (Allium sativum) against lead (Pb) intoxication on body weight, dressing percentages, feed consumption and feed conversion ratio in lead induced broiler chickens. Bangl J Vet Med 12(1):1–7
Jamil S, Jamil G, Mesameh H, Qureshi A, AlKaabi J, Sharma C, Aziz F, Al-Shamsi AR, Yasin J (2021) Risk factor comparison in young patients presenting with acute coronary syndrome with atherosclerotic coronary artery disease vs. angiographically normal coronaries. Int J Med Sci 18(15):3526–3532
Jia Z, Li W, Bian P, Yang L, Liu H, Pan D, Dou Z (2021) Ursolic acid treats renal tubular epithelial cell damage induced by calcium oxalate monohydrate via inhibiting oxidative stress and inflammation. Bioeng 12(1):5450–5461
Karaarslan K, Abud B, Karacelik MCB (2021) Cardioplegia application with a hand-squeezed cardioplegia bag. Is it safe? Heart Surg Forum 24(4):E619–E623
Khan AA, Alsahli MA, Rahmani AH (2018) Myeloperoxidase as an active disease biomarker: recent biochemical and pathological perspectives. Med Sci (basel, Switzerland) 6(2):33
Kovacevic S, Ivanov M, Zivotic M, Brkic P, Miloradovic Z, Jeremic R, Mihailovic-Stanojevic N, Vajic UJ, Karanovic D, Jovovic D, Nesovic Ostojic J (2021) Immunohistochemical analysis of 4-HNE, NGAL, and HO-1 tissue expression after apocynin treatment and HBO preconditioning in postischemic acute kidney injury induced in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Antioxidants (basel) 10(8):1163
Kucukler S, Benzer F, Yildirim S, Gur C, Kandemir FM, Bengu AS, Ayna A, Caglayan C, Dortbudak MB (2021) Protective effects of chrysin against oxidative stress and inflammation induced by lead acetate in rat kidneys: a biochemical and histopathological approach. Biol Trace Elem Res 199(4):1501–1514
Liu CM, Zheng GH, Ming QL, Sun JM, Cheng C (2013) Protective effect of puerarin on lead-induced mouse cognitive impairment via altering activities of acetyl cholinesterase, monoamine oxidase and nitric oxide synthase. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 35(3):502–510
Long X, Sun F, Wang Z, Liu T, Gong J, Kan X, Zou Y, Zhao X (2021) Lactobacillus fermentum CQPC08 protects rats from lead-induced oxidative damage by regulating the Keap1/Nrf2/ARE pathway. Food Funct 12(13):6029–6044
Matović V, Buha A, Ðukić-Ćosić D, Bulat Z (2015) Insight into the oxidative stress induced by lead and/or cadmium in blood, liver and kidneys. Food Chem Toxicol 78:130–140
Misra HP, Fridovich I (1972) The role of superoxide anion in the autoxidation of epinephrine and a simple assay for superoxide dismutase. J Biol Chem 217:3170–3175
Monclús L, Shore RF, Krone O (2020) Lead contamination in raptors in Europe: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci Total Environ 15(748):141437
Moussa SA, Bashandy SA (2008) Biophysical and Biochemical changes in the blood of rats exposed to lead toxicity. Romanian J Biophys 18(2):123–133
Najafi L, Keshtkar Rajabi S, Pirsaheb S, Keyvani H, Khajavi A, Shati M, Hadavand F, Amouzegar A (2021) Assessment of serum and urine neurophil gelatinase- associated lipocalin (s-NGAL and u-NGAL) level as a predictive factor of disease progression in diabetic nephropathy in type 2 DM. Iran J Kidney Dis 15(4):270–278
Nasiruddin Rana M, Karim N, Changlek S, Atiar Rahman M, Tangpong J, Hajjar D, Alelwani W, Makki AA (2020) Thunbergia laurifolia leaf extract partially recovers lead-induced renotoxicity through modulating the cell signaling pathways. Saudi J Biol Sci 27(12):3700–3710
Olaleye SB, Adaramoye OA, Erigbali PP, Adeniyi OS (2007) Lead exposure increases oxidative stress in gastric mucosa of HCL/ethanol exposed rat. World J Gastreoenterol 13:5121–5126
Omobowale TO, Oyagbemi AA, Akinrinde AS, Sabab AB, Daramolaa OT, Ogunpolua BS, Olopade JO (2014) Failure of recovery from lead induced hepatoxicity and disruption of erythrocyte antioxidant defense system in Wistar rats. Environ Toxicol Pharm 37:1202–1211
Omobowale TO, Oyagbemi AA, Akinleye SA, Ola-Davies OE, Adebowale BS, Olopade JO, Adedapo AA (2016) Effect of exposure and withdrawal on lead-induced toxicity and oxidative stress in cardiac tissues of rats. Toxicol Intern 23(1):12–17
Oyagbemi AA, Omobowale TO, Akinrinde AS, Saba AB, Ogunpolu BS, Daramola O (2015) Lack of reversal of oxidative damage in renal tissues of lead acetate-treated rats. Environ Toxicol 30:1235–1243
Oyagbemi AA, Omobowale TO, Awoyomi OV, Ajibade TO, Falayi OO, Ogunpolu BS, Okotie UJ, Asenuga ER, Adejumobi OA, Hassan FO, Ola-Davies OE, Saba AB, Adedapo AA, Yakubu MA (2019) Cobalt chloride toxicity elicited hypertension and cardiac complication via induction of oxidative stress and upregulation of COX-2/Bax signaling pathway. Hum Exp Toxicol 38(5):519–532
Oyem JC, Chris-Ozoko LE, Enaohwo MT, Otabor FO, Okudayo VA, Udi OA (2021) Antioxidative properties of Ocimum gratissimum alters lead acetate induced oxidative damage in lymphoid tissues and hematological parameters of adult Wistar rats. Toxicol Rep 10(8):215–222
Peng L, Li X, Li Y, Zhao W, Nie S, Yu H, Qi Y, Qin Y, Zhang H (2021) Increased concentrations of myeloperoxidase in serum and serum extracellular vesicles are associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Clin Chim Acta 522:70–76
Peng S, Zhang H, Song D, Chen H, Lin X, Wang Y, Ji L (2022) Distribution of antibiotic, heavy metals and antibiotic resistance genes in livestock and poultry feces from different scale of farms in Ningxia. China J Hazard Mater 440:129719. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.129719
Puspita FM, Yunir E, Agustina PS, Sauriasari R (2021) Effect of angiotensin receptor blocker and angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor on kidney function and blood potassium level in indonesian type 2 diabetes mellitus with hypertension: a three-month cohort study. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes 7(14):3841–3849
Rani N, Bharti S, Manchanda M, Nag T, Ray R, Chauhan S, Kumari S, Dharamvir A (2013) Regulation of heat shock proteins 27 and 70, p-Akt/p-eNOS and MAPKs by naringin dampens myocardial injury and dysfunction in vivo after ischemia/reperfusion. PLoS One 8:e82577. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0082577
Reza B, Ali N, Azhdar H, Alireza A, Ali K (2008) Effects of low-level lead exposure on blood pressure and function of the rat isolated heart. Indian J Pharmacol 40(2):69–72
Sandamali JAN, Hewawasam RP, Jayatilaka KAPW, Mudduwa LKB (2021) Cinnamomum zeylanicum Blume (Ceylon cinnamon) bark extract attenuates doxorubicin induced cardiotoxicity in Wistar rats. Saudi Pharm J 29(8):820–832
Shvachiy L, Geraldes V, Amaro-Leal Â, Rocha I (2020) Persistent effects on cardiorespiratory and nervous systems induced by long-term lead exposure: results from a longitudinal study. Neurotox Res 37(4):857–870
Tang X, Xu Y, Dai X, Xing Y, Yang D, Huang Q, Li H, Lv X, Wang Y, Lu D, Wang H (2021) The long-term effect of dobutamine on intrinsic myocardial function and myocardial injury in septic rats with myocardial dysfunction. Shock 56(4):582–592
Thomas AB and Merle MA (2016) Pharmaceutical products commonly used in avian medicine. Edited by: Jaime Samour. ISBN: 978–0–7234–3832–8. 637–678
Thuppil V, Tannir S (2013) Treating lead toxicity: possibilities beyond synthetic chelation. J Krishna Inst Med Sci Univ 2:4–31
Varshney R, Kale RK (1990) Effect of calmodulin antagonists on radiation induced lipid peroxidation in microsomes. Int J Radiat Biol 58:733–743
Vaziri ND (2008) Mechanisms of lead-induced hypertension and cardiovascular disease. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 295:H454–H465
Veltman D, Wu M, Pokreisz P, Claus P, Gillijns H, Caluwé E, Vanhaverbeke M, Gsell W, Himmelreich U, Sinnaeve PR, Janssens SP (2021) Clec4e-receptor signaling in myocardial repair after ischemia-reperfusion injury. JACC Basic Transl Sci 6(8):631–646
Venkateswara RP, Kiran SDVS, Rohini P, Bhagyasree P (2017) Flavonoid: a review on naringenin. J Pharmacog Phytochem 6(5):2778–2783
Wei H, Xue Q, Sun L, Lv J (2021) BRD4 inhibition protects against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by suppressing inflammation and oxidative stress through PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 78(6):839–846
Wildemann TM, Mirhosseini N, Siciliano SD, Weber LP (2015) Cardiovascular responses to lead are biphasic, while methylmercury, but not inorganic mercury, monotonically increases blood pressure in rats. Toxicol 3(328):1–11
Wolff SF (1994) Ferrous ion oxidation in the presence of ferric ion indicator xylenol orange for measurement of hydrogen peroxides. Methods Enzymol 233:182–189
Wu Y, Cai C, Xiang Y, Zhao H, Lv L, Zeng C (2021) Naringin ameliorates monocrotaline-induced pulmonary arterial hypertension through endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition inhibition. Front Pharmacol 12:696135
Xia Y, Zweiler JL (1997) Measurement of myeloperoxidase in leucocyte containing tissue. Anal Biochem 245:93–96
Xie J, Du G, Zhang Y, Zhou F, Wu J, Jiao H, Li Y, Chen Y, Ouyang L, Bo D, Feng C, Yang W, Fan G (2019) ECG conduction disturbances and ryanodine receptor expression levels in occupational lead exposure workers. Occup Environ Med 76(3):151–156
Xu L-H, Mu F-F, Zhao J-H, He Q, Cao C-L, Yang H, Liu Q, Liu XH, Sun XJ (2015) Lead induces apoptosis and histone hyperacetylation in rat cardiovascular tissues. PLoS One 10(6):e0129091. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0129091
Xu W, Zhao A, Zuo F, Khan R, Hussain HMJ, Li J (2020) A highly sensitive DNAzyme-based SERS biosensor for quantitative detection of lead ions in human serum. Anal Bioanal Chem 412(19):4565–4574
Yuan Z, Wang L, Chen J, Su W, Li A, Su G, Liu P, Zhou X (2021) Electrochemical strategies for the detection of cTnI. Analyst 146(18):5474–5495
Yuniarti WM, Krismaharani N, Ciptaningsih P, Celia K, Veteriananta KD, Ma’ruf A, Lukiswanto BS (2021) The protective effect of Ocimum sanctum leaf extract against lead acetate-induced nephrotoxicity and hepatotoxicity in mice (Mus musculus). Vet World 14(1):250–258
Zahler D, Merdler I, Banai A, Shusterman E, Feder O, Itach T, Robb L, Banai S, Shacham Y (2022) Predictive value of elevated neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) levels for assessment of cardio-renal interactions among ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction patients. J Clin Med 11(8):2162. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11082162
Acknowledgements
The authors deeply thank the African Union through the Pan African University Institute of Earth and Life Sciences Institute (PAULESI) for funding this work and Cardio-renal laboratory, University of Ibadan for the facilities used.
Funding
The study was funded by the African Union.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The authors, Chinomso Gift Ebirim, Oluwaseun Esan, Ademola Adetokunbo Oyagabemi, and Temidayo Olutayo Omobowale, designed the experiment. Chinomso Gift Ebirim, Oluwaseun Esan, and Ademola Adetokunbo Oyagabemi performed the immunohistochemistry and biochemical assays. The blood pressure and electrocardiogram was performed by Gift Ebirim, Oluwaseun Esan, and Temidayo Olutayo Omobowale. Moses Olusola Adetona, Ademola Adetokunbo Oyagabemi, Temidayo Olutayo Omobowale Omolade Abodunrin Oladele, Adeolu Alex Adedapo, Oluwafemi Oguntibeju, Momoh Audu Yakubu supervised, proof-read and approved the submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
The study was conducted following guidelines approved by the Animal Care and Use Research Ethics Committee (ACUREC) of the University of Ibadan (Approval number: UI-ACUREC/021–0421/16).
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Mohamed M. Abdel-Daim
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ebirim, C.G., Esan, O., Adetona, M.O. et al. Naringin administration mitigates oxidative stress, anemia, and hypertension in lead acetate-induced cardio-renal dysfunction in cockerel chicks. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 34890–34903 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-24656-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-24656-4