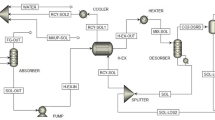
Abstract
The slow kinetics of CO2 absorption and high energy cost of CO2 desorption were the main challenges for CO2 capture technology. To overcome these drawbacks, a novel tri-solvent MEA (monoethanolamine) + EAE (2-(ethylamino)ethanol) + AMP (2-amino-2-methyl-1-propanol) was prepared at different amine concentrations of 0.1 ~ 0.5 + 2 + 2 mol/L. The CO2 absorption and desorption experiments were conducted on MEA + EAE + AMP and their precursor MEA + EAE to evaluate the absorption–desorption parameters. Results demonstrated that the optimized concentrations of the bi-blend were 0.2 + 2 mol/L for absorption and 0.4 + 2 mol/L for desorption. For the tri-solvent, the optimized concentration was 0.2 + 2 + 2 mol/L, consistently for both abs-desorption sides. Compared with tri-solvent of MEA + BEA + AMP, MEA + EAE + AMP proved better in absorption but poorer in desorption, while its CO2 loading of operation line was 0.35 ~ 0.70 mol/mol, higher than that of 0.30–0.60 mol/mol MEA + BEA + AMP. These results led to another tri-solvent candidate of amine solvents in an industrial pilot plant.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- AMP:
-
2-Amino-2-methyl-1-propanol
- BEA:
-
Butylethanolamine
- DEA:
-
Diethanolamine
- EAE:
-
2-(Ethylamino) ethanol
- MEA:
-
Monoethanolamine
- α:
-
Solution CO2 loading (mol CO2/mol amine)
- αeq:
-
CO2 loading of solution in equilibrium with PCO2
References
Bairq ZAS, Gao H, Huang Y, Zhang H, Liang Z (2019) Enhancing CO2 desorption performance in rich MEA solution by addition of SO42-/ZrO2/SiO2 bifunctional catalyst. Appl Energy 252:113440
Bernhardsen IM, Knuutila HK (2017) A review of potential amine solvents for CO2 absorption process: absorption capacity, cyclic capacity and pKa. Int J Greenhouse Gas Control 61:27–48
Chikezie N*, Beaulieu M, Tontiwachwuthikul P, Gibson MD (2018): Techno-ecomic analysis of CO2 capture from a 1.2 million MTPA cement plant using AMP-PZ-MEA blend. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control 78, 400-412
Ciftja AF, Hartono A, Svendsen HF (2014) Experimental study on carbamate formation in the AMP–CO2–H2O system at different temperatures. Chem Eng Sci 107:317–327
El Hadri N, Quang DV, Goetheer ELV, Abu Zahra MRM (2017) Aqueous amine solution characterization for post-combustion CO2 capture process. Appl Energy 185:1433–1449
Gao H, Gao G, Liu H, Luo X, Liang Z, Idem RO (2017) Density, viscosity, and refractive index of aqueous CO2-loaded and -unloaded ethylaminoethanol (EAE) solutions from 293.15 to 323.15 K for post combustion CO2 capture. J Chem Eng Data 62:4205–4214
Gao H, Wang N, Du J, Luo X, Liang Z (2020) Comparative kinetics of carbon dioxide (CO2) absorption into EAE, 1DMA2P and their blends in aqueous solution using the stopped-flow technique. Int J Greenh Gas Control 94:102948
Gelowitz D, Supap T, Naami A, Teerawat S, Idem R, Tontiwachwuthikul P (2013) Part 8: Post-combustion CO2 capture pilot plant operation issues. Carbon Manag 4:215–231
Hairul NAH, Shariff AM, Bustam MA (2017) Process behaviour in a packed absorption column for high pressure CO2 absorption from natural gas using PZ+AMP blended solution. Fuel Process Technol 157:20–28
Hartono A, Ahmad R, Usman M, Asif N, Svendsen HF (2020) Solubility of CO2 in 0.1M, 1M and 3M of 2-amino-2-methyl-1-propanol (AMP) from 313 to 393K and model representation using the eNRTL framework. Fluid Phase Equilib 511:112485
Hassankiadeh MN, Jahangiri A (2018) Application of aqueous blends of AMP and piperazine to the low CO2 partial pressure capturing: new experimental and theoretical analysis. Energy 165:164–178
Horwitz W (1975) Association of Official Analytical Chemists (AOAC) Methods. George Banta Co., Menasha, WI, USA
Hwang SJ, Kim J, Kim H, Lee KS (2017) Solubility of carbon dioxide in aqueous solutions of three secondary amines: 2-(butylamino)ethanol, 2-(isopropylamino)ethanol, and 2-(ethylamino)ethanol secondary alkanolamine solutions. J Chem Eng Data 62:2428–2435
Idem R, Supap T, Shi H, Gelowitz D, Ball M, Campbell C, Tontiwachwuthikul P (2015) Practical experience in post-combustion CO2 capture using reactive solvents in large pilot and demonstration plants. Int J Greenhouse Gas Control 40:6–25
Jahangiri A, Nabipoor Hassankiadeh M (2018) Effects of piperazine concentration and operating conditions on the solubility of CO2 in AMP solution at low CO2 partial pressure. Sep Sci Technol 54:1067–1078
Liang Z, Idem R, Tontiwachwuthikul P, Yu F, Liu H, Rongwong W (2016) Experimental study on the solvent regeneration of a CO2-loaded MEA solution using single and hybrid solid acid catalysts. AIChE J 62:753–765
Liu H, Li M, Luo X, Liang Z, Idem R, Tontiwachwuthikul P (2018) Investigation mechanism of DEA as an activator on aqueous MEA solution for postcombustion CO2 capture. AIChE J 64:2515–2525
Liu S, Gao H, He C, Liang Z (2019) Experimental evaluation of highly efficient primary and secondary amines with lower energy by a novel method for post-combustion CO2 capture. Appl Energy 233–234:443–452
Muchan P, Saiwan C, Narku-Tetteh J, Idem R, Supap T, Tontiwachwuthikul P (2017) Screening tests of aqueous alkanolamine solutions based on primary, secondary, and tertiary structure for blended aqueous amine solution selection in post combustion CO2 capture. Chem Eng Sci 170:574–582
Narku-Tetteh J, Muchan P, Saiwan C, Supap T, Idem R (2017) Selection of components for formulation of amine blends for post combustion CO2 capture based on the side chain structure of primary, secondary and tertiary amines. Chem Eng Sci 170:542–560
Natewong P, Prasongthum N, Reubroycharoen P, Idem R (2019) Evaluating the CO2 capture performance using a BEA-AMP biblend amine solvent with novel high-performing absorber and desorber catalysts in a bench-scale CO2 capture pilot plant. Energy Fuels 33:3390–3402
Nwaoha C, Saiwan C, Supap T, Idem R, Tontiwachwuthikul P, Rongwong W, Al-Marri MJ, Benamor A (2016a) Carbon dioxide (CO2) capture performance of aqueous tri-solvent blends containing 2-amino-2-methyl-1-propanol (AMP) and methyldiethanolamine (MDEA) promoted by diethylenetriamine (DETA). Int J Greenhouse Gas Control 53:292–304
Nwaoha C, Saiwan C, Tontiwachwuthikul P, Supap T, Rongwong W, Idem R, Al-Marri MJ, Benamor A (2016b) Carbon dioxide (CO2) capture: absorption-desorption capabilities of 2-amino-2-methyl-1-propanol (AMP), piperazine (PZ) and monoethanolamine (MEA) tri-solvent blends. J Nat Gas Sci Eng 33:742–750
Nwaoha C, Idem R, Supap T, Saiwan C, Tontiwachwuthikul P, Rongwong W, Al-Marri MJ, Benamor A (2017) Heat duty, heat of absorption, sensible heat and heat of vaporization of 2-amino-2-methyl-1-propanol (AMP), piperazine (PZ) and monoethanolamine (MEA) tri-solvent blend for carbon dioxide (CO2) capture. Chem Eng Sci 170:26–35
Nwaoha C, Tontiwachwuthikul P, Benamor A (2018a) A comparative study of novel activated AMP using 1,5-diamino-2-methylpentane vs MEA solution for CO2 capture from gas-fired power plant. Fuel 234:1089–1098
Nwaoha C, Tontiwachwuthikul P, Benamor A (2018b) CO2 capture from lime kiln using AMP-DA2MP amine solvent blend: a pilot plant study. J Environ Chem Eng 6:7102–7110
Pandey D, Kumar Mondal M (2021) Thermodynamic modeling and new experimental CO2 solubility into aqueous EAE and AEEA blend, heat of absorption, cyclic absorption capacity and desorption study for post-combustion CO2 capture. Chem Eng J 410:128334
Pandey D, Mondal MK (2021) Experimental data and modeling for density and viscosity of carbon dioxide (CO2)-loaded and -unloaded aqueous blend of 2-(ethylamino)ethanol (EAE) and aminoethylethanolamine (AEEA) for post-combustion CO2 capture. J Mol Liquids 330:115678
Prasongthum N, Natewong P, Reubroycharoen P, Idem R (2019) Solvent regeneration of a CO2-loaded BEA–AMP Bi-blend amine solvent with the aid of a solid Brønsted Ce(SO4)2/ZrO2 superacid catalyst. Energy Fuels 33:1334–1343
Idem R, Wilson M, Tontiwachwuthikul P, Chakma A, Veawab A, Aroonwilas A, Gelowitz D (2006): Pilot Plant Studies of the CO2 Capture Performance of Aqueous MEA and Mixed MEA/MDEA Solvents at the University of Regina CO2 Capture Technology Development Plant and the Boundary Dam CO2 Capture Demonstration Plant. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 45, 2414-2420
Rochelle GT (2009) Amine Scrubbing for CO2 capture. Science 325:1652–1654
Shi H, Naami A, Idem R, Tontiwachwuthikul P (2014) Catalytic and non catalytic solvent regeneration during absorption-based CO2 capture with single and blended reactive amine solvents. Int J Greenhouse Gas Control 26:39–50
Shi H, Zheng L, Huang M, Zuo Y, Kang S, Huang Y, Idem R, Tontiwachwuthikul P (2018a) Catalytic-CO2-desorption studies of DEA and DEA–MEA blended solutions with the aid of Lewis and Brønsted acids. Ind Eng Chem Res 57:11505–11516
Shi H, Zheng L, Huang M, Zuo Y, Li M, Jiang L, Idem R, Tontiwachwuthikul P (2018b) CO2 desorption tests of blended monoethanolamine-diethanolamine solutions to discover novel energy efficient solvents. Asia-Pac J Chem Eng 13:e2186
Shi H, Fu J, Wu Q, Huang M, Jiang L, Cui M, Idem R, Tontiwachwuthikul P (2020) Studies of the coordination effect of DEA-MEA blended amines (within 1 + 4 to 2 + 3 M) under heterogeneous catalysis by means of absorption and desorption parameters. Sep Purif Technol 236:116179
Shi H, Cui M, Fu J, Dai W, Huang M, Han J, Quan L, Tontiwachwuthikul P, Liang Z (2021a) Application of “coordinative effect” into tri-solvent MEA+BEA+AMP blends at concentrations of 0.1 + 2 + 2∼0.5 + 2 + 2 mol/L with absorption, desorption and mass transfer analyses. Int J Greenhouse Gas Control 107:103267
Shi H, Feng H, Yang X, Zou T, Tontiwachwuthikul P, Jiang L (2021b) Study of “coordinative effect” within bi-blended amine MEA + AMP and MEA + BEA at 0.1 + 2–0.5 + 2 mol/L with absorption–desorption parameter analyses. Asia-Pac J Chem Eng 16:e2645
Shi H, Yang X, Feng H, Fu J, Zou T, Yao J, Wang Z, Jiang L, Tontiwachwuthikul P (2021c) Evaluating energy-efficient solutions of CO2 capture within Tri-solvent MEA+BEA+AMP within 0.1+2+2–0.5+2+2 mol/L combining heterogeneous acid–base catalysts. Ind Eng Chem Res 60:7352–7366
Spietz T, Dobras S, Chwoła T, Wilk A, Krótki A, Więcław-Solny L (2020) Experimental results of amine emission from the CO2 capture process using 2-amino-2-methyl-1-propanol (AMP) with piperazine (PZ). Int J Greenhouse Gas Control 102:103155
Wai SK, Nwaoha C, Saiwan C, Idem R, Supap T (2018) Absorption heat, solubility, absorption and desorption rates, cyclic capacity, heat duty, and absorption kinetic modeling of AMP–DETA blend for post–combustion CO2 capture. Sep Purif Technol 194:89–95
Xiao M, Liu H, Idem R, Tontiwachwuthikul P, Liang Z (2016) A study of structure–activity relationships of commercial tertiary amines for post-combustion CO2 capture. Appl Energy 184:219–229
Xiao S, Liu H, Gao H, Xiao M, Luo X, Idem R, Tontiwachwuthikul P, Liang Z (2017a) Kinetics and mechanism study of homogeneous reaction of CO2 and blends of diethanolamine and monoethanolamine using the stopped-flow technique. Chem Eng J 316:592–600
Zhang X, Huang Y, Gao H, Luo X, Liang Z (2019) Zeolite catalyst-aided tri-solvent blend amine regeneration: an alternative pathway to reduce the energy consumption in amine-based CO2 capture process. Appl Energy 240:827–841
Yan J, Zhang Z (2019) Carbon capture, utilization and storage (CCUS). Appl Energy 235:1289–1299
Zhang R, Zhang X, Yang Q, Yu H, Liang Z, Luo X (2017) Analysis of the reduction of energy cost by using MEA-MDEA-PZ solvent for post-combustion CO2 capture (PCC). Appl Energy 205:1002–1011
Zhang X, Zhang R, Liu H, Gao H, Liang Z (2018) Evaluating CO2 desorption performance in CO2-loaded aqueous tri-solvent blend amines with and without solid acid catalysts. Appl Energy 218:417–429
Acknowledgements
The NSERC grant and Saskatchewan Innovation Scholarship was gratefully acknowledged. The research funding of National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC Nos. 21606150, 51521006), Bureau of Municipal of Huzhou Science and Technology Project (2021ZD 2043) were acknowledged.
Funding
The research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC Nos. 21606150) and Huzhou Science and Technology Project (2021ZD 2043).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Cheng X., Peng J., and Feng H. conducted research; Shi H. wrote the paper; Tontiwachwuthikul P. revised the paper; Hu J. conducted literature study.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Tito Roberto Cadaval Jr
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights of novelty
1. The tri-solvent MEA+EAE+AMP was developed and compared with MEA+BEA+AMP in terms of absorption and desorption comprehensively.
2. The “coordinative effect” was investigated for bi-solvents of MEA+EAE(RR’NH) and the tri-solvent of MEA+EAE+AMP, and the optimized ratio of MEA/RR’NH was carefully studied for consistency.
3. The structure activity correlation of DEA and EAE as secondary amines were investigated and compared.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, H., Cheng, X., Peng, J. et al. The CO2 absorption and desorption analysis of tri-solvent MEA + EAE + AMP compared with MEA + BEA + AMP along with “coordination effects” evaluation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 40686–40700 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-18792-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-18792-0