Abstract
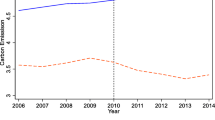
Manufacturing servitization, a new industrial form that integrates manufacturing and service, promotes not only high-quality economic development but also carbon mitigation. By employing the panel data of 14 manufacturing sectors and 17 service sectors from 1995 to 2009 in China, this study sheds light on the effect of manufacturing input servitization on carbon reduction. Results show that input servitization reduces carbon intensity. In terms of the manufacturing heterogeneity, the carbon abatement effect of input servitization in pollution-intensive sectors is greater than that in non-pollution sectors; with respect to the service heterogeneity, more emphasis shall be placed on transportation and business services among all manufacturing industries to curb carbon emissions. Furthermore, the mechanism analysis demonstrates that input servitization reduces carbon intensity by substituting energy elements, promoting technological innovation, and optimizing structure. These conclusions reveal that increasing the level of input servitization helps to coordinate manufacturing industry’s development with carbon abatement commitment in China.


Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The data sets supporting the results of this article are included within the article and its additional files.
Notes
The servitization levels of major developed countries such as USA and Japan are calculated by the authors.
References
Alcántara V, Padilla E (2009) Input–output subsystems and pollution: an application to the service sector and CO2 emissions in Spain. Ecol Econ 68(3):905–914. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2008.07.010
Arnold JM, Javorcik BS, Mattoo A (2006) Does services liberalization benefit manufacturing firms? Evidence from the Czech Republic. SSRN Electron J 85(1):136–146. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.932031
Cheng DZ, Cheng Z (2015) Analysis on the services content of Chinese exports. Stat Res (3) 46–53. https://doi.org/10.19343/j.cnki.11-1302/c.2015.03.006
Dai X (2016) Evolution and determinants of service added value embodied in China’s manufactured exports. Econ Res J (in Chinese) 9: 44–57. https://doi.org/CNKI:SUN:JJYJ.0.2016-09-005
Dong F, Li YF, Qin C, Sun JJ (2021a) How industrial convergence affects regional green development efficiency: a spatial conditional process analysis. J Environ Manage 300:113738. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JENVMAN.2021.113738
Dong F, Li YF, Zhang XY, Zhu J, Zheng L (2021b) How does industrial convergence affect the energy efficiency of manufacturing in newly industrialized countries? Fresh evidence from China. J Clean Prod 316:128316. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCLEPRO.2021.128316
Dong F, Yu BL, Hadachin T, Dai YJ, Wang Y, Zhang SN, Long RY (2018) Drivers of carbon emission intensity change in China. Resour Conserv Recycl 129:187–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2017.10.035
Doni F, Corvino A, Martini SB (2019) Servitization and sustainability actions. Evidence from European manufacturing companies. J Environ Manage 234:367–378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.01.004
Haraguchi N, Cheng CFC, Smeets E (2017) The importance of manufacturing in economic development: has this changed? World Dev 93:293–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.worlddev.2016.12.013
Huang YX, Xie JG (2019) Input servitization of manufacturing industry and carbon emission intensity —empirical analysis based on WIOD’s cross-country panel. Finance & Trade Economics (08): 100–115. https://doi.org/10.19795/j.cnki.cn11-1166/f.20190806.008
Jiang XM, Zhang SX (2021) Visualizing the services embodied in global manufacturing exports. Physica A 571:125365. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PHYSA.2020.125365
Kamal MM, Sivarajah U, Bigdeli AZ, Missi F, Koliousis Y (2020) Servitization implementation in the manufacturing organisations: classification of strategies, definitions, benefits and challenges. Int J Inf Manage 55:102206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2020.102206
Koopman R, Wang Z, Wei SJ (2014) Tracing value-added and double counting in gross exports. American Economic Review 104(2):459–494. https://doi.org/10.1257/aer.104.2.459
Koopman R, Powers W, Wang Z, Wei SJ (2010) Give credit where credit is due: tracing value added in global production chains (No. w16426). SSRN Electronic Journal. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.1949669
Lay G, Copani G, Jäger A, Biege S (2010) The relevance of service in European manufacturing industries. J Serv Manag. https://doi.org/10.1108/09564231011092908
Li XZ, Chen HL, Zhang XD (2017) Research on the industrial performance of the convergence of information industry with manufacturing industry—based on the data of Zhejiang Province. China Soft Science 1:22–30. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1002-9753.2017.01.003
Li XZ, Wang XJ, Zhang Y, Miao X (2021) Spatial differences in emission reduction effect of servitization of manufacturing industry export in China. Emerg Mark Financ Trade 57(8):2331–2355. https://doi.org/10.1080/1540496x.2020.1799782
Liu B, Wang NJ (2016) Input servitization of manufacturing and dual margins of firms’ export—an empirical study based on the data of Chinese micro-enterprise. China Industrial Economics. (9), 59–74. https://doi.org/10.19581/j.cnki.ciejournal.2016.09.004
Liu B, Wei Q, Lyu Y, Zhu KF (2016) Servitization of manufacturing and value chain upgrading. Econ Res J 51(03):151–162 (CNKI:SUN:JJYJ.0.2016-03-023)
Lu Y (2009) Do environmental regulations influence the competitiveness of pollution-intensive products? Econ Res J 44(04):28–40 (CNKI:SUN:JJYJ.0.2009-04-005)
Mont O (2002) Drivers and barriers for shifting towards more service-oriented businesses: analysis of the PSS field and contributions from Sweden. J Sustain Prod Des 2(3):89–103. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JSPD.0000031027.49545.2b
Neely A (2008) Exploring the financial consequences of the servitization of manufacturing. Oper Manag Res 1(2):103–118. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12063-009-0015-5
Okushima S, Tamura M (2010) What causes the change in energy demand in the economy? The role of technological change. Energy Econ 32:S41–S46
Pal R, Gander J (2018) Modelling environmental value: an examination of sustainable business models within the fashion industry. J Clean Prod 184:251–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.02.001
Pei JS, Meng B, Wang F, Xue JJ, Zhao ZX (2018) Production sharing, demand spillovers and CO2 emissions: the case of Chinese regions in global value chains. Singap Econ Rev 63(02):275–293. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0217590817400112
Peng SJ, Li HJ (2014) Empirical study on relationships between producer services, manufacturing industry and export trade in China. Journal of International Trade. (10) 67–76. https://doi.org/10.13510/j.cnki.jit.2014.10.007
Rahman J, Zhao MT (2013) Export performance in Europe: what do we know from supply links? Int Monet Fund. https://doi.org/10.5089/9781475516555.001
Rothenberg S (2007) Sustainability through servicizing. MIT Sloan Manag Rev 48(2):83–89
Shi D (2018) The green development and the new stage of global industrialization: progress in China and comparison with others. China Ind Econ 27(10):5–18. https://doi.org/10.19581/j.cnki.ciejournal.2018.10.001
Sung B, Song WY, Park SD (2018) How foreign direct investment affects CO2 emission levels in the Chinese manufacturing industry: evidence from panel data. Econ Syst 42(2):320–331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecosys.2017.06.002
Tong XH, Zhou HY, Chen W, Duan ZY, Xu MH, Duan HY (2020) Study on the measurement of carbon-driven effect from different development stages of industrialization. China Popul Resour Environ 30(5):26–35
Xiao T (2018) Can Chinese manufacturing get performance dividend through servitization. Finance Trade Econ 39(03):138–153. https://doi.org/10.19795/j.cnki.cn11-1166/f.2018.03.011
Xu HL, Cheng LH, Sun TY (2017) The effect of the input servitization of manufacturing on upgrading export domestic value added of enterprises—empirical evidence from Chinese micro-enterprise. China Ind Econ 76(10):62–80. https://doi.org/10.19581/j.cnki.ciejournal.2017.10.005
Xu HL, Wang HC (2016) The effect of minimum wage standards on firms’ export quality. J World Econ (07): 73–96. https://doi.org/CNKI:SUN:SJJJ.0.2016-07-005
Xu YZ, Sun J (2009) The convergence of information industry and manufacturing—an analysis based on industry performance. China Ind Econ (7): 56–66. https://doi.org/10.19581/j.cnki.ciejournal.2009.07.006
Ye CS, Ye Q, Shi XP, Sun YP (2020) Technology gap, global value chain and carbon intensity: evidence from global manufacturing industries. Energy Policy 137:111094. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2019.111094
You WH, Zhu HM, Yu K, Peng C (2015) Democracy, financial openness, and global carbon dioxide emissions: heterogeneity across existing emission levels. World Dev 66:189–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.worlddev.2014.08.013
Zhao D, Chen J (2021) An analysis of the impact of service inputs in manufacturing industries on eco-efficiency: evidence from China. Environ Sci Pollut Res. (43). https://doi.org/10.1007/S11356-021-15092-X
Zhu SJ, Tang YD, Qiao XZ, You WH, Peng C (2021) Spatial effects of participation in global value chains on CO2 emissions: a global spillover perspective. Emerging Markets Finance and Trade, 1-14. https://doi.org/10.1080/1540496X.2021.1911801
Zhu SJ, Xie Y, Duan F (2019) Manufacturing servitization, technological innovation and quality of export products. Econ Rev (6): 3–16. https://doi.org/10.19361/j.er.2019.06.01
Zhu SJ, Xie Y, Wu DS (2020) A study on the energy-saving effect of manufacturing servitization and its intermediary mechanism. Financ Trade Econ (11): 126–140. https://doi.org/10.19795/j.cnki.cn11-1166/f.20201106.008
Funding
This work was supported by the Postgraduate Scientific Research Innovation Project of Hunan Province [CX20210385].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the conception and design of this study. The empirical work and the manuscript’s first draft were performed by Mingrui Hao; the methodology guidance and software support were provided by Yiding Tang; the conceptualization was provided by Shujin Zhu. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publish
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hao, M., Tang, Y. & Zhu, S. Effect of input servitization on carbon mitigation: evidence from China’s manufacturing industry. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 27819–27831 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-18428-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-18428-9