Abstract
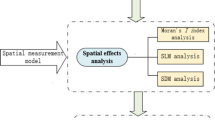
In order to explore the evolution process of regional vegetable circulation efficiency and its influencing factors, this paper uses Super-SBM model considering unexpected output and GML index to calculate the vegetable circulation efficiency of 13 provinces (cities) in Central China and its surrounding areas from 2015 to 2019, then conducts spatial autocorrelation analysis on the vegetable circulation efficiency in this region through Moran index. Finally, SPDM model is constructed to explore the spatial effect of the influencing factors on the vegetable circulation efficiency in this region. The results show that (1) the vegetable circulation efficiency of most provinces (cities) in this region is low. (2) The Global Moran’s I of the vegetable circulation efficiency in this region is positive, that is, the vegetable circulation efficiency in this region shows a certain degree of spatial agglomeration effect. (3) The level of scientific and technological innovation and the degree of government support have significant positive direct and indirect effects on the efficiency of vegetable circulation in the region, the quality of workers has significant positive indirect effects, and the level of economic development and industrial structure have significant negative indirect effects.
Graphical abstract



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Bai D, Dong Q, Khan S, Chen Y, Wang D, Yang L (2021) Spatial analysis of logistics ecological efficiency and its influencing factors in China: based on super-SBM-undesirable and spatial Dubin models 29. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16323-x
Cai L, Wang J (2020) Efficiency analysis of logistics industry in 12 western provinces based on DEA. J Math Prac Theory 50(2):141–149
Deng F, Xu L, Fang Y, Gong Q, Li Z (2020) PCA-DEA-tobit regression assessment with carbon emission constraints of China’s logistics industry. J Clean Prod 271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122548
Gong X (2022) Measurement of regional logistics efficiency and analysis of influencing factors. Stat Decision 38(12). https://doi.org/10.13546/j.cnki.tjyjc.2022.12.022
Gong X, Gong L (2019) Research on China's provincial logistics efficiency based on DEA-Malmquist model——An empirical analysis from inter provincial panel data. J Hebei Univ Econ Trade 40(5):60–69
Gong Y, Wan J, Feng F (2019) Research on the measurement of regional logistics efficiency and its influencing factors——Based on DEA and Tobit model. Jiangxi Social Sci 39(10):72–80
Guo J (2022) Driving mechanism and spatial effect decomposition of ecological efficiency of logistics industry——a comparative study based on the Yangtze River economic belt and provinces. J Comm Econ 5:108–112
Guo M, Li H, Lin W (2021) The impact of economic growth, FDI, and innovation on environmental efficiency of the logistics industry in provinces along the belt and road in China: An empirical study based on the panel Tobit model. Sci Prog 104(2). https://doi.org/10.1177/00368504211018054
Li J, Tian L, Wang Y (2018) Spatial effect analysis of regional logistics industry efficiency considering unexpected output. J Arid Land Resour Environ 32(08):67–73. https://doi.org/10.13448/j.cnki.jalre.2018.237
Liao N, Luo X, Wu J (2021) Economic output, energy consumption and energy efficiency of logistics industry. Stat Decision 37(18):113–116. https://doi.org/10.13546/j.cnki.tjyjc.2021.18.025
Long R, Ouyang H, Guo H (2020) Super-slack-based measuring data envelopment analysis on the spatial–temporal patterns of logistics ecological efficiency using global Malmquist Index model 18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2020.100770
Ma F, Hu J, Sun Q, Xu Y, Shang Z, Ke H (2021) Research on carbon emission performance measurement and driving factors of China's inter provincial logistics industry. Ecol Econ 37(9):27-33+39
Mu X, Wang L, Xu R, Guo Z (2020) Research on decoupling and influencing factors of carbon emissions from logistics industry in western provinces. Environ Sci Technol 43(4):214–219. https://doi.org/10.19672/j.cnki.1003-6504.2020.04.031
Ran W, Liu R, Liu S (2022) Area differences in regional logistics efficiency and the law governing its temporal and spatial evolution. J Adv Transp 2022. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/3596524
Tian Q, Liu Y, Li N, Wu Q, Liu M (2020) Research on efficiency evaluation of logistics industry in Pan Bohai economic circle based on DEA. J Highw Transport Res Dev 37(1):149–158
Tone K (2001) A slacks-based measure of efficiency in data envelopment analysis. Eur J Oper Res 130(3):498–509. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0377-2217(99)00407-5
Wang J, Cui L (2021) Spatial and temporal evolution of logistics efficiency of provinces along the new land sea corridor in the West and its influencing factors——an empirical analysis based on panel data of provinces along the corridor. J Chongqing Univ Technol(Natural Science) 35(12):243–255
Yang X, Ma S, Lu Y (2019) Logistics efficiency evaluation under carbon emission constraints——Take one belt, one road, and ten inland provinces as examples. Ecol Econ 35(6):66–71
Yao S, Ma L, Lai Y (2020) One belt, one road, key provinces, low carbon logistics efficiency measurement. Ecol Econ 36(11):18–24
Yuan L (2022) Analysis on carbon emission efficiency and influencing factors of china's logistics industry under carbon emission constraints. J Environ Prot Ecol 23(1):426–436
Zhang Y, Liu Z, Ouyang H, Song L (2020) A comprehensive study on the efficiency of regional logistics industry in a low carbon environment——an empirical analysis based on 19 provinces in the Yangtze River Protection Area. Modern Manag 40, 33(02):–40. https://doi.org/10.19634/j.cnki.11-1403/c.2020.02.008
Zhu T, Xu Y, Bao B (2021) Analysis of regional logistics development characteristics and efficiency——analysis based on carbon emission and LMDI method. Technoecon Manag Res 6:104–108
Funding
This work was supported by the Key Project of Soft Science Research in Henan Province (202400410051).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Bingjun Li was responsible for proposing the overall idea and framework of the manuscript. Xueqiang Guo was responsible for data processing and writing of the first draft of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Ethical approval was obtained from School of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering, Henan Agricultural University.
Consent for publication
All authors are informed and agreed to the study.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, X., Li, B. Analysis of regional vegetable circulation efficiency and its spatial effect considering carbon emission. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 81917–81928 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22740-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22740-3