Abstract
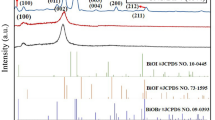
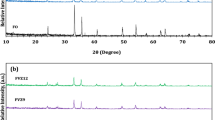
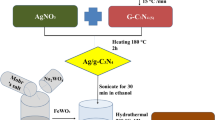
Azo dyes such as Reactive Red 120 raise great concerns about their increased harmfulness. Photocatalytic degradation is considered to be one of the most efficient techniques for Reactive Red 120 degradation. Herein, a highly solar active graphitic carbon nitride–assisted bismuth phosphate nanocomposite (BiPO4@g-C3N4) was synthesized by the thermal decomposition of melamine followed by the co-precipitation method. Various analytical techniques were utilized to characterize the prepared BiPO4, g-C3N4, and BiPO4@g-C3N4 nanocomposites. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) shows the nanorods and particle morphology of the bare BiPO4 and g-C3N4 respectively. Furthermore, the optical band gap energies of the BiPO4, g-C3N4, and BiPO4@g-C3N4 nanocomposite have been calculated to be 4.20, 2.66, and 2.68 eV respectively. Under sunlight, the BiPO4@g-C3N4 nanocomposite showed higher photocatalytic activity towards the degradation of RR120. The BiPO4@g-C3N4 nanocomposite efficiently degrades the RR120 under sunlight with a higher first-order reaction rate constant of 0.0145 min−1. This is seven times higher than that of bare BiPO4 (0.0019 min−1) nanorods and four times greater than g-C3N4 (0.0036 min−1). The photocatalytic efficiency was found to be maximum at pH 4 and decreased as the pH of the solution increased. Even after five recycle runs, the catalyst performance of the RR120 dye has decreased by less than 5%, indicating the high stability of the BiPO4@g-C3N4 nanocomposite. Furthermore, the radical trapping experiment demonstrates that the active species in the dye degradation process are holes and hydroxide radicals. The photocatalytic mechanism was proposed for the BiPO4@g-C3N4 nanocomposite and further validated by the electrochemical impedance spectroscopy analysis.















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Alves de Lima RO, Bazo AP, Salvadori DMF et al (2007) Mutagenic and carcinogenic potential of a textile azo dye processing plant effluent that impacts a drinking water source. Mutat Res Toxicol Environ Mutagen 626:53–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MRGENTOX.2006.08.002
An W, Cui W, Liang Y et al (2015) Surface decoration of BiPO4 with BiOBr nanoflakes to build heterostructure photocatalysts with enhanced photocatalytic activity. Appl Surf Sci 351:1131–1139. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.APSUSC.2015.06.098
Ben SK, Gupta S, Raj KK, Chandra V (2021) Synthesis of g-C3N4, Zn3(PO4)2 and g-C3N4/Zn3(PO4)2 composites for application in photodegradation of crystal violet dye under solar light. ChemistrySelect 6:7002–7011. https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.202101718
Bouddouch A, Amaterz E, Bakiz B et al (2020) Role of thermal decomposition process in the photocatalytic or photoluminescence properties of BiPO4 polymorphs. Water Environ Res 92:1874–1887. https://doi.org/10.1002/WER.1340
Brookstein DS (2009) Factors associated with textile pattern dermatitis caused by contact allergy to dyes, finishes, foams, and preservatives. Dermatol Clin 27:309–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.DET.2009.05.001
Cardoso NF, Lima EC, Pinto IS et al (2011) Application of cupuassu shell as biosorbent for the removal of textile dyes from aqueous solution. J Environ Manage 92:1237–1247. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JENVMAN.2010.12.010
Carneiro PA, Umbuzeiro GA, Oliveira DP, Zanoni MVB (2010) Assessment of water contamination caused by a mutagenic textile effluent/dyehouse effluent bearing disperse dyes. J Hazard Mater 174:694–699. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHAZMAT.2009.09.106
Castro FD, Bassin JP, Dezotti M (2017) Treatment of a simulated textile wastewater containing the Reactive Orange 16 azo dye by a combination of ozonation and moving-bed biofilm reactor: evaluating the performance, toxicity, and oxidation by-products. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:6307–6316. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7119-x
Celekli A, Yavuzatmaca M, Bozkurt H (2010) Modeling the removal of Reactive Red 120 on pistachio husk. CLEAN – Soil. Air, Water 38:173–180. https://doi.org/10.1002/CLEN.200900197
Chen F, Yang Q, Sun J et al (2016) Enhanced photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline by AgI/BiVO4 heterojunction under visible-light irradiation: mineralization efficiency and mechanism. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:32887–32900. https://doi.org/10.1021/ACSAMI.6B12278
Chu S, Wang Y, Guo Y et al (2013) Band structure engineering of carbon nitride: In search of a polymer photocatalyst with high photooxidation property. ACS Catal 3:912–919. https://doi.org/10.1021/cs4000624
Cui S, Xie B, Li R et al (2020) g-C3N4/CeO2 binary composite prepared and its application in automobile exhaust degradation. Materials (Basel) 13:1274. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13061274
David PS, Karunanithi A, Fathima NN (2020) Improved filtration for dye removal using keratin–polyamide blend nanofibrous membranes. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:45629–45638. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11356-020-10491-Y/FIGURES/7
Dong H, Zeng G, Tang L et al (2015) An overview on limitations of TiO2-based particles for photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants and the corresponding countermeasures. Water Res 79:128–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.WATRES.2015.04.038
Du Q, Rao R, Bi F et al (2022) Preparation of modified zirconium-based metal-organic frameworks (Zr-MOFs) supported metals and recent application in environment: a review and perspectives. Surfaces and Interfaces 28:101647. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfin.2021.101647
Duan Z, Zhao X, Wei C, Chen L (2020) Ag-Bi/BiVO4 chain-like hollow microstructures with enhanced photocatalytic activity for CO2 conversion. Appl Catal A Gen 594:117459. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.APCATA.2020.117459
Durairaj A, Sakthivel T, Ramanathan S, Vasanthkumar S (2019) Quenching-induced structural distortion of graphitic carbon nitride nanostructures: enhanced photocatalytic activity and electrochemical hydrogen production. ACS Omega 4:6476–6485. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.8b03279
Dutta S, Srivastava SK, Gupta B, Gupta AK (2021) Hollow polyaniline microsphere/MnO2/Fe3O4 nanocomposites in adsorptive removal of toxic dyes from contaminated water. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 13:54324–54338. https://doi.org/10.1021/ACSAMI.1C15096/SUPPL_FILE/AM1C15096_SI_001.PDF
Fujishima A, Honda K (1972) Electrochemical photolysis of water at a semiconductor electrode. Nature 238:37–38. https://doi.org/10.1038/238037a0
Ganesh R, Boardman GD, Michelsen D (1994) Fate of azo dyes in sludges. Water Res 28:1367–1376. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(94)90303-4
Gnanamozhi P, Rajivgandhi G, Alharbi NS et al (2020a) Enhanced antibacterial and photocatalytic degradation of reactive red 120 using lead substituted ZnO nanoparticles prepared by ultrasonic-assisted co-precipitation method. Ceram Int 46:19593–19599. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.05.020
Gnanamozhi P, Renganathan V, Chen SM et al (2020b) Influence of Nickel concentration on the photocatalytic dye degradation (methylene blue and reactive red 120) and antibacterial activity of ZnO nanoparticles. Ceram Int 46:18322–18330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.05.054
Gong Y, Wang Y, Lin N et al (2022) Iron-based materials for simultaneous removal of heavy metal(loid)s and emerging organic contaminants from the aquatic environment: Recent advances and perspectives. Environ Pollut 299:118871. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENVPOL.2022.118871
Govindasamy M, Wang SF, Alothman AA et al (2021) Synergetic effect of the ultrasonic-assisted hydrothermal process on the photocatalytic performance of MoS2 and WS2 nanoparticles. J Mater Sci Mater Electron. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-06934-y
Harijan DKL, Gupta S, Ben SK et al (2022) High photocatalytic efficiency of α-Fe2O3 - ZnO composite using solar energy for methylene blue degradation. Phys B Condens Matter 627:413567. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PHYSB.2021.413567
Kayalvizhi S, Sengottaiyan A, Selvankumar T et al (2020) Eco-friendly cost-effective approach for synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles for enhanced photocatalytic performance. Optik (Stuttg) 202:163507. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2019.163507
Kim YW, Kim JH, Moon DH, Shin HJ (2018) Adsorption and precipitation of anionic dye Reactive Red 120 from aqueous solution by aminopropyl functionalized magnesium phyllosilicate. Korean J Chem Eng 2019 361(36):101–108. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11814-018-0168-8
Kite SV, Kadam AN, Sathe DJ et al (2021) Nanostructured TiO2 sensitized with MoS2 nanoflowers for enhanced photodegradation efficiency toward methyl orange. ACS Omega 6:17071–17085. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.1c02194
Koutavarapu R, Tamtam MR, Myla CR et al (2021) Enhanced solar-light-driven photocatalytic properties of novel Z-scheme binary BiPO4 nanorods anchored onto NiFe2O4 nanoplates: efficient removal of toxic organic pollutants. J Environ Sci 102:326–340. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JES.2020.09.021
Krishnakumar B, Ravikumar S, Pandiyan V et al (2020) Synthesis, characterization of porphyrin and CdS modified spherical shaped SiO2 for Reactive Red 120 degradation under direct sunlight. J Mol Struct 1210:128021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2020.128021
Li G, Nie X, Chen J et al (2015) Enhanced visible-light-driven photocatalytic inactivation of Escherichia coli using g-C3N4/TiO2 hybrid photocatalyst synthesized using a hydrothermal-calcination approach. Water Res 86:17–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.WATRES.2015.05.053
Li M, He Z, Xu J (2021a) A comparative study of ozonation on aqueous reactive dyes and reactive-dyed cotton. Color Technol 137:376–388. https://doi.org/10.1111/COTE.12534
Li Y, Li Z, Xia Y et al (2021b) Fabrication of ternary AgBr/BiPO4/g-C3N4 heterostructure with dual Z-scheme and its visible light photocatalytic activity for Reactive Blue 19. Environ Res 192:110260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2020.110260
Liang Q, Jin J, Liu C et al (2018) A stable BiPO4/g-C3N4 nanosheet composite with highly enhanced visible light photocatalytic activity. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 29:2509–2516. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10854-017-8173-Y/FIGURES/7
Liu G, Liu S, Lu Q et al (2014) Synthesis of mesoporous BiPO4 nanofibers by electrospinning with enhanced photocatalytic performances. Ind Eng Chem Res 53:13023–13029. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie4044357
Liu N, Lu N, Yu HT et al (2022) Enhanced degradation of organic water pollutants by photocatalytic in-situ activation of sulfate based on Z-scheme g-C3N4/BiPO4. Chem Eng J 428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.132116
Liu X, Yan L, He L et al (2020) An experimental study on the Co-C3N4/BiPO4composite for efficient photocatalytic water splitting. New J Chem 44:10739–10746. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0nj01329c
Lops C, Ancona A, Di Cesare K et al (2019) Sonophotocatalytic degradation mechanisms of Rhodamine B dye via radicals generation by micro- and nano-particles of ZnO. Appl Catal B Environ 243:629–640. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.APCATB.2018.10.078
Ma S, Zhan S, Jia Y et al (2016) Enhanced disinfection application of Ag-modified g-C3N4 composite under visible light. Appl Catal B Environ 186:77–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.APCATB.2015.12.051
Mei J, Tao Y, Gao C et al (2021) Photo-induced dye-sensitized BiPO4/BiOCl system for stably treating persistent organic pollutants. Appl Catal B Environ 285:119841. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.APCATB.2020.119841
Meng L, Zhang X, Tang Y et al (2015) Hierarchically porous silicon–carbon–nitrogen hybrid materials towards highly efficient and selective adsorption of organic dyes. Sci Reports 51(5):1–16. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep07910
Miao X, Yue X, Ji Z et al (2018) Nitrogen-doped carbon dots decorated on g-C3N4/Ag3PO4 photocatalyst with improved visible light photocatalytic activity and mechanism insight. Appl Catal B Environ 227:459–469. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.APCATB.2018.01.057
Naidu BS, Vishwanadh B, Sudarsan V, Vatsa RK (2012) BiPO4: a better host for doping lanthanide ions. Dalt Trans 41:3194–3203. https://doi.org/10.1039/C2DT11944G
Narenuch T, Senasu T, Chankhanittha T, Nanan S (2021) Sunlight-active BiOI photocatalyst as an efficient adsorbent for the removal of organic dyes and antibiotics from aqueous solutions. Molecules 26:5624
Nithya VD, Hanitha B, Surendran S et al (2015) Effect of pH on the sonochemical synthesis of BiPO4 nanostructures and its electrochemical properties for pseudocapacitors. Ultrason Sonochem 22:300–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ULTSONCH.2014.06.014
Nur Fadzeelah AK, Ahmad Fadzri R (2016) Sonophotocatalytic degradation of Reactive Red 120 (RR120) in the presence of TiO2: kinetic study. AIP Conf Proc 1774:040003. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4965085
Ong YP, Ho LN, Ong SA et al (2019) A synergistic heterostructured ZnO/BaTiO3 loaded carbon photoanode in photocatalytic fuel cell for degradation of Reactive Red 120 and electricity generation. Chemosphere 219:277–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.12.004
Pan C, Zhu Y (2010) New Type of BiPO4 Oxy-acid salt photocatalyst with high photocatalytic activity on degradation of dye. Environ Sci Technol 44:5570–5574. https://doi.org/10.1021/es101223n
Paul DR, Gautam S, Panchal P et al (2020) ZnO-modified g-C3N4: a potential photocatalyst for environmental application. ACS Omega 5:3828–3838. https://doi.org/10.1021/ACSOMEGA.9B02688
Rostamizadeh M, Jafarizad A, Gharibian S (2018) High efficient decolorization of Reactive Red 120 azo dye over reusable Fe-ZSM-5 nanocatalyst in electro-Fenton reaction. Sep Purif Technol 192:340–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2017.10.041
Royer B, Cardoso NF, Lima EC et al (2010) A useful organofunctionalized layered silicate for textile dye removal. J Hazard Mater 181:366–374. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHAZMAT.2010.05.019
Samanta S, Martha S, Parida K (2014) Facile synthesis of Au/g-C3N4 nanocomposites: an inorganic/organic hybrid plasmonic photocatalyst with enhanced hydrogen gas evolution under visible-light irradiation. ChemCatChem 6:1453–1462. https://doi.org/10.1002/cctc.201300949
Samsami S, Mohamadi M, Sarrafzadeh MH et al (2020) Recent advances in the treatment of dye-containing wastewater from textile industries: overview and perspectives. Process Saf Environ Prot 143:138–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PSEP.2020.05.034
Sathishkumar P, Mangalaraja RV, Anandan S, Ashokkumar M (2013) CoFe2O4/TiO2 nanocatalysts for the photocatalytic degradation of Reactive Red 120 in aqueous solutions in the presence and absence of electron acceptors. Chem Eng J 220:302–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.01.036
Schneider J, Matsuoka M, Takeuchi M et al (2014) Understanding TiO2 photocatalysis: mechanisms and materials. Chem Rev 114:9919–9986. https://doi.org/10.1021/CR5001892
Senasu T, Chankhanittha T, Hemavibool K, Nanan S (2021) Visible-light-responsive photocatalyst based on ZnO/CdS nanocomposite for photodegradation of reactive red azo dye and ofloxacin antibiotic. Mater Sci Semicond Process 123:105558. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2020.105558
Shokrgozar A, Seifpanahi-Shabani K, Mahmoodi B et al (2021) Synthesis of Ni-Co-CNT nanocomposite and evaluation of its photocatalytic dye (Reactive red 120) degradation ability using response surface methodology. Desalin Water Treat 216:389–400. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2021.26804
Subash B, Krishnakumar B, Swaminathan M, Shanthi M (2013a) Highly efficient, solar active, and reusable photocatalyst: Zr-loaded Ag-ZnO for reactive red 120 dye degradation with synergistic effect and dye-sensitized mechanism. Langmuir 29:939–949. https://doi.org/10.1021/la303842c
Subash B, Krishnakumar B, Swaminathan M, Shanthi M (2013b) Synthesis and characterization of cerium-silver co-doped zinc oxide as a novel sunlight-driven photocatalyst for effective degradation of Reactive Red 120 dye. Mater Sci Semicond Process 16:1070–1078. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2013.04.001
Suwannaruang T, Rivera KKP, Neramittagapong A, Wantala K (2015) Effects of hydrothermal temperature and time on uncalcined TiO2 synthesis for reactive red 120 photocatalytic degradation. Surf Coatings Technol 271:192–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2014.12.041
Tan G, She L, Liu T et al (2017) Ultrasonic chemical synthesis of hybrid mpg-C3N4/BiPO4 heterostructured photocatalysts with improved visible light photocatalytic activity. Appl Catal B Environ 207:120–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.APCATB.2017.02.025
Tang WZ, Huren A (1995) UV/TiO2 photocatalytic oxidation of commercial dyes in aqueous solutions. Chemosphere 31:4157–4170. https://doi.org/10.1016/0045-6535(95)80015-D
Tao R, Yang S, Shao C et al (2019) Reusable and flexible g-C3N4/Ag3PO4/polyacrylonitrile heterojunction nanofibers for photocatalytic dye degradation and oxygen evolution. ACS Appl Nano Mater 2:3081–3090. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.9b00428
Thanavel M, Bankole PO, Selvam R et al (2020) (2020) Synergistic effect of biological and advanced oxidation process treatment in the biodegradation of Remazol yellow RR dye. Sci Reports 101(10):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-77376-5
Thangavel S, Raghavan N, Kadarkarai G et al (2015) Graphene-oxide (GO)-Fe3+ hybrid nanosheets with effective sonocatalytic degradation of Reactive Red 120 and study of their kinetics mechanism. Ultrason Sonochem 24:123–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2014.11.019
Thiagarajan S, Thaiyan M, Ganesan R (2015) Physical property exploration of highly oriented V2O5 thin films prepared by electron beam evaporation. New J Chem 39:9471–9479. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5NJ01582K
Vaithiyanathan R, Sivakumar T (2011) Studies on photocatalytic activity of the synthesised TiO2 and Ag/TiO2 photocatalysts under UV and sunlight irradiations. Water Sci Technol 63:377–384. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2011.231
Veldurthi NK, Eswar NK, Singh SA, Madras G (2018) Heterojunction ZnWO4/ZnFe2O4 composites with concerted effects and integrated properties for enhanced photocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Catal Sci Technol 8:1083–1093. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CY02281F
Velmurugan R, Krishnakumar B, Swaminathan M (2014) Synthesis of Pd co-doped nano-TiO2-SO42- and its synergetic effect on the solar photodegradation of Reactive Red 120 dye. Mater Sci Semicond Process 25:163–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2013.10.024
Velmurugan R, Sreedhar B, Swaminathan M (2011) Nanostructured AgBr loaded TiO2: an efficient sunlight active photocatalyst for degradation of Reactive Red 120. Chem Cent J 5:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1186/1752-153X-5-46
Velmurugan R, Swaminathan M (2011) An efficient nanostructured ZnO for dye sensitized degradation of Reactive Red 120 dye under solar light. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 95:942–950. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solmat.2010.11.029
Villabona-Leal EG, Escobar-Villanueva AG, Ovando-Medina VM et al (2020) Semiconducting polypyrrole@TiO2 pure anatase nanoparticles for photodegradation of reactive red 120 azo dye. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 31:12178–12190. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-03764-2
Wang CC, Li JR, Lv XL et al (2014) Photocatalytic organic pollutants degradation in metal-organic frameworks. Energy Environ. Sci. 7:2831–2867. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4EE01299B
Wang J, Wang G, Cheng B et al (2020) Sulfur-doped g-C3N4/TiO2 S-scheme heterojunction photocatalyst for Congo red photodegradation. Chinese J Catal 42:56–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1872-2067(20)63634-8
Wang J, Wang S (2021) Effect of inorganic anions on the performance of advanced oxidation processes for degradation of organic contaminants. Chem Eng J 411:128392. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CEJ.2020.128392
Wang X, Wang F, Sang Y et al (2017) Full-Spectrum solar-light-activated photocatalysts for light–chemical energy conversion. Adv Energy Mater 7:1700473. https://doi.org/10.1002/AENM.201700473
Wu R, Song H, Luo N, Ji G (2018) Hydrothermal preparation of 3D flower-like BiPO4/Bi2WO6 microsphere with enhanced visible-light photocatalytic activity. J Colloid Interface Sci 524:350–359. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCIS.2018.03.031
Xia H, Li C, Yang G et al (2022) A review of microwave-assisted advanced oxidation processes for wastewater treatment. Chemosphere 287:131981. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CHEMOSPHERE.2021.131981
Xia Y, Tian Z, Heil T et al (2019) Highly selective CO2 capture and its direct photochemical conversion on ordered 2D/1D heterojunctions. Joule 3:2792–2805. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joule.2019.08.011
Xie M, Zhang T (2018) One-pot, facile fabrication of a Ag3PO4-based ternary Z-scheme photocatalyst with excellent visible-light photoactivity and anti-photocorrosion performance. Appl Surf Sci 436:90–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.11.234
Xu Q, Jiang C, Cheng B, Yu J (2017) Enhanced visible-light photocatalytic H2-generation activity of carbon/g-C3N4 nanocomposites prepared by two-step thermal treatment. Dalt Trans 46:10611–10619. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7DT00629B
Xue J, Ma S, Zhou Y et al (2015) Facile photochemical synthesis of Au/Pt/g-C3N4 with plasmon-enhanced photocatalytic activity for antibiotic degradation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:9630–9637. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b01212
Yan R, Zada A, Sun L et al (2022) Comparative study of metal oxides and phosphate modification with different mechanisms over g-C3N4 for visible-light photocatalytic degradation of metribuzin. Rare Met 41:155–165. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-021-01857-3
Yang Y, Li X, Gu Y et al (2022) Adsorption property of fluoride in water by metal organic framework: optimization of the process by response surface methodology technique. Surfaces and Interfaces 28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfin.2021.101649
Ye H, Lin H, Cao J et al (2015) Enhanced visible light photocatalytic activity and mechanism of BiPO4 nanorods modified with AgI nanoparticles. J Mol Catal A Chem 397:85–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MOLCATA.2014.11.005
Yu H, Quan X, Chen S et al (2008) TiO2–carbon nanotube heterojunction arrays with a controllable thickness of TiO2 layer and their first application in photocatalysis. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 200:301–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JPHOTOCHEM.2008.08.007
Yu J, Wang S, Low J, Xiao W (2013) Enhanced photocatalytic performance of direct Z-scheme g-C3N4–TiO2 photocatalysts for the decomposition of formaldehyde in air. Phys Chem Chem Phys 15:16883–16890. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CP53131G
Zhang D, Su C, Yao S et al (2020) Facile in situ chemical transformation synthesis, boosted charge separation, and increased photocatalytic activity of BiPO4/BiOCl p-n heterojunction photocatalysts under simulated sunlight irradiation. J Phys Chem Solids 147:109630. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2020.109630
Zhang Y, Shen B, Huang H et al (2014) BiPO4/reduced graphene oxide composites photocatalyst with highphotocatalytic activity. Appl Surf Sci 319:272–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.07.052
Zhao J, Ge K, Zhao L et al (2017) Enhanced photocatalytic properties of CdS -decorated BiPO4 heterogeneous semiconductor catalyst under UV-light irradiation. J Alloys Compd 729:189–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.09.149
Zhao M, Li G, Zheng J et al (2011) Preparation and polymorph-sensitive luminescence properties of BiPO4:Eu, Part I: room-temperature reaction followed by a heat treatment. CrystEngComm 13:6251–6257. https://doi.org/10.1039/C1CE05629H
Zhao M, Li L, Yang L et al (2013) Exploring the unique electrical properties of metastable BiPO4 through switchable phase transitions. CrystEngComm 15:609–615. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2ce26168e
Zheng Y, Jiao Y, Chen J et al (2011) Nanoporous graphitic-C3N4@carbon metal-free electrocatalysts for highly efficient oxygen reduction. J Am Chem Soc 133:20116–20119. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja209206c
Zheng Y, Yang Y, Zhang Y et al (2019) Facile one-step synthesis of graphitic carbon nitride-modified biochar for the removal of reactive red 120 through adsorption and photocatalytic degradation. Biochar 11(1):89–96. https://doi.org/10.1007/S42773-019-00007-4
Zhu B, Xia P, Li Y et al (2017) Fabrication and photocatalytic activity enhanced mechanism of direct Z-scheme g-C3N4/Ag2WO4 photocatalyst. Appl Surf Sci 391:175–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.07.104
Zou X, Dong Y, Chena Z et al (2016) Synthesis and characterization of BiPO4/g-C3N4 nanocomposites with significantly enhanced visible- light photocatalytic activity for Benzene degradation Xuejun. RSC Adv 25:20664–20670. https://doi.org/10.1039/x0xx00000x
Funding
This work was financially supported by the DST-SERB project under grant no (SERB/EMR/2016/007607) and instrumental facility provided by the SIC of the university.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SKB: investigation; methodology, data analysis, software, and writing — original draft preparation; SG: conceptualization; data curation; formal analysis; investigation; methodology; AKH: conceptualization; formal analysis; investigation; KKR: formal analysis; VC: conceptualization, funding acquisition, supervision, and review.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Sami Rtimi
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ben, S.K., Gupta, S., Harit, A.K. et al. Enhanced photocatalytic degradation of Reactive Red 120 dye under solar light using BiPO4@g-C3N4 nanocomposite photocatalyst. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 84325–84344 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21675-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21675-z