Abstract
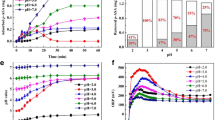
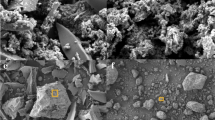
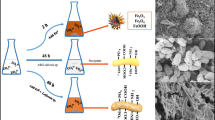
The serious environmental risks caused by Pb(II) and Sb(V) co-contamination increase the need for their efficient and simultaneous removal. In this study, the remediation feasibility by Fe-doped phosphogypsum (FPG) was elucidated for single systems with Pb or Sb pollutant and coexisting systems with both from water. As for single systems, Fe doping effectively enhanced the Pb(II) removal performance by phosphogypsum (PG) at low Pb(II) concentrations of below 100 mg/L via the combination of precipitation and complexation. The optimal removal rate of Sb(V) by FPG increased by 2.08–3.31 times as compared to that of by PG (10–120 mg/L), mainly due to the strong affinity of iron hydroxyl (≡Fe–O–H) towards Sb(V). Compared with the single systems, the coexistence greatly enhanced the Pb(II) and Sb(V) removal performance by FPG, and the interaction behavior between Pb(II) and Sb(V) on the FPG was concentration dependent. Briefly, the sorption of FPG controlled the elimination of low coexisting concentrations of Pb(II) and Sb(V), whereas the co-precipitation process between Pb(II) and Sb(V) predominated with high ions concentration. The significant synergistic effects were found during the removal of Pb(II) and Sb(V) on FPG in the coexisting system, which mainly attributed to precipitation, bridging complexation and electrostatic attraction. Considering the advantages such as facile preparation, low cost and high removal capacity, FPG is a promising material to uptake Pb(II) and/or Sb(V) from contaminated water.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Ahmad M, Lee SS, Lim JE, Lee SE, Cho JS, Moon DH, Hashimoto Y, Ok YS (2014) Speciation and phytoavailability of lead and antimony in a small arms range soil amended with mussel shell, cow bone and biochar: EXAFS spectroscopy and chemical extractions. Chemosphere 95:433–441
Ahmad M, Ok YS, Rajapaksha AU, Lim JE, Kim BY, Ahn JH, Lee YH, Al-Wabel MI, Lee SE, Lee SS (2016) Lead and copper immobilization in a shooting range soil using soybean stover- and pine needle-derived biochars: chemical, microbial and spectroscopic assessments. J Hazard Mater 301:179–186
Aljerf L (2018) High-efficiency extraction of bromocresol purple dye and heavy metals as chromium from industrial effluent by adsorption onto a modified surface of zeolite: kinetics and equilibrium study. J Environ Manage 225:120–132
Altaş L, Balkaya N, Cesur H (2017) Pb(II) Removal from aqueous solution and industrial wastewater by raw and lime-conditioned phosphogypsum. Int J Environ Res 11:111–123
Awual MR (2019) Mesoporous composite material for efficient lead(II) detection and removal from aqueous media. J Environ Chem Eng 7:103124
Awual MR, Hasan MM (2019) A ligand based innovative composite material for selective lead(II) capturing from wastewater. J Mol Liq 294:111679
Awual MR, Islam A, Hasan MM, Rahman MM, Asiri AM, Khaleque MA, Sheikh MC (2019) Introducing an alternate conjugated material for enhanced lead(II) capturing from wastewater. J Clean Prod 224:920–929
Barker AJ, Clausen JL, Douglas TA, Bednar AJ, Griggs CS, Martin WA (2021) Environmental impact of metals resulting from military training activities: a review. Chemosphere 265:129110
Chen H-X, Xu F-N, Chen Z-Z, Jiang O-Y, Gustave W, Tang X-J (2020) Arsenic and cadmium removal from water by a calcium-modified and starch-stabilized ferromanganese binary oxide. J Environ Sci 96:186–193
Cornelis G, Gerven TV, Snellings R, Verbinnen B, Elsen J, Vandecasteele C (2011) Stability of pyrochlores in alkaline matrices: solubility of calcium antimonate. Appl Geochemistry 26:809–817
Cornelis G, Etschmann B, Gerven TV, Vandecasteele C (2012) Mechanisms and modelling of antimonate leaching in hydrated cement paste suspensions. Cem Concr Res 42:1307–1316
Dehghani A, Aslani F, Panah NG (2021) Effects of initial SiO2/Al2O3 molar ratio and slag on fly ash-based ambient cured geopolymer properties. Constr Build Mater 293:123527
Dinake P, Kelebemang R (2019) Critical assessment of mechanistic pathways for chemical remediation techniques applied to Pb impacted soils at shooting ranges – a review. Env Pollut Bioavail 31:282–305
El-Didamony H, Gado HS, Awwad NS, Fawzy MM, Attallah MF (2013) Treatment of phosphogypsum waste produced from phosphate ore processing. J Hazard Mater 244–245:596–602
Feng Z-Y, Chen N, Liu T, Feng C-P (2022) KHCO3 activated biochar supporting MgO for Pb(II) and Cd(II) adsorption from water: experimental study and DFT calculation analysis. J Hazard Mater 426:128059
Garau G, Lauro GP, Diquattro S, Garau M, Castaldi P (2019) Sb(V) adsorption and desorption onto ferrihydrite: influence of pH and competing organic and inorganic anions. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:27268–27280
Griggs CS, Martin WA, Larson SL, O’Connnor G, Fabian G, Zynda G, Mackie D (2011) The effect of phosphate application on the mobility of antimony in firing range soils. Sci Total Environ 409:2397–2403
Guaya D, Jiménez R, Sarango J, Valderrama C, Cortina JL (2021) Iron-doped natural clays: Low-cost inorganic adsorbents for phosphate recovering from simulated urban treated wastewater. J Water Process Eng 43:102274
Guo H-B, Barnard AS (2013) Naturally occurring iron oxide nanoparticles: morphology, surface chemistry and environmental stability. J Mater Chem a 1:27–42
Guo X-J, Wu Z-J, He M-C, Meng X-G, Jin X, Qiu N, Zhang J (2014) Adsorption of antimony onto iron oxyhydroxides: adsorption behavior and surface structure. J Hazard Mater 276:339–345
He X-Y, Min X-B, Peng T-Y, Ke Y, Zhang F-P, Wang Y-Y, Sillanpaa M (2019) Highly efficient antimonate removal from water by pyrite/hematite bi-mineral: performance and mechanism studies. J Chem Eng Data 64:5910–5919
He X-Y, Min X-B, Peng T-Y, Ke Y, Zhao F-P, Sillanpää M, Wang Y-Y (2020) Enhanced adsorption of antimonate by ball-milled microscale zero valent iron/pyrite composite: adsorption properties and mechanism insight. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:16484–16495
Heier LS, Lien IB, Strømseng AE, Ljønes M, Rosseland BO, Tollefsen K, Salbu B (2009) Speciation of lead, copper, zinc and antimony in water draining a shooting range—time dependant metal accumulation and biomarker responses in brown trout (Salmo trutta L.). Sci Total Environ 407:4047–4055
Herath I, Vithanage M, Bundschuh J (2017) Antimony as a global dilemma: geochemistry, mobility, fate and transport*. Environ Pollut 223:545–559
Johnson CA, Moench H, Wersin P, Kugler P, Wenger C (2005) Solubility of antimony and other elements in samples taken from shooting ranges. J Environ Qual 34:248–254
Kameda K, Hashimoto Y, Wang S-L, Hirai Y, Miyahara H (2017) Simultaneous and continuous stabilization of As and Pb in contaminated solution and soil by a ferrihydrite-gypsum sorbent. J Hazard Mater 327:171–179
Klitzke S, Lang F (2009) Mobilization of soluble and dispersible lead, arsenic, and antimony in a polluted, organic-rich soil − effects of pH increase and counterion valency. J Environ Qual 38:933–939
Lamzougui G, Es-Said A, Nafai H, Chafik D, Bouhaouss A, Bchitou R (2021) Optimization and modeling of Pb(II) adsorption from aqueous solution onto phosphogypsum by application of response surface methodology. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat Elem 196(6):521–529
Li R, Li Q, Sun X-Y, Li J-S, Shen J-Y, Han W-Q, Wang L-J (2019) Efficient and rapid removal of EDTA-chelated Pb(II) by the Fe(III)/flue gas desulfurization gypsum (FGDG) system. J Colloid Interface Sci 542:379–386
Li Q, Li R, Ma X-Y, Sarkar B, Sun X-Y, Bolan N (2020) Comparative removal of As(V) and Sb(V) from aqueous solution by sulfide-modified a-FeOOH*. Environ Pollut 267:115658
Li J, Zhao Z-J, Song Y-R, You Y, Li J, Cheng X-W (2021a) Synthesis of Mg(II) doped ferrihydrite-humic acid coprecipitation and its Pb(II)/Cd(II) ion sorption mechanism. Chin Chem Lett 32(10):3231–3236
Li B-Y, Wei D-N, Zhou Y-M, Huang Y-Y, Tie B-Q (2021b) Mechanisms of arsenate and cadmium co-immobilized on ferrihydrite inferred from ternary surface configuration. Chem Eng J 424:130410
Li L, Wang B, Li W, Liu T-Z, Wu P, Xu Q-Y, Liu S-R (2022) Effective Sb(V) from aqueous solution using phosphogypsum-modified biochar. Environ Pollut 301:119032
Liao Q, Tu G-Y, Yang Z-H, Wang H-Y, He L-X, Tang J-Q, Yang W-C (2019) Simultaneous adsorption of As(III), Cd(II) and Pb(II) by hybrid bio-nanocomposites of nano hydroxy ferric phosphate and hydroxy ferric sulfate particles coating on aspergillus niger. Chemosphere 223:551–559
Liu R-P, Liu F, Hu C-Z, He Z, Liu H-J, Qu J-H (2015) Simultaneous removal of Cd(II) and Sb(V) by Fe–Mn binary oxide: positive effects of Cd(II) on Sb(V) adsorption. J Hazard Mater 300:847–854
Liu B, Jian M-P, Wang H, Zhang G-S, Liu R-P, Zhang X-W, Qu J-H (2018) Comparing adsorption of arsenic and antimony from single-solute and bi-solute aqueous systems onto ZIF-8. Colloid Surface a 538:164–172
Liu Y-W, Luan J-D, Zhang C-Y, Ke X, Zhang H-J (2019a) The adsorption behavior of multiple contaminants like heavy metal ions and p-nitrophenol on organic-modified montmorillonite. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:10387–10397
Liu J-Q, Wu P-X, Li S-S, Chen M-Q, Cai W-T, Zou D-H, Zhu N-W, Dang Z (2019b) Synergistic deep removal of As(III) and Cd(II) by a calcined multifunctional MgZnFe-CO3 layered double hydroxide: photooxidation, precipitation and adsorption. Chemosphere 225:115–125
Long X-J, Wang X, Guo X-J, He M-C (2020) A review of removal technology for antimony in aqueous solution. J Environ Sci 90:189–204
Luo J-M, Luo X-B, Crittenden J, Qu J-H, Bai Y-H, Peng Y, Li J-H (2015) Removal of antimonite (Sb(III)) and antimonate (Sb(V)) from aqueous solution using carbon nanofibers that are decorated with zirconium oxide (ZrO2). Environ Sci Technol 49:11115–11124
Maneechakr P, Karnjanakom S (2021) Facile utilization of magnetic MnO2@Fe3O4@sulfonated carbon sphere for selective removal of hazardous Pb(II) ion with an excellent capacity: adsorption behavior/ isotherm/ kinetic/ thermodynamic studies. J Environ Chem Eng 9:106191
Mariussen E, Johnsen IV, Strømseng AE (2015) Selective adsorption of lead, copper and antimony in runoff water from a small arms shooting range with a combination of charcoal and iron hydroxide. J Environ Manage 150:281–287
Meng K-Y, Wu X-W, Zhang X-Y, Su S-M, Huang Z-H, Min X, Liu Y-G, Fang M-H (2019) Efficient adsorption of the Cd(II) and As(V) using novel adsorbent ferrihydrite/manganese dioxide composites. ACS Omega 4:18627–18636
Morales J, Astilleros JM, Fernández-Díaz L, Álvarez-Lloret P, Jiménez A (2013) Anglesite (PbSO4) epitactic overgrowths and substrate-induced twinning on anhydrite (CaSO4) cleavage surfaces. J Cryst Growth 380:130–137
Morales J, Astilleros JM, Jiménez A, Göttlicher J, Steininger R, Fernández-Díaz L (2014) Uptake of dissolved lead by anhydrite surfaces. Appl Geochemistry 40:89–96
Mousa SM, Ammar NS, Ibrahim HA (2016) Removal of lead ions using hydroxyapatite nano-material prepared from phosphogypsum waste. J Saudi Chem Soc 20:357–365
Ogawa S, Katoh M, Sato T (2014) Contribution of hydroxyapatite and ferrihydrite in combined applications for the removal of lead and antimony from aqueous solutions. Water Air Soil Pollut 225:2023–2034
Okkenhaug G, Zhu Y-G, Luo L, Lei M, Li X, Mulder J (2011) Distribution, speciation and availability of antimony (Sb) in soils and terrestrial plants from an active Sb mining area. Environ Pollut 159:2427–2434
Okkenhaug G, Amstatter K, Bue HL, Cornelissen G, Breedveld GD, Henriksen T, Mulder J (2013) Antimony (Sb) contaminated shooting range soil: Sb mobility and immobilization by soil amendments. Environ Sci Technol 47:6431–6439
Okkenhaug G, Gebhardt KAG, Amstaetter K, Bue HL, Herzel H, Mariussen E, Almås AR, Cornelissen G, Breedveld GD, Rasmussen G, Mulder J (2016) Antimony (Sb) and lead (Pb) in contaminated shooting range soils: Sb and Pb mobility and immobilization by iron based sorbents, a field study. J Hazard Mater 307:336–343
Oladoye PO (2022) Natural, low-cost adsorbents for toxic Pb(II) ion sequestration from (waste) water: A state-of-the-art review. Chemosphere 287:132130
Pain DJ, Dickie I, Green RE, Kanstrup N, Cromie R (2019) Wildlife, human and environmental costs of using lead ammunition: an economic review and analysis. AMBIO J Hum Environ 48:969–988
Qi P-F, Pichler T (2016) Sequential and simultaneous adsorption of Sb(III) and Sb(V) on ferrihydrite: implications for oxidation and competition. Chemosphere 145:55–60
Qi Z-L, Joshi TP, Liu R-P, Liu H-J, Qu J-H (2017) Synthesis of Ce(III)-doped Fe3O4 magnetic particles for efficient removal of antimony from aqueous solution. J Hazard Mater 329:193–204
Shi M-Q, Min X-B, Ke Y, Li Z, Yang Z-H, Wang S, Peng N, Yan X, Luo S, Wu J-H, Wei Y-J (2021) Recent progress in understanding the mechanism of heavy metals retention by iron (oxyhydr)oxides. Sci Total Environ 752:141930
Silva LFO, Oliveira MLS, Crissien TJ, Santosh M, Bolivar J, Shao L-Y, Dotto GL, Gasparotto J, Schindler M (2022) A review on the environmental impact of phosphogypsum and potential health impacts through the release of nanoparticles. Chemosphere 286:131513
Skalny AV, Aschner M, Bobrovnitsky IP, Chen P, Tsatsakis A, Paoliello MMB, Djordevic AB, Tinkov AA (2021) Environmental and health hazards of military metal pollution. Environ Res 201:111568
Song L, Feng Y-F, Zhu C-Q, Liu F-Q, Li A-M (2020) Enhanced synergistic removal of Cr(VI) and Cd(II) with bi-functional biomass-based composites. J Hazard Mater 388:121776
Strømseng AE, Ljønes M, Bakka L, Mariussen E (2009) Episodic discharge of lead, copper and antimony from a Norwegian small arm shooting range. J Environ Monitor 11:1259–1267
Teng F-Y, Zhang Y-X, Wang D-Q, Shen M-C, Hu D-F (2020) Iron-modified rice husk hydrochar and its immobilization effect for Pb and Sb in contaminated soil. J Hazard Mater 398:122977
Wang L, Wan C-L, Zhang Y, Lee DJ, Liu X, Chen X-F, Tay J-H (2015) Mechanism of enhanced Sb(V) removal from aqueous solution using chemically modified aerobic granules. J Hazard Mater 284:43–49
Wang W, Hua Y-L, Li S-L, Yan W-L, Zhang W-X (2016) Removal of Pb(II) and Zn(II) using lime and nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI): a comparative study. Chem Eng J 304:79–88
Wang L, Li Z-T, Wang Y, Brookes P-C, Wang F, Zhang Q-C, Xu J-M, Liu X-M (2021) Performance and mechanisms for remediation of Cd(II) and As(III) co-contamination by magnetic biochar-microbe biochemical composite: Competition and synergy effects. Sci Total Environ 750:141672
Xie Y-Y, Yuan X-Z, Wu Z-B, Zeng G-M, Jiang L-B, Peng X, Li H (2019) Adsorption behavior and mechanism of Mg/Fe layered double hydroxide with Fe3O4-carbon spheres on the removal of Pb(II) and Cu(II). J Colloid Interface Sci 536:440–455
Xie H-Y, Liu Y-H, Rao B, Wu J-Z, Gao L-K, Chen L-Z, Tian X-S (2021) Selective passivation behavior of galena surface by sulfuric acid and a novel flotation separation method for copper-lead sulfide ore without collector and inhibitor. Sep Purif Technol 267:118621
Xu J, Li X-G, Liu X-B, Dong C-F, Deem N, Barbero E (2005) X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy study of passive layers formed on Pb-Sn and Pb-Sb alloys. Metall Mater Trans A 36:2175–2190
Yan Y-B, Li Q, Sun X-Y, Ren Z-Y, He F, Wang Y-L, Wang L-J (2015) Recycling flue gas desulphurization (FGD) gypsum for removal of Pb(II) and Cd(II) from wastewater. J Colloid Interface Sci 457:86–95
Yang K-L, Zhou C-C, Li C, Dou S, Li X-G, Wang X (2021) Efficient removal of Sb(V) in textile wastewater through novel amorphous Si-doped Fe oxide composites: phase composition, stability and adsorption mechanism. Chem Eng J 407:127217
Zhang X-D, Shi D-Y, Li X, Zhang Y-J, Wang J-J, Fan J (2019) Nanoscale dispersing of zero-valent iron on CaCO3 and their significant synergistic effect in high performance removal of lead. Chemosphere 224:390–397
Zhang S-J, Shi Q-T, Chou T-M, Christodoulatos C, Korfiatis GP, Meng X-G (2020) Mechanistic study of Pb(II) removal vy TiO2 and effect of PO4. Langmuir 36(46):13918–13927
Zhang Y, Li H, Jiang Q, Jiang S-M, Wang Y-F, Wang L (2021a) One-pot synthesis of a novel P-doped ferrihydrite nanoparticles for efficient removal of Pb(II) from aqueous solutions: performance and mechanism. J Environ Chem Eng 9(4):105721
Zhang X-Y, Xie N-Y, Guo Y, Niu D, Sun H-B, Yang Y (2021b) Insights into adsorptive removal of antimony contaminants: functional materials, evaluation and prospective. J Hazard Mater 418:126345
Zhang Z, Wang T, Zhang H-X, Liu Y-H, Xing B-S (2021c) Adsorption of Pb(II) and Cd(II) by magnetic activated carbon and its mechanism. Sci Total Environ 757:143910
Zhang C, Liu L-B, Chen X-Y, Dai Y-C, Jia H-Z (2022) Mechanistic understanding of antimony(V) complexation on montmorillonite surfaces: insights from first-principles molecular dynamics. Chem Eng J 428:131157
Zhu K-C, Duan Y-Y, Wang F, Gao P, Jia H-Z, Ma C-Y, Wang C-Y (2017) Silane-modified halloysite/Fe3O4 nanocomposites: simultaneous removal of Cr(VI) and Sb(V) and positive effects of Cr(VI) on Sb(V) adsorption. Chem Eng J 311:236–246
Ziegenheim S, Szabados M, Kónya Z, Kukovecz Á, Pálinkó I, Sipos P (2021) Manipulating the crystallization kinetics and morphology of gypsum, CaSO4·2H2O via addition of citrate at high levels of supersaturation and the effect of high salinity. Polyhedron 204:115253
Funding
This work was supported by the Science and Technology Department of Jiangsu Province, China (BK20161497), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No.30917011308).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xinyue Ma: investigation, methodology, writing-original draft. Qiao Li: investigation, methodology, formal analysis, resources, writing-review&editing. Rui Li and Wei Zhang: methodology, resources. writing-review. Xiuyun Sun: conceptualization, methodology, writing-review. Jiansheng Li: resources, writing-review. Jinyou Shen: writing-review. Weiqing Han: writing-review.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All authors have read this manuscript and consent for publication in Environmental Science and Pollution Research.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Guilherme L. Dotto
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, X., Li, Q., Li, R. et al. Removal performance and mechanisms of Pb(II) and Sb(V) from water by iron-doped phosphogypsum: single and coexisting systems. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 87413–87425 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21862-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21862-y