Abstract
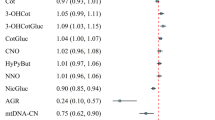
The influence of tobacco smoke has been a controversial and very questionable subject within the field of neurological behaviours. To examine the dose–response relationships between tobacco smoke and neurological performance, we investigated whether mitochondrial DNA copy number (mtDNAcn) mediates these relationships. We used restricted cubic spline models to estimate the dose–response relationships. A mediation model was also used to detect the mediating effect. Increased cotinine was negatively associated with auditory memory scores and a 0.51 decrease in mtDNAcn. MtDNAcn acts as a mediator between cotinine and auditory memory. Tobacco smoke levels were inversely associated with mtDNAcn and neurobehavioural changes, and there was a mediation effect between cotinine levels and auditory memory by mtDNAcn.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- AD:
-
Alzheimer’s disease
- 3HC:
-
Trans-3-Hydroxycotinine
- mtDNAcn:
-
Mitochondrial DNA copy number
- POMSA:
-
Anger-hostility
- POMSC:
-
Confusion-bewilderment
- POMSD:
-
Depression-dejection
- POMSF:
-
Fatigue-inertia
- POMST:
-
Tension-anxiety
- POMSV:
-
Vigor-activity
- DSP:
-
Total digit span
References
Andrews SJ, Goate AM (2020) Mitochondrial DNA copy number is associated with cognitive impairment. Alzheimer’s Dement 16:1–2. https://doi.org/10.1002/alz.047543
Anger WK (2003) Neurobehavioural tests and systems to assess neurotoxic exposures in the workplace and community. Occup Environ Med 60:531–538. https://doi.org/10.1136/oem.60.7.531
Ashar FN, Zhang Y, Longchamps RJ et al (2017) Association of mitochondrial DNA copy number with cardiovascular disease. JAMA Cardiol 2:1247–1255. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamacardio.2017.3683
Benowitz NL (1999) Biomarkers of environmental tobacco smoke exposure. Environ Health Perspect 107:349–355. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.99107s2349
Benowitz NL, Jacob P, Ahijevych K et al (2002) Biochemical verification of tobacco use and cessation. Nicotine Tob Res 4:149–159. https://doi.org/10.1080/14622200210123581
Benowitz NI, Dains KM, Dempsey D et al (2009) Urine nicotine metabolite concentrations in relation to plasma cotinine during low-level nicotine exposure. Nicotine Tob Res 11:954–960. https://doi.org/10.1093/ntr/ntp092
Carugno M, Pesatori AC, Dioni L et al (2012) Increased mitochondrial DNA copy number in occupations associated with low-dose benzene exposure. Environ Health Perspect 5:210–215
Cervilla JA, Prince M, Mann A (2000) Smoking, drinking, and incident cognitive impairment : a cohort community based study included in the Gospel Oak project. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 68:622–626. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.68.5.622
Cuijpers P, Smit F, Have M, De GR (2007) Smoking is associated with first-ever incidence of mental disorders : a prospective population-based study. Addiction 102:1303–1309. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1360-0443.2007.01885.x
Doll R, Peto R, Boreham J, Sutherland I (2000) Smoking and dementia in male British doctors: prospective study. Br Med J 320:1097–1102. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.320.7242.1097
Edelstein SL, Sc M, Kritz-silverstein D et al (1998) Prospective association of smoking and alcohol use with cognitive function in an elderly cohort. J Women’s Health 7:1271–1281. https://doi.org/10.1089/jwh.1998.7.1271
Ford AB, Mefrouche Z, Friedland RP, Debanne SM (1996) Smoking and cognitive impairment: a population-based study. J Am Geriatr Soc 44:905–909. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1532-5415.1996.tb01858.x
Giordano L, Deceglie S, D’Adamo P et al (2015) Cigarette toxicity triggers Leber’s hereditary optic neuropathy by affecting mtDNA copy number, oxidative phosphorylation and ROS detoxification pathways. Cell Death Dis 6:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2015.364
Graves AB, Duijn CMVAN, Fratiglioni L et al (1991) Alcohol and tobacco consumption as risk factors for Alzheimer’s disease : a collaborative re-analysis of case-control studies. Int J Epidemiol 20:S48-57. https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/20.supplement_2.s48
Haufroid V, Lison D (1998) Urinary cotinine as a tobacco-smoke exposure index. A minireview. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 71:162–168. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004200050266
Herzig KE, Callaway E, Halliday R et al (1998) Effects of cotinine an information processing in nonsmokers. Psychopharmacology 135:127–132. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002130050493
Jacob P, Yu L, Duan M et al (2011) Determination of the nicotine metabolites cotinine and trans-3’-hydroxycotinine in biologic fluids of smokers and non-smokers using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry: biomarkers for tobacco smoke exposure and for phenotyping cytochrome P450 2. J Chromatogr B Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci 879:267–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2010.12.012
Jarvis MJ, Tunstall-Pedoe H, Feyerabend C et al (1987) Comparison of tests used to distinguish smokers from nonsmokers. Am J Public Health 77:1435–1438. https://doi.org/10.2105/AJPH.77.11.1435
Kalmijn S, Van BMPJ, Verschuren MWM et al (2002) Cigarette smoking and alcohol consumption in relation to cognitive performance in middle age. Am J Epidemiol 156:936–944. https://doi.org/10.1093/aje/kwf135
Klietz M-L, Kaiser HW, Machens H-G, Aitzetmüller MM (2019) How is exposure to tobacco outlets within activity spaces associated with daily tobacco use among youth? A Mediation Analysis. 22:958–966. https://doi.org/10.1093/ntr/ntz088
Koch M, Fitzpatrick AL, Rapp SR et al (2019) Alcohol consumption and risk of dementia and cognitive decline among older adults with or without mild cognitive impairment. JAMA Netw Open 2:e1910319. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.10319
Lin MT, Beal MF (2006) Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases. Nature 443:787–795. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05292
Lindqvist D, Wolkowitz OM, Picard M et al (2018) Circulating cell-free mitochondrial DNA, but not leukocyte mitochondrial DNA copy number, is elevated in major depressive disorder. Neuropsychopharmacology 43:1557–1564. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41386-017-0001-9
Liu Y, Li H, Wang J et al (2020) Association of cigarette smoking with cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers of neurodegeneration, neuroinflammation, and oxidation. JAMA Netw Open 3:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.18777
Mattson MP, Liu D (2002) Energetics and oxidative stress in synaptic plasticity and neurodegenerative disorders. NeuroMolecular Med 2:215–231. https://doi.org/10.1385/NMM:2:2:215
Qiu C, Peng B, Cheng S et al (2013) The effect of occupational exposure to benzo[a]pyrene on neurobehavioral function in coke oven workers. Am J Ind Med 56:347–355. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajim.22119
Reddy PH, Beal MF (2008) Amyloid beta, mitochondrial dysfunction and synaptic damage: implications for cognitive decline in aging and Alzheimer’s disease. Trends Mol Med 14:45–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmed.2007.12.002
Richards M, Jarvis MJ, Thompson N, Wadsworth MEJ (2003) Cigarette smoking and cognitive decline in midlife : evidence from a prospective birth cohort study. Am J Public Health 93:994–998. https://doi.org/10.2105/ajph.93.6.994
Rosso M, Chitnis T (2020) Association between cigarette smoking and multiple sclerosis: a review. JAMA Neurol 77:245–253. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaneurol.2019.4271
Sabbagh MN (2002) The nicotinic acetylcholine receptor smoking and alzheimer s disease revisited. J Alzheimer’s Dis 4:317–325. https://doi.org/10.2741/e367
Saenen ND, Provost EB, Cuypers A et al (2019) Child’s buccal cell mitochondrial DNA content modifies the association between heart rate variability and recent air pollution exposure at school. Environ Int 123:39–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2018.11.028
Suzuki S, Cohen SM, Arnold LL et al (2020) Cotinine, a major nicotine metabolite, induces cell proliferation on urothelium in vitro and in vivo. Toxicology 429:152325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2019.152325
Swan GE, Lessov-Schlaggar CN (2007) The effects of tobacco smoke and nicotine on cognition and the brain. Neuropsychol Rev 17:259–273. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11065-007-9035-9
Thomas CE, Wang R, Adams-Haduch J et al (2020) Urinary cotinine is as good a biomarker as serum cotinine for cigarette smoking exposure and lung cancer risk prediction. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 29:127–132. https://doi.org/10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-19-0653
Ungvari Z, Tarantini S, Donato AJ et al (2018) Mechanisms of vascular aging. Circ Res 123:849–867. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.118.311378
Van Duijn CM, Clayton DG, Chandra V et al (1994) Interaction between genetic and environmental risk factors for Alzheimer’s disease: a reanalysis of case-control studies. Genet Epidemiol 11:539–551. https://doi.org/10.1002/gepi.1370110609
Van Gool CH, Kempen GIJM, Bosma H et al (2007) Associations between lifestyle and depressed mood: longitudinal results from the Maastricht aging study. Am J Public Health 97:887–894. https://doi.org/10.2105/AJPH.2004.053199
Vine MF, Hulka BS, Margolin BH et al (1993) Cotinine concentrations in semen, urine, and blood of smokers and nonsmokers. Am J Public Health 83:1335–1338. https://doi.org/10.2105/AJPH.83.9.1335
Vyas CM, Ogata S, Reynolds CF et al (2020) Lifestyle and behavioral factors and mitochondrial DNA copy number in a diverse cohort of mid-life and older adults. PLoS One 15:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0237235
Wang H, Chen H, Han S et al (2021) Decreased mitochondrial DNA copy number in nerve cells and the hippocampus during nicotine exposure is mediated by autophagy. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 226:112831. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112831
Wu NN, Zhang Y, Ren J (2019a) Mitophagy, mitochondrial dynamics, and homeostasis in cardiovascular aging. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2019:10–12. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/9825061
Wu S, Li X, Meng S et al (2019b) Fruit and vegetable consumption, cigarette smoke, and leukocyte mitochondrial DNA copy number. Am J Clin Nutr 109:424–432. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/nqy286
Yu M (2011) Generation, function and diagnostic value of mitochondrial DNA copy number alterations in human cancers. Life Sci 89:65–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2011.05.010
Yuan Y, Ju YS, Kim Y et al (2020) Comprehensive molecular characterization of mitochondrial genomes in human cancers. Nat Genet 52:342–352. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-019-0557-x
Zhang WZ, Rice MC, Hoffman KL et al (2020) Association of urine mitochondrial DNA with clinical measures of COPD in the SPIROMICS cohort. JCI Insight 5:e133984. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.133984
Funding
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81673143, 81072279, and 30800899), Shanxi Province Natural Science Foundation (2010021034–3 and 2015011128), and the Research Project Supported by Shanxi Scholarship Council (2016–057).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Huimin Wang: writing—original draft, methodology, formal analysis, writing—review and editing. Mengmeng Fu: writing—original draft, methodology, formal analysis, writing—review and editing. Yifei Ma: project administration, writing—review and editing. Chengjuan Liu: investigation, data curation, resources, writing—review and editing. Min Wu: investigation, writing—review and editing. Jisheng Nie: funding acquisition, conceptualization, supervision, project administration, writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This study was approved by the medical ethics committee of the School of Public Health, Shanxi Medical University.
Consent to participate
All participants gave their informed consent.
Consent for publication
Consent was given by all contributing authors.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Lotfi Aleya
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H., Fu, M., Ma, Y. et al. Tobacco smoke exposure and mitochondrial DNA copy number on neurobehavioural performance: A community study. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 84180–84190 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20921-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20921-8