Abstract
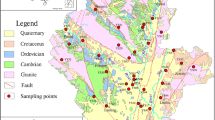
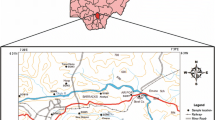
Water resource is in high demand within the Yangtze River Delta, given its developed economy. Long-term exploitation of this resource has posed risks of artificial pollution and seawater intrusion to the shallow groundwater. This study aims to reveal the hydrochemical characteristics and health risks of shallow groundwater in the coastal plain of the Yangtze River Delta, as well as to discuss the possible factors affecting groundwater quality. Standard methods for hydrochemical parameter measurements, water quality assessment, and health risk models were applied to fulfill the objectives of the study. The results showed that the shallow groundwater was slightly alkaline, and the average values of total dissolved solids (TDS) and total hardness (TH) were 930.74 mg/L and 436.20 mg/L, respectively. The main hydrochemical types of groundwater were HCO3–Ca·Mg and HCO3–Ca·Na, accounting for 44.3% and 47.5%, respectively. In addition, As concentration was generally high, with a mean value of 0.0115 mg/L. The principal factors affecting the groundwater components include water-rock interactions (especially silicate), cation exchange, seawater intrusion, and human activities. The data also showed that As is strongly influenced by the redox of Fe, Mn, and NO3−. The results of the groundwater quality evaluation indicated that the shallow groundwater in some regions was unsuitable for drinking and agricultural irrigation. Health risk assessment showed that 44.3% of the water samples had significant health risks, which was attributed to the high As concentration. Therefore, it is urgent to establish long-term As monitoring to maintain sustainable groundwater management and drinking water safety. The results of this study provide essential data for water resource management and human health security in the Yangtze River Delta.








Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
Supplementary Material data to this article can be found in the online version of this article.
References
Appelo CAJ, Postma D (2005) Geochemistry, groundwater and pollution, second ed. A.A. Balkema Publishers, Leiden.
Argamasilla M, Barberá J, Andreo B (2017) Factors controlling groundwater salinization and hydrogeochemical processes in coastal aquifers from southern Spain. Sci Total Environ 580:50–68
Cao T, Han D, Song X, Trolle D (2020) Subsurface hydrological processes and groundwater residence time in a coastal alluvium aquifer: evidence from environmental tracers (δ18O, δ2H, CFCs, 3H) combined with hydrochemistry. Sci Total Environ 743:140684
Chen L, Ma T, Wang Y, Zheng J (2020) Health risks associated with multiple metal (loid) s in groundwater: a case study at Hetao Plain, northern China. Environ Pollut 263:114562
Du Y, Deng Y, Ma T, Lu Z, Shen S, Gan Y, Wang Y (2018) Hydrogeochemical evidences for targeting sources of safe groundwater supply in arsenic-affected multi-level aquifer systems. Sci Total Environ 645:1159–1171
Duan Y, Gan Y, Wang Y, Liu C, Yu K, Deng Y, Zhao K, Dong C (2017) Arsenic speciation in aquifer sediment under varying groundwater regime and redox conditions at Jianghan Plain of Central China. Sci Total Environ 607:992–1000
Gao Y, Qian H, Ren W, Wang H, Liu F, Yang F (2020) Hydrogeochemical characterization and quality assessment of groundwater based on integrated-weight water quality index in a concentrated urban area. J Clean Prod 260:121006
Gibbs RJ (1970) Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry. Science 170:1088–1090
Han D, Post VE, Song X (2015) Groundwater salinization processes and reversibility of seawater intrusion in coastal carbonate aquifers. J Hydrol 531:1067–1080
Hao C, Zhang W, Gui H (2020) Hydrogeochemistry characteristic contrasts between low-and high-antimony in shallow drinkable groundwater at the largest antimony mine in Hunan province. China. Appl Geochem 117:104584
Hou Q, Zhang Q, Huang G, Liu C, Zhang Y (2020) Elevated manganese concentrations in shallow groundwater of various aquifers in a rapidly urbanized delta, south China. Sci Total Environ 701:134777
Islam ARMT, Al Mamun A, Rahman MM, Zahid A (2020) Simultaneous comparison of modified-integrated water quality and entropy weighted indices: implication for safe drinking water in the coastal region of Bangladesh. Ecol Indic 113:106229
Li Q, Zhang Y, Chen W, Yu S (2018) The integrated impacts of natural processes and human activities on groundwater salinization in the coastal aquifers of Beihai, southern China. Hydrogeol J 26:1513–1526
Li X, Tang C, Cao Y, Li D (2020) A multiple isotope (H, O, N, C and S) approach to elucidate the hydrochemical evolution of shallow groundwater in a rapidly urbanized area of the Pearl River Delta. China. Sci Total Environ 724:137930
Lima IQ, Ramos OR, Munoz MO, Aguirre JQ, Duwig C, Maity JP, Sracek O, Bhattacharya P (2020) Spatial dependency of arsenic, antimony, boron and other trace elements in the shallow groundwater systems of the Lower Katari Basin. Bolivian Altiplano. Sci Total Environ 719:137505
Liu J, Peng Y, Li C, Gao Z, Chen S (2021a) Characterization of the hydrochemistry of water resources of the Weibei Plain, Northern China, as well as an assessment of the risk of high groundwater nitrate levels to human health. Environ Pollut 268
Liu J, Peng Y, Li C, Gao Z, Chen S (2021b) An investigation into the hydrochemistry, quality and risk to human health of groundwater in the central region of Shandong Province. North China. J Clean Prod 282:125416
Liu X, Wang X, Zhang L, Fan W, Yang C, Li E, Wang Z (2021c) Impact of land use on shallow groundwater quality characteristics associated with human health risks in a typical agricultural area in Central China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 28:1712–1724
Long J, Luo K (2020) Elements in surface and well water from the central North China Plain: enrichment patterns, origins, and health risk assessment. Environ. Pollut. 258:113725
Long X, Liu F, Zhou X, Pi J, Yin W, Li F, Huang S, Ma F (2021) Estimation of spatial distribution and health risk by arsenic and heavy metals in shallow groundwater around Dongting Lake plain using GIS mapping. Chemosphere 269:128698
Ma Q, Luo Z, Howard KW, Wang Q (2018) Evaluation of optimal aquifer yield in Nantong City, China, under land subsidence constraints. Q J Eng Geol Hydrogeol 51:124–137
Mao C, Tan H, Song Y, Rao W (2020) Evolution of groundwater chemistry in coastal aquifers of the Jiangsu, east China: insights from a multi-isotope (δ2H, δ18O, 87Sr/86Sr, and δ11B) approach. J Contam Hydrol 235:103730
Mao R, Guo H, Xiu W, Yang Y, Huang X, Zhou Y, Li X, Jin J (2018) Characteristics and compound-specific carbon isotope compositions of sedimentary lipids in high arsenic aquifers in the Hetao basin, Inner Mongolia. Environ Pollut 241:85–95
Mountadar S, Younsi A, Hayani A, Siniti M, Tahiri S (2018) Groundwater salinization process in the coastal aquifer sidi abed-ouled ghanem (province of el Jadida, Morocco). J African Earth Sci 147:169–177
Najib S, Fadili A, Mehdi K, Riss J, Makan A, Guessir H (2016) Salinization process and coastal groundwater quality in Chaouia, Morocco. J African Earth Sci 115:17–31
Narayanamoorthy S, Annapoorani V, Kang D, Baleanu D, Jeon J, Kureethara JV, Ramya L (2020) A novel assessment of bio-medical waste disposal methods using integrating weighting approach and hesitant fuzzy MOOSRA. J Clean Prod 275:122587
Peng H, Yao F, Xiong S, Wu Z, Niu G, Lu T (2021a) Strontium in public drinking water and associated public health risks in Chinese cities. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:23048–23059
Peng H, Zou P, Ma C, Xiong S, Lu T (2021b) Elements in potable groundwater in Rugao longevity area, China: hydrogeochemical characteristics, enrichment patterns and health assessments. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 218:112279
Peng H, Yang W, Ferrer ASN, Xiong S, Li X, Niu G, Lu T (2022) Hydrochemical characteristics and health risk assessment of groundwater in karst areas of southwest China: a case study of Bama. Guangxi. J Clean Prod 341:130872
Podgorski J, Berg M (2020) Global threat of arsenic in groundwater. Science 368:845–850
Saha N, Rahman MS (2020) Groundwater hydrogeochemistry and probabilistic health risk assessment through exposure to arsenic-contaminated groundwater of Meghna floodplain, central-east Bangladesh. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 206:111349
Samsudin AR, Haryono A, Hamzah U, Rafek A (2008) Salinity mapping of coastal groundwater aquifers using hydrogeochemical and geophysical methods: a case study from north Kelantan, Malaysia. Environ Geol 55:1737–1743
Selinus O, Alloway B, Centeno JA, Finkelman RB, Fuge R, Lindh U, Smedley P (2016) Essentials of medical geology. Springer, Dordrecht
Wang L, Yin Z, Jing C (2020) Metagenomic insights into microbial arsenic metabolism in shallow groundwater of Datong basin. China. Chemosphere 245:125603
Wu C, Fang C, Wu X, Zhu G (2020) Health-risk assessment of arsenic and groundwater quality classification using random forest in the Yanchi Region of Northwest China. Expos Health 12:761–774
Wu C, Luo Y, Gui T, Yan S (2014) Characteristics and potential health hazards of organochlorine pesticides in shallow groundwater of two cities in the Yangtze River Delta. Clean–Soil Air Water 42:923–931
Wu J, Sun Z (2016) Evaluation of shallow groundwater contamination and associated human health risk in an alluvial plain impacted by agricultural and industrial activities, mid-west China. Expos Health 8:311–329
Xiao J, Wang L, Deng L, Jin Z (2019) Characteristics, sources, water quality and health risk assessment of trace elements in river water and well water in the Chinese Loess Plateau. Sci Total Environ 650:2004–2012
Xie Z, Wang J, Wei X, Li F, Chen M, Wang J, Gao B (2018) Interactions between arsenic adsorption/desorption and indigenous bacterial activity in shallow high arsenic aquifer sediments from the Jianghan Plain, Central China. Sci Total Environ 644:382–388
Zhang Q, Qian H, Xu P, Hou K, Yang F (2021a) Groundwater quality assessment using a new integrated-weight water quality index (IWQI) and driver analysis in the Jiaokou Irrigation District. China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 212:111992
Zhang Q, Xu P, Qian H (2020) Groundwater quality assessment using improved water quality index (WQI) and human health risk (HHR) evaluation in a semi-arid region of northwest China. Expos Health 12:487–500
Zhang Y, Dai Y, Wang Y, Huang X, Xiao Y, Pei Q (2021b) Hydrochemistry, quality and potential health risk appraisal of nitrate enriched groundwater in the Nanchong area, southwestern China. Sci Total Environ 784:147186
Zhao Q, Su X, Kang B, Zhang Y, Wu X, Liu M (2017) A hydrogeochemistry and multi-isotope (Sr, O, H, and C) study of groundwater salinity origin and hydrogeochemcial processes in the shallow confined aquifer of northern Yangtze River downstream coastal plain, China. Appl Geochem 86:49–58
Zheng T, Deng Y, Wang Y, Jiang H, Xie X, Gan Y (2020) Microbial sulfate reduction facilitates seasonal variation of arsenic concentration in groundwater of Jianghan Plain. Central China. Sci Total Environ 735:139327
Zhi C, Cao W, Zhang Z, Li Z, Ren Y (2021) Hydrogeochemical characteristics and processes of shallow groundwater in the Yellow River Delta. China. Water 13:534
Funding
This project was supported by New Era Health Industry (Group) Co. Ltd. (ZAT2019X01002) and the China Scholarship Council (201708420145).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TL: Conceptualization, methodology, investigation, writing-original draft preparation. RL: Methodology and investigation. ASNF: Resources. SX: Software and investigation. PZ: Supervision and funding acquisition. HP: Formal analysis, writing-original draft preparation, and writing-reviewing and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Xianliang Yi
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 1317 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, T., Li, R., Ferrer, A.S.N. et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and quality assessment of shallow groundwater in Yangtze River Delta of eastern China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 57215–57231 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19881-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19881-w