Abstract
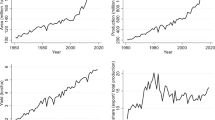
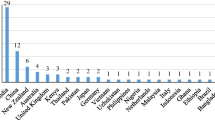
Rice is an important cereal and a staple food in many countries in the world. Climate change is a significant challenge that affects paddy production and threatens food security. However, research and development in this area continue to work to ensure the supply of rice fulfils the demands of the population. The study aims to analyse the transformation of international research power in trends in climate change that threaten food security (rice) worldwide. This study evaluates existing publications, especially research works from the period 1970 to 2020. The Web of Science database and the VOSviewer software were used together to generate a systematic analysis. A total of 1181 publications on climate change and paddy production were identified, written by 2249 authors from 56 countries. The highest number of publications was from China with 240 publications with 4609 citations, followed by India, with 225 publications and 2070 citations. Yield and adaptation are the most frequently used keywords that reflect this field's current significant research direction. Besides that, developing countries have received greater attention from researchers to focus on science, agriculture, climatology, and agriculture engineering as their domains. Therefore, socio-economic aspects should also be highlighted to raise awareness of the dangers of climate change and improve the farmers' economy by increasing paddy production. Attention was given by all countries globally, especially by researchers and stakeholders who need to plan holistic policies and strategies to encourage sustainable rice production and at the same time reduce the impact of climate change worldwide.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable.
References
Alam MM, Siwar C, Talib B, Toriman MEB (2014) Impacts of Climatic Changes on Paddy Production in Malaysia: Micro Study on IADA at North West Selangor. Res J Environ Earth Sci 6(5):251–258. https://doi.org/10.19026/rjees.6.5767
Alam M, Utara U, Drift M. M, Countries A, Institutions S. M, Chini T, Reserve B. (2015). The Impacts of Agricultural Supports for Climate Change Adaptation : Farm Level Assessment Study on Paddy Farmers. https://doi.org/10.3844/ajessp.2011.178.182
Arunrat N, Pumijumnong N, Sereenonchai S, Chareonwong U, Wang C. (2020). Assessment of climate change impact on rice yield and water footprint of large-scale and individual farming in Thailand. Science of the Total Environment. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137864
Arunrat N, Sereenonchai S, Chaowiwat W, Wang C. (2022). Climate change impact on major crop yield and water footprint under CMIP6 climate projections in repeated drought and flood areas in Thailand. Science of the Total Environment, 807. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.150741
Arunrat N, Sereenonchai S, Wang C. (2021). Carbon footprint and predicting the impact of climate change on carbon sequestration ecosystem services of organic rice farming and conventional rice farming: A case study in Phichit province, Thailand. Journal of Environmental Management 289:112458. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112458
Baharudin R. A, Hashim N, Malek J. A. (2020). Bibliometric Analysis of Knowledge and Awareness about Climate Change from in a decade, pp 1577–1589
Chauhan B. S, Jabran K, Mahajan G. (2017). Rice Production Worldwide. Rice Production Worldwide. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-47516-5
Chen H, Jiang W, Yang Y, Yang Y, Man X (2015) Global trends of municipal solid waste research from 1997 to 2014 using bibliometric analysis. J Air Waste Manag Assoc 65(10):1161–1170. https://doi.org/10.1080/10962247.2015.1083913
De Silva CS, Weatherhead EK, Knox JW, Rodriguez-Diaz JA (2007) Predicting the impacts of climate change-A case study of paddy irrigation water requirements in Sri Lanka. Agric Water Manag 93(1–2):19–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2007.06.003
Gavel Y, Iselid L (2008) Web of Science and Scopus: A journal title overlap study. Online Inf Rev 32(1):8–21. https://doi.org/10.1108/14684520810865958
Haunschild R, Bornmann L, Marx W (2016) Climate change research in view of bibliometrics. PLoS ONE 11(7):1–19. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0160393
IPCC (2021) Bulletin of the Chinese Academy of Sciences. Summary for Policymakers. In: Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change 34(2):F0003-F003. https://doi.org/10.3724/sp.j.7103161536
Kang Y, Khan S, Ma X (2009) Climate change impacts on crop yield, crop water productivity and food security - A review. Prog Nat Sci 19(12):1665–1674. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnsc.2009.08.001
Kim HY, Ko J, Kang S, Tenhunen J (2013) Impacts of climate change on paddy rice yield in a temperate climate. Glob Change Biol 19(2):548–562. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.12047
Knox J, Hess T, Daccache A, Wiebe K, Lotze-campen H, Sands R, Beach RH, Cai Y, Thomson A, Müller C, Elliott J, Chryssanthacopoulos J, Knox J, Daccache A, Hess T, Haro D (2016) emissions scenarios Global crop yield response to extreme heat stress under multiple climate change futures Meta-analysis of climate impacts and uncertainty on crop yields in Europe. Environ Res Lett 11(November 2016):1–10
Kontgis C, Schneider A, Ozdogan M (2015) Mapping rice paddy extent and intensification in the Vietnamese Mekong River Delta with dense time stacks of Landsat data. Remote Sens Environ. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2015.08.004
Lal R (2013) Food security in a changing climate. Ecohydrol Hydrobiol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecohyd.2013.03.006
Lawas LMF, Shi W, Yoshimoto M, Hasegawa T, Hincha DK, Zuther E, Jagadish SVK (2018) Combined drought and heat stress impact during flowering and grain filling in contrasting rice cultivars grown under field conditions. Field Crop Res 229(August):66–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2018.09.009
Li S, Wang Q, Chun JA (2017) Impact assessment of climate change on rice productivity in the Indochinese Peninsula using a regional-scale crop model. Int J Climatol 37(December):1147–1160. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.5072
Liao J, Hu Y, Zhang H, Liu L, Liu Z, Tan Z, Wang G (2018) A rice mapping method based on time-series Landsat data for the extraction of growth period characteristics. Sustain (switzerland) 10(7):1–19. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10072570
Matthews RB, Kropff MJ, Horie T, Bachelet D (1997) Simulating the impact of climate change on rice production in asia and evaluating options for adaptation. Agric Syst 54(3):399–425. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0308-521X(95)00060-I
Nguyen TT, Hoang TD, Pham MT, Vu TT, Nguyen TH, Huynh QT, Jo J (2020) Monitoring agriculture areas with satellite images and deep learning. App Soft Comput J 95:106565. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2020.106565
Oh YG, Yoo SH, Lee SH, Choi JY (2011) Prediction of paddy field change based on climate change scenarios using the CLUE model. Paddy Water Environ 9(3):309–323. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10333-010-0244-0
Pinheiro A, Govind M (2020) Emerging global trends in urban agriculture research: A scientometric analysis of peer-reviewed journals. J Scientometr Res 9(2):163–173. https://doi.org/10.5530/JSCIRES.9.2.20
Rajwade YA, Swain DK, Tiwari KN, Mohanty UC, Goswami P (2015) Evaluation of Field Level Adaptation Measures under the Climate Change Scenarios in Rice Based Cropping System in India. Environ Process 2(4):669–687. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40710-015-0115-1
Reay D, Sabine C, Smith P, Hymus G. (2007). Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Fourth Assessment Report. Geneva, Switzerland: Inter-governmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge; UK: Cambridge University Press; 2007. Available from: https://www.ipcc.ch. In Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. https://doi.org/10.1038/446727a
Riadi B, Geospasial BI, Barus B, Widiatmaka W (2018) Spatial modeling of land use / land cover changes for flood hazard analysis on paddy fields and their impact on rice production. Journal of Engineering and Applied Sciences 13:4496–4502
Ricky R, Rustiadi E, Barus B (2017) A projection of land needed for settlements and conversion of paddy fields in solok city. J Region City Plan 28(3):186–203. https://doi.org/10.5614/jrcp.2017.28.3.3
Darwin R. (2001). Climate change in Food Security. Agriculture Information Bulletin, pp 13–14
Skinner C, Gattinger A, Muller A, Mäder P, Flie A, Stolze M, Ruser R, Niggli U (2014) Science of the Total Environment Greenhouse gas fluxes from agricultural soils under organic and non-organic management. A global meta-analysis. 469:553–563. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.08.098
Sunquist ET, Broecker WS (1986) The Carbon Cycle and Atmospheric CO 2. EOS Trans Am Geophys Union 67(15):191. https://doi.org/10.1029/eo067i015p00191
Washio K (2014) The Prediction of Climate Change and Rice Production in Japan. Rice Research: Open Access 2(1):2–4. https://doi.org/10.4172/jrr.1000e103
Yang Y, Bao W, Liu Y (2020) Land Use Policy Scenario simulation of land system change in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. Land Use Policy 96(November 2019):104677. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2020.104677
Zhuang Y, Liu H, Zhang L, Li S (2020) Research perspectives on paddy field systems: ecological functions and environmental impacts. Int J Agric Sustain 0(0):1–16. https://doi.org/10.1080/14735903.2020.1793652
Funding
The authors would like to thank Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia for providing financial assistance through the Geran Galakan Penyelidikan research grant (GGP-2017–016).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Nurul Izzati Mohd Ali helped in conceptualization, formal analysis, writing—original draft, methodology and software; Kadaruddin Aiyub was involved in investigation, project administration funding acquisition and supervision; Kuok Choy Lam contributed to data curation and resources; Azlan Abas helped in resources, resources, validation writing—review & editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This chapter does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Consent to Publish
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The author declares that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ali, N.I.M., Aiyub, K., Lam, K.C. et al. A bibliometric review on the inter-connection between climate change and rice farming. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 30892–30907 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-18880-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-18880-1