Abstract
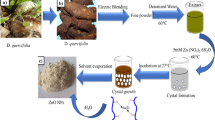
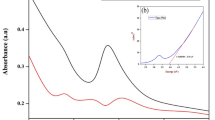
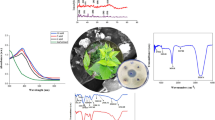
Rubia cordifolia represents the pivotal plant resource belonging to traditional Chinese medicine and Indian Ayurveda. The present study aims to synthesize biocompatible copper oxide nanoparticles (CuONPs) using R. cordifolia bark extracts, characterize the incumbent chemical transitions, and explore their biomedical and environmental applications. The absorbance peak between 250 and 300 nm clearly demonstrates the formation of CuONPs in the UV–visible spectrum. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy results showed the presence of functional groups essential for copper ion reduction. Field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM) and dynamic light scattering analysis revealed that the CuONPs are spherical-shaped with a mean particle size of 50.72 nm. Additionally, the zeta potential demonstrates its robustness at 11.2 mV. X-ray diffraction pattern showed mixed phases (Cu, Cu2O, and CuO) of cubic monoclinic crystalline nature. CuONPs exhibited noticeable antibacterial activity against Gram-negative (Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa) and Gram-positive (Staphylococcus aureus and Bacillus cereus) pathogenic bacteria. Bacterial cell damages were affirmed through FE-SEM imaging when treated with CuONPs. Further, CuONPs demonstrated considerable antioxidant activities by quenching free radicals such as DPPH (60.75%), ABTs (70.88%), nitric oxide (65.48%) and reducing power (71.44%) in a dose-dependent way. CuONPs showed significant larvicidal activity against Aedes aegypti (65 ± 8.66%), Anopheles stephensi (80 ± 13.69%), and Culex quinquefasciatus (72 ± 13.04%) mosquito larvae. The photocatalytic activity of the CuONPs demonstrates the methylene blue (81.84%) and crystal violet (64.0%) dye degradation potentials, indicating the environmental bioremediation efficacy. Hence the present study is the first report in accounting for the versatile applications of the phyto-CuONPs. Moreover, the green synthesis of CuONPS has future applications in designing the drug for life-threatening diseases and various environmental issues.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated and analyzed during this study are included in this article.
References
Abbott WS (1925) A method of computing the effectiveness of an insecticide. J Econ Entomol 18:265–267
Al-Saeedi SI, Al-Senani GM, Abd-Elkader OH, Deraz NM (2021) One pot synthesis, surface and magnetic properties of Cu2O/Cu and Cu2O/CuO nanocomposites. Curr Comput-Aided Drug Des 11:751
Amer M, Awwad A (2021) Green synthesis of copper nanoparticles by Citrus limon fruits extract, characterization and antibacterial activity. Chem Int 7:1–8
Angajala G, Pavan P, Subashini R (2018) One-step cost effective biofabrication of copper nanoparticles from Aegle marmelos correa aqueous leaf extract and evaluation of its anti-inflammatory and mosquito larvicidal efficacy. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 16:586–593
Burlacu E, Tanase C (2021) Anticancer Potential of natural bark products—a review. Plants 10:1895
Chen X-Q, Li Z-H, Liu L-L, Wang H, Yang S-H, Zhang J-S, Zhang Y (2021) Green extraction using deep eutectic solvents and antioxidant activities of flavonoids from two fruits of Rubia species. LWT - Food Sci Technol 148:111708
Chung IM, Abdul Rahuman A, Marimuthu S, Vishnu Kirthi A, Anbarasan K, Padmini P, Rajakumar G (2017) Green synthesis of copper nanoparticles using Eclipta prostrata leaves extract and their antioxidant and cytotoxic activities. Exp Ther Med 14:18–24
Deshkar N, Tilloo S, Pande V (2008) A comprehensive review of Rubia cordifolia Linn. Pharmacogn Rev 2:124
Finney D (1971) Probit analysis method, 2nd edn. Press, Camp. Uni
Gleba M, VandenBerghe I, Aldenderfer M (2016) Textile technology in Nepal in the 5th-7th centuries CE: the case of Samdzong. STAR: Science Technology of Archaeological Research 2:25–35
Gong X-P, Sun Y-Y, Chen W, Guo X, Guan J-K, Li D-Y, Du G (2017) Anti-diarrheal and anti-inflammatory activities of aqueous extract of the aerial part of Rubia cordifolia. BMC Complement Altern Med 17:1–9
Gopinath V, Priyadarshini S, Al-Maleki A, Alagiri M, Yahya R, Saravanan S, Vadivelu J (2016) In vitro toxicity, apoptosis and antimicrobial effects of phyto-mediated copper oxide nanoparticles. RSC Adv 6:110986–110995
Hu Y-y, Zhang X-j, Zhang Z-h, Wang Z, Tan N-h (2020) Qualitative and quantitative analyses of quinones in multi-origin Rubia species by ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry combined with chemometrics. J Pharm Biomed Anal 189:113471
Lee HJ, Song JY, Kim BS (2013) Biological synthesis of copper nanoparticles using Magnolia kobus leaf extract and their antibacterial activity. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 88:1971–1977
Mali SC, Dhaka A, Githala CK, Trivedi R (2020) Green synthesis of copper nanoparticles using Celastrus paniculatus Willd. leaf extract and their photocatalytic and antifungal properties. Biotechnol. Rep. 27:e00518
Mani VM, Kalaivani S, Sabarathinam S, Vasuki M, Soundari AJPG, Das MA, Elfasakhany A, Pugazhendhi A (2021) Copper oxide nanoparticles synthesized from an endophytic fungus Aspergillus terreus: Bioactivity and anti-cancer evaluations. Environ Res 201:111502
Mariswamy SD, Thimmaiah CK, Basappachidananda VK, Basavaraju M, Arkeswaraiah CN (2021) Antimicrobial, haemolytic and antibiofilm assay of green synthesized silver nanoparticles by aqueous extracts of Rubia cordifolia. Int J Pharm Sci Rev Res 28:174–184
Meena V (2015) Manjistha (Rubia cordifolia)-a helping herb in cure of acne. Journal of Ayurveda Holistic Medicine 3:11–17
Murthy H, Desalegn T, Kassa M, Abebe B, Assefa T (2020) Synthesis of green copper nanoparticles using medicinal plant Hagenia abyssinica (Brace) JF. Gmel. leaf extract: Antimicrobial properties. J Nanomater 2020:1–12
Nasrollahzadeh M, Sajadi SM, Khalaj M (2014) Green synthesis of copper nanoparticles using aqueous extract of the leaves of Euphorbia esula L and their catalytic activity for ligand-free Ullmann-coupling reaction and reduction of 4-nitrophenol. RSC Adv 4:47313–47318
Negi DS (2018) Antioxidant and Photocatalytic activity of green synthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles using stem extract of Rubia cordifolia. International Journal of Engineering, Science and Mathematics 7:402–412
Rajeshkumar S, Menon S, Kumar SV, Tambuwala MM, Bakshi HA, Mehta M, Satija S, Gupta G, Chellappan DK, Thangavelu L (2019) Antibacterial and antioxidant potential of biosynthesized copper nanoparticles mediated through Cissus arnotiana plant extract. J Photochem Photobiol B: Biol 197:111531
Sankar R, Maheswari R, Karthik S, Shivashangari KS, Ravikumar V (2014) Anticancer activity of Ficus religiosa engineered copper oxide nanoparticles. Mater Sci Eng C 44:234–239
Sarwar N, Humayoun UB, Kumar M, Zaidi SFA, Yoo JH, Ali N, Jeong DI, Lee JH, Yoon DH (2021) Citric acid mediated green synthesis of copper nanoparticles using cinnamon bark extract and its multifaceted applications. J Clean Prod 292:125974
Sathiyavimal S, Vasantharaj S, Bharathi D, Saravanan M, Manikandan E, Kumar SS, Pugazhendhi A (2018) Biogenesis of copper oxide nanoparticles (CuONPs) using Sida acuta and their incorporation over cotton fabrics to prevent the pathogenicity of Gram negative and Gram positive bacteria. J Photochem Photobiol B: Biol 188:126–134
Sathiyavimal S, Vasantharaj S, Veeramani V, Saravanan M, Rajalakshmi G, Kaliannan T, Al-Misned FA, Pugazhendhi A (2021) Green chemistry route of biosynthesized copper oxide nanoparticles using Psidium guajava leaf extract and their antibacterial activity and effective removal of industrial dyes. J Environ Chem Eng 9:105033
Sebeia N, Jabli M, Ghith A, Saleh TA (2020) Eco-friendly synthesis of Cynomorium coccineum extract for controlled production of copper nanoparticles for sorption of methylene blue dye. Arab J Chem 13:4263–4274
Sekar S, Mariappan S (2010) Fermented medicines of Ayurveda: a treatise. LAP LAMBERT Academic Publishing, Germany
Shende S, Ingle AP, Gade A, Rai M (2015) Green synthesis of copper nanoparticles by Citrus medica Linn. (Idilimbu) juice and its antimicrobial activity. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 31:865–873
Singh J, Kumar V, Kim K-H, Rawat M (2019) Biogenic synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles using plant extract and its prodigious potential for photocatalytic degradation of dyes. Environ Res 177:108569
Vasantharaj S, Sathiyavimal S, Saravanan M, Senthilkumar P, Gnanasekaran K, Shanmugavel M, Manikandan E, Pugazhendhi A (2019) Synthesis of ecofriendly copper oxide nanoparticles for fabrication over textile fabrics: characterization of antibacterial activity and dye degradation potential. J Photochem Photobiol B: Biol 191:143–149
Velsankar K, RM AK, Preethi R, Muthulakshmi V, Sudhahar S (2020) Green synthesis of CuO nanoparticles via Allium sativum extract and its characterizations on antimicrobial, antioxidant, antilarvicidal activities. J Environ Chem Eng 8:104123
Vinotha V, Yazhiniprabha M, Raj DS, Mahboob S, Al-Ghanim KA, Al-Misned F, Govindarajan M, Vaseeharan B (2020) Biogenic synthesis of aromatic cardamom-wrapped zinc oxide nanoparticles and their potential antibacterial and mosquito larvicidal activity: An effective eco-friendly approach. J Environ Chem Eng 8:104466
Vinothkanna A, Sekar S (2018) Antioxidant activity of fermented traditional medicines of Indian Ayurveda-Ashokarishta, Aswagandharishta and Dasamoolarishta. Biosci Biotechnol Res Asia 15:699–709
Vivekanandhan P, Swathy K, Thomas A, Kweka EJ, Rahman A, Pittarate S, Krutmuang P (2021) Insecticidal efficacy of microbial-mediated synthesized copper nano-pesticide against insect pests and non-target organisms. Int J Environ Res Public Health 18:10536
Warnes S, Keevil C (2011) Mechanism of copper surface toxicity in vancomycin-resistant enterococci following wet or dry surface contact. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:6049–6059
Yugandhar P, Vasavi T, Devi PUM, Savithramma N (2017) Bioinspired green synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles from Syzygium alternifolium (Wt.) Walp: characterization and evaluation of its synergistic antimicrobial and anticancer activity. Appl Nanosci 7:417–427
Yusuf M, Shahid M, Khan MI, Khan SA, Khan MA, Mohammad F (2015) Dyeing studies with henna and madder: a research on effect of tin (II) chloride mordant. J Saudi Chem Soc 19:64–72
Yusuf M, Mohammad F, Shabbir M (2017) Eco-friendly and effective dyeing of wool with anthraquinone colorants extracted from Rubia cordifolia roots: optimization, colorimetric and fastness assay. J King Saud Univ Sci 29:137–144
Zhao H, Su H, Ahmeda A, Sun Y, Li Z, Zangeneh MM, Nowrozi M, Zangeneh A, Moradi R (2020) Biosynthesis of copper nanoparticles using Allium eriophyllum Boiss leaf aqueous extract; characterization and analysis of their antimicrobial and cutaneous wound‐healing potentials. Appl Organomet Chem 34:e5587
Acknowledgements
The first author (A.V) is thankful for the Award of UGC-RGN Fellowship, Govt. of India and Postdoctoral Researcher at Jiangsu University, PR, China. The authors (A.V and Y.M) acknowledge the“Foreign Scientist Talented Project”awarded by the Ministry of Science and Technology, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A. Vinothkanna: Conceptualization, Methodology, Formal analysis, Validation, Visualization, Writing-original draft. K. Mathivanan: Formal analysis and validation. S. Ananth: Formal analysis and validation Y. Ma: Project administration, Validation, Visualization, Writing-review and editing. S. Sekar: Conceptualization, Supervision, Project administration, Funding acquisition, Writing-review and editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Sami Rtimi
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vinothkanna, A., Mathivanan, K., Ananth, S. et al. Biosynthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles using Rubia cordifolia bark extract: characterization, antibacterial, antioxidant, larvicidal and photocatalytic activities. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 42563–42574 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-18996-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-18996-4