Abstract
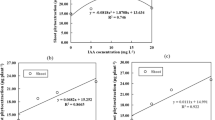
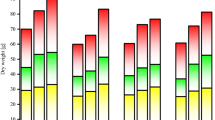
Dissolved organic matter (DOM) is a novel Cd-contaminated soils amendment for phytoremediation. However, the phytoremediation efficiency for different DOM doses has been insufficiently investigated. In this study, we investigated the effect of five DOM doses (v/w, 0%, 1%, 2%, 4% and 8%) on the phytoremediation efficiency of cotton in Cd-contaminated soil through pot experiment. The results showed that bioavailable Cd concentrations and organic matter in the soil increased with the increased of DOM dosage. The DOM dose increased the chlorophyll content, photosynthesis, and the total biomass of cotton. In addition, the DOM application increased the Cd content in cotton roots and changed the Cd uptake in cotton shoots, increasing shoot Cd extraction efficiency by 8.53–20%. Simultaneously, soil Cd phytoextraction efficiency significantly increased. Furthermore, applying a 1% DOM dose resulted in safeguarding fibre biomass and maximising the efficiency of shoot extraction. Redundancy analysis showed that the Mn content in leaves is critical for increasing cotton biomass, anti-oxidation competence and phytoremediation efficiency under 1% DOM dose. In conclusion, DOM enhanced cotton remediation in Cd-contaminated soils and applying DOM at 1% was a suitable choice for Cd-contaminated soils.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data are available from the corresponding author.
References
Aiken GR, Gilmour CC, Krabbenhoft DP, Orem W (2011) Dissolved organic matter in the Florida Everglades: implications for ecosystem restoration. Crit Rev Env Sci Tec 41:217–248
Almasi A, Mohammadi M, Mosavi SA, Eghbali S (2019) Phytoremediation potential of sewage sludge using native plants: Gossypium hirsutum L. and Solanum lycopersicum L. Int J Environ Sci Te 16(10):6237–6246
Bao SD (2000) Soil Agrochemical Analysis, 3rd edn. China Agriculture Press, Beijing, China
Bolan N, Kunhikrishnan A, Thangarajan R, Kumpiene J, Park J, Makino T, Kirkham MB, Scheckel K (2014) Remediation of heavy metal (loid) s contaminated soils-to mobilize or to immobilize? J Hazard Mater 266:141–166
Borggaard OK, Holm PE, Strobel BW (2019) Potential of dissolved organic matter (DOM) to extract As, Cd Co, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb and Zn from polluted soils: a review. Geoderma 343:235–246
Brams E, Anthony W (1983) Cadmium and lead through an agricultural food chain. Sci Total Environ 28:295–306
Bravin MN, Tentscher P, Rose J, Hinsinger P (2009) Rhizosphere pH gradient controls copper availability in a strongly acidic soil. Env Sci Tec 43(15):5686–5691
Chen MS, Ding SM, Li C, Tang YZ, Fan XF, Xu HC, Tsang DCW, Zhang CS (2021) High cadmium pollution from sediments in a eutrophic lake caused by dissolved organic matter complexation and reduction of manganese oxide. Water Res 190:116711
Chen ZF, Zhao Y, Fan LD, Xing LT, Yang YJ (2015) Cadmium (Cd) localization in tissues of cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.), and its phytoremediation rotential for Cd-contaminated soils. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 95(6):784–789
Cornu JY, Schneider A, Jezequel K, Denaix L (2011) Modelling the complexation of Cd in soil solution at different temperatures using the UV-absorbance of dissolved organic matter. Geoderma 162(1):65–70
Dou XK, Dai HP, Skuza L, Wei SH (2019) Bidens pilosa L. hyperaccumulating Cd with different species in soil and the role of EDTA on the hyperaccumulation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(25):25668–25675
Fernandez-Bayo JD, Shea EA, Parr AE, Achmon Y, Stapleton JJ, VanderGheynst JS, Hodson AK, Simmons CW (2020) Almond processing residues as a source of organic acid biopesticides during biosolarization. Waste Manage 101:74–82
Gong JZ, Zhang XR, Li ZY, Zhao AK, Gong XY (2021) Effects of organic fertilizer combined with exogenous cadmium addition on soil physical and chemical properties, rape growth and cadmium accumulation. Chin J Soil Sci 52(3):679–685 (in Chinese)
Grcman H, Velikonja-Bolta S, Vodnik D, Kos B, Lestan D (2001) EDTA enhanced heavy metal phytoextraction: metal accumulation, leaching and toxicity. Plant Soil 235(1):105–114
Gui I, Manzoor M, Hashim N, Shah GM, Waani SPT, Shahid M, Antoniadis V, Rinklebe J, Arshad M (2021) Challenges in microbially and chelate-assisted phytoextraction of cadmium and lead-A review. Environ Pollut 287:117667
Guo XJ, Xie X, Liu YD, Wang C, Yang M, Huang Y (2020a) Effects of digestate DOM on chemical behavior of soil heavy metals in an abandoned copper mining areas. J Hazard Mater 393:122436
Guo JM, Yang J, Yang JX, Zheng GD, Chen TB, Huang J, Bian JL, Meng XF (2020b) Water-soluble chitosan enhances phytoremediation efficiency of cadmium by Hylotelephium spectabile in contaminated soils. Carbohydr Polym 246:116559
Harris NS, Taylor GJ (2013) Cadmium uptake and partitioning in durum wheat during grain filling. BMC Plant Biol 13:103
Hasan MM, Uddin MN, Ara-Sharmeen I, Alharby HF, Alzahrani Y, Hakeem KR, Zhang L (2019) Assisting phytoremediation of heavy metals using chemical amendments. Plants-Basel 8(9):295
He YL, Yu J, Xie SQ, Li PR, Zhou K, He H (2020) Enhanced phytoextraction of cadmium contaminated soil by Trifolium repens with biodegradable chelate GLDA. Environ Sci 41(2):979–985 (in Chinese)
Hou FL (2004) Plant physiology experimental course, 3rd edn. Science Press, Beijing, China
Huang M, Li ZW, Luo NL, Yang R, Wen JJ, Huang B, Zeng GM (2019) Application potential of biochar in environment: insight from degradation of biochar-derived DOM and complexation of DOM with heavy metals. Sci Total Environ 646:220–228
Huang YF, Chen JH, Zhang DR, Fang B, YangJin T, Zou JW, Chen YH, Su NN, Cui J (2021) Enhanced vacuole compartmentalization of cadmium in root cells contributes to glutathione-induced reduction of cadmium translocation from roots to shoots in pakchoi (Brassica chinensis L.). Ecotox Environ Safe 208:111616
Jagetiya B, Sharma A (2013) Optimization of chelators to enhance uranium uptake from tailings for phytoremediation. Chemosphere 91(5):692–696
Jan AU, Hadi F, Shah A, Ditta A, Nawaz MA, Tariq M (2021) Plant growth regulators and EDTA improve phytoremediation potential and antioxidant response of Dysphania ambrosioides (L.) Mosyakin & Clemants in a Cd-spiked soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(32):43417–43430
Khan AR, Ullah I, Khan AL, Park GS, Waqas M, Hong SJ, Jung BK, Kwak Y, Lee IJ, Shin JH (2015) Improvement in phytoremediation potential of Solanum nigrum under cadmium contamination through endophytic-assisted Serratia sp. RSC-14 inoculation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(18):14032–14042
Khaokaew S, Chaney RL, Landrot G, Ginder-Vogel M, Sparks DL (2011) Speciation and release kinetics of cadmium in an alkaline paddy soil under various flooding periods and draining conditions. Environ Sci Technol 45(10):4249–4255
Li B, Yang L, Wang CQ, Zheng SQ, Xiao R, Guo Y (2018) Effects of organic-inorganic amendments on the cadmium fraction in soil and its accumulation in rice (Oryzasativa L.). Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(14):13762–13772
Li SS, Guo Q, Jiang L, Ahmed Z, Dang Z, Wu PX (2021a) The influence mechanism of dissolved organic matter on the adsorption of Cd (II) by calcite. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(28):37120–37129
Li B, Duan MM, Zeng XB, Zhang Q, Xu C, Zhu HH, Zhu QH, Huang DY (2021b) Effects of composited organic mobilizing agents and their application periods on cadmium absorption of Sorghum bicolor L. in a Cd-contaminated soil. Chemosphere 263:128136.
Li GH, Shah AA, Khan WU, Yasin NA, Ahmad A, Abbas M, Ali A, Safdar N (2021c) Hydrogen sulfide mitigates cadmium induced toxicity in Brassica rapa by modulating physiochemical attributes, osmolyte metabolism and antioxidative machinery. Chemosphere 263:127999
Liang YQ, Wang XH, Guo ZH, Xiao XY, Peng C, Yang J, Zhou C, Zeng P (2019) Chelator-assisted phytoextraction of arsenic, cadmium and lead by Pteris vittata L. and soil microbial community structure response. Int J Phytoremed 21(10):1032–1040.
Liu ZL, He XY, Chen W, Yuan FH, Yan K, Tao DL (2009) Accumulation and tolerance characteristics of cadmium in a potential hyperaccumulator-Lonicera japonica Thunb. J Hazard Mater 169(1):170–175
Liu LW, Li W, Song WP, Guo MX (2018) Remediation techniques for heavy metal-contaminated soils: principles and applicability. Sci Total Environ 633:206–219
Liu SM, Yang B, Liang YS, Xiao YH, Fang J (2020) Prospect of phytoremediation combined with other approaches for remediation of heavy metal-polluted soils. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(14):16069–16085
Liu CF, Xiao RB, Dai WJ, Huang F, Yang XJ (2021) Cadmium accumulation and physiological response of Amaranthus tricolor L. under soil and atmospheric stresses. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(11):14041–14053.
Luo CL, Shen ZG, Lou LQ, Li XD (2006) EDDS and EDTA-enhanced phytoextraction of metals from artificially contaminated soil and residual effects of chelant compounds. Environ Pollut 144(3):862–871
Lux A, Martinka M, Vaculik M, White PJ (2011) Root responses to cadmium in the rhizosphere: a review. J Exp Bot 62(1):21–37
Mansoor S, Kour N, Manhas S, Zahid S, Wani OA, Sharma V, Wijaya L, Alyemeni MN, Alsahli AA, ElSerehy HA (2021) Biochar as a tool for effective management of drought and heavy metal toxicity. Chemosphere 271:129458
Mehrab N, Chorom M, Norouzi MM, de Souza MF, Meers E (2021) Alteration in chemical form and subcellular distribution of cadmium in maize (Zea mays L.) after NTA-assisted remediation of a spiked calcareous soil. Ara J Geosci 14(21).
Min T, Luo T, Chen LL, Lu WD, Wang Y, Cheng LY, Ru SB, Li JH (2021) Effect of dissolved organic matter on the phytoremediation of Cd-contaminated soil by cotton. Ecotox Environ Safe 226:112842
Palusinska M, Barabasz A, Kozak K, Papierniak A, Maslinska K, Antosiewicz DM (2020) Zn/Cd status-dependent accumulation of Zn and Cd in root parts in tobacco is accompanied by specific expression of ZIP genes. BMC Plant Boil 20(1).
Pinto ISS, Neto IFF, Soares HMVM (2014) Biodegradable chelating agents for industrial, domestic, and agricultural applications-a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21(20):11893–11906
Qin JJ, Tang SS, Jiang K, Huang J, Hou HB, Long J, Peng PQ (2020) Effects of chelate GLDA on the remediation of cadmium contaminated farmland by Pennisetum purpureum schum. Environmental Science 41(8):3862–3869 (in Chinese)
Ramana S, Tripathi AK, Kumar A, Singh AB, Bharati K, Sahu A, Rajput PS, Saha JK, Srivastava S, Dey P (2021) Potential of cotton for remediation of Cd-contaminated soils. Environ Monit Assess 193(4).
Rudiger W (2002) Biosynthesis of chlorophyll b and the chlorophyll cycle. Photosynth Res 74(2):187–193
Rukshana F, Butterly CR, Baldock JA, Tang CX (2011) Model organic compounds differ in their effects on pH changes of two soils differing in initial pH. Biol Fert Soils 47(1):51–62
Sarwar N, Imran M, Shaheen MR, Ishaque W, Kamran MA, Matloob A, Rehim A, Hussain S (2017) Phytoremediation strategies for soils contaminated with heavy metals: modifications and future perspectives. Chemosphere 171:710–721
Sebastian A, Prasad MNV (2015) Iron- and manganese-assisted cadmium tolerance in Oryza sativa L.: lowering of rhizotoxicity next to functional photosynthesis. Planta 241(6): 1519–1528.
Skorka M, Sieprawska A, Telk A (2022) The implication of manganese surplus on plant cell homeostasis: a review. J. Plant Growth Regul.
Sterckeman T, Thomine S (2020) Mechanisms of cadmium accumulation in plants. Crit Rev Plant Sci 39(4):322–359
Suman J, Uhlik O, Viktorova J, Macek T (2018) Phytoextraction of heavy metals: a promising tool for clean-up of polluted environment? Front Plant Sci 9:1476
Tie DX, Hu HL, Yu XY, Shu YJ, Zhang J (2020) Responses of phptpsynthetic characteristics and chlorophyll fluoresence parameters of Phoebe zhennan saplings to cadmium stress. Acta Ecol Sin 40(11):3738–3746 (in Chinese)
Tinkov AA, Filippini T, Ajsuvakova OP, Aaseth J, Gluhcheva YG, Ivanova JM, Bjorklund G, Skalnaya MG, Gatiatulina ER, Popova EV, Nemereshina ON, Vinceti M, Skalny AV (2017) The role of cadmium in obesity and diabetes. Sci Total Environ. 601:(741–755).
Wang GY, Zhang SR, Xu XX, Zhong QM, Zhang CE, Jia YX, Li T, Deng OP, Li Y (2016) Heavy metal removal by GLDA washing: optimization, redistribution, recycling, and changes in soil fertility. Sci Total Environ 569:557–568
Wang L, Zou R, Wang XB, Huo WM, Chi KY, Fan HL (2020) Effective stimulation of phytoremediation of Amaranshus mangostanus L. in cadmium contaminated soils through reasonable phosphorous fertilizer rate. J Plant Nut Fert 26(2):354–361 (in Chinese).
Wang YL, Xu YM, Qin X, Zhao LJ, Huang QQ, Liang XF (2021a) Effects of S,S-ethylenediamine disuccinic acid on the phytoextraction efficiency of Solanum nigrum L. and soil quality in Cd-contaminated alkaline wheat soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(31):42959–42974.
Wang HR, Zhang Y, Yu CM, Dong QZ, Li WW, Hu KF, Zhang MM, Xue H, Yang MP, Song JL, Wang K, Yang XY, Qiu LJ (2021b) Fine mapping of yellow-green leaf gene (ygl2) in soybean (Glycine max L.) Acta Agronomica Sinica. 48(4):791–800.
Wang F, Xiao Y, Cheng XM, Huang XX (2021c) Effects of cadmium stress on growth and cadmium enrichment of Chlorophytum comosum and Chlorophytum comosum var. variegatum. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology 32(5):1835–1844.(in Chinese)
Wong JWC, Li KL, Zhou LX, Selvam A (2007) The sorption of Cd and Zn by different soils in the presence of dissolved organic matter from sludge. Geoderma 137(3):310–317
Xiao QT, Wang YJ, Lu QX, Wen HH, Han BL, Chen S, Zheng XY, Lin RY (2020) Responses of glutathione and phytochelatins biosysthesis in a cadmium accumulator of Perilla frutescens (L.) Britt. under cadmium contaminated conditions. Ecotox Environ Safe 201:110805.
Yang ZP, Lu WX, Long YQ, Bao XH, Yang QC (2011) Assessment of heavy metals contamination in urban topsoil from Changchun City. China J Geochem Explor 108(1):27–38
Yang W, Dai HP, Wei SH (2020) The front-heavy and back-light nitrogen application mode to increase stem and leaf biomass significantly improved cadmium accumulation in Solanum nigrum L. J Hazard Mater 393:122482
Yang SL, Zhang J, Chen LH (2021) Growth and physiological responses of Pennisetum sp. to cadmium stress under three different soils. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(12):14867–14881.
Yu F, Yi LT, Mao XY, Song Q, Korpelainen H, Liu M (2022) Nitrogen addition alleviated sexual differences in responses to cadmium toxicity by regulating the antioxidant system and root characteristics, and inhibiting Cd translocation in mulberry seedlings. Ecotox Environ Safe 232:113288
Yuan LZ, Guo PH, Guo SH, Wang JN, Huang YJ (2022) Influence of C14 alkane stress on antioxidant defense capacity, mineral nutrient element accumulation, and cadmium uptake of ryegrass. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(10):13857–13868
Zaheer MM, Yasin NA, Ahmad SR, Khan WU, Ahmad A, Ali A, Rehman SU (2018) Amelioration of cadmium stress in gladiolus (Gladiolus grandiflora L.) by application of potassium and silicon. J Plant Nutr 41(4):461–476.
Zhang SK (2020) Study on three soil amendments enhanced Ryegrass remediation of copper and cadmium contaminated red soil. Dissertation, University of Nanchang.
Zhang XX, Rui HY, Zhang FQ, Hu ZB, Xia Y, Shen ZG (2018) Overexpression of a functional Vicia sativa PCS1 homolog increases cadmium tolerance and phytochelatins synthesis in Arabidopsis. Front Plant Sci 9:107
Zhang ZY, Dong XX, Wang SM, Pu XZ (2020) Benefits of organic manure combined with biochar amendments to cotton root growth and yield under continuous cropping systems in Xinjiang, China. Sci Rep 1(10).
Zhao M, Li TX, Yu HY, Zhang XZ, Zheng ZC, Wang YD, Liu T, Gupta DK, Huang HG (2020) Fractionation and chemical structure of dissolved organic matter in the rhizosphere associated with cadmium accumulation in tobacco lines (Nicotiana tabacum L.). Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(15):17794–17803.
Zhou T, Wu LH, Luo YM, Christie P (2018) Effects of organic matter fraction and compositional changes on distribution of cadmium and zinc in long-term polluted paddy soils. Environ Pollut 232:514–522
Zhu HH, Chen C, Xu C, Zhu QH, Huang DY (2016) Effects of soil acidification and liming on the phytoavailability of cadmium in paddy soils of central subtropical China. Environ Pollut 219:99–106
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31660598) and the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2018YFD0200406).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors designed the study. Tao Min, Jie Qing, Yan Wang and Liyang Cheng performed the experiments. Tong Luo and Hao He discussed the data. Sibo Ru and Junhua Li modified some experimental methods.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All authors have read and approved the final manuscript for publication.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Gangrong Shi
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Min, T., Luo, T., He, H. et al. Dissolved organic matter–assisted phytoremediation potential of cotton for Cd-contaminated soil: a relationship between dosage and phytoremediation efficiency. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 84640–84650 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21485-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21485-3