Abstract
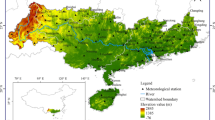
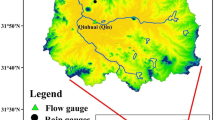
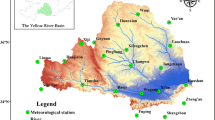
The refined assessment of the spatiotemporal characteristics of droughts is of great significance for drought evaluation. Based on monthly precipitation and temperature grid data (1961–2019) in the middle reaches of the Yellow River basin (MYRB), the standardized precipitation evapotranspiration index (SPEI) was calculated at monthly, seasonal, and annual scales. The run theory was used to extract the drought features at the monthly scale, and the spatiotemporal characteristics of different drought levels were analyzed using Mann–Kendall mutation tests and spatial interpolation. The Moran’ I was used to analyze the spatial heterogeneity of droughts. The results showed that the drought trend in the MYRB increased from 1961 to 2019, with the SPEI exhibiting an overall decreasing rate of − 0.1145/decade. Decreasing rates were observed in spring (− 0.1356/decade), summer (− 0.0362/decade), and autumn (− 0.0745/decade), whereas an increasing rate was observed in winter (0.0781/decade). Only extreme droughts were long term, with an intensity as low as − 22.29. The highest frequencies were observed for mild–moderate droughts, which mainly showed high-value clusters in the western and central regions. The frequencies of severe–extreme droughts mainly presented low-value clusters in the northern and southwestern areas. The frequencies of mild and severe droughts exhibited significant spatial cluster characteristics, while the drought intensity showed non-significant spatial clusters and a random distribution. The high and low values of drought intensity were mainly clustered in the middle–upper reaches. The research results provide reference for disaster prevention and mitigation, agricultural planning, and water resource allocation in the MYRB.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Ahmadalipour A, Moradkhani H (2017) Analyzing the uncertainty of ensemble-based gridded observations in land surface simulations and drought assessment. J Hydrol 555:557–568. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2017.10.059
Arshad A, Zhang W, Zhang Z, Wang S, Zhang B, Cheema M, Shalamzari M (2021) Reconstructing high-resolution gridded precipitation data using an improved downscaling approach over the high altitude mountain regions of Upper Indus Basin (UIB). Sci Total Environ 784:147140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.147140
Ayantobo OO, Yi L, Song S, Yao N (2017) Spatial comparability of drought characteristics and related return periods in mainland China over 1961–2013. J Hydrol 550:549–567. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2017.05.019
Bao Z, Zhang J, Wang G, Chen Q, Guan T, Yan X et al (2019) The impact of climate variability and land use/cover change on the water balance in the Middle Yellow River Basin. China. J Hydrol 577:123942
Chen Y, Fu B, Zhao Y, Wang K, Zhao M, Ma J et al (2020) Sustainable development in the Yellow River Basin: issues and strategies. J Clean Prod 263:121223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121223
Cook BI, Ault TR, Smerdon JE (2015) Unprecedented 21st century drought risk in the American Southwest and Central Plains. Sci Adv 1(1):e1400082. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.1400082
Giorgi F (2008) Regionalization of climate change information for impact assessment and adaptation. Bull World Meteorol Organization 57(2):86–92. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.4036
Guo E, Liu X, Zhang J, Wang Y, Wang C, Wang R, Wang D (2017) Assessing spatiotemporal variation of drought and its impact on maize yield in Northeast China. J Hydrol 553:231–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2017.07.060
Han Z, Huang Q, Huang S, Leng G, Bai Q, Liang H et al (2021) Spatial-temporal dynamics of agricultural drought in the Loess Plateau under a changing environment: characteristics and potential influencing factors. Agric Water Manag 244:106540. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2020.106540
Hao Z, Aghakouchak A, Nakhjiri N, Farahmand A (2014) Global integrated drought monitoring and prediction system. Scientific Data 1:140001. https://doi.org/10.1038/sdata.2014.1
Hisdal H, Tallaksen LM, Clausen B, Peters E, Gustard A (2004) Hydrological drought characteristics. Dev Water Sci 48:139–198
Hong M, Lee SH, Lee SJ, Choiet JY (2021) Application of high-resolution meteorological data from NCAM-WRF to characterize agricultural drought in small-scale farmlands based on soil moisture deficit. Agric Water Manag 243:106494. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2020.106494
Hu Y, Zhou B, Han T, Li H, Wang H (2021) Out-of-phase decadal change in drought over northeast china between early spring and late summer around 2000 and its linkage to the Atlantic Sea surface temperature. J Geophys Res Atmos 126(9):e2020JD034048. https://doi.org/10.1029/2020JD034048
Huang S, Wang L, Wang H, Huang Q, Leng G, Fang W, Zhang Y (2019) Spatio-temporal characteristics of drought structure across China using an integrated drought index. Agric Water Manag 218:182–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2019.03.053
Huang S, Wang L, Wang H, Huang Q, Leng G, Fang W, Zhang Y (2019) Spatio-temporal characteristics of drought structure across China using an integrated drought index. Agric Water Manag 218:182–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2019.03.053
Huo S, Wang H, Peng M (1998) Analysis on no-flow in the lower Yellow River in 1997. Yellow River 20(1):1–3 (In Chinese)
Kim W, Iizumi T, Nishimori M (2019) Global patterns of crop production losses associated with droughts from 1983 to 2009. J Appl Meteorol Climatol 58(6):1233–1244. https://doi.org/10.1175/JAMC-D-18-0174.1
Kumari M, Sarma K, Sharma R (2019) Using Moran’s I and GIS to study the spatial pattern of land surface temperature in relation to land use/cover around a thermal power plant in Singrauli district, Madhya Pradesh, India. Remote Sens Appl Soc Environ 15:100239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsase.2019.100239
Lhotka O, Trnka M, Kyselý J, Markonis J, Baiek J, Možný M (2020) Atmospheric circulation as a factor contributing to increasing drought severity in central Europe. J Geophys Res Atmos 125(18):e2019JD032269. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019JD032269
Li J, Wang J, Zhang J, Zhang J, Kong H (2021) Dynamic changes of vegetation coverage in China-Myanmar economic corridor over the past 20 years. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf 102:102378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2021.102378
Liu Y, Zhu Y, Ren L, Singh V, Yong B, Jiang S, Fei Y, Yang X (2019) Understanding the spatiotemporal links between meteorological and hydrological droughts from a three-dimensional perspective. J Geophys Res Atmos 124(6):3090–3109. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018JD028947
Mathbout S, Lopez-Bustins J, Martin-Vide J, Bech J, Rodrigo F (2017) Spatial and temporal analysis of drought variability at several time scales in Syria during 1961–2012. Atmos Res 200:153–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2017.09.016
McKee TB, Doesken NJ, Kleist J (1993) The relationship of drought frequency and duration to time scales. Proceedings of the 8th Conference on Applied Climatology 17(22):179–183
Mishra AK, Singh VP (2010) A review of drought concepts. J Hydrol 391(1–2):202–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2010.07.012
Omer A, Ma Z, Zheng Z, Saleem F (2020) Natural and anthropogenic influences on the recent droughts in Yellow River Basin. China Science of the Total Environment 704:135428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135428
Pachauri RK, Reisinger A (2007) IPCC fourth assessment report. IPCC, Geneva
Palmer WC (1965) Meteorological drought. US Department of Commerce, Weather Bureau 1965
Palmer WC, Wayne C (1968) Keeping track of crop moisture conditions, nationwide: the new crop moisture index. Weatherwise 21(4):156–161. https://doi.org/10.1080/00431672.1968.9932814
Peng SM, Zheng XK, Wang Y, Li K (2019) Synergetic optimal operation of cascade reservoirs in mainstream of Yellow River responding to drought. Energy Procedia 158:6288–6295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2019.01.445
Prudhomme C, Giuntoli I, Robinson E, Clark D, Arnell N, Dankers R et al (2014) Hydrological droughts in the 21st century, hotspots and uncertainties from a global multimodel ensemble experiment. Proc Natl Acad Sci 111(9):3262–3267. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1222473110
Rajsekhar D, Singh VP, Mishra AK (2015) Integrated drought causality, hazard, and vulnerability assessment for future socioeconomic scenarios: an information theory perspective. J Geophys Res Atmos 120(13):6346–6378. https://doi.org/10.1002/2014JD022670
Rashid MM, Johnson F, Sharma A (2018) Identifying sustained drought anomalies in hydrological records: a wavelet approach. J Geophys Res Atmos 123(14):7416–7432. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018JD028455
Son B, Park S, Im J, Park S, Ke Y, Quackenbush L (2021) A new drought monitoring approach: vector projection analysis (VPA). Remote Sens Environ 252:112145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2020.112145
Sun H, Zhao X, Chen Y, Gong A, Yang J (2013) A new agricultural drought monitoring index combining MODIS NDWI and day-night land surface temperatures: a case study in China. Int J Remote Sens 34(24):8986–9001. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431161.2013.860659
Tirivarombo S, Osupile D, Eliasson P (2018) Drought monitoring and analysis: standardised precipitation evapotranspiration index (SPEI) and standardised precipitation index (SPI). Phys Chem Earth 106:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pce.2018.07.001
Vicente-Serrano SM, Beguería S, López-Moreno JI (2010) A multiscalar drought index sensitive to global warming: the standardized precipitation evapotranspiration index. J Clim 23(7):1696–1718. https://doi.org/10.1175/2009JCLI2909.1
Wang H, Chen Y, Pan Y, Li W (2015) Spatial and temporal variability of drought in the arid region of China and its relationships to teleconnection indices. J Hydrol 523:283–296. https://doi.org/10.1175/2009JCLI2909.1
World Meteorological Organization (WMO) (2007) United nations environment programme (UNEP): scientific assessment of ozone depletion: 2006, WMO, Geneva, Switzerland
World Meteorological Organization (WMO) (2019) Extreme-scale computing and data handling - the heart of progress in weather and climate prediction: 2018, WMO, Geneva, Switzerland
World Meteorological Organization (WMO) (2020) The Atlas of mortality and economic losses from weather, climate and water extremes (1970–2019), WMO, Geneva, Switzerland
Wu J, Miao C, Zheng H, Duan Q, Lei X, Li H (2018) Meteorological and hydrological drought on the Loess Plateau, China: evolutionary characteristics, impact, and propagation. J Geophys Res Atmos 123(20):11569–11584. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018JD029145
Wang Y, Wang S, Zhao W., Liu Y (2021) The increasing contribution of potential evapotranspiration to severe droughts in the Yellow River basin. J Hydrol 127310.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2021.127310
Xu C, Guan Q, Lin J, Luo H, Yang L, Tan Z (2020) Spatiotemporal variations and driving factors of dust storm events in northern China based on high-temporal-resolution analysis of meteorological data (1960–2007). Environ Pollut 260:114084. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114084
Xu K, Yang D, Yang H, Li Z (2015) Spatio-temporal variation of drought in China during 1961–2012: a climatic perspective. J Hydrol 526:253–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114084
Xu Y, Zhang X, Hao Z, Hao F, Li C (2021a) Projections of future meteorological droughts in China under CMIP6 from a three imensional perspective. Agric Water Manag 252:106849. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2021.106849
Xu Z, Zhang S, Yang X (2021b) Water and sediment yield response to extreme rainfall events in a complex large river Basin: a case study of the Yellow River Basin. China J Hydrol 597(2):126183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2021.126183
Yang Y, Sun L, Guo C (2018) Aero-Material consumption prediction based on linear regression model. Procedia Comput Sci 131:825–831. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2018.04.271
Yerdelen C, Abdelkader M, Eris E (2021) Assessment of drought in SPI series using continuous wavelet analysis for GEDIZ Basin Turkey. Atmos Res 260:105687. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2021.105687
Yu M, Li Q, Hayes MJ, Svoboda MD, Heim RR (2014) Are droughts becoming more frequent or severe in China based on the standardized precipitation evapotranspiration index: 1951–2010? Int J Climatol 34(3):545–558. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.3701
Yuan Y, Cave M, Zhang C (2018) Using local Moran’s I to identify contamination hotspots of rare earth elements in urban soils of London. Appl Geochem 88:167–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2017.07.011
Zeng P, Sun F, Liu Y, Wang Y, Li G, Che Y (2021) Mapping future droughts under Global warming across China: a combined multi-timescale meteorological drought index and SOM-Kmeans approach. Weather Clim Extremes 31:100304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wace.2021.100304
Zhai J, Huang J, Su B, Cao L, Wang Y, Jiang T, Fischer T (2017) Intensity-area-duration analysis of droughts in China 1960–2013. Clim Dyn 48(1–2):151–168. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-016-3066-y
Zhang Q, Yu H, Sun P, Singh VP, Shi P (2019) Multisource data based agricultural drought monitoring and agricultural loss in China. Global Planet Change 172:298–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloplacha.2018.10.017
Zhao H, Gao G, An W, Zou X, Hou M (2017) Timescale differences between SC-PDSI and SPEI for drought monitoring in China. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Parts a/b/c 102:48–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pce.2015.10.022
Zhao J, Li C, Yang T, Tang Y, Yin Y, Luan X, Sun S (2020) Estimation of high spatiotemporal resolution actual evapotranspiration by combining the SWH model with the METRIC model. J Hydrol 586:124883. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.124883
Zhao Y, Zhu J, Xu Y (2014) Establishment and assessment of the grid precipitation datasets in China for recent 50 years. J Meteorol Sci 143:845–863 (In Chinese)
Zhou K, Wang Y, Chang J, Zhou S, Guo A (2021) Spatial and temporal evolution of drought characteristics across the Yellow River basin. Ecol Ind 131:108207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.108207
Zhu Y, Liu Y, Wang W, Singh V, Ma X, Yu Z (2019) Three dimensional characterization of meteorological and hydrological droughts and their probabilistic links. J Hydrol 578:124016. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.1240
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the use of data from the National Meteorological Information Centre of the Chinese Meteorological Administration (http://cdc.nmic.cn) and Geospatial Data Cloud (http://www.gscloud.cn).
Funding
This research was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 52079060) and Liaoning Revitalization Talents Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ying Li: conceptualization; formal analysis; supervision; roles/writing—original draft; writing—review and editing. Chenchen Jia: data curation; methodology; visualization; roles/writing—original draft; writing—review and editing. Shuang Ma: methodology; resources; visualization; writing—review and editing. Zhentai Hu: data curation; software; visualization; writing—review and editing. Jin Sun: resources; software; validation; writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• Spatiotemporal distribution characteristics of droughts in the middle reaches of the Yellow River basin (1961–2019) were effectively analyzed using grid data.
• The frequency and intensity of drought in the middle reaches of the Yellow River basin were higher in the south and lower in the north.
• The spatial patterns of drought frequency and intensity mainly showed clusters and a random distribution.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Jia, C., Ma, S. et al. Refined spatiotemporal analysis of drought characteristics under different characteristic variable matchings: a case study of the middle reaches of the Yellow River basin, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 60440–60458 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20146-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20146-9