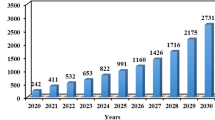
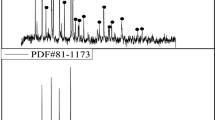
Abstract
Recycling cathodic materials from spent lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) is crucial not just for the environmental aspects but also for the supply of precious raw materials such as cobalt and lithium. As a result, developing a leaching process with low acid consumption, cost-effectiveness, low environmental impact, and high metal recovery is essential. In this article, the sustainable hydrometallurgical route for recovery of Li and Co from spent LIBs using DL-lactic acid as lixiviant is proposed. The different leaching parameters were studied to optimize the leaching conditions. With increasing lactic acid concentration from 0.1 mol/L to 1.0 mol/L, the leaching efficiency of Li and Co increased from 23% to 41% and 2% to 14%, respectively. The reductant H2O2 has a major role which reduced Co3+ to Co2+ and increasing the leaching efficiency of Co from 15.2% (1% H2O2) to 73.4% (6% H2O2). The maximum leaching efficiency of Li (99.8%) and Co (99%) was attained with 1.0 mol/L lactic acid, 6% H2O2, 60 °C, S/L ratio of 10 g/L, and 60 min leaching duration. The R2 values for the surface chemical reaction model were greater than 0.98, indicating that the lactic acid leaching process was controlled by the surface chemical reaction model. With 1.0 mol/L 70% saponified Cyanex 272, a solvent extraction study showed a higher separation factor (βCo/Li) of 35.7 compared to other saponified and nonsaponified organophosphorus extractants. Using the precipitation method, 99.9% of Co and 99% of Li were precipitated as \({\mathrm{CoC}}_{2}{\mathrm{O}}_{4}\cdot 2{\mathrm{H}}_{2}\mathrm{O}\) and \({\mathrm{Li}}_{2}{\mathrm{CO}}_{3}\) with a purity of 99.4% and 98.3%, respectively.















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
An JW, Kang DJ, Tran KT, Kim MJ, Lim T, Tran T (2012) Recovery of lithium from Uyuni salar brine. Hydrometallurgy 117:64–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2012.02.008
Bandara AMTS, Senanayake G (2015) Leachability of rare-earth, calcium and minor metal ions from natural fluorapatite in perchloric, hydrochloric, nitric and phosphoric acid solutions: effect of proton activity and anion participation. Hydrometallurgy 153:179–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2015.02.002
Chen X, Fan B, Xu L, Zhou T, Kong J (2016) An atom-economic process for the recovery of high value-added metals from spent lithium-ion batteries. J Clean Prod 112:3562–3570. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.10.132
Chen X, Ma H, Luo C, Zhou T (2017) Recovery of valuable metals from waste cathode materials of spent lithium-ion batteries using mild phosphoric acid. J Hazard Mater 326:77–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.12.021
Choubey PK, Chung KS, Kim MS, Lee JC, Srivastava RR (2017) Advance review on the exploitation of the prominent energy-storage element Lithium. Part II: from sea water and spent lithium ion batteries (LIBs). Miner Eng 110:104–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2017.04.008
Dalini EA, Karimi G, Zandevakili S (2021) Treatment of valuable metals from leaching solution of spent lithium-ion batteries. Miner Eng 173:107226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2021.107226
de Oliveira Demarco J, Cadore JS, de Oliveira FDS, Tanabe EH, Bertuol DA (2019) Recovery of metals from spent lithium-ion batteries using organic acids. Hydrometallurgy 190:105169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2019.105169
Dutta D, Kumari A, Panda R, Jha S, Gupta D, Goel S, Jha MK (2018) Close loop separation process for the recovery of Co, Cu, Mn, Fe and Li from spent lithium-ion batteries. Sep Purif Technol 200:327–334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2018.02.022
Etacheri V, Marom R, Elazari R, Salitra G, Aurbach D (2011) Challenges in the development of advanced Li-ion batteries: a review. Energy Environ Sci 4(9):3243–3262. https://doi.org/10.1039/C1EE01598B
Gao W, Song J, Cao H, Lin X, Zhang X, Zheng X, Zhang Y, Sun Z (2018) Selective recovery of valuable metals from spent lithium-ion batteries–process development and kinetics evaluation. J Clean Prod 178:833–845. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.01.040
Golmohammadzadeh R, Rashchi F, Vahidi E (2017) Recovery of lithium and cobalt from spent lithium-ion batteries using organic acids: process optimization and kinetic aspects. Waste Manage 64:244–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2017.03.037
Golmohammadzadeh R, Faraji F, Rashchi F (2018) Recovery of lithium and cobalt from spent lithium ion batteries (LIBs) using organic acids as leaching reagents: a review. Resour Conserv Recycl 136:418–435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2018.04.024
Gu F, Guo J, Yao X, Summers PA, Widijatmoko SD, Hall P (2017) An investigation of the current status of recycling spent lithium-ion batteries from consumer electronics in China. J Clean Prod 161:765–780. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.05.181
Hayashi M, Takahashi M, Shodai T (2009) Preparation and electrochemical properties of pure lithium cobalt oxide films by electron cyclotron resonance sputtering. J Power Sources 189(1):416–422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2008.07.050
Horeh NB, Mousavi SM, Shojaosadati SA (2016) Bioleaching of valuable metals from spent lithium-ion mobile phone batteries using Aspergillus niger. J Power Sources 320:257–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2016.04.104
Innocenzi V, De Michelis I, Vegliò F (2017) Design and construction of an industrial mobile plant for WEEE treatment: investigation on the treatment of fluorescent powders and economic evaluation compared to other e-wastes. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 80:769–778. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2017.09.019
Jadhav UU, Hocheng H (2012) A review of recovery of metals from industrial waste. J Achiev Mater Manuf Eng 54(2):159–167
Jian YANG, Jiang LX, Liu FY, Ming JIA, Lai YQ (2020) Reductive acid leaching of valuable metals from spent lithium-ion batteries using hydrazine sulfate as reductant. Trans Nonferrous Metals Soc China 30(8):2256–2264. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(20)65376-6
Kong L, Wang Z, Shi Z, Hu X, Liu A, Tao W, ... & Wang Q (2022). Leaching valuable metals from spent lithium-ion batteries using the reducing agent methanol. Environ SciPollut Res, 1-11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22414-0
Li L, Ge J, Chen R, Wu F, Chen S, Zhang X (2010) Environmental friendly leaching reagent for cobalt and lithium recovery from spent lithium-ion batteries. Waste Manage 30(12):2615–2621. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2010.08.008
Li G, Rao M, Jiang T, Huang Q, Peng Z (2011) Leaching of limonitic laterite ore by acidic thiosulfate solution. Miner Eng 24(8):859–863. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2011.03.010
Li L, Lu J, Ren Y, Zhang XX, Chen RJ, Wu F, Amine K (2012) Ascorbic-acid-assisted recovery of cobalt and lithium from spent Li-ion batteries. J Power Sources 218:21–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2012.06.068
Li L, Qu W, Zhang X, Lu J, Chen R, Wu F, Amine K (2015) Succinic acid-based leaching system: a sustainable process for recovery of valuable metals from spent Li-ion batteries. J Power Sources 282:544–551. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2015.02.073
Li L, Fan E, Guan Y, Zhang X, Xue Q, Wei L, Wu F, Chen R (2017) Sustainable recovery of cathode materials from spent lithium-ion batteries using lactic acid leaching system. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 5(6):5224–5233. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.7b00571
Li L, Bian Y, Zhang X, Guan Y, Fan E, Wu F, Chen R (2018a) Process for recycling mixed-cathode materials from spent lithium-ion batteries and kinetics of leaching. Waste Manage 71:362–371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2017.10.028
Li L, Bian Y, Zhang X, Xue Q, Fan E, Wu F, Chen R (2018b) Economical recycling process for spent lithium-ion batteries and macro-and micro-scale mechanistic study. J Power Sources 377:70–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2017.12.006
Makuza B, Tian Q, Guo X, Chattopadhyay K, Yu D (2021) Pyrometallurgical options for recycling spent lithium-ion batteries: a comprehensive review. J Power Sources 491:229622. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2021.229622
Martin G, Rentsch L, Höck M, Bertau M (2017) Lithium market research–global supply, future demand and price development. Energy Storage Mater 6:171–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ensm.2016.11.004
Meng F, Liu Q, Kim R, Wang J, Liu G, Ghahreman A (2020) Selective recovery of valuable metals from industrial waste lithium-ion batteries using citric acid under reductive conditions: leaching optimization and kinetic analysis. Hydrometallurgy 191:105160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2019.105160
Meshram P, Pandey BD, Mankhand TR (2015) Recovery of valuable metals from cathodic active material of spent lithium ion batteries: leaching and kinetic aspects. Waste Manage 45:306–313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2015.05.027
Mohanty A, Sahu S, Sukla LB, Devi N (2021) Application of various processes to recycle lithium-ion batteries (LIBs): a brief review. Mater Today: Proc 47:1203–1212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2021.03.645
Musariri B, Akdogan G, Dorfling C, Bradshaw S (2019) Evaluating organic acids as alternative leaching reagents for metal recovery from lithium ion batteries. Miner Eng 137:108–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2019.03.027
Nayl AA, Elkhashab RA, Badawy SM, El-Khateeb MA (2017) Acid leaching of mixed spent Li-ion batteries. Arab J Chem 10:S3632–S3639. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2014.04.001
Ordoñez J, Gago EJ, Girard A (2016) Processes and technologies for the recycling and recovery of spent lithium-ion batteries. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 60:195–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.12.363
Parhi PK, Park KH, Senanayake G (2013) A kinetic study on hydrochloric acid leaching of nickel from Ni–Al2O3 spent catalyst. J Ind Eng Chem 19(2):589–594. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2012.09.028
Perez E, Andre ML, Amador RN, Hyvrard F, Borrini J, Carboni M, Meyer D (2016) Recovery of metals from simulant spent lithium-ion battery as organophosphonate coordination polymers in aqueous media. J Hazard Mater 317:617–621. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.06.032
Pinna EG, Ruiz MC, Ojeda MW, Rodriguez MH (2017) Cathodes of spent Li-ion batteries: dissolution with phosphoric acid and recovery of lithium and cobalt from leach liquors. Hydrometallurgy 167:66–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2016.10.024
Roshanfar M, Golmohammadzadeh R, Rashchi F (2019) An environmentally friendly method for recovery of lithium and cobalt from spent lithium-ion batteries using gluconic and lactic acids. J Environ Chem Eng 7(1):102794. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2018.11.039
Sahu S, Mohapatra M, Devi N (2022) Effective hydrometallurgical route for recovery of energy critical elements from E-wastes and future aspects. Materials Today: Proceedings. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2022.05.491
Santhosh G, Nayaka GP (2021) Cobalt recovery from spent Li-ion batteries using lactic acid as dissolution agent. Clean Eng Technol 3:100122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clet.2021.100122
Sarkar A, Shrotriya P, Nlebedim IC (2022) Electrochemical-driven green recovery of lithium, graphite and cathode from lithium-ion batteries using water. Waste Manage 150:320–327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2022.07.026
Senanayake G, Das GK, De Lange A, Li JD, Robinson DJ (2015) Reductive atmospheric acid leaching of lateritic smectite/nontronite ores in H2SO4/Cu (II)/SO2 solutions. Hydrometallurgy 152:44–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2014.12.001
Shuva MAH, Kurny ASW (2013) Hydrometallurgical recovery of value metals from spent lithium ion batteries. Am J Mater Eng Technol 1(1):8–12. https://doi.org/10.12691/materials-1-1-2
Sole KC, Parker J, Cole PM, Mooiman MB (2019) Flowsheet options for cobalt recovery in African copper-cobalt hydrometallurgy circuits. Miner Process Extr Metall Rev 40(3):194–206. https://doi.org/10.1080/08827508.2018.1514301
Sun L, Qiu K (2012) Organic oxalate as leachant and precipitant for the recovery of valuable metals from spent lithium-ion batteries. Waste Manage 32(8):1575–1582. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2012.03.027
Swain B, Jeong J, Lee JC, Lee GH, Sohn JS (2007) Hydrometallurgical process for recovery of cobalt from waste cathodic active material generated during manufacturing of lithium ion batteries. J Power Sources 167(2):536–544. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2007.02.046
Tesfaye F, Lindberg D, Hamuyuni J, Taskinen P, Hupa L (2017) Improving urban mining practices for optimal recovery of resources from e-waste. Miner Eng 111:209–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2017.06.018
Verma A, Johnson GH, Corbin DR, Shiflett MB (2020) Separation of lithium and cobalt from LiCoO2: a unique critical metals recovery process utilizing oxalate chemistry. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 8(15):6100–6108. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c01128
Wang RC, Lin YC, Wu SH (2009) A novel recovery process of metal values from the cathode active materials of the lithium-ion secondary batteries. Hydrometallurgy 99(3–4):194–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2009.08.005
Wang MM, Zhang CC, Zhang FS (2017) Recycling of spent lithium-ion battery with polyvinyl chloride by mechanochemical process. Waste Manage 67:232–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2017.05.013
Winslow KM, Laux SJ, Townsend TG (2018) A review on the growing concern and potential management strategies of waste lithium-ion batteries. Resour Conserv Recycl 129:263–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2017.11.001
Yan S, Sun C, Zhou T, Gao R, Xie H (2021) Ultrasonic-assisted leaching of valuable metals from spent lithium-ion batteries using organic additives. Sep Purif Technol 257:117930. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2020.117930
Yin X, Wu Y, Tian X, Yu J, Zhang YN, Zuo T (2016) Green recovery of rare earths from waste cathode ray tube phosphors: oxidative leaching and kinetic aspects. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 4(12):7080–7089. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.6b01965
Yu M, Zhang Z, Xue F, Yang B, Guo G, Qiu J (2019) A more simple and efficient process for recovery of cobalt and lithium from spent lithium-ion batteries with citric acid. Sep Purif Technol 215:398–402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2019.01.027
Zhao S, Quan J, Wang T, Song D, Huang J, He W, Li G (2021) Unveiling the recycling characteristics and trends of spent lithium-ion battery: a scientometric study. Environ Sci Pollut Res, 1-14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17814-7
Zhu SG, He WZ, Li GM, Xu Z, Zhang XJ, Huang JW (2012) Recovery of Co and Li from spent lithium-ion batteries by combination method of acid leaching and chemical precipitation. Trans Nonferrous Metals Soc China 22(9):2274–2281. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(11)61460-X
Acknowledgements
The authors express their gratitude to S'O'A (Deemed to be University) for providing the research facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Sibananda Sahu (first author): writing—original draft, visualization, data curation, formal analysis, investigation, software. Niharbala Devi (corresponding author): conceptualization, methodology, supervision, writing—review and editing, validation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
There is no ethical issue in this paper.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
This paper has been read by all authors and given their approval for publication.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: George Z. Kyzas
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sahu, S., Devi, N. Effective leaching of spent lithium-ion batteries using DL-lactic acid as lixiviant and selective separation of metals through precipitation and solvent extraction. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 90152–90167 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-24560-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-24560-x