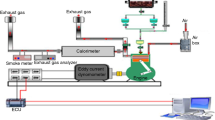
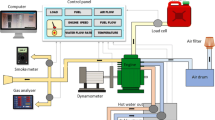
Abstract
Fuel economy improvement and reducing exhaust emissions are drivers for advancement in engine technology and fuel quality enhancement. The latest generation diesel engine uses a high pressure common rail fuel injection system and after-treatment devices such as selective catalyst reduction (SCR) and diesel particulate filters (DPF) to meet the stringent emission norms. The performance of engine can be further improved by using better quality fuel than the minimum requirement. Fuel quality improvement can be achieved through modifying blending components and/ or using additives. This study investigates the effect of high cetane diesel on the performance and emission behavior of SCR fitted heavy-duty engines. Normal diesel is doped with diesel multi-functional additives containing cetane improver, and thereby cetane number enhanced to 55 from 52. Fuel consumption and exhaust emission were evaluated over the European stationary cycle (ESC) under the controlled test cell conditions. The fuel consumption with the high cetane diesel was 0.5% lower; CO, HC, and NOx emissions were lower by 12%, 6%, and 8% respectively over the ESC. This paper also highlights mode-wise engine performance, emissions, noise, and combustion behavior of the engine while using a cetane improver in diesel over the ESC cycle. Noise level reduced by 1 dB in the wide-open throttle performance tests when the cetane number increased by 3 units.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be available to present.
References
Ashok B, Nanthagopal K, Mohan A, Johny A, Tamilarasu A (2017) Comparative analysis on the effect of zinc oxide and ethanox as additives with biodiesel in CI engine. Energy 140(Part1). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2017.09.021
Awad OI et al (2020) Overview of polyoxymethylene dimethyl ether additive as an eco-friendly fuel for an internal combustion engine: current application and environmental impacts. Sci Total Environ 715:136849
Barbier P (2000) "Evaluation of cetane improver effects on regulated emissions from a passenger car equipped with a common rail diesel engine," SAE Technical Paper 2000–01–1853
der Wiesche S (2007) Numerical heat transfer and thermal engineering of AdBlue (SCR) tanks for combustion engine emission reduction. Appl Therm Eng 27(11–12):1790–1798
Green G, Henly T, Starr M, Assanis D et al (1997a) "Fuel economy and power benefits of cetane-improved fuels in heavy-duty diesel engines," SAE Technical Paper 972900, 1997a, https://doi.org/10.4271/972900
Green G, Henly T, Starr M, Assanis D, Syrimis M, Kanafani F (1997b) “Fuel economy and power benefits of cetane improved fuels in heavy duty diesel engine”, SAE Technical Paper, 972900, (1997b). https://doi.org/10.4271/972900
Haupt D, Nord K, Tingvall B, Ahlvik P et al. (2004) “Investigating the potential to obtain low emissions from a diesel engine running on ethanol and equipped with EGR, catalyst and DPF,” SAE Technical Paper 2004–01–1884, 2004, https://doi.org/10.4271/2004-01-1884. https://www.mckinseyenergyinsights.com/resources/refinery-reference-desk/cetane-improvers/
Labeckas G, Slavinskas S (2021) Comparative evaluation of the combustion process and emissions of a diesel engine operating on the cetane improver 2-ethylhexyl nitrate doped rapeseed oil and aviation JP-8 fuel. Energy Conversion and Management: X 11:100106
Ladommatos N, Parsi M, Knowles A (1996) The effect of fuel cetane improver on diesel pollutant emissions. Fuel 75(1):8–14
Liu J et al (2021) Effects of PODE/diesel blends on particulate matter emission and particle oxidation characteristics of a common-rail diesel engine. Fuel Process Technol 212:106634
Malchuk VI, Shatrow MG, Dunin AY (2007) Equipment and some test results of a prototype model diesel that implements zonal mixture formation using ethanol. Transport technology. Bulletin MADI (Moscow Automobile and Highway Institute—State Technical University) 2007;1(8):35–40 (in Russian)
Mohankumar S, Senthilkumar P (2017) Particulate matter formation and its control methodologies for diesel engine: a comprehensive review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 80:1227–1238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2017.05.133
Qi DHLM, Geng H, Chen Y, Bian ZHJ, Liu X, Ren CH (2009) “Combustion and performance evaluation of a diesel engine fueled with biodiesel produced from soybean crude oil”, Renew. Energy 34 (12) (2009) 2706–2713, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2009.05.004. Elsevier Ltd.
Reşitoglu LA, Altinişik K, Keskin A (2015) The pollutant emissions from diesel-engine vehicles and exhaust aftertreatment systems. Clean Technol Environ Policy 17(1):15–27
Schwab S, Guinther G, Henly T, Miller K (1999) "The effects of 2-ethylhexyl nitrate and di-tertiary-butyl peroxide on the exhaust emissions from a heavy-duty diesel engine," SAE Technical Paper 1999–01–1478
Singh A, Sinha S, Choudhary AK, Sharma D, Panchal H, Sadasivuni KK (2021) An experimental investigation of emission performance of heterogenous catalyst jatropha biodiesel using RSM. Case Stud Thermal Eng 25(2):1–14
Srivastava SP, Hancsok J (2014) Fuels and fuel additives. John Wiley & Sons, New Jersy, USA
Yang HH, Lee WJ, Mi HH, Wong CH, Chen CB (1998) PAH emission influenced by MN-based additive and turbo-charging from a heavy-duty diesel engine. Environ Int 24:389–403
Zhao Y, Geng C (2021) Weibo E, Xiaoquan Li, Peiyuan Cheng & Tianlin Niu, “Experimental study on the effects of blending PODE on performance, combustion and emission characteristics of heavy-duty diesel engines meeting China VI emission standard. Sci Rep 11:9514
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the management of Indian Oil Corporation Ltd. R&D Centre for publishing this technical paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors—NS, RAS, MC, SM, MM, DS—contributed to the full paper. NS, RAS, MC are involved in development of fuels and engine testing. SM, MM, DS analyzed the test results and contributed in development of the manuscript.
All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The manuscript should not be submitted to more than one journal for simultaneous consideration.
The submitted work is original and should not have been published elsewhere in any form or language (partially or in full).
Consent to participate
All authors gave consent to publish and participate.
Consent for publication
All authors gave consent to publish and participate.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• Investigated the effect of high cetane number diesel on diesel, engine performance, gaseous, and noise emissions under European stationary cycle and full-throttle performance.
• High cetane number diesel improved the fuel economy by 0.5% and reduced gaseous emissions by 10%.
• High cetane diesel decreased the number count of < 10 nm particles by approximately 10%.
• Three units cetane number increase in diesel (52 to 55) reduced noise up to 1 dB.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Saikia, N., Sakunthalai, R.A., Chakradhar, M. et al. Effects of high cetane diesel on combustion, performance, and emissions of heavy-duty diesel engine. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 61246–61256 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23262-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23262-8