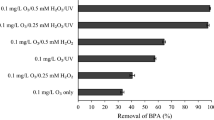
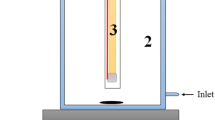
Abstract
2,4-Dinitrophenol (2,4-DNP) is a toxic compound that is widely used in many industrial and agricultural processes. This compound has low biodegradability in the environment due to its aromatic structure, and it is unsuccessfully eliminated by other chemical methods. Therefore, in this study, an integrated oxidation and reduction method was used to remove 2,4-DNP from the aqueous medium, in order to simultaneously use the benefits of oxidizing and reducing radicals in 2,4-DNP degradation. 2,4-DNP degradation was modeled by response surface methodology (RSM) and central composite design (CCD). According to the results obtained from RSM, the optimal values for the studied parameters were obtained at pH = 8.9, time = 25 min, ZnO dose = 0.78 g/L, SO3 = 1.89 mmolL−1 and 2,4-DNP concentration = 5 mg/L. Also, the removal efficiency with the integrated process was 3 to 4 times higher than the advanced oxidation or advanced reduction processes alone. Analysis of the data showed that at the time of the study, 2,4-DNP had been converted to linear hydrocarbons, and increased periods of time were required for complete mineralization. A decrease in the first-order model rate constant (kobs) and an increase in 2,4-DNP degradation rate (robs) were observed at higher DNP concentrations.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Only the data described in this work is available, and there are no other links.
References
Ahuja S (2018) Advances in water purification techniques, 1st edn. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Azarpira H, Sadani M, Abtahi M, Vaezi N, Rezaei S, Atafar Z et al (2019) Photo-catalytic degradation of triclosan with UV/iodide/ZnO process: performance, kinetic, degradation pathway, energy consumption and toxicology. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 371:423–432
Azizi S, Sarkhosh M, Asghar A, Mohseni M, Maaza M, Sadani M (2021) Degradation of codeine phosphate by simultaneous usage of eaq- and •OH radicals in photo-redox processes: influencing factors, energy consumption, kinetics, intermediate products and degradation pathways. Optik 243:167415
Bagal VM, Lele BJ, Gogate PR (2013) Removal of 2,4-dinitrophenol using hybrid methods based on ultrasound at an operating capacity of 7 L. Ultrason Sonochem 20(5):1217–1225
Behnajady MA, Vahid B, Modirshahla N, Shokri M (2009) Evaluation of electrical energy per order (EEO) with kinetic modeling on the removal of malachite green by US/UV/H2O2 process. Desalination 249:99–103
Dadban S, Sadeghi M, Shahryari A, Okhovat N, Bahrami F, Baneshi MM (2015) Heterogeneous catalytic ozonation of 2, 4-dinitrophenol in aqueous solution by magnetic carbonaceous nanocomposite: catalytic activity and mechanism. Deswater 57(43):20447–20456
Daneshvar N, Aleboyeh A, Khatae AR (2005) The evaluation of electrical energy per order (EEo) for photooxidative decolorization of four textile dye solutions by the kinetic model. Chemosphere 59:761–767
Daraei H, Manshouri M, Yazdanbakhsh AR (2010) Removal of phenol from aqueous solution using ostrich feathers ash. J Maz Univ Med Sci 20(79):81–87
Daraei H, Abdeltif A, Kamali H (2017) Assessment of phenol removal efficiency by synthesized zero iron nanoparticles and Fe powder using the response surface methodology. Iran J Chem Chem Eng 36:137–146
Dehghani M, Jaafari J, Alghasi A, Porkar G (2011) Using medium pressure ultraviolet reactor for removing azo dyes in textile wastewater treatment plant. World Appl Sci J 12(6):797–802
Deng Y, Ezyske CM (2011) Sulfate radical-advanced oxidation process (SR-AOP) for simultaneous removal of refractory organic contaminants and ammonia in landfill leachate. Water Res 45(18):6189–6194
Entezari M, Godini H, Sheikhmohammadi A, Esrafili A (2019) Enhanced degradation of polychlorinated biphenyls with simultaneous usage of reductive and oxidative agents over UV/sulfite/TiO2 process as a new approach of advanced oxidation/reduction processes. J Water Process Eng 32:100983
González-Sarrías A, Espín JC, Tomás-Barberán FA (2017) Non-extractable polyphenols produce gut microbiota metabolites that persist in circulation and show anti-inflammatory and free radical-scavenging effects. Trends Food Sci Technol 69:281–288
Jeong J, Song W, Cooper WJ, Jung J, Greaves J (2010) Degradation of tetracycline antibiotics: mechanisms and kinetic studies for advanced oxidation/reduction processes. Chemosphere 78(5):533–540
Khan S, He X, Khan JA, Khan HM, Boccelli DL, Dionysiou DD (2017) Kinetics and mechanism of sulfateradical- and hydroxyl radical-induced degradation of highly chlorinated pesticide lindane in UV/peroxymonosulfate system. Chem Eng J 318:135–142
Khan MF, Yu L, Achari G, Tay JH (2019) Degradation of sulfolane in aqueous media by integrating activated sludge and advanced oxidation process. Chemosphere 222:1–8
Liu X, Yoon S, Batchelor B, Wahab AA (2013) Degradation of vinyl chloride (VC) by the sulfite/UV advanced reduction process (ARP): effects of process variables and a kinetic model. Sci Total Environ 454–455:578–583
Liu X, Zhong J, Fang L, Wang L, Ye M, Shao Y, Li J, Zhang T (2016) Trichloroaceticacid reduction by an advanced reduction process based on carboxyl anion radical. Chem Eng J 303:56–63
Mei Q, Wei F, Han D, An Z, Sun J, Li M, Wei B, Xie J, He M (2021) Degradation mechanisms, kinetics and eco-toxicity assessment of 2,4-dinitrophenol by oxygen-containing free radicals in aqueous solution. Mol Phys 119(9):1886365
Milh H, Yu X, Cabooter D, Dewil R (2021) Degradation of ciprofloxacin using UV-based advanced removal processes: comparison of persulfate-based advanced oxidation and sulfite-based advanced reduction processes. Sci Total Environ 764:144510
Moussavi G, Rezaei M (2017) Exploring the advanced oxidation/reduction processes in the VUV photoreactor for dechlorination and mineralization of trichloroacetic acid: parametric experiments, degradation pathway and bioassessment. Chem Eng J 328:331–342
Noorisepehr M, Kakavandi B, Isaric AA, Ghanbari F, Dehghanifard E, Ghomie N, Kamrani F (2020) Sulfate radical-based oxidative degradation of acetaminophen over an efficient hybrid system: peroxydisulfate decomposed by ferroferric oxide nanocatalyst anchored on activated carbon and UV light. Sep Purif Technol 250:116950
Nuengmatcha P, Chanthai S, Mahachai R, Oh WC (2016) Sonocatalytic performance of ZnO/graphene/TiO2 nanocomposite for degradation of dye pollutants (methylene blue, texbrite BAC-L, texbrite BBU-L and texbrite NFW-L) under ultrasonic irradiation. DyesPigm 134:487–497
Paisio CE, Agostini E, González PS, Bertuzzi ML (2009) Lethal and teratogenic effects of phenol arenarum embryos. J Hazard Mater 167(1-3):64–68
Penalver JJL, Pacheco CVG, Polo MS, Utrilla JR (2013) Degradation of tetracyclines in different water matrices by advanced oxidation/reduction processes based on gamma radiation. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 88:1096–1108
Ramteke LP, Gogate PR (2015) Removal of ethylbenzene and p-nitrophenol using combined approach of advanced oxidation with biological oxidation based on the use of novel modified prepared activated sludge. Process Saf Environ Prot 95:146–158
Trojanowicz M, Bojanowska-Czajka A, Capodaglio AG (2017) Can radiation chemistry supply a highly efficient AO(R) P process for organics removal from drinking and waste water: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(25):20187–20208
Völker J, Castronovo S, Wick A, Ternes TA, Joss A, Oehlmann J, Wanger M (2016) Advancing biological wastewater treatment: extended anaerobic conditions enhance the removal of endocrine and dioxin-like activities. Environ Sci Technol 50(19):10606–10615
Xiong Z, Zhang H, Zhang W, Lai B, Yao G (2019) Removal of nitrophenols and their derivatives by chemical redox : a review. Chem Eng J 359:13–31
Yanga L, He L, Xue J, Ma Y, Shi Y, Wu L, Zhang Z (2020) UV/SO32−based advanced reduction processes of aqueous contaminants: current status and prospects. Chem Eng J 397:125412
Yazdanbakhsh A, Eslami A, Moussavi G, Rafiee M, Sheikhmohammadi A (2018) Photo-assisted degradation of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol by an advanced reduction process based on sulfite anion radical: degradation, dechlorination and mineralization. Chemosphere 191:156–165
Yazdanbakhsh A, Eslami A, Mahdipour F, Ghanbari F, Ghasemi M, Atamaleki A, Sharifi H, Lin KL (2021) Dye degradation in aqueous solution by dithionite/UV-C advanced reduction process (ARP): Kinetic study, dechlorination, degradation pathway and mechanism. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 407:112995
Yu H, Nie E, Xu J, Yan S, Cooper WJ, Song W (2013) Degradation of diclofenac by advanced oxidation and reduction processes: kinetic studies, degradation pathways and toxicity assessments. Water Res 47(5):1909–19018
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Environmental Health Engineering Research Center, the Kerman University of Medical Sciences, for their scientific supports.
Funding
This work was supported by the vice-chancellor for Research and Technology of Kerman University of Medical Sciences (Grant No. 99000827) and the code of research ethics certificate IR.KMU.REC.1400.015.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HD conceived, designed and performed the experiments, analyzed and interpreted the data, and wrote the paper; KT performed the bibliographic revision, carried out the comparison of results and collaborated in the discussion of results.; AM, JM, AM analyzed and interpreted the data and critically revised the work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This work does not contain any studies with human participants or animals.
Consent to participate
All authors provided informed consent to participate in this research study.
Consent for publication
No applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ricardo A. Torres-Palma
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 119 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Daraei, H., Mittal, A., Toolabian, K. et al. Study on the biodegradability improvement of 2,4 dinitrophenol in wastewater using advanced oxidation/reduction process with UV/SO3/ZnO. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 22273–22283 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23231-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23231-1