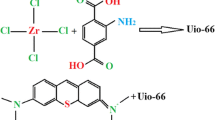
Abstract
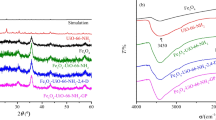
The efficient and rapid removal of organic dyes from wastewater remains a complex and challenging task. In this study, UiO-66-NH2 was prepared by solvothermal synthesis, and then, UiO-66-NS was prepared by compounding l-cysteine with UiO-66-NH2 via the Ugi reaction for the efficient removal of methyl orange. UiO-66-NS was prepared by the addition of 1 mmol l-cysteine and showed good adsorption of methyl orange with 92.00% removal. Pseudo-second-order kinetics and Langmuir isotherms more accurately described the adsorption process of UiO-66-NS on methyl orange, which indicated that the adsorption process was dominated by monolayer adsorption of chemical reactions, and the maximum adsorption amounts of UiO-66-NS on methyl orange were 242.72 mg/g at 298 K. In addition, UiO-66-NS exhibited ultrahigh stability in acidic, neutral, and alkaline media (pH = 3–10), but its adsorption of methyl orange after 5 cycles was only 59.53% of the maximum adsorption amount. The adsorption mechanism is primarily electrostatic adsorption of UiO-66-NS with methyl orange, hydrogen bonding, and π-π interactions. This atomically economical Ugi multicomponent reaction provides new ideas for the preparation of structurally designable adsorbents with excellent performance.
Graphical abstract












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References s
Aghili F, Ghoreyshi AA et al (2021) Introducing gel-based UiO-66-NH2 into polyamide matrix for preparation of new super hydrophilic membrane with superior performance in dyeing wastewater treatment. J Environ Chem Eng 9(4):105484
Aknin K, Gauriot M et al (2012) Squaric acid is a suitable building-block in 4C-Ugi reaction: access to original bivalent compounds. Tetrahedron Lett 53(4):458–461
Alqadami AA, Naushad M et al (2018) Adsorptive performance of MOF nanocomposite for methylene blue and malachite green dyes: Kinetics, isotherm and mechanism. J Environ Manage 223:29–36
Bai Y, Dou Y et al (2016) Zr-based metal-organic frameworks: design, synthesis, structure, and applications. Chem Soc Rev 45(8):2327–2367
Bulgariu L, Escudero LB et al (2019) The utilization of leaf-based adsorbents for dyes removal: A review. J Mol Liq 276:728–747
Cavka JH, Jakobsen S et al (2008) A new zirconium inorganic building brick forming metal organic frameworks with exceptional stability. J Am Chem Soc 130(42):13850–13851
Chen C, Li X et al (2021) Structural modulation of UiO-66-NH2 metal-organic framework via interligands cross-linking: cooperative effects of pore diameter and amide group on selective CO2 separation. Appl Surf Sci 553:149547
Cioc RC, Ruijter E et al (2014) Multicomponent reactions: advanced tools for sustainable organic synthesis. Green Chem Int J Green Chem Resour GC 16(6):2958–2975
Dehghan, A. and A. A. Mohammadi, et al. (2019). “Enhanced kinetic removal of ciprofloxacin onto metal-organic frameworks by sonication, process optimization and metal leaching study.” NANOMATERIALS 9 (10).
Embaby MS, Elwany SD et al (2018) The adsorptive properties of UiO-66 towards organic dyes: A record adsorption capacity for the anionic dye Alizarin Red S. Chin J Chem Eng 26(4):731–739
Fan Y, Zhang S et al (2018) An enhanced adsorption of organic dyes onto NH 2 functionalization titanium-based metal-organic frameworks and the mechanism investigation. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 263:120–127
Fu L, Wang S et al (2019) Post-functionalization of UiO-66-NH2 by 2,5-Dimercapto-1,3,4-thiadiazole for the high efficient removal of Hg(II) in water. J Hazard Mater 368:42–51
Ghadiri, S. K. and H. Alidadi, et al. (2020). “Valorization of biomass into amine-functionalized bio graphene for efficient ciprofloxacin adsorption in water-modeling and optimization study.” PLOS ONE 15 (4).
Haque E, Lee JE et al (2010) Adsorptive removal of methyl orange from aqueous solution with metal-organic frameworks, porous chromium-benzenedicarboxylates. J Hazard Mater 181(1–3):535–542
Holkar CR, Jadhav AJ et al (2016) A critical review on textile wastewater treatments: possible approaches. J Environ Manage 182:351–366
Hollanders C, Elsocht M et al (2021) 3-Substituted 2-isocyanopyridines as versatile convertible isocyanides for peptidomimetic design. Chem Commun 57(56):6863–6866
Huang Z, Zhao M et al (2020) Selective removal mechanism of the novel Zr-based metal organic framework adsorbents for gold ions from aqueous solutions. Chem Eng J 384:123343
Li J, Gong J et al (2019a) The performance of UiO-66-NH2/graphene oxide (GO) composite membrane for removal of differently charged mixed dyes. Chemosphere 237:124517
Li W, Mu B et al (2019b) Feasibility of industrial-scale treatment of dye wastewater via bio-adsorption technology. Biores Technol 277:157–170
Liang Z, Qu C et al (2018) Pristine metal-organic frameworks and their composites for energy storage and conversion. Adv Mater 30(37):1702891
Lin J, Liu Y et al (2021) Ultra-fast adsorption of four typical pollutants using magnetically separable ethanolamine-functionalized graphene. Sep Purif Technol 271:118862
Liu J, Yu H et al (2020) Superior absorption capacity of tremella like ferrocene based metal-organic framework in removal of organic dye from water. J Hazard Mater 392:122274
Liu Q, Zang GL et al (2021) Removal of copper ions by functionalized biochar based on a multicomponent Ugi reaction. RSC Adv 11(42):25880–25891
Lu Y, Jiang B et al (2016) High performance NiFe layered double hydroxide for methyl orange dye and Cr(VI) adsorption. Chemosphere 152:415–422
Lv S, Liu J et al (2019) Simultaneous adsorption of methyl orange and methylene blue from aqueous solution using amino functionalized Zr-based MOFs. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 282:179–187
Meng J, Liu X et al (2020) Advances in metal-organic framework coatings: versatile synthesis and broad applications. Chem Soc Rev 49(10):3142–3186
Min X, Wu X et al (2019) Ultra-high capacity of lanthanum-doped UiO-66 for phosphate capture: Unusual doping of lanthanum by the reduction of coordination number. Chem Eng J 358:321–330
Mittal A, Malviya A et al (2007) Studies on the adsorption kinetics and isotherms for the removal and recovery of Methyl Orange from wastewaters using waste materials. J Hazard Mater 148(1–2):229–240
Mittal J (2020) Permissible synthetic food dyes in India. Reson J Sci Ed 25(4):567–577
Mittal, J. and A. Mariyam, et al. (2021). “Batch and bulk adsorptive removal of anionic dye using metal/halide-free ordered mesoporous carbon as adsorbent.” J Clean Prod 321.
Mohammadi AA, Dehghani MH et al (2020) Adsorptive removal of endocrine disrupting compounds from aqueous solutions using magnetic multi-wall carbon nanotubes modified with chitosan biopolymer based on response surface methodology: Functionalization, kinetics, and isotherms studies. Int J Biol Macromol 155:1019–1029
Niu C, Zhang N et al (2021) Preparation of a novel citric acid-crosslinked Zn-MOF/chitosan composite and application in adsorption of chromium(VI) and methyl orange from aqueous solution. Carbohyd Polym 258:117644
Niu P, Lu N et al (2019) Water-induced synthesis of hierarchical Zr-based MOFs with enhanced adsorption capacity and catalytic activity. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 281:92–100
Patel A, Soni S et al (2021) Sequestration of crystal violet from aqueous solution using ash of black turmeric rhizome. Desalin Water Treat 220:342–352
Qiu J, Feng Y et al (2017) Acid-promoted synthesis of UiO-66 for highly selective adsorption of anionic dyes: Adsorption performance and mechanisms. J Colloid Interface Sci 499:151–158
Rezaei A, Akhavan O et al (2016) Toward Chemical perfection of graphene-based gene carrier via Ugi multicomponent assembly process. Biomacromol 17(9):2963–2971
Tang J, Chen Y et al (2021) Phenylthiosemicarbazide-functionalized UiO-66-NH2 as highly efficient adsorbent for the selective removal of lead from aqueous solutions. J Hazard Mater 413:125278
Tchalala, M. R. and P. M. Bhatt, et al. (2019). “Fluorinated MOF platform for selective removal and sensing of SO2 from flue gas and air.” Nature Communications 10 (1).
Wang C, An B et al (2019a) Metal–organic frameworks in solid–gas phase catalysis. ACS Catal 9(1):130–146
Wang R, Liu L et al (2020a) Engineering pH-switchable UiO-66 via in-situ amino acid doping for highly selective adsorption of anionic dyes. Chem Eng J 395:124958
Wang Y, Yan J et al (2020b) Metal-organic frameworks for stimuli-responsive drug delivery. Biomaterials 230:119619
Wang Z, Song L et al (2019b) Lightweight UiO-66/cellulose aerogels constructed through self-crosslinking strategy for adsorption applications. Chem Eng J 371:138–144
Wang Z, Jia Y et al (2021) Optimization of boron adsorption from desalinated seawater onto UiO-66-NH2/GO composite adsorbent using response surface methodology. J Clean Prod 300:126974
Winarta J, Shan B et al (2020) A decade of UiO-66 research: a historic review of dynamic structure, synthesis mechanisms, and characterization techniques of an archetypal metal–organic framework. Cryst Growth Des 20(2):1347–1362
Yao S, Liu S et al (2019) A ZnII-based metal–organic framework with a rare tcj topology as a turn-on fluorescent sensor for acetylacetone. Inorg Chem 58(6):3578–3581
Yousefi, M. and M. Gholami, et al. (2021). “Comparison of LSSVM and RSM in simulating the removal of ciprofloxacin from aqueous solutions using magnetization of functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes: Process optimization using GA and RSM techniques.” J Environ Chem Eng 9 (4).
Zeng Y, Li Y et al (2020) Antibacterial self-healing hydrogel via the Ugi reaction. ACS Appl Polym Mater 2(2):404–410
Zha Q, Sang X et al (2019) Modification of hydrophilic amine-functionalized metal-organic frameworks to hydrophobic for dye adsorption. J Solid State Chem 275:23–29
Zhang M, Yang K et al (2020) 3D-agaric like core-shell architecture UiO-66-NH2@ZIF-8 with robust stability for highly efficient REEs recovery. Chem Eng J 386:124023
Zhang Q, Cui Y et al (2019) Goal-directed design of metal–organic frameworks for liquid-phase adsorption and separation. Coord Chem Rev 378:310–332
Zhang Y, Ruan Q et al (2018) Synthesis of hierarchical-pore metal-organic framework on liter scale for large organic pollutants capture in wastewater. J Colloid Interface Sci 525:39–47
Zhao J, Wang C et al (2020) Experimental and DFT study of selective adsorption mechanisms of Pb(II) by UiO-66-NH2 modified with 1,8-dihydroxyanthraquinone. J Ind Eng Chem 83:111–122
Zhao MH, Huang Z et al (2019) Design of L-cysteine functionalized UiO-66 MOFs for selective adsorption of Hg(II) in aqueous medium. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11(50):46973–46983
Zhi SJ, Ma XM et al (2019) Consecutive multicomponent reactions for the synthesis of complex molecules. Org Biomol Chem 17(33):7794–7794
Zhou Y, Lu J et al (2019) Recent advances for dyes removal using novel adsorbents: a review. Environ Pollut 252:352–365
Funding
This study was supported by the NSFC (Grant Number 21607113), the Natural Science Foundation of Tianjin City (Grant Number 17JCQNJC07700), and the National Key Research and Development Program-China (Grant Number 2017YFE0127200).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Qi Liu: conceptualization, methodology, investigation, resources, data curation, writing—review and editing, visualization. Guolong Zang: conceptualization, writing—review and editing, supervision, formal analysis, project administration, funding acquisition. Quan Zhao: conceptualization, methodology, investigation, supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study did not involve human participants, human data, or human tissue.
Consent to publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Tito Roberto Cadaval Jr.
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Q., Zang, GL. & Zhao, Q. Removal of methyl orange wastewater by Ugi multicomponent reaction functionalized UiO-66-NS. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 76833–76846 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21175-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21175-0