Abstract
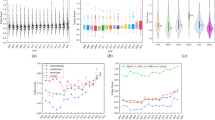
As China’s economy began transitioning from one focused on high-speed growth to one focusing on high-quality development, sustainable green development has become the main goal pursued by the government. This study empirically measures the marginal impact of per capita GDP, technological innovation level, industrial structure, openness, fiscal decentralization, and urbanization level on per capita wastewater discharge in 11 provinces (cities) along the Yangtze River Economic Belt (YREB) from 2008 to 2018 using a quantile model. The key findings were as follows: (1) factors such as the per capita GDP, industrial structure, foreign direct investment, and urbanization in the YREB significantly increased water resource pollution; (2) the quantile model regression results showed that the relationship between economic growth and ecological pollution followed the so-called environmental Kuznets inverted U-curve. Wastewater discharge per capita was low in areas with low per capita GDP, meaning that the ecological environment in these areas was more fragile and that the environmental pollution costs due to economic growth were therefore relatively much higher in these areas; (3) fiscal decentralization significantly reduced water resource pollution in relatively developed areas although the effects in the relatively developing areas were not significant; and (4) the effects of technological innovation on reducing water resource pollution in the YREB were positive but not very significant. The results also confirmed that traditional patterns of economic growth increased water pollution in the YREB. For this reason, the government needs to urgently improve policies—for example, upgrading economic structures, preventing over-urbanization, speeding up technological innovation, introducing environmentally friendly foreign investment, and providing more rewards to best practitioners of environmental governance—that is conducive to the achievement of green ecological development.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
Notes
Zhou, F.Q., Cheng, J., Chen N., et al. Environmental performance assessment report of Yangtze River economic zone [M] Shanghai: Shanghai Academy of Social Sciences Press, (2016).
CPC Central Committee and the State Council. Outline of the development plan of the Yangtze River Economic Belt. (2016). http://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2016-09/12/content_5107501.htm
References
Adu DT, Denkyirah EK (2017) Economic growth and environmental pollution in West Africa: testing the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis. Kasetsart Journal of Social Sciences 40(2):281–288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.kjss.2017.12.008
Ai XQ, Chen LL, Zhu LN (2017) Research on the relationship between air pollution and economic growth— based on the spatial econometric model of China’s provincial panel data. East China Economic Management 31(03):69–76. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1007-5097.2017.03.009
Apergis N, Ozturk I (2015) Testing environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis in Asian countries. Ecol Ind 52:16–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2014.11.026
Chen JX, Zhang Y, Zheng S (2019) Ecoefficiency, environmental regulation opportunity costs, and interregional industrial transfers: evidence from the Yangtze River Economic Belt in China. J Clean Prod 233:611–625. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.06.117
Chen YS, Zhang SH, Huang DS, Li BL, Liu JG, Liu WJ, Ma J, Wang F, Wang Y, Wu SJ, Wu YG, Yan JY, Guo CB, Xin W, Wang H (2017) The development of China’s Yangtze River Economic Belt: how to make it in a green way. Science Bulletin 62(9):648–651. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scib.2017.04.009
Clement MT (2011) The jevons paradox and anthropogenic global warming: a panel analysis of state-level carbon emissions in the united states, 1963–1997. Soc Nat Resour 24(9):951–961. https://doi.org/10.1080/08941920903482937
Degefu DM, He WJ, Liao ZY, Yuan L, Huang ZW, An M (2018) Mapping monthly water scarcity in global transboundary basins at country-basin mesh-based spatial resolution. Sci Rep 8:2144. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-20032-w
Diao XD, Zeng SX, Tam CM, Tam VWY (2009) EKC analysis for studying economic growth and environmental quality: a case study in China. J Clean Prod 17(5):541–548. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2008.09.007
Ding X, Cai Z, Xiao Q, Gao S (2019a) A study on the driving factors and spatial spillover of carbon emission intensity in the Yangtze River Economic Belt under double control action. Int J Environ Res Public Health 16(22):4452. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16224452
Ding XH, Gao SH, Wu FP (2019b) Study on the spatial spillover effect of environmental regulation, FDI agglomeration and water utilization efficiency in the Yangtze River Economic Belt. China Popul, Resour Environ 29(08):148–155. https://doi.org/10.12062/cpre.2019b0304
Fan ZY, Zhang J (2009) Fiscal decentralization and the efficiency of China’s economic growth -- an analysis based on the unexpected output model. Management world, (07):15–25 + 187. https://doi.org/10.19744/j.cnki.11-1235/f.2009.07.003
Feng Y, Li XN, Qu GJ, Xu M (2017) Study on water environmental pollution and economic growth in China. Journal of Northwest A&F University (Social Science Edition), 17(06):66–74. https://doi.org/10.13968/j.cnki.1009-9107.2017.06.09
Fodha M, Zaghdoud O (2010) Economic growth and pollutant emissions in Tunisia: an empirical analysis of the environmental Kuznets curve. Energy Policy 38(2):1150–1156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2009.11.002
Halliru AM, Loganathan N, Hassan AAG, Mardani A, Kamyab H (2020) Re-examining the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis in the economic community of West African states: a panel quantile regression approach. J Clean Prod 276:124247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.124247
Iammarino S, McCann P (2006) The structure and evolution of industrial clusters: transactions, technology, and knowledge spillovers. Res Policy 35(7):1018–1036. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.respol.2006.05.004
Jayanthakumaran K, Liu Y (2012) Openness and the environmental kuznets curve: evidence from China. Econ Model 29(3):566–576. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.econmod.2011.12.011
Jia X, O’Connor D, Hou D, Jin Y, Li G, Zheng C, Sik Ok Y, Tsang DCW, Luo J (2019) Groundwater depletion and contamination: spatial distribution of groundwater resources sustainability in China. Sci Total Environ 672:551–562. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.03.457
Koenker R, Bassett G (1978) Regression Quantiles Econometric 46(1):33–50. https://doi.org/10.2307/1913643
Lan J, Kakinaka M, Huang XG (2012) Foreign direct investment, human capital and environmental pollution in China. Environ Resource Econ 51:255–275. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10640-011-9498-2
Li B, Li T (2014) An empirical study of the environmental Kuznets curve for China’s air pollution: by GMN model and threshold effect with dynamic panel data. On Economic Problems 04:17–22. https://doi.org/10.16011/j.cnki.jjwt.2014.04.001
Li Y, Shan P, Zhou JC (2022) The impact of the development strategy of the Yangtze River Economic Belt on economy and environment -- experimental evidence based on SCM method. Soft science.
Liang XD, Yang XB, Zhou ZC (2021) A study of impact of fiscal decentralization on environmental quality: technological innovation as an intermediate variable. Fujian Tribune 09:35–52
Liu JM, Wang B, Chen X (2015) A study on the nonlinear effect of political decentralization on environmental pollution—based on the PSTR model analysis of the panel data in 272 cities. China Economic Perspectives 03:82–89
Lorenzo JSL, San Tam WW, Seow WJ (2021) Association between air quality, meteorological factors and COVID-19 infection case numbers. Environ Res 197:111024. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.111024
Lu YQ, Zhang DG (2016) Environmental decentralization, market segmentation and carbon emissions. China population, resources and environment 26(06):107–115. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1002-2104.2016.06.014
Magazzino C, Mele M, Sarkodie SA (2021) The nexus between COVID-19 deaths, air pollution and economic growth in New York state: evidence from deep machine learning. J Environ Manage 286:112241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112241
Pan D, Hong W, Kong F (2020) Efficiency evaluation of urban wastewater treatment: evidence from 113 cities in the Yangtze River Economic Belt of China. J Environ Manage 270:110940. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110940
Peng X (2020) Strategic interaction of environmental regulation and green productivity growth in China: green innovation or pollution refuge? Sci Total Environ 732:139200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139200
Qu WH, Yan ZJ (2015) The influence of environmental pollution, economic growth and healthcare services to public health based on China’s provincial panel data. Chin J Manag Sci 23(07):166–176. https://doi.org/10.16381/j.cnki.issn1003-207x.2015.07.021
Sauvant KP, Mallampally P (2015) Policy options for promoting foreign direct investment in the least developed countries. Transnational Corporations Review 7(3):237–268. https://doi.org/10.5148/tncr.2015.7301
Shao Q (2020) Nonlinear effects of marine economic growth and technological innovation on marine pollution: panel threshold analysis for China’s 11 coastal regions. Mar Policy 121:104110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpol.2020.104110
She Y, Liu Y, Jiang L, Yuan H (2019) Is China’s river chief policy effective? Evidence from a quasi-natural experiment in the Yangtze River Economic Belt. China Journal of Cleaner Production 220:919–930. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.02.031
Shi HP, Yi ML (2020) Environmental governance, high-quality development and residents’ happiness——empirical study based on CGSS (2015) micro survey data. Manage Rev 32(09):18–33. https://doi.org/10.14120/j.cnki.cn11-5057/f.2020.09.002
Soumaré I, Gohou G, Kouadio H (2016) Comparative study of the characteristics of FDI from China to Africa versus developed countries. Transl Corp Rev 8(3):165–177. https://doi.org/10.1080/19186444.2016.1233715
Strandholm JC, Espinola-Arredondo A, Munoz-Garcia F (2018) Regulation, free-riding incentives, and investment in R&D with spillovers. Resour Energy Econ 53:133–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reseneeco.2018.04.002
Udemba EN, Yalçıntaş S (2021) Interacting force of foreign direct invest (FDI), natural resource and economic growth in determining environmental performance: a nonlinear autoregressive distributed lag (NARDL) approach. Resour Policy 73:102168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resourpol.2021.102168
Wang KL, Wang J, Wang J, Ding L, Zhao M, Wang Q (2020) Investigating the spatiotemporal differences and influencing factors of green water use efficiency of Yangtze River Economic Belt in China. PLoS ONE 15(4):e0230963. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0230963
Wang M, Huang Y (2015) China’s environmental pollution and economic growth. China Economic Quarterly 14(02):557–578. https://doi.org/10.13821/j.cnki.ceq.2015.02.007
Xie B, Xiang C (2016) Fiscal decentralization, environmental pollution and regional economic growth -- an empirical measurement based on the panel data of 112 prefecture level cities. Soft Sci 30(11):40–43 + 60. https://doi.org/10.13956/j.ss.1001–8409.2016.11.09.
Xie W, Deng H, Chong Z (2019) The spatial and heterogeneity impacts of population urbanization on fine particulate (PM2.5) in the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. Int J Environ Res Publ Health 16(6):1058. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16061058
Xu H, Yang Y, Nie D (2017) Influencing path of fiscal decentralization on environmental pollution in China’s top 10urban agglomerations. Urban Problems (06):14–24. https://doi.org/10.13239/j.bjsshkxy.cswt.170602
Yang CJ, Bi KX, Hu RQ (2018) Green innovation power transmission mechanism of industrial enterprises under open economy. Syst Eng 36(09):79–90
Yang TB, Zhu YM, Liu MH, Zhou B (2020) Industrial co-agglomeration, marketization and environmental pollution in resource-based cities. Ind Econ Res (06):15–27+112. https://doi.org/10.13269/j.cnki.ier.2020.06.002
Ye L, Wu X, Huang D (2020) Industrial energy-related CO2 emissions and their driving factors in the Yangtze River Economic Zone (China): an extended LMDI analysis from 2008 to 2016. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17(16):5880. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17165880
York R (2012) Asymmetric effects of economic growth and decline on CO2 emissions. Nature Clim Nature Climate Change 2:762–764. https://doi.org/10.1038/nclimate1699
Yu YZ, Liu FJ (2017) Impact of spatial agglomeration of producer services on environmental pollution. Research on Financial and Economic Issues 08:23–29. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1000-176X.2017.08.004
Zang JN, Liu LL (2020) Fiscal decentralization, government environmental preference, and regional environmental governance efficiency: evidence from China. Ann Reg Sci 65:439–457. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00168-020-00989-1
Zhang C, Zhu QL, Tong S (2011) Relationship between environmental pollution and economic growth. Statistical Research 28(01):59–67. https://doi.org/10.19343/j.cnki.11-1302/c.2011.01.011
Zhao JF, Han ZA (2019) Research on coupling relationship between environmental quality and regional economic growth based on VAR model. Clust Comput 22:5881–5891. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-017-1662-1
Zheng FH, Li J (2022) The impact of scientific and technological environmental regulation on industrial green innovation in resource-based cities -- an example from the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Urban Problems, (02), 35–45 + 75. https://doi.org/10.13239/j.bjsshkxy.cswt.220204.
Zugravu-Soilita N (2017) How does foreign direct investment affect pollution? Toward a better understanding of the direct and conditional effects. Environ Resource Econ 66:293–338. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10640-015-9950-9
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the editor and anonymous reviewers of this paper. They also acknowledge the Yangtze River Delta Science Data Center, CSMAR database, and China Statistical Yearbook for providing data.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 71904045).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Maosheng Ye and Wan Chen designed and performed the experiments, analyzed the data, and prepared the paper. Ling Guo and Yuqin Li participated to collect the materials related to the experiment.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Eyup Dogan
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ye, M., Chen, W., Guo, L. et al. “Green” economic development in China: quantile regression evidence from the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 60572–60583 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20197-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20197-y