Abstract
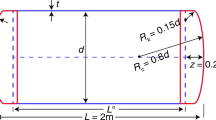
Fuel cells are gaining popularity because of their efficient energy production without causing environmental pollution. Recently, DRDO has developed a fuel cell-based air-independent propulsion (AIP) system. In this system, the hydrogen is produced onboard while oxygen is carried in liquefied form (LOX) from the land in specially designed insulated storage vessels called dewars. Such vessels are needed because LOX has a low boiling point (NBP ~ 90 K) and heat of vaporization (~ 213 kJ/kg), due to which it boils off easily even when there is a small amount of heat inleak from the ambient. A typical dewar consists of two vessels separated by insulation. Support members are used to hold the two vessels together. Heat inleak through the supports and the insulation of the dewar causes the boiling of LOX. The vessels are subjected to dynamic loads during the voyage due to the filling and consumption of LOX. Therefore, the support system should be designed to withstand the dynamic loads experienced by the dewar. While the support system should have enough mechanical strength to withstand the loads it is subjected to, it should also restrict the heat inleak from the ambient to minimize the LOX boil-off. To meet this requirement, we need to optimize the support system design. Design optimization of support systems is especially critical in submarines to reduce the snorkeling frequency. Even though the dewars are available commercially for various applications, their design methodologies are not available in the open literature. Cylindrical rods are generally used as support members. In earlier studies, the authors have shown that helical coils give better thermal performance than tension rods as dewar supports. These two support systems involve different design criteria. It is important to evolve an optimal design of the support system to maximize the mechanical strength of the support while minimizing the heat inleak through the support. In this paper, we present a design methodology for optimizing helical support. We have proposed a modified optimization technique derived from the classical genetic algorithm (GA) for this purpose. The modification has been done by ensuring the design feasibility of the coil at each step of the algorithm. The proposed optimization technique has been tested on a LOX dewar, and an optimal design of the helical coil support has been obtained.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Ahmadzadeh A, Salimpour MR, Sedaghat A (2017) Thermal and exergoeconomic analysis of a novel solar driven combined power and ejector refrigeration (CPER) system. Int J Refrig 83:143–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrefrig.2017.07.015
Alkhatib R, Jazar GN, Golnaraghi MF (2004) Optimal design of passive linear suspension using genetic algorithm. J Sound Vib 275(3–5):665–691. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsv.2003.07.007
Barron RF (1985) Cryogenic systems. Oxford University Press, New York
Benedict JR (2005) The unraveling and revitalization of US Navy antisubmarine warfare. Naval War College Review 58(2):93–120
Bertsimas D, Vempala S (2004) Solving convex programs by random walks. Journal of the ACM (JACM) 51(4):540–556. https://doi.org/10.1145/1008731.1008733
Bradley PE, Radebaugh R (2013) Properties of selected materials at cryogenic temperatures. NIST Publ 680:1–14
Dai YH, Ni Q (2003) Testing different conjugate gradient methods for large-scale unconstrained optimization. Journal of Computational Mathematics 21(3):311–320
de Troya JJ, Alvarez C, Fernández-Garrido C, Carral L (2016) Analysing the possibilities of using fuel cells in ships. Int J Hydrogen Energy 41(4):2853–2866. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2015.11.145
Deb K (1998) Genetic algorithm in search and optimization: the technique and applications. Proceedings of International Workshop on Soft Computing and Intelligent Systems, ISI, Calcutta, India, pp 58–87
Dorigo M, Di Caro G (1999) Ant colony optimization: a new meta-heuristic. In Proceedings of the 1999 congress on evolutionary computation-CEC99 (Cat. No. 99TH8406). IEEE 2:1470–1477. https://doi.org/10.1109/CEC.1999.782657
Fliege J, Svaiter BF (2000) Steepest descent methods for multicriteria optimization. Math Methods Oper Res 51(3):479–494. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001860000043
Foerg W (2002) History of cryogenics: the epoch of the pioneers from the beginning to the year 1911. Int J Refrig 25(3):283–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-7007(01)00020-2
He J, Guo Y, Miao J, Ding T, Zhang H, Chen Y, Lin G (2019) Pre-flight thermal performance test of a 35 K cryogenic integrated system. Int J Refrig 98:372–380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrefrig.2018.11.020
Hibl JJ, Sutton HE, Beech Aircraft Corp (1975) Cryogenic tank support system. U.S. Patent 3,905,508
Hongze X, Ye WX, Maosheng X (2000) Schema analysis of multi-points crossover genetic algorithm. In Proceedings of the 3rd World Congress on Intelligent Control and Automation (Cat. No. 00EX393). IEEE 1:521–524. https://doi.org/10.1109/WCICA.2000.860022
Jacob S, Kasthurirengan S, Karunanithi R (1993) Concentric tubular support design for cryogenic tanks. Cryogenics 33(4):435–437. https://doi.org/10.1016/0011-2275(93)90173-L
Kirkpatrick S, Gelatt C, Vecchi M (1983) Optimization by Simulated Annealing. Science 220(4598):671–680. https://www.science.org/doi/abs/10.1126/science.220.4598.671
Kittel P (1993) Comparison of Dewar supports for space applications. Cryogenics 33(4):429–434. https://doi.org/10.1016/0011-2275(93)90172-K
Krumme DW, Ackley DH (1982) A practical method for code generation based on exhaustive search. ACM SIGPLAN Notices 17(6):185–196. https://dl.acm.org/doi/abs/10.1145/872726.806994
Li M, Azarm S, Aute V (2005) A multi-objective genetic algorithm for robust design optimization. In Proceedings of the 7th annual conference on Genetic and evolutionary computation, pp 771–778. https://doi.org/10.1145/1068009.1068140
Lim SP, Haron H (2013) Performance of different techniques applied in genetic algorithm towards benchmark functions. In Asian Conference on Intelligent Information and Database Systems. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 255–264. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-36546-1_27
Lingaiah K (2003) Machine design databook (vol 2). McGraw-Hill, New York
Meng QC, Feng TJ, Chen Z, Zhou CJ, Bo JH (1999) Genetic algorithms encoding study and a sufficient convergence condition of GAs. In IEEE SMC'99 Conference Proceedings. 1999 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (Cat. No. 99CH37028). IEEE 1:649–665. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICSMC.1999.814168
Mohebbi A, Taheri M, Soltani A (2008) A neural network for predicting saturated liquid density using genetic algorithm for pure and mixed refrigerants. Int J Refrig 31(8):1317–1327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrefrig.2008.04.008
Nitin B, Sandilya P (2018) Structural and thermal analysis of dewar supports for low boil-off long duration storage of cryogenic liquids. Indian Journal of Cryogenics 43(1):33–39. https://doi.org/10.5958/2349-2120.2018.00005.5
Nitin B, Sandilya P, Chakraborty G (2022) Revisiting the dewar design for liquid oxygen storage in fuel cell energy systems. Int Commun Heat Mass Transfer 134:105975. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2022.105975
Nitin B, Sandilya P, Chakraborty G (2020) Design of dewar supports through topology optimization. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering. IOP Publishing 755(1):012054. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/755/1/012054
Nitin B, Sandilya P, Chakraborty G (2021) Theoretical Comparison of the Thermo-Mechanical fatigue characteristics of a tension rod and coil used as dewar supports. Presented at CEC/ICMC 21, 17–23 July 2021
Poli R, Kennedy J, Blackwell T (2007) Particle Swarm Optimization Swarm Intelligence 1(1):33–57. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11721-007-0002-0.pdf
Pratihar DK (2007) Soft computing. Oxford: Alpha Science International, Ltd
Reed RP, Golda M (1997) Cryogenic composite supports: a review of strap and strut properties. Cryogenics 37(5):233–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0011-2275(97)00004-0
Sadd MH (2009) Elasticity: theory, applications, and numerics. Academic Press
Saha P, Nitin B, Sandilya P (2018) Optimization of the performance of injection cooling system using genetic algorithm. Indian Journal of Cryogenics 43(1):16–21. https://doi.org/10.5958/2349-2120.2018.00002.X
Shigley JE, Mischke CR, Budnyas RG, Nisbett KJ (2008) Shigley’s Mechanical Engineering Design (In SI Units). Tata McGraw-Hill
Silver DM, Dehaas N, Johns Hopkins University (1985) Cryogenic tank support system. U.S. Patent 4,496,073
Subramanian M, Sakthivel M, Sooryaprakash K, Sudhakaran R (2013) Optimization of cutting parameters for cutting force in shoulder milling of Al7075-T6 using response surface methodology and genetic algorithm. Procedia Engineering 64:690–700. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2013.09.144
Virdi PS, Nitin B, Sandilya P, Chakraborty G (2019) Theoretical comparison of thermo-mechanical behavior of a tension rod and a coil as dewar support. Indian Journal of Cryogenics (2019):216–221. https://doi.org/10.5958/2349-2120.2019.00038.4
Wang C, Quan H, Xu X (1996) Optimal design of multiproduct batch chemical process using genetic algorithms. Ind Eng Chem Res 35(10):3560–3566. https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/ie9506633
Ya’ari YD (1997) A case for maneuverability. Naval War College Review 50(4):125–132. http://www.jstor.org/stable/44638783
Yu H, Fang H, Yao P, Yuan Y (2000) A combined genetic algorithm/simulated annealing algorithm for large scale system energy integration. Comput Chem Eng 24(8):2023–2035. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0098-1354(00)00601-3
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the National Supercomputing Mission (NSM) for providing computing resources of “PARAM Shakti” at IIT Kharagpur, which is implemented by C-DAC and supported by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) and Department of Science and Technology (DST), Government of India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BN: conceptualization, methodology, investigation, formal analysis, visualization, writing—original draft.
PS: conceptualization, methodology, investigation, formal analysis, resources, visualization, writing—review and editing, supervision, project administration.
GC: writing—review and editing, supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nitin, B., Sandilya, P. & Chakraborty, G. Optimal design of a helical coil support for dewars in fuel cell applications. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 24963–24974 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20286-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20286-y