Abstract
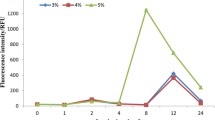
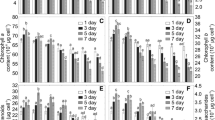
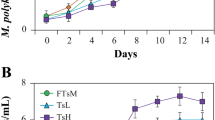
The inhibitory effect of plants on algae offers a new and promising alternative method for controlling harmful algal blooms. Previous studies showed that anti-algal effects might be obvious from extracts of fallen leaves from terrestrial plants, which had great potential for cyanobacterial control in field tests. To investigate the anti-algal activities and main algicidal mechanisms of Ginkgo biloba fallen leaves extracts (GBE) on Microcystis flos-aquae, the cell density, photosynthetic fluorescence, and gene expression under different concentrations of GBE treatments were tested. GBE (3.00 g L−1) showed a strong inhibitory effect against M. flos-aquae with an IC50 (96h) of 0.79 g L−1. All the inhibition rates of maximal quantum yield (Fv/Fm), effective quantum yield (Fq’/Fm’), and maximal relative electron transfer rate (rETRmax) were more than 70% at 96 h at 3.00 g L−1 and more than 90% at 6.00 g L−1. Further results of gene expression of the core proteins of PSII (psbD), limiting enzyme in carbon assimilation (rbcL), and phycobilisome degradation protein (nblA) were downregulated after exposure. These findings emphasized that photosynthetic damage is one of the main toxic mechanisms of GBE on M. flos-aquae. When exposed to 12.00 g L−1 GBE, no significant influence on the death rate of zebrafish or photosynthetic activity of the three submerged plants was found. Therefore, appropriate use of GBE could control the expansion of M. flos-aquae colonies without potential risks to the ecological safety of aquatic environments, which means that GBE could actually be used to regulate cyanobacterial blooms in natural waters.
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The related data generated during this study are included in this published article and are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Baker NR (2008) Chlorophyll fluorescence: a probe of photosynthesis in vivo. Annu Rev Plant Biol 59:89–113. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.59.032607.092759
Belshe EF, Durako MJ, Blum JE (2007) Photosynthetic rapid light curves (RLC) of Thalassia testudinum exhibit diurnal variation. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 342:253–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jembe.2006.10.056
Brooks BW, Lazorchak JM, Howard MD, Johnson MV, Morton SL, Pwekins DAK, Reavie ED, Scott GI, Smith SA, Steevens JA (2016) Are harmful algal blooms becoming the greatest inland water quality threat to public health and aquatic ecosystems? Environ Toxicol Chem 35(1):6–13. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.3220
Bukowska A, Kalinski T, Koper M, Kostrzewska-Szlakowska I, Kwiatowski J, Mazur-Marzec H, Jasser I (2017) Predicting blooms of toxic cyanobacteria in eutrophic lakes with diverse cyanobacterial communities. Sci Rep 7(1):8342. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-08701-8
Busquet F, Strecker R, Rawlings JM, Belanger SE, Braunbeck T, Carr GJ, Cenijn P, Fochtman P, Gourmelon A, Hübler N, Kleensang A, Knöbel M, Kussatz C, Legler J, Lillicrap A, Martínez-Jerónimo F, Polleichtner C, Rzodeczko H, Salinas E et al (2014) OCED validation study to assess intra- and inter-laboratory reproducibility of the zebrafish embryo toxicity test for acute aquatic toxicity testing. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 69(3):496–511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yrtph.2014.05.018
Chen GN, Pan LS, Sun Z, Xiong JH, Zhu HX, Wang SF, Song HN, Lin HF, Chen YL, Liang JX (2020) Removal of nitrogen and phosphorus from black-odor water by different submerged plants. J Biobased Mater Bio 14(4):524–530. https://doi.org/10.1166/jbmb.2020.1972
Chen L, Mao FJ, Kirumba GC, Jiang C, Manefield M, He YL (2015) Changes in metabolites, antioxidant system, and gene expression in Microcystis aeruginosa under sodium chloride stress. Ecotox Environ Safe 122:126–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2015.07.011
Chen SL, Zheng TF, Ye CL, Huannixi WL, Yakefu Z, Meng YY, Peng X, Tian ZF, Wang JH, Ma YD, Yang YY, Ma ZQ, Zuo ZJ (2018) Algicidal properties of extracts from Cinnamomum camphora fresh leaves and their main compounds. Ecotox Environ Safe 15(163):594–603. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.07.115
Crafton EA, Glowczewski J, Ott DW, Cutright TJ (2018) In situ field trial to evaluate the efficacy of Cutrine Ultra to manage a cyanobacteria population in a drinking water source. Environ Sci Water Res Technol 4:863–871. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ew00124c
Guo PY, Liu Y, Liu C (2015) Effects of chitosan, gallic acid, and algicide on the physiological and biochemical properties of Microcystis flos-aquae. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:13514–13521. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4500-0
Hedgpeth BM, Redman AD, Alyea RA, Letinski DJ, Connelly MJ, Butler JD, Zhou HP, Lampi MA (2019) Analysis of sublethal toxicity in developing zebrafish embryos exposed to a range of petroleum substances. Environ Toxicol Chemi 38(6):1302–1312. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.4428
Hou XY, Huang J, Tang JH, Wang N, Zhang L, Gu L, Sun YF, Yang Z, Huang Y (2019) Allelopathic inhibition of juglone (5-hydroxy-1, 4-naphthoquinone) on the growth and physiological performance in Microcystis aeruginosa. J Environ Manage 232:382–386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.11.105
Hua Q, Liu YG, Yan ZL, Zeng GM, Liu SB, Wang WJ, Tan XF, Deng JQ, Tang X, Wang QP (2018) Allelopathic effect of the rice straw aqueous extract on the growth of Microcystis aeruginosa. Ecotox Environ Safe 148:953–959. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.11.049
Huang HM, Xiao X, Ghadouani A, Wu JP, Nie ZY, Peng C, Xu XH, Shi JY (2015) Effects of natural flavonoids on photosynthetic activity and cell integrity in Microcystis aeruginosa. Toxins 7:66–80. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7010066
Kalaji HM, Jajoo A, Oukarroum A, Brestic M, Zivcak M, Samborska IA, Cetner MD, Lukasik I, Goltsev V, Ladle RJ (2016) Chlorophyll a fluorescence as a tool to monitor physiological status of plants under abiotic stress conditions. Acta Physiol Plant 38:102. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-016-2113-y
Kato-Noguchi H, Takeshita S (2013) Contribution of a phytotoxic compound to the allelopathy of Ginkgo biloba. Plant Signal Behav 8:e26999. https://doi.org/10.4161/psb.26999
Leu E, Krieger-Liszkay A, Goussias C, Gross EM (2002) Polyphenolic allelochemicals from the aquatic angiosperm Myriophyllum spicatum inhibit photosystem II. Plant Physiol 130(4):2011–2018. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.011593
Li HA, Ai HN, Kang L, Sun XF, He Q (2016) Simultaneous Microcystis algicidal and microcystin degrading capability by a single Acinetobacter bacterial strain. Environ Sci Technol 50(21):11903–11911. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b03986
Lin L, Feng C, Li QY, Wu M, Zhao LY (2015) Effects of electrolysis by low-amperage electric current on the chlorophyll fluorescence characteristics of Microcystis aeruginosa. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:14932–14939. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4708-z
Lu YP, Wang J, Yang Y, Shi LM, Kong FX (2014) Changes in the physiology and gene expression of Microcystis aeruginosa under EGCG stress. Chemosphere 117:164–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.06.040
Lürling M, Mackay E, Reitzel K, Spears BM (2016) Editorial – a critical perspective on geo-engineering for eutrophication management in lakes. Water Res 97:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.03.035
Mackey KRM, Paytan A, Caldeira K, Grossman AR, Moran D, McIlvin M, Saito M (2013) Effect of temperature on photosynthesis and growth in marine Synechococcus spp. Plant Physiol 163:815–829. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.113.221937
Mahadevan S, Park Y (2008) Multifaceted therapeutic benefits of Ginkgo biloba L.: chemistry, efficacy, safety, and uses. J Food Sci 74:14–19. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1750-3841.2007.00597.x
Meng P, Pei H, Hu W (2015) Allelopathic effects of Ailanthus altissima extracts on Microcystis aeruginosa growth, physiological changes and microcystins release. Chemosphere 141:219–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.07.057
Nishiyama Y, Allakhverdiev SI, Murata N (2006) A new paradigm for the action of reactive oxygen species in the photoinhibition of photosystem II. Biochim Biophys Acta 1757:742–749. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbabio.2006.05.013
Patino R, Rashel RH, Rubio A, Longing S (2018) Growth-suppressing and algicidal properties of an extract from Arundo donax, an invasive riparian plant, against prymnesium parvum, an invasive harmful alga. Harmful Algae 71(JAN.):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hal.2017.11.005
Qian HF, Li J, Pan XJ, Chen J, Zhou DM, Chen ZG, Zhang L, Fu ZW (2012) Analyses of gene expression and physiological changes in Microcystis aeruginosa reveal the phytotoxicities of three environmental pollutants. Ecotoxicology 3:847–859. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-011-0845-4
Qian HF, Yu SQ, Sun ZQ, Xie XC, Liu WP, Fu ZW (2010) Effects of copper sulfate, hydrogen peroxide and N-phenyl-2-naphthylamine on oxidative stress and the expression of genes involved photosynthesis and microcystin disposition in Microcystis aeruginosa. Aquat Toxicol 99(3):405–412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2010.05.018
Qian YP, Li XT, Tian RN (2019) Effects of aqueous extracts from the rhizome of Pontederia cordata on the growth and interspecific competition of two algal species. Ecotoxicol Environ Safe 168:401–407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.10.086
Rajasekhar P, Fan LH, Nguyen T, Roddick FA (2012) A review of the use of sonication to control cyanobacterial blooms. Water Res 46(14):4319–4329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2012.05.054
Roháček K (2010) Method for resolution and quantification of components of the non-photochemical quenching (qN). Photosynth Res 105(2):101–113. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11120-010-9564-6
Sati P, Dhyani P, Bhatt ID, Pandey A (2019) Ginkgo biloba flavonoid glycosides in antimicrobial perspective with reference to extraction method. J Tradit Complem Med 9(1): 15-23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtcme.2017.10.003
Schreiber U (1998) Chlorophyll fluorescence: new instruments for special applications. Photosynthesis: mechanisms and effects:4253–4258. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-011-3953-3_984
Shao JH, Liu DM, Gong DX, Zeng QR, Yan ZY, Gu JD (2013) Inhibitory effects of sanguinarine against the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa NIES-843 and possible mechanisms of action. Aquat Toxicol 142-143:257–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2013.08.019
Shao JH, Wu ZX, Yu GL, Peng X, Li RH (2009) Allelopathic mechanism of pyrogallol to Microcystis aeruginosa pcc7806 (cyanobacteria): from views of gene expression and antioxidant system. Chemosphere 75(7):924–928. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2009.01.021
Shao JH, Yu GL, Wang ZJ, Wu ZX, Peng X, Li RH (2010) Towards clarification of the inhibitory mechanism of wheat bran leachate on Microcystis aeruginosa NIES-843 (cyanobacteria): physiological responses. Ecotoxicology 19:1634–1641. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-010-0549-1
Shao L, Li JY, Zhang YJ, Song YY, Yu KF, He PM, Shen AL (2018) Herbicidal effects of Chinese herbal medicine Coptis chinensis Franch extract on duckweed Spirodela polyrhiza (L.) Schleid.). Ecological Engineering 115:9–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2018.02.002
Shi YX, Shen AL, Tan M, He PM, Shao L (2020) The effect of plant extracts on growth and photosynthetic fluorescence characteristics of Microcystis flos-aquae. Water Sci Technol 82(6):1102–1110. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2020.312
Sinha AK, Eggleton MA, Lochmann RT (2018) An environmentally friendly approach for mitigating cyanobacterial bloom and their toxins in hypereutrophic ponds: potentiality of a newly developed granular hydrogen peroxide-based compound. Sci Total Environ 637-638:524–537. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.05.023
Song CY, Horiuchi T, Oba S (2002) Effects of dried fine pieces of herb plants on growth of large crabgrass (Digitaria adscendens Henr.). J Weed Sci 47(3):153–160. https://doi.org/10.3719/weed.47.153
Sun RG, Fan L (2019) Purification of eutrophic water by five aqua-cultured plants in lake Hongfeng, Guiyang, China. Wuhan Univ J Nat Sci 24(1):37–44. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11859-019-1366-x
Tazart Z, Douma M, Tebaa L, Loudiki M (2018) Use of macrophytes allelopathy in the biocontrol of harmful Microcystis aeruginosa blooms. Water Sci Technol 19(1):245–253. https://doi.org/10.2166/ws.2018.072
Terada R, Vo TD, Nishihara GN, Matsumoto K, Kokubu S, Watanabe Y, Kawaguchi S (2016) The effect of photosynthetically active radiation and temperature on the photosynthesis of two Vietname sespecies of Sargassum, S. Mcclurei and S. oligocystum, based on the field and laboratory measurements. Phycol Res 64(4):230–240. https://doi.org/10.1111/pre.12143
Visser PM, Ibelings BW, Bormans M, Huisman J (2016) Artificial mixing to control cyanobacterial blooms: a review. Aquat Ecol 50(3):423–441. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10452-015-9537-0
Wang SB, Wang YN, Ma XX, Xu ZR (2016a) Effects of garlic and diallyl trisulfide on the growth, photosynthesis, and alkaline phosphatase activity of the toxic cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 23:5712–5720. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5809-4
Wang XX, Jiang CC, Szeto YT, Li HK, Yam KL, Wang XJ (2016b) Effects of Dracontomelon duperreanum defoliation extract on Microcystis aeruginosa: physiological and morphological aspects. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:731–8740 https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs11356-016-6119-1
Wang XX, Szeto YT, Jiang CC, Wang XJ, Tao Y, Tu JG, Chen J (2018) Effects of Dracontomelon duperreanum leaf litter on the growth and photosynthesis of Microcystis aeruginosa. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 100:690–694. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-018-2289-5
Wang YC, Li ZK, Zhou L, Feng LL, Fan NW, Shen J (2013) Effects of macrophyte-associated nitrogen cycling bacteria on denitrification in the sediments of the eutrophic Gonghu Bay, Taihu Lake. Hydrobiologia 700(1):329–341. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-012-1241-7
Wu X, Wu H, Wang SJ, Wang YM, Zhang RF, Hu XB, Ye JY (2018) Effect of propionamide on the growth of Microcystis flos-aquae colonies and the underlying physiological mechanisms. Sci Total Environ 630:526–535. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.02.217
Wu Z, Shi J, Yang S (2013) The effect of pyrogallic acid on growth, oxidative stress, and gene expression in Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Cyanobacteria). Ecotoxicol 22:271–278. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-012-1023-z
Xu CC, Huang ST, Huang YZ, Effiong K, Yu SM, Hu J, Xiao X (2020) New insights into the harmful algae inhibition by Spartina alterniflora: cellular physiology and metabolism of extracellular secretion. Sci Total Environ 714:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.136737
Yakefu Z, Huannixi W, Ye C, Zheng T, Chen S, Peng X, Tian ZF, Wang JH, Yang YY, Ma ZQ, Zuo ZJ (2018) Inhibitory effects of extracts from Cinnamomum camphora fallen leaves on algae. Water Sci Technol 77(11):2545–2554. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2018.199
Yi YL, Lei Y, Yin YB, Zhang HY, Wang GX (2012) The antialgal activity of 40 medicinal plants against Microcystis aeruginosa. J Appl Phycol 24(4):847–856. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-011-9703-2
Yuan R, Li Y, Li JH, Ji SH, Wang S, Kong FL (2020) The allelopathic effects of aqueous extracts from Spartina alterniflora on controlling the Microcystis aeruginosa blooms. Sci Total Environ 712:136332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.136332
Zhang C, Ling F, Yi YL, Zhang HY, Wang GX (2014) Algicidal activity and potential mechanisms of ginkgolic acids isolated from Ginkgo biloba exocarp on Microcystis aeruginosa. J Appl Phycol 26:323–332. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-013-0057-9
Zhang C, Yi YL, Hao K, Liu GL, Wang GX (2013) Algicidal activity of Salvia miltiorrhiza Bung on Microcystis aeruginosa—towards identification of algicidal substance and determination of inhibition mechanism. Chemosphere 93:997–1004. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.05.068
Zhang TT, Zheng CY, Hu W, Xu WW, Wang HF (2010) The allelopathy and allelopathic mechanism of phenolic acids on toxic Microcystis aeruginosa. J Appl Phycol 22(1):71–77. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-009-9429-6
Zhao W, Zheng Z, Zhang JL, Roger SF, Luo XZ (2019) Allelopathically inhibitory effects of eucalyptus extracts on the growth of Microcystis aeruginosa. Chemosphere 225:424–433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.03.070
Zhao Y, Liu WS, Li Q, Yang Q, Chai WB, Zeng MJ, Li RH, Peng YY (2015) Multiparameter-based bioassay of 2-(4-chlorophenyl)-4-(4-methoxyphenyl) quinazoline, a newly-synthesized quinazoline derivative, toward Microcystis aeruginosa HAB5100 (Cyanobacteria). Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 943:376–381. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-015-1459-y
Zheng W, Li XM, Zhang L, Zhang YZ, Lu XP, Tian JK (2015) Improved metabolites of pharmaceutical ingredient grade Ginkgo biloba and the correlated proteomics analysis. Proteomics 15(11):1868–1883. https://doi.org/10.1002/pmic.201400258
Zhou Q, Han SQ, Yan SH, Guo JY, Song W, Liu GF (2014) Impacts of Eichhornia crassipes (Mart.) Solms stress on the physiological characteristics, microcystin production and release of Microcystis aeruginosa. Biochem Syst Ecol 55:148–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bse.2014.03.008
Zhou W, Chai H, Lin PH, Lumsden AB, Yao QZ, Chen CY (2004) Clinical use and molecular mechanisms of action of extract of Ginkgo biloba leaves in cardiovascular diseases. Cardiovascular Drug Reviews 22(4):309–319. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1527-3466.2004.tb00148.x
Zhu JY, Liu BY, Wang J, Gao YN, Wu ZB (2010) Study on the mechanism of allelopathic influence on cyanobacteria and chlorophytes by submerged macrophyte (Myriophyllum spicatum) and its secretion. Aquat Toxicol 98(2):196–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2010.02.011
Funding
This work was supported by the Shanghai Science and Technology innovation action plan (19DZ1204500), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31502172), and the Major Projects of Water Pollution Control and Management of China (2017ZX07205003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Yuxin Shi, Liu Shao, and Peimin He planned and constructed the experimental setup. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Yuxin Shi. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Yuxin Shi and Liu Shao. Anglu Shen and Peimin He reviewed and edited the manuscript together. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Vitor Vasconcelos
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• Ginkgo biloba extracts was found to be an efficient botanical algaecide.
• The expression of some key photosynthesis related genes was influenced by GBE
• Photosynthetic damage is one of the main toxic mechanisms of GBE on M. flos-aquae.
• GBE (< 12.00 g L−1) had no significant potential risk to aquatic ecological safety.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, Y., Shen, A., Shao, L. et al. Effects of Ginkgo biloba extract on growth, photosynthesis, and photosynthesis-related gene expression in Microcystis flos-aquae. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 87446–87455 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21663-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21663-3