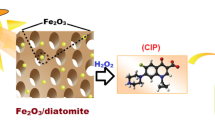
Abstract
Ciprofloxacin (CIP) is a third-generation fluoroquinolones (FQs) antibiotic, and the occurrence of CIP in the water environment has raised growing concerns owning to its environmental toxicity. In this paper, a novel α-(Fe, Cu)OOH/RGO nanocomposite was synthesized via a one-step reflux method for CIP degradation through a photo-Fenton-like process. When the RGO content was 1 wt%, CIP degradation ratio by the α-(Fe, Cu)OOH/RGO nanocomposite reached 100% under visible light irradiation within 120 min, and total organic carbon (TOC) removal ratio reached 60% within 180 min. The result of molecular fluorescence spectra highlighted that the loading of RGO on the α-(Fe, Cu)OOH significantly increased the content of hydroxyl radicals (·OH) in the heterogeneous photo-Fenton-like system and simultaneously inhibited the recombination of photogenerated electron and hole, which played critical roles in the enhancement of CIP degradation. In addition, 11 main intermediates were identified as the degradation products of CIP in the α-(Fe, Cu)OOH/RGO/H2O2/visible light reaction systems using liquid chromatograph–mass spectrometer (LC-MS) analyses. The results demonstrated that three degradation pathways for CIP removal by α-(Fe, Cu)OOH/RGO nanocomposite occurred, including (i) oxidation on the piperazine ring and dealkylation, (ii) defluorination and decarboxylation, and (iii) hydroxylation on the quinolone ring. This work would provide a novel insight of CIP degradation pathways in photo-Fenton-like processes.
Graphical abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data materials analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Bagherzadeh SB, Kazemeini M, Mahmoodi NM (2021) Preparation of novel and highly active magnetic ternary structures (metal-organic framework/cobalt ferrite/graphene oxide) for effective visible-light-driven photocatalytic and photo-Fenton-like degradation of organic contaminants. J Colloid Interface Sci 602:73–94
Chen HF, Wei GD, Han X, Li S, Wang PP, Chubik M et al (2010) Large-scale synthesis of hierarchical alpha-FeOOH flowers by ultrasonic-assisted hydrothermal route. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 22:252–259
Chen L, Ni R, Yuan T, Gao Y, Kong W, Zhang P et al (2020) Effects of green synthesis, magnetization, and regeneration on ciprofloxacin removal by bimetallic nZVI/Cu composites and insights of degradation mechanism. J Hazard Mater 382:121008
Chen Y, Wang A, Zhang Y, Bao R, Tian X, Li J (2017) Electro-Fenton degradation of antibiotic ciprofloxacin (CIP): Formation of Fe3+-CIP chelate and its effect on catalytic behavior of Fe2+/Fe3+ and CIP mineralization. Electrochim Acta 256:185–195
De Witte B, Dewulf J, Demeestere K, Van Langenhove H (2009) Ozonation and advanced oxidation by the peroxone process of ciprofloxacin in water. J Hazard Mater 161:701–708
Deng J, Xu M, Feng S, Qiu C, Li X, Li J (2019) Iron-doped ordered mesoporous Co3O4 activation of peroxymonosulfate for ciprofloxacin degradation: Performance, mechanism and degradation pathway. Sci Total Environ 658:343–356
Fernández-Perales M, Rozalen M, Sánchez-Polo M, Rivera-Utrilla J, López-Ramón MV, Álvarez MA (2020) Solar Degradation of Sulfamethazine Using rGO/Bi Composite Photocatalysts. Catalysts 10
Genc N, Dogan EC, Yurtsever M (2013) Bentonite for ciprofloxacin removal from aqueous solution. Water Sci Technol 68:848–855
Giri AS, Golder AK (2014) Ciprofloxacin degradation from aqueous solution by Fenton oxidation: reaction kinetics and degradation mechanisms. RSC. Advances 4
Gu M, Farooq U, Lu S, Zhang X, Qiu Z, Sui Q (2018) Degradation of trichloroethylene in aqueous solution by rGO supported nZVI catalyst under several oxic environments. J Hazard Mater 349:35–44
Guo H, Jiang N, Wang H, Shang K, Lu N, Li J et al (2019) Pulsed discharge plasma induced WO3 catalysis for synergetic degradation of ciprofloxacin in water: Synergetic mechanism and degradation pathway. Chemosphere 230:190–200
Guo S, Zhang G, Yu JC (2015) Enhanced photo-Fenton degradation of rhodamine B using graphene oxide-amorphous FePO4 as effective and stable heterogeneous catalyst. J Colloid Interface Sci 448:460–466
Hu X, Hu X, Peng Q, Zhou L, Tan X, Jiang L et al (2020) Mechanisms underlying the photocatalytic degradation pathway of ciprofloxacin with heterogeneous TiO2. Chem Eng J 380
Hummers J, Offeman RE (1958) Preparation of Graphitic Oxide. Am Chem Soc 80:1339–1339
Jia Z, Li T, Zheng Z, Zhang J, Liu J, Li R et al (2020) The BiOCl/diatomite composites for rapid photocatalytic degradation of ciprofloxacin: Efficiency, toxicity evaluation, mechanisms and pathways. Chem Eng J 380
Klauson D, Babkina J, Stepanova K, Krichevskaya M, Preis S (2010) Aqueous photocatalytic oxidation of amoxicillin. Catal Today 151:39–45
Li P, Cao W, Zhu Y, Teng Q, Peng L, Jiang C et al (2020) NaOH-induced formation of 3D flower-sphere BiOBr/Bi4O5Br2 with proper-oxygen vacancies via in-situ self-template phase transformation method for antibiotic photodegradation. Sci Total Environ 715:136809
Liu Q, Guo Y, Chen Z, Zhang Z, Fang X (2016) Constructing a novel ternary Fe(III)/graphene/g-C3 N4 composite photocatalyst with enhanced visible-light driven photocatalytic activity via interfacial charge transfer effect. Appl Catal B Environ 183:231–241
Liu Y, Jin W, Zhao Y, Zhang G, Zhang W (2017a) Enhanced catalytic degradation of methylene blue by α-Fe2O3/graphene oxide via heterogeneous photo-Fenton reactions. Appl Catal B Environ 206:642–652
Liu Y, Liu X, Zhao Y, Dionysiou DD (2017b) Aligned α-FeOOH nanorods anchored on a graphene oxide-carbon nanotubes aerogel can serve as an effective Fenton-like oxidation catalyst. Appl Catal B Environ 213:74–86
Ma Y, Wang B, Wang Q, Xing S (2018) Facile synthesis of α-FeOOH/γ-Fe2O3 by a pH gradient method and the role of γ-Fe2O3 in H2O2 activation under visible light irradiation. Chem Eng J 354:75–84
Malakootian M, Yaseri M, Faraji M (2019) Removal of antibiotics from aqueous solutions by nanoparticles: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:8444–8458
Narciso-da-Rocha C, Manaia CM (2016) Multidrug resistance phenotypes are widespread over different bacterial taxonomic groups thriving in surface water. Sci Total Environ 563-564:1–9
Nie Y, Hu C, Qu J, Zhao X (2009) Photoassisted degradation of endocrine disruptors over CuOx–FeOOH with H2O2 at neutral pH. Appl Catal B Environ 87:30–36
Padhi DK, Parida K (2014) Facile fabrication of α-FeOOH nanorod/RGO composite: a robust photocatalyst for reduction of Cr(VI) under visible light irradiation. J Mater Chem A 2:10300–10312
Raza W, Faraz M (2020) Novel g-C3N4/Fe-ZnO/RGO nanocomposites with boosting visible light photocatalytic activity for MB, Cr(VI), and outstanding catalytic activity toward para-nitrophenol reduction. Nanotechnology 31:325603
Rusevova K, Köferstein R, Rosell M, Richnow HH, Kopinke F-D, Georgi A (2014) LaFeO3 and BiFeO3 perovskites as nanocatalysts for contaminant degradation in heterogeneous Fenton-like reactions. Chem Eng J 239:322–331
Santoke H, Song W, Cooper WJ, Greaves J, Miller GE (2009) Free-Radical-Induced Oxidative and Reductive Degradation of Fluoroquinolone Pharmaceuticals: Kinetic Studies and Degradation Mechanism. J Phys Chem A 113:7846–7851
Tong G, Guan J, Zhang Q (2011) Goethite hierarchical nanostructures: Glucose-assisted synthesis, chemical conversion into hematite with excellent photocatalytic properties. Mater Chem Phys 127:371–378
Villegas-Guzman J, Torres-Palma RA (2017) Comparative Evaluation of Photo-Chemical AOPs for Ciprofoxacin Degradation: Elimination in Natural Waters and Analysis of pH Effect, Primary Degradation By-Products, and the Relationship with the Antibiotic Activity. Water Air Soil Pollut 228
Wajahat R, Yasar A, Khan AM, Tabinda AB, Bhatti S (2019) Ozonation and Photo-Driven Oxidation of Ciprofloxacin in Pharmaceutical Wastewater: Degradation Kinetics and Energy Requirements. Pol J Environ Stud 28:1933–1938
Wang F, Yu X, Ge M, Wu S (2020) One-step synthesis of TiO2/γ-Fe2O3/GO nanocomposites for visible light-driven degradation of ciprofloxacin. Chem Eng J 384
Wang Y, Fang J, Crittenden JC, Shen C (2017) Novel RGO/alpha-FeOOH supported catalyst for Fenton oxidation of phenol at a wide pH range using solar-light-driven irradiation. J Hazard Mater 329:321–329
Wang Z, Cai X, Xie X, Li S, Zhang X, Wang Z (2021) Visible-LED-light-driven photocatalytic degradation of ofloxacin and ciprofloxacin by magnetic biochar modified flower-like Bi2WO6: The synergistic effects, mechanism insights and degradation pathways. Sci Total Environ 764:142879
Wetzstein HG, Stadler M, Tichy HV, Dalhoff A, Karl W (1999) Degradation of ciprofloxacin by basidiomycetes and identification of metabolites generated by the brown rot fungus Gloeophyllum striatum. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:1556–1563
Xiao X, Zeng X, Lemley AT (2010) Species-dependent degradation of ciprofloxacin in a membrane anodic Fenton system. J Agric Food Chem 58:10169–10175
Xu J, Li Y, Yuan B, Shen C, Fu M, Cui H et al (2016) Large scale preparation of Cu-doped α-FeOOH nanoflowers and their photo-Fenton-like catalytic degradation of diclofenac sodium. Chem Eng J 291:174–183
Yahya M, Oturan N, El Kacemi K, El Karbane M, Aravindakumar CT, Oturan MA (2014) Oxidative degradation study on antimicrobial agent ciprofloxacin by electro-Fenton process: kinetics and oxidation products. Chemosphere 117:447–454
Yu L, Chen J, Liang Z, Xu W, Chen L, Ye D (2016) Degradation of phenol using Fe3O4-GO nanocomposite as a heterogeneous photo-Fenton catalyst. Sep Purif Technol 171:80–87
Yu X, Zhang J, Zhang J, Niu J, Zhao J, Wei Y et al (2019) Photocatalytic degradation of ciprofloxacin using Zn-doped Cu2O particles: Analysis of degradation pathways and intermediates. Chem Eng J 374:316–327
Zhang H, Huang C-H (2005) Oxidative transformation of fluoroquinolone antibacterial agents and structurally related amines by manganese oxide. Environ Sci Technol 39:4474–4483
Zhang T, Liu J, Wang D, Zhao Z, Wei Y, Cheng K et al (2014) Selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 over HZSM-5-supported Fe–Cu nanocomposite catalysts: The Fe–Cu bimetallic effect. Appl Catal B Environ 148-149:520–531
Zhang T, Qian C, Guo P, Gan S, Dong L, Bai G et al (2020) A Novel Reduced Graphene Oxide-Attapulgite (RGO-ATP) Supported Fe2O3 Catalyst for Heterogeneous Fenton-like Oxidation of Ciprofloxacin: Degradation Mechanism and Pathway. Catalysts 10
Zhang X, Li R, Jia M, Wang S, Huang Y, Chen C (2015) Degradation of ciprofloxacin in aqueous bismuth oxybromide (BiOBr) suspensions under visible light irradiation: A direct hole oxidation pathway. Chem Eng J 274:290–297
Zhang Y, Chen Z, Zhou L, Wu P, Zhao Y, Lai Y et al (2019) Heterogeneous Fenton degradation of bisphenol A using Fe3O4@beta-CD/rGO composite: Synergistic effect, principle and way of degradation. Environ Pollut 244:93–101
Acknowledgments
This research was financially supported by the Science and Technology Project of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of Fujian (No. 2019-K-50), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51778146) and the Outstanding Youth Fund of Fujian Province in China (No. 2018J06013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Junge Xu was involved in conceptualization, supervision, project administration, writing, reviewing and editing, resources, and funding acquisition; Die Hu carried out formal analysis and validation, and wrote the original draft; Yingmu Wang was responsible for conceptualization, formal analysis, and writing, reviewing and editing; Ziwei Zhang took part in data curation, and writing, reviewing and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent to Publish
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ricardo A. Torres-Palma
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 755 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, J., Hu, D., Wang, Y. et al. α-(Fe, Cu)OOH/RGO nanocomposites for heterogeneous photo-Fenton-like degradation of ciprofloxacin under visible light irradiation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 78874–78886 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21245-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21245-3