Abstract
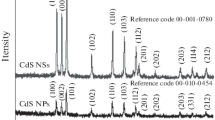
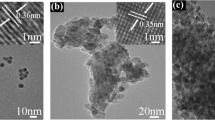
In this study, mercaptosuccinic acid capped CdSe nanocrystals were successfully synthesized and used as photocatalyst for the effective removal of methylene blue (MB) inaqueous solution under visible light and sunlight irradiations including its analysis with statistical physics theory. Dye adsorption properties of these nanocrystals were investigated via experimental kinetics and equilibrium studies. These experimental data were modeled via the application of statistical physics theory to explain the corresponding adsorption mechanism and to characterize the steric and energetic parameters involved in the dye removal. A maximum adsorption capacity of 27.07 mg g−1 (80% of dye removal) was observed in 10 min using an initial concentration of 30 mg L−1. Statistical physics calculations indicated that the adsorption energy was lower than 40 kJ mol−1. It was also established that the dye adsorption was associated to the electrostatic interactions and hydrogen bonding where dye aggregation and multi-molecular adsorption were expected. Overall, the dye removal was a spontaneous, feasible and exothermic. It was concluded that adsorption properties of CdSe-MSA nanocrystals improved the dye photo-catalytic degradation efficiency under visible light thus achieving up to 80% degradation efficiency in 60 min. The synergic effect of adsorption and photo-catalytic degradation performance was mainly due to the surface area (136.43 m2 g−1), small size (3.7 nm), and structural defects (selenium vacancies Se, interstitial of cadmium ICd) of CdSe nanocrystals, which enhanced both the response of these nanomaterials to visible light and their photo-catalytic activity. In summary, these nanocrystals are promising materials to be used in wastewater treatment under sunlight for the removal of organic compounds like dyes.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data and materials are contained within the article.
References
Abd El-sadek MS, Babu SM (2011) A controlled approach for synthesizing CdTe@CrOOH (core-shell) composite nanoparticles. CurrAppl Phys 11:926–932. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cap.2010.12.022
Abideen ZU, Teng F (2018) Enhanced photochemical activity and stability of ZnS by a simple alkaline treatment approach. Cryst Eng Comm 20:7866–7879. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8CE01417E
Abu-Alsoud GF, Hawboldt KA, Bottaro CS (2020) Comparison of four adsorption isotherm models for characterizing molecular recognition of individual phenolic compounds in porous tailor-made molecularly imprinted polymer films. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12:11998–12009. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b21493
Arivarasan A, Bharathi S, Ezhilarasi S et al (2019) Photovoltaic performances of Yb doped CdTe QDs sensitized TiO2 photoanodes for solar cell applications. J Inorg Organomet Polym Mater 29:859–868. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-018-01060-5
Asfaram A, Ghaedi M, Hajati S et al (2015) Rapid removal of auramine-O and methylene blue by ZnS:Cu nanoparticles loaded on activated carbon: a response surface methodology approach. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 53:80–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2015.02.026
Atrous M, Sellaoui L, Bouzid M et al (2019) Adsorption of dyes acid red 1 and acid green 25 on grafted clay: modeling and statistical physics interpretation. J Mol Liq 294:111610. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2019.111610
Bacherikov YY, Davydenko MO, Dmytruk AM et al (2006) CdSe nanoparticles grown with different chelates. Semicond Phys Quantum Electron Optoelectron. 9:75–79. https://doi.org/10.15407/spqeo9.02.075
Bel Haj Mohamed N, Haouari M, Zaaboub Z et al (2014) Effect of surface on the optical structure and thermal properties of organically capped CdS nanoparticles. J Phys Chem Solids 75:936–944. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2014.03.007
Bel Haj Mohamed N, Ben Brahim N, Mrad R et al (2018) Use of MPA-capped CdS quantum dots for sensitive detection and quantification of Co2+ ions in aqueous solution. Anal Chim Acta 1028:50–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2018.04.041
Bel Haj Mohamed N, Bouzidi M, Ben Brahim N et al (2021) Impact of the stacking fault and surface defects states of colloidal CdSe nanocrystals on the removal of reactive black 5. Mater Sci Eng B 265:115029. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2020.115029
Belver C, Bedia J, Peñas-Garzón M et al (2020) 3 - Structured photocatalysts for the removal of emerging contaminants under visible or solar light. In: Sacco O, Vaiano V (eds) Visible Light Active Structured Photocatalysts for the Removal of Emerging Contaminants. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 41–98
Ben Brahim N, Bel Haj Mohamed N, Poggi M et al (2017) Interaction of l-cysteine functionalized CdSe quantum dots with metallic cations and selective binding of cobalt in water probed by fluorescence. Sensors Actuators B Chem 243:489–499. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.12.003
Borges ME, Sierra M, Méndez-Ramos J et al (2016) Solar degradation of contaminants in water: TiO2 solar photocatalysis assisted by up-conversion luminescent materials. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 155:194–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solmat.2016.06.010
Bouzid M, Sellaoui L, Khalfaoui M et al (2016) Adsorption of ethanol onto activated carbon: modeling and consequent interpretations based on statistical physics treatment. Phys Stat Mech Its Appl 444:853–869. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physa.2015.09.097
Bouzid M, Bouaziz N, Torkia YB, Lamine AB (2019) Statistical physics modeling of ethanol adsorption onto the phenol resin based adsorbents: stereographic, energetic and thermodynamic investigations. J Mol Liq 283:674–687. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2019.03.129
Chaparro AM, Martìnez MA, Guillén C et al (2000) SnO 2 substrate effects on the morphology and composition of chemical bath deposited ZnSe thin films. Thin Solid Films 361–362:177–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-6090(99)00791-9
Cheng L, Xiang Q, Liao Y, Zhang H (2018) CdS-based photocatalysts. Energy Environ Sci 11:1362–1391. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7EE03640J
Côrtes LN, Druzian SP, Streit AFM et al (2019) Biochars from animal wastes as alternative materials to treat colored effluents containing basic red 9. J Environ Chem Eng 7:103446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2019.103446
Dake DV, Raskar ND, Mane VA et al (2020) Exploring the role of defects on diverse properties of Cr-substituted ZnS nanostructures for photocatalytic applications. Appl Phys A Mater Sci Process 126:640. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-020-03669-1
Deng Y, Zhao R (2015) Advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) in wastewater treatment. Curr Pollut Rep 1:167–176. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40726-015-0015-z
Freundlich H (1907) Über die Adsorption in Lösungen. Z Für Phys Chem 57U:385–470. https://doi.org/10.1515/zpch-1907-5723
Gaponenko SV (1998) Optical properties of semiconductor nanocrystals. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Ghasemi M, Ghasemi N, Zahedi G et al (2014) Kinetic and equilibrium study of Ni(II) sorption from aqueous solutions onto Peganumharmala-L. Int J Environ Sci Technol 11:1835–1844. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-014-0617-9
Gómez-Avilés A, Peñas-Garzón M, Bedia J et al (2019) Mixed Ti-Zr metal-organic-frameworks for the photodegradation of acetaminophen under solar irradiation. Appl Catal B Environ 253:253–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.04.040
Guo H, Ke Y, Wang D et al (2013) Efficient adsorption and photocatalytic degradation of Congo red onto hydrothermally synthesized NiS nanoparticles. J Nanopart Res 15:1475. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-013-1475-y
Han K, Peng X-L, Li F, Yao M-M (2018) SnO2 composite films for enhanced photocatalytic activities. Catalysts 8:453. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8100453
Hashimoto K, Irie H, Fujishima A (2005) TiO2 photocatalysis: a historical overview and future prospects. Jpn J Appl Phys 44:8269–8285. https://doi.org/10.1143/JJAP.44.8269
Ho YS, McKay G (1999) Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem 34:451–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-9592(98)00112-5
Huang C, Liu S, Chen T, Li Y (2008) A new approach for quantitative determination of glucose by using CdSe/ZnS quantum dots. Sensors Actuators B Chem 130:338–342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2007.08.021
Ilgin P, Ozay H, Ozay O (2019) Selective adsorption of cationic dyes from colored noxious effluent using a novel N-tert-butylmaleamicacid based hydrogels. React Funct Polym 142:189–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2019.06.018
Im SH, Lee YH, Seok SI (2010) Photoelectrochemical solar cells fabricated from porous CdSe and CdS layers. Electrochim Acta 55:5665–5669. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2010.04.106
Jabeen U, Shah SM, Khan SU (2017) Photo catalytic degradation of Alizarin red S using ZnS and cadmium doped ZnS nanoparticles under unfiltered sunlight. Surf Interfaces 6:40–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfin.2016.11.002
Jaseela PK, Garvasis J, Joseph A (2019) Selective adsorption of methylene blue (MB) dye from aqueous mixture of MB and methyl orange (MO) using mesoporous titania (TiO2) – poly vinyl alcohol (PVA) nanocomposite. J Mol Liq 286:110908. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2019.110908
Jung YW, Yoon JJ, Byun JS, Kim YD (2008) Dielectric function analysis of ZnSe and CdSe using parametric semiconductor model. Microelectron J 39:570–572. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mejo.2007.07.038
Kaur R, Kaur A, Umar A et al (2019) Metal organic framework (MOF) porous octahedral nanocrystals of Cu-BTC: synthesis, properties and enhanced adsorption properties. Mater Res Bull 109:124–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2018.07.025
Klimov VI, McBranch DW, Leatherdale CA, Bawendi MG (1999) Electron and hole relaxation pathways in semiconductor quantum dots. Phys Rev B 60:13740–13749. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.60.13740
Kopp G, Lean JL (2011) A new, lower value of total solar irradiance: evidence and climate significance. Geophys Res Lett 38. https://doi.org/10.1029/2010GL045777
Kotkata MF, Masoud AE, Mohamed MB, Mahmoud EA (2009) Structural characterization of chemically synthesized CdSe nanoparticles. Phys E Low-Dimens Syst Nanostructures 41:640–645. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physe.2008.10.019
Kuriakose S, Satpati B, Mohapatra S (2014) Enhanced photocatalytic activity of Co doped ZnOnanodisks and nanorods prepared by a facile wet chemical method. Phys Chem Chem Phys 16:12741. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4cp01315h
Lagergren SK (1898) About the theory of so-called adsorption of soluble substances. Vetenskapsakad Handingarl 24:1–39
Lakshmipathy R, Kesarla MK, Nimmala AR et al (2017) ZnS nanoparticles capped with watermelon rind extract and their potential application in dye degradation. Res Chem Intermed 43:1329–1339. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-016-2700-y
Langmuir I (1918) The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J Am Chem Soc 40:1361–1403. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja02242a004
Li Z, Hanafy H, Zhang L et al (2020) Adsorption of Congo red and methylene blue dyes on an ashitaba waste and a walnut shell-based activated carbon from aqueous solutions: experiments, characterization and physical interpretations. Chem Eng J 388:124263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.124263
Lo S, Lin C, Wu C, Hsieh P (2004) Capability of coupled CdSe/TiO for photocatalytic degradation of 4-chlorophenol. J Hazard Mater 114:183–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2004.08.007
Mohamed B, Qingyu ZD, Moggridge G, Abdelmottaleb BL (2018) New insight in adsorption of pyridine on the two modified adsorbents types MN200 and MN500 by means of grand canonical ensemble. J Mol Liq 263:413–421. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.05.008
Nath D, Singh F, Das R (2020) X-ray diffraction analysis by Williamson-Hall, Halder-Wagner and size-strain plot methods of CdSe nanoparticles- a comparative study. Mater Chem Phys 239:122021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2019.122021
Nayak B, Samant A, Patel R, Misra PK (2017) Comprehensive understanding of the kinetics and mechanism of fluoride removal over a potent nanocrystalline hydroxyapatite surface. ACS Omega 2:8118–8128. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.7b00370
Neto ESF, Dantas NO, da Silva SW et al (2010) Confirming the lattice contraction in CdSe nanocrystals grown in a glass matrix by Raman scattering. J Raman Spectrosc 41:1302–1305. https://doi.org/10.1002/jrs.2565
Ouni S, Bel Haj Mohamed N, Bouzidi M et al (2021) High impact of thiol capped ZnS nanocrystals on the degradation of single and binary aqueous solutions of industrial azo dyes under sunlight. J Environ Chem Eng 9:105915. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.105915
Pan B, Sun K, Xing B (2010) Adsorption kinetics of 17α-ethinyl estradiol and bisphenol A on carbon nanomaterials. II Concentration-dependence. J SoilsSediments 10:845–854. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-009-0185-7
Pang X, Bouzid M, dos Santos JMN et al (2020) Theoretical study of indigotine blue dye adsorption on CoFe2O4/chitosan magnetic composite via analytical model. Colloids Surf Physicochem Eng Asp 589:124467. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2020.124467
Peng WQ, Qu SC, Cong GW et al (2005) Optical and magnetic properties of ZnS nanoparticles doped with Mn2+. J Cryst Growth 282:179–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcrysgro.2005.05.005
Ramki K, RajaPriya A, Sakthivel P et al (2020) Rapid degradation of organic dyes under sunlight using tin-doped ZnS nanoparticles. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 31:8750–8760. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-03410-x
Raskar ND, Dake DV, Mane VA et al (2019) One step synthesis of vertically grown Mn-doped ZnO nanorods for photocatalytic application. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 30:10886–10899. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-01433-7
Redlich O, Peterson DL (1959) A useful adsorption isotherm. J Phys Chem 63:1024–1024. https://doi.org/10.1021/j150576a611
Safardoust-Hojaghan H, Salavati-Niasari M (2017) Degradation of methylene blue as a pollutant with N-doped graphene quantum dot/titanium dioxide nanocomposite. J Clean Prod 148:31–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.01.169
Sajab MS, Chia CH, Zakaria S, Khiew PS (2013) Cationic and anionic modifications of oil palm empty fruit bunch fibers for the removal of dyes from aqueous solutions. BioresourTechnol 128:571–577. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.11.010
Sghaier W, Ben Torkia Y, Bouzid M, Ben Lamine A (2021) CO2 adsorption investigation by statistical physics: thermodynamic analysis for cooling cycle application. J Environ Chem Eng 9:105108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.105108
Shahi AK, Pandey BK, Singh BP, Gopal R (2016) Structural and optical properties of solvothermal synthesized nearly monodispersed CdSe nanocrystals. Adv Nat Sci Nanosci Nanotechnol 7:035010–035018. https://doi.org/10.1088/2043-6262/7/3/035010
Smida A, Zaaboub Z, Mohamed NBH et al (2018) Photoluminescence behavior in the synthesized CdSe thin films deposited on ITO substrates. J Lumin 194:686–691. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2017.09.036
Soheyli E, Sahraei R, Nabiyouni G (2017) pH-dependent optical properties of N-acetyl-L-cysteine-capped ZnSe(S) nanocrystals with intense/stable emissions. J Nanopart Res 19:92. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-017-3792-z
Soltani N, Saion E, Mahmood Mat Yunus W et al (2013) Photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue under visible light using PVP-capped ZnS and CdS nanoparticles. Sol Energy 97:147–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2013.08.023
Sousa JCG, Ribeiro AR, Barbosa MO et al (2018) A review on environmental monitoring of water organic pollutants identified by EU guidelines. J Hazard Mater 344:146–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.09.058
Stokes AR, Wilson AJC (1944) The diffraction of X rays by distorted crystal aggregates - I. Proc Phys Soc 56:174–181. https://doi.org/10.1088/0959-5309/56/3/303
Takeda N, Torimoto T, Sampath S et al (1995) Effect of inert supports for titanium dioxide loading on enhancement of photodecomposition rate of gaseous propionaldehyde. J Phys Chem 99:9986–9991. https://doi.org/10.1021/j100024a047
Thandavan TMK, Gani SMA, Wong CS, Nor RM (2015) Evaluation of Williamson–Hall strain and stress distribution in ZnO nanowires prepared using aliphatic alcohol. J NondestructEval 34:14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10921-015-0286-8
Todescato F, Minotto A, Signorini R et al (2013) Investigation into the heterostructure interface of CdSe-based core–shell quantum dots using surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. ACS Nano 7:6649–6657. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn402022z
Tschirner N, Lange H, Schliwa A et al (2012) Interfacial alloying in CdSe/CdS heteronanocrystals: a Raman spectroscopy analysis. Chem Mater 24:311–318. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm202947n
Wang Q, Ye F, Fang T et al (2011) Bovine serum albumin-directed synthesis of biocompatible CdSe quantum dots and bacteria labeling. J Colloid Interface Sci 355:9–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2010.11.035
Wang J, Zhao H, Zhu Y, Song Y (2017) Shape-controlled synthesis of CdSe nanocrystals via a programmed microfluidic process. J Phys Chem C 121:3567–3572. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.6b10901
Williamson GK, Hall WH (1953) X-ray line broadening from filed aluminium and wolfram. Acta Metall 1:22–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/0001-6160(53)90006-6
Wu P-J, Stetsko YP, Tsuei K-D et al (2007) Size dependence of tetrahedral bond lengths in CdSe nanocrystals. Appl Phys Lett 90:161911. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2727559
Yang J, Tang A, Zhou R, Xue J (2011) Effects of nanocrystal size and device aging on performance of hybrid poly(3-hexylthiophene):CdSe nanocrystal solar cells. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 95:476–482. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solmat.2010.09.005
Yazidi A, Sellaoui L, Dotto GL et al (2019) Monolayer and multilayer adsorption of pharmaceuticals on activated carbon: application of advanced statistical physics models. J Mol Liq 283:276–286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2019.03.101
Zhao Q, Xie Y, Zhang Z, Bai X (2007) Size-selective synthesis of zinc sulfide hierarchical structures and their photocatalytic activity. CrystGrowth Des 7:153–158. https://doi.org/10.1021/cg060521j
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Naim Bel Haj M: visualization, writing — review and editing, conceptualization, and methodology. SabriOuni: writing — original draft, visualization, conceptualization, and methodology. Mohamed bouzid: resources and writing — review and editing. Mohamed bouzidi: resources and writing — review and editing. Adrian Bonilla-Petriciolet: writing — reviewing and editing. Mohamed Haouari: Writing — reviewing and editing, visualization, and supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable for this study.
Consent for publication
All authors consent to this publication.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Guilherme L. Dotto
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 1990 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bel Haj Mohamed, N., Ouni, S., Bouzid, M. et al. Synthesis and preparation of acid capped CdSe nanocrystals as successful adsorbent and photocatalyst for the removal of dyes from water and its statistical physics analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 72747–72763 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20990-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20990-9