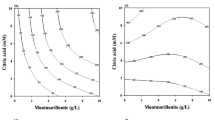
Abstract
Organic matter (OM) has an excellent retention effect on stabilizing chromium (Cr), and functional groups on OM play a predominant role in this process. Based on this result, it is found that a considerable amount of Cr in tannery sludge is immobilized from ion exchangeable species into bound species, benefiting from complexing reaction with functional groups. Especially, the mentioned immobilizing process is enhanced in way of adding with montmorillonite (MMT) which performs adsorption reaction with Cr, as well as plays interaction with functional groups. The result is confirmed by employing density functional theory (DFT) analysis, suggesting the binding ability among Cr, functional groups, and MMT is stronger (− 77.36503 eV) than that of the system of Cr and MMT (− 61.29942 eV), indicating the synergetic roles of OM and MMT. This synergetic role could also be illustrated by a new peak (Cr-OH 20.1%) shown in XPS result. Meanwhile, DFT analysis emphasizes that functional groups on OM give the response for binding with Cr in the order of hydroxyl (-OH) > carboxyl (-COOH) > epoxy (-COC), and all the functional groups tend to donate electron to bind with Cr. In addition, the stabilizing process shows a better fitting effect with pseudo second-order kinetic model (R2 > 0.94), indicating that exchangeable Cr mass transfer and chemical adsorption occur simultaneously.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Abreu MA, Toffoli SM (2009) Characterization of a chromium-rich tannery waste and its potential use in ceramics. Ceram Int 35:2225–2234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2008.12.011
Alibardi L, Cossu R (2016) Pre-treatment of tannery sludge for sustainable landfilling. Waste Manage 52:202–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2016.04.008
Arunachalam J, Emons H, Krasnodebska B, Mohl C (1996) Sequential extraction studies on homogenized forest soil samples. Sci Total Environ 181:147–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/0048-9697(95)05005-1
Banks MK, Schwab AP, Henderson C (2006) Leaching and reduction of chromium in soil as affected by soil organic content and plants. Chemosphere 62:255–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.05.020
Calvanese G, Cioffi R, Santoro L (2002) Cement stabilization of tannery sludge using quaternary ammonium salt exchanged bentonite as pre-solidification adsorbent. Environ Techno 23:1051–1062. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593332308618351
Chen W, Habibul N, Liu X-Y, Sheng G-P, Yu H-Q (2015) FTIR and synchronous fluorescence heterospectral two-dimensional correlation analyses on the binding characteristics of copper onto dissolved organic matter. Environ Sci Technol 49:2052–2058. https://doi.org/10.1021/es5049495
Chen H, Li Q, Wang M, Ji D, Tan W (2020) XPS and two-dimensional FTIR correlation analysis on the binding characteristics of humic acid onto kaolinite surface. Sci Total Environ 724:138154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138154
Concas A, Montinaro S, Pisu M, Cao G (2007) Mechanochemical remediation of heavy metals contaminated soils: Modelling and experiments. Chem Eng Sci 62:5186–5192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2007.02.024
Fathima A, Raghava Rao J, Unni Nair B (2012) Trivalent chromium removal from tannery effluent using kaolin-supported bacterial biofilm of Bacillus sp isolated from chromium polluted soil. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 87:271–279. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.2710
Guan X-H, Chen G-H, Shang C (2007) ATR-FTIR and XPS study on the structure of complexes formed upon the adsorption of simple organic acids on aluminum hydroxide. J Environ Sci 19:438–443. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1001-0742(07)60073-4
Han Y, Hu J, Jiang L (2018) Collagen skin, a water-sensitive shape memory material. J Mater Chem B 6:5144–5152. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8tb01346b
Han Y, Jiang Y, Hu J, Chen X (2020) Achieving coalesced breathability, mechanical and shape memory properties of collagen fibrous matrix through complexing with chromium (III). Mater Des 186:108206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2019.108206
Kokkinos E, Proskynitopoulou V, Zouboulis A (2019) Chromium and energy recovery from tannery wastewater treatment waste: investigation of major mechanisms in the framework of circular economy. J Environ Chem Eng 7:103307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2019.103307
G Lagaly, M Ogawa, I Dékány (2006) Chapter 7.3 Clay mineral organic interactions. 1 309–377 https://doi.org/10.1016/s1572-4352(05)01010-x
Liu H-B, Liu S-J, He X-S, Dang F, Tang Y-Y, Xi B-D (2021) Effects of landfill refuse on the reductive dechlorination of pentachlorophenol and speciation transformation of heavy metals. Sci Total Environ 760:144122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.144122
De Mário EA, Liu C, Ezugwu CI, Mao S, Jia F, Song S (2020) Molybdenum disulfide/montmorillonite composite as a highly efficient adsorbent for mercury removal from wastewater. Appl Clay Sci 184:105370–105380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2019.105370
Ma H, Li X, Zhu C, Chen F, Yang Y, Chen X (2020) Liberation and recovery of Cr from real tannery sludge by ultrasound-assisted supercritical water oxidation treatment. J Clean Prod 267:122064. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122064
Mao L, Deng N, Liu L, Cui H, Zhang W (2016) Inhibition of Cr(III) oxidation during thermal treatment of simulated tannery sludge: the role of phosphate. Chem Eng J 294:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.02.102
Oruko RO, Selvarajan R, Ogola HJO, Edokpayi JN, Odiyo JO (2020) Contemporary and future direction of chromium tanning and management in sub Saharan Africa tanneries. Process Saf Environ Protect 133:369–386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2019.11.013
Oyeyiola AO, Olayinka KO, Alo BI (2011) Comparison of three sequential extraction protocols for the fractionation of potentially toxic metals in coastal sediments. Environ Monit Assess 172:319–327. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1336-4
Peng K, Fu L, Ouyang J, Yang H (2016a) Emerging parallel dual 2D composites: natural clay mineral hybridizing MoS2 and interfacial structure. Adv Funct Mater 26:2666–2675. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201504942
Peng C, Min F, Liu L, Chen J (2016b) A periodic DFT study of adsorption of water on sodium-montmorillonite (001) basal and (010) edge surface. Appl Surf Sci 387:308–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.06.079
Ramírez C, Rico M, Torres A, Barral L, López J, Montero B (2008) Epoxy/POSS organic–inorganic hybrids: ATR-FTIR and DSC studies. Eur Polym J 44:3035–3045. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2008.07.024
Rauret G, López-Sánchez JF, Sahuquillo A, Rubio R, Davidson C, Ure A, Quevauviller PH (1999) Improvement of the BCR three step sequential extraction procedure prior to the certification of new sediment and soil reference materials. J Environ Monit 1:57–61. https://doi.org/10.1039/A807854H
Reijonen I, Hartikainen H (2016) Oxidation mechanisms and chemical bioavailability of chromium in agricultural soil – pH as the master variable. Appl Geochem 74:84–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2016.08.017
Tun PP, Wang J, Khaing TT, Wu X, Zhang G (2020) Fabrication of functionalized plasmonic Ag loaded Bi2O3/montmorillonite nanocomposites for efficient photocatalytic removal of antibiotics and organic dyes. J Alloys Compd 818:152836–152849. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.152836
Wang L, Chen M, Li J, Jin Y, Zhang Y, Wang Y (2020) A novel substitution-based method for effective leaching of chromium (III) from chromium-tanned leather waste: the thermodynamics, kinetics and mechanism studies. Waste Manage 103:276–284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2019.12.039
Wei D, Zhao C, Khan A, Sun L, Ji Y, Ai Y, Wang X (2019) Sorption mechanism and dynamic behavior of graphene oxide as an effective adsorbent for the removal of chlorophenol based environmental-hormones: a DFT and MD simulation study. Chem Eng J 375:121964. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.121964
Wu P, Tang Y, Wang W, Zhu N, Li P, Wu J, Dang Z, Wang X (2011) Effect of dissolved organic matter from Guangzhou landfill leachate on sorption of phenanthrene by montmorillonite. J Colloid Interf Scie 361:618–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2011.06.019
Xu T, Nan F, Jiang X, Tang Y, Zeng Y, Zhang W, Shi B (2020) Effect of soil pH on the transport, fractionation, and oxidation of chromium(III). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 195:110459. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110459
Yang Y, Ma H, Chen X, Zhu C, Li X (2020) Effect of incineration temperature on chromium speciation in real chromium-rich tannery sludge under air atmosphere. Environ Res 183:109159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2020.109159
Yang S, Xiao X, Tao E (2021) Removing low concentration of Cr (III) from wastewater: using titanium dioxide surface modified montmorillonite as a selective adsorbent. Inorg Chem Commun 125:108464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inoche.2021.108464
Yang S, Zou H, Cheng Y, Tao E (2022) Immobilizing chromium in tannery sludge via adding collagen protein waste: an in-depth study on mechanism. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 29:30337–30347. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17919-z
Yuan W, Kuang J, Yu M, Huang Z, Zou Z, Zhu L (2021) Facile preparation of MoS2@Kaolin composite by one-step hydrothermal method for efficient removal of Pb(II). J Hazard Mater 405:124261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124261
Zhang J, Yin H, Chen L, Liu F, Chen H (2018) The role of different functional groups in a novel adsorption-complexation-reduction multi-step kinetic model for hexavalent chromium retention by undissolved humic acid. Environ Pollut 237:740–746. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.10.120
Zhang H, Ma J, Wang F, Chu Y, Yang L, Xia M (2020) Mechanism of carboxymethyl chitosan hybrid montmorillonite and adsorption of Pb(II) and Congo red by CMC-MMT organic-inorganic hybrid composite. Int J Biol Macromol 149:1161–1169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.01.201
Funding
The research was supported by Liaoning Province (Jinzhou) Fur Green Manufacturing Industry Technology Innovation Strategic Alliance (201854), research on resource recycling technology of tanned chromium-containing waste dander (2018020190–301), The “Seedling” Project named “Research on Graphene-based 3D Material Construction and Key Technologies for Industrialization Application” for Youth Science and Technology Talents of Education Department of Liaoning Province (LQ2020011), and Environmental Risk Analysis of Heavy Metals in Jinzhou Coastal Zone and Research on Advanced Treatment of Lead (BDHYYJY2021005) (this study were supported by the Open Fund of Institute of Ocean Research, Bohai University).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Shuyi Yang: investigation, data curation, and writing original draft preparation. Ying Cheng: methodology and validation. Hongtao Zou: conceptualization, editing, review, and revision. Tao E: conceptualization and methodology.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All authors have agreed with the content, and all have given explicit consent to publish.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ioannis A. Katsoyiannis
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, S., Cheng, Y., Zou, H. et al. Synergistic roles of montmorillonite and organic matter in reducing bioavailable state of chromium in tannery sludge. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 87298–87309 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21897-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21897-1